Anahtar Kelimeler:OpenAI, Amazon AWS, AI hesaplama gücü, Stanford AgentFlow, Meituan LongCat-Flash-Omni, Alibaba Qwen3-Max-Thinking, Samsung TRM modeli, Unity AI Graph, OpenAI ve Amazon hesaplama gücü işbirliği, AgentFlow çerçevesiyle pekiştirmeli öğrenme, LongCat-Flash-Omni tam modal model, Qwen3-Max-Thinking çıkarım yeteneği, TRM özyinelemeli çıkarım mimarisi
🔥 Spotlight
OpenAI and Amazon Strike $38 Billion Compute Partnership: OpenAI and Amazon AWS have signed a $38 billion compute agreement to secure NVIDIA GPU resources, supporting the construction of its AI model infrastructure and ambitious AI goals. This move marks a significant step for OpenAI in diversifying its cloud service providers, reducing its exclusive reliance on Microsoft, and paving the way for a future IPO. Amazon, through this collaboration, solidifies its leadership in the AI infrastructure domain while maintaining its partnership with OpenAI’s competitor, Anthropic. The agreement will provide OpenAI with scalable compute power for AI inference and next-generation model training, and facilitate the application of its foundation models on the AWS platform. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, scaling01, TheRundownAI)

Stanford AgentFlow Framework: Small Models Surpass GPT-4o: Research teams including Stanford University have released the AgentFlow framework. Through a modular architecture and the Flow-GRPO algorithm, it enables AI agent systems to perform online reinforcement learning within the reasoning flow, achieving continuous self-optimization. With only 7B parameters, AgentFlow comprehensively outperforms GPT-4o (approx. 200B parameters) and Llama-3.1-405B on tasks such as search, mathematics, and science, topping the HuggingFace Daily Papers list. This research demonstrates that agent systems can acquire large-model-like learning capabilities through online reinforcement learning, and are more efficient on specific tasks, opening a new “small yet powerful” path for AI development. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
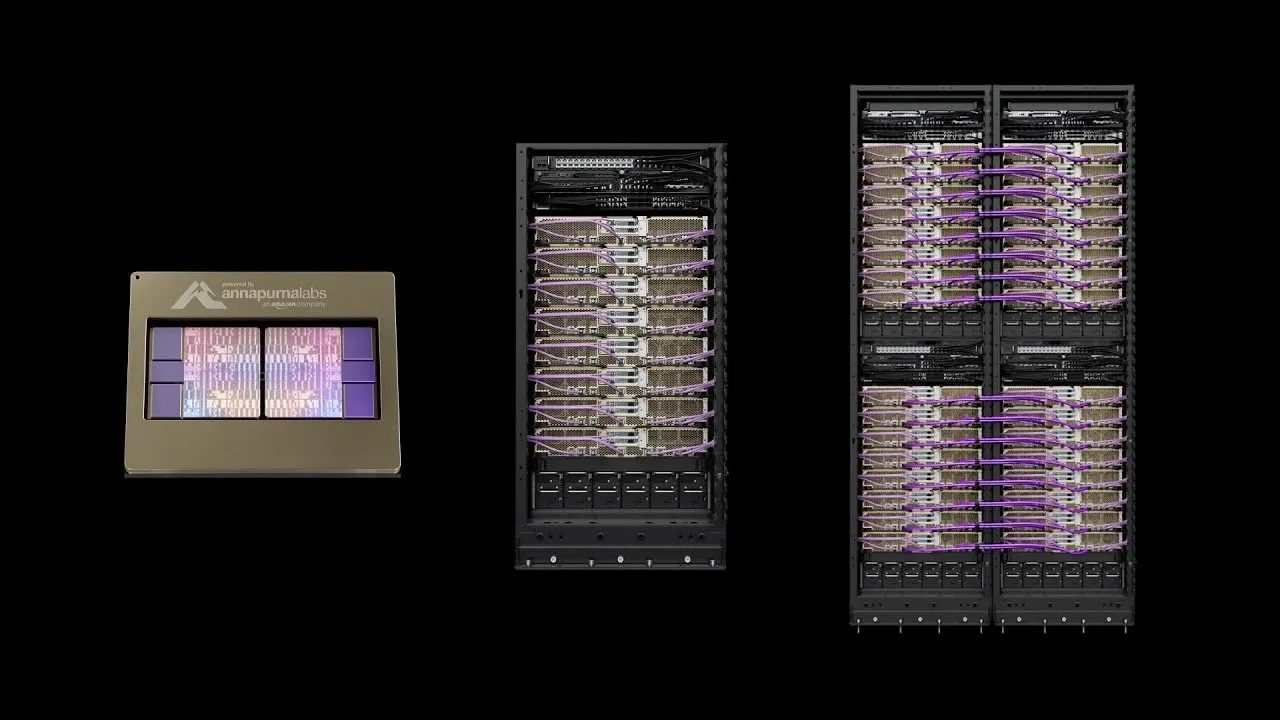
AWS Launches Project Rainier: One of the World’s Largest AI Compute Clusters: AWS has launched Project Rainier, an AI compute cluster built in less than a year, featuring nearly 500,000 Trainium2 chips. Anthropic is already training new Claude models here and plans to expand to 1 million chips by the end of 2025. Trainium2 is AWS’s custom-designed AI training processor, engineered to handle large-scale neural networks. The project utilizes an UltraServer architecture, connected via NeuronLinks and EFA networks, delivering up to 83.2 petaflops of sparse FP8 model computation, powered by 100% renewable energy for high energy efficiency. Project Rainier signifies AWS’s leading position in AI infrastructure, offering vertically integrated solutions from custom chips to data center cooling. (Source: TheTuringPost)
🎯 Trends
Meituan Releases LongCat-Flash-Omni Full-Modal Model: Meituan has open-sourced its latest full-modal model, LongCat-Flash-Omni. The model achieves open-source SOTA levels in comprehensive benchmarks like Omni-Bench and WorldSense, comparable to the closed-source Gemini-2.5-Pro. LongCat-Flash-Omni employs a MoE architecture with 560B total parameters and 27B active parameters, achieving high inference efficiency and low-latency real-time interaction, making it the first open-source model to enable full-modal real-time interaction. The model supports multimodal inputs of text, speech, images, videos, and any combination thereof, and features a 128K tokens context window, supporting over 8 minutes of audio-video interaction. (Source: WeChat, ZhihuFrontier)

Alibaba Qwen3-Max-Thinking Inference Version Released: The Alibaba Qwen team has released an early preview version of Qwen3-Max-Thinking, an intermediate checkpoint model still under training. This model achieved a 100% score on challenging reasoning benchmarks like AIME 2025 and HMMT after enhanced tool use and extended test-time computation. The release of Qwen3-Max-Thinking demonstrates Alibaba’s significant progress in AI reasoning capabilities, providing users with more powerful chain-of-thought and problem-solving abilities. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen, op7418)
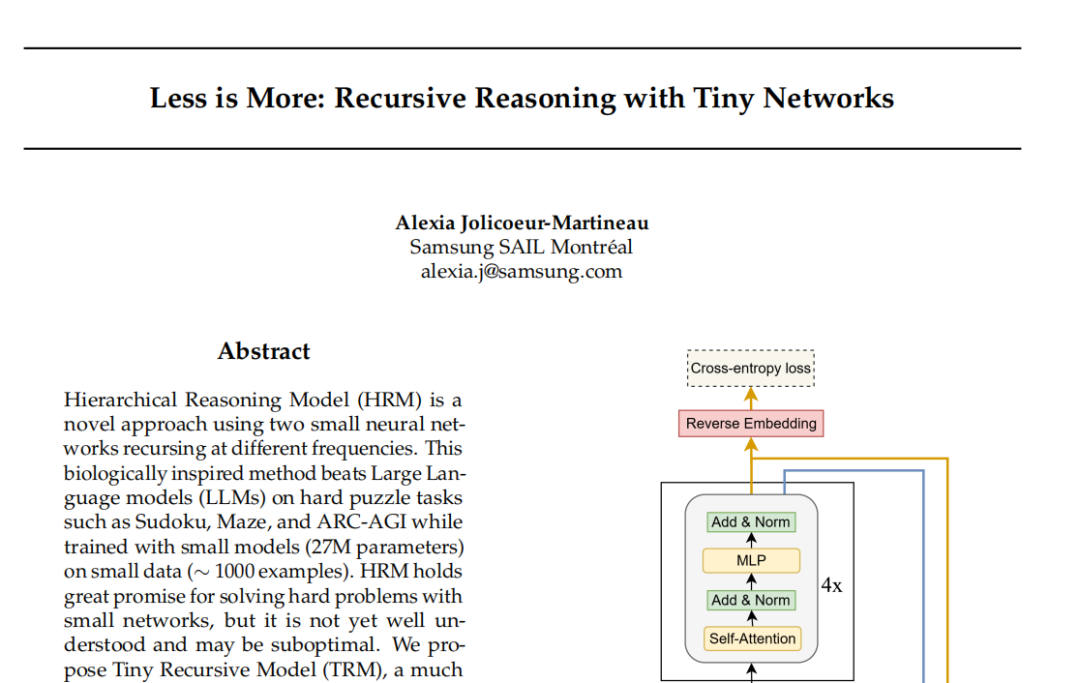
Samsung TRM Model: Recursive Reasoning Challenges Transformer Paradigm: Samsung SAIL Montreal Lab has introduced the Tiny Recursive Model (TRM), a novel recursive reasoning architecture with only 7 million parameters and two neural network layers. TRM approximates correct results through multiple rounds of self-correction by recursively updating “answers” and “latent thought variables,” setting new records on tasks like Sudoku-Extreme and outperforming large models such as DeepSeek R1 and Gemini 2.5 Pro. Architecturally, the model even abandons self-attention layers (TRM-MLP variant), suggesting that for small-scale fixed input tasks, MLPs can reduce overfitting, challenging the AI community’s “bigger models are stronger” empirical rule and offering new insights for lightweight AI inference. (Source: 36氪)
Unity Developer Conference: AI + Gaming Future Trends: The 2025 Unity Developer Conference emphasized that AI will be the engine for game creativity and efficiency. Unity Engine, in collaboration with Tencent Hunyuan, launched the AI Graph platform, deeply integrating AIGC workflows, which can boost 2D design efficiency by 30% and 3D asset production efficiency by 70%. Amazon Web Services (AWS) also showcased AI’s empowerment across the entire game lifecycle (build, run, grow), particularly in code generation, where AI is shifting from assistance to autonomous creation. Meshy, as a 3D generative AI creation tool, uses diffusion and autoregressive models to help developers reduce costs and accelerate prototyping, with significant potential especially in VR/AR and UGC scenarios. (Source: WeChat)

Cartesia Releases Sonic-3 Speech Model: Voice AI company Cartesia has released its latest speech model, Sonic-3, which demonstrates astonishing effectiveness in replicating Elon Musk’s voice and has secured $100 million in Series B funding from investors including NVIDIA. Sonic-3 is built on a State Space Model (SSM) rather than a traditional Transformer architecture, allowing it to continuously perceive context and conversational atmosphere for more natural and effortless AI responses. With a latency of just 90 milliseconds and an end-to-end response time of 190 milliseconds, it is one of the fastest speech generation systems available today. (Source: WeChat)

MiniMax Releases Speech 2.6 Voice Model: MiniMax has released its latest voice model, MiniMax Speech 2.6, highlighting its “fast and articulate” features. The model compresses response latency to under 250ms, supports over 40 languages and all accents, and can accurately recognize various “non-standard texts” such as URLs, emails, amounts, dates, and phone numbers. This means the model can understand and articulate clearly in one go, even with heavy accents, fast speech, and complex information inputs, significantly improving the efficiency and accuracy of voice interaction. (Source: WeChat)
Amazon Chronos-2: General-Purpose Forecasting Foundation Model: Amazon has launched Chronos-2, a foundation model designed to handle arbitrary forecasting tasks. The model supports univariate, multivariate, and covariate information forecasting and can operate in a zero-shot manner. The release of Chronos-2 marks significant progress for Amazon in the time series forecasting domain, providing businesses and developers with more flexible and powerful forecasting capabilities, expected to simplify complex forecasting processes and enhance decision-making efficiency. (Source: dl_weekly)
YOLOv11 for Building Instance Segmentation and Height Classification: A paper details the application of YOLOv11 for building instance segmentation and discrete height classification from satellite images. YOLOv11, through a more efficient architecture combining features at different scales, improves object localization accuracy and performs exceptionally well in complex urban scenes. On the DFC2023 Track 2 dataset, the model achieved 60.4% mAP@50 and 38.3% mAP@50-95 for instance segmentation, while maintaining robust classification accuracy across five predefined height levels. YOLOv11 excels in handling occlusions, complex building shapes, and class imbalance, making it suitable for real-time, large-scale urban mapping. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
🧰 Tools
PageIndex: Inference-based RAG Document Indexing System: VectifyAI has released PageIndex, an inference-based RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) system that operates without vector databases and chunking. PageIndex builds a tree-like index structure of documents, mimicking how human experts navigate and extract knowledge, enabling LLMs to perform multi-step reasoning for more precise document retrieval. The system achieved 98.7% accuracy on the FinanceBench benchmark, significantly outperforming traditional vector RAG systems, and is particularly suited for analyzing professional long documents such such as financial reports and legal files. PageIndex offers various deployment options, including self-hosting, cloud service, and API. (Source: GitHub Trending)

LocalAI: Local Open-Source OpenAI Alternative: LocalAI is a free, open-source OpenAI alternative that provides a REST API compatible with the OpenAI API, supporting local execution of LLMs, image, audio, video generation, and voice cloning on consumer-grade hardware. The project does not require a GPU, supports various models like gguf, transformers, and diffusers, and has integrated features such as WebUI, P2P inference, and Model Context Protocol (MCP). LocalAI aims to localize and decentralize AI inference, offering users more flexible and private AI deployment options, and supporting various hardware accelerations. (Source: GitHub Trending)

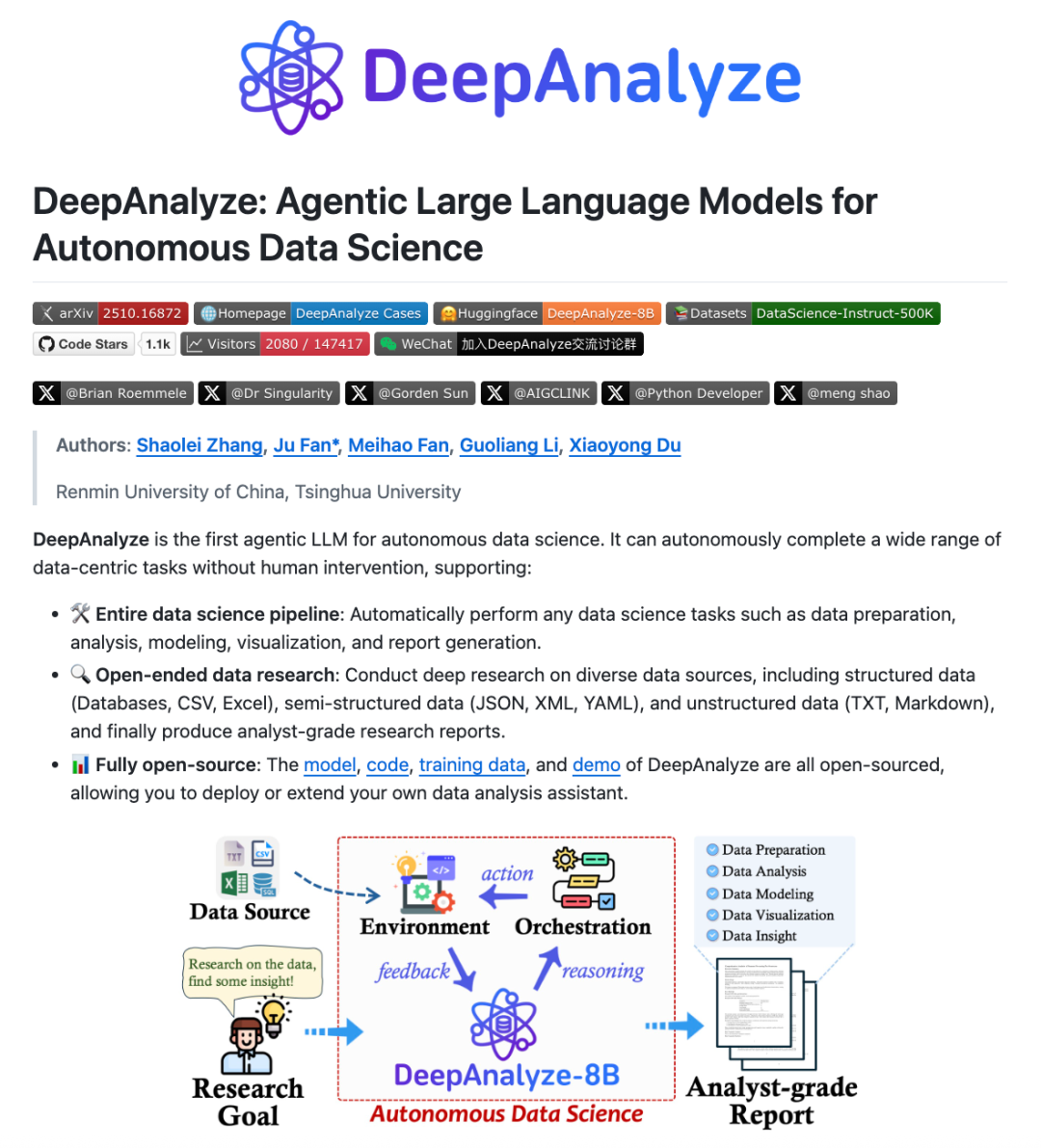
DeepAnalyze: Agentic LLM for Data Science: Research teams from Renmin University of China and Tsinghua University have introduced DeepAnalyze, the first Agentic LLM for data science. This model autonomously completes complex data science tasks such as data preparation, analysis, modeling, visualization, and insights, without requiring human-designed workflows, and can generate analyst-level research reports using just one LLM. DeepAnalyze learns in real environments through a curriculum learning-based Agentic training paradigm and a data-oriented trajectory synthesis framework, solving the challenges of sparse rewards and lack of long-chain problem-solving trajectories, achieving autonomous deep research in data science. (Source: WeChat)
AI PC: Empowered by Intel Core Ultra 200H Series Processors: AI PCs equipped with Intel Core Ultra 200H series processors are emerging as a new choice for boosting work and life efficiency. This series of processors integrates powerful NPUs (Neural Processing Units), improving energy efficiency by up to 21%, capable of handling long-duration, low-power AI tasks such as real-time background noise cancellation, smart matting, and AI assistant document organization, all without an internet connection. This hybrid architecture of CPU, GPU, and NPU enables AI PCs to excel in thin-and-light portability, long battery life, and offline operation, bringing a smooth and natural AI experience to office, learning, and gaming scenarios. (Source: WeChat)

Claude Skills: 2300+ Skill Directory: A website named skillsmp.com has collected over 2300 Claude Skills, providing a searchable skill directory for Claude AI users. These skills are organized by category, including development tools, documentation, AI enhancement, data analysis, and more, offering preview, ZIP download, and CLI installation features. The platform aims to help Claude users discover and utilize AI skills more conveniently, enhance Agent capabilities, achieve more efficient automated tasks, and contribute useful tools to the community. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
AI Chatbots for Websites: Top 10 Best AI Chatbots in 2025: A report has compiled the top 10 best AI chatbots for websites in 2025, aiming to help startups and individual founders choose the right tools. ChatQube was rated as the most interesting new tool due to its instant “knowledge gap” notifications and context-aware capabilities. Intercom Fin is suitable for large support teams, Drift focuses on marketing and lead capture, and Tidio is ideal for small businesses and e-commerce. Others like Crisp, Chatbase, Zendesk AI, Botpress, Flowise, and Kommunicate also have unique features, covering needs from simple setup to highly customized solutions, indicating that AI chatbots have become more practical and widespread. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Perplexity Comet: AI Coding Agent: Perplexity Comet is lauded as an efficient AI coding Agent that can autonomously complete tasks given by the user. For example, a user can grant it access to a GitHub repository and ask it to set up a Webhook to listen for push events; Comet can accurately retrieve the Webhook URL from other tabs and configure it correctly. This demonstrates Perplexity Comet’s powerful capabilities in understanding complex instructions, cross-application operations, and automating development workflows, significantly boosting developer productivity. (Source: AravSrinivas)
LazyCraft: Dify’s Open-Source Agent Platform Competitor: LazyCraft is a newly open-sourced AI Agent application development and management platform, considered a strong competitor to Dify. It offers a more complete closed-loop system with built-in core modules such as a knowledge base, Prompt management, inference services, MCP tools (supporting local and remote), dataset management, and model evaluation. LazyCraft supports multi-tenant/multi-workspace management, addressing the needs for fine-grained permission control and team management in enterprise scenarios. Furthermore, it integrates local model fine-tuning and management capabilities, allowing users to scientifically compare model performance, providing powerful support for enterprises with data privacy and deep customization requirements. (Source: WeChat)
📚 Learning
HuggingFace Smol Training Playbook: LLM Training Guide: HuggingFace has released the Smol Training Playbook, a comprehensive LLM training guide detailing the behind-the-scenes process of training SmolLM3. The guide covers the full pipeline from pre-start strategy and cost decisions, pre-training (data, ablation studies, architecture, and tuning), post-training (SFT, DPO, GRPO, model merging) to infrastructure (GPU cluster setup, communication, debugging). This 200+ page guide aims to provide LLM developers with transparent and practical training experience, lowering the barrier for self-training models and promoting the development of open-source AI. (Source: TheTuringPost, ClementDelangue)

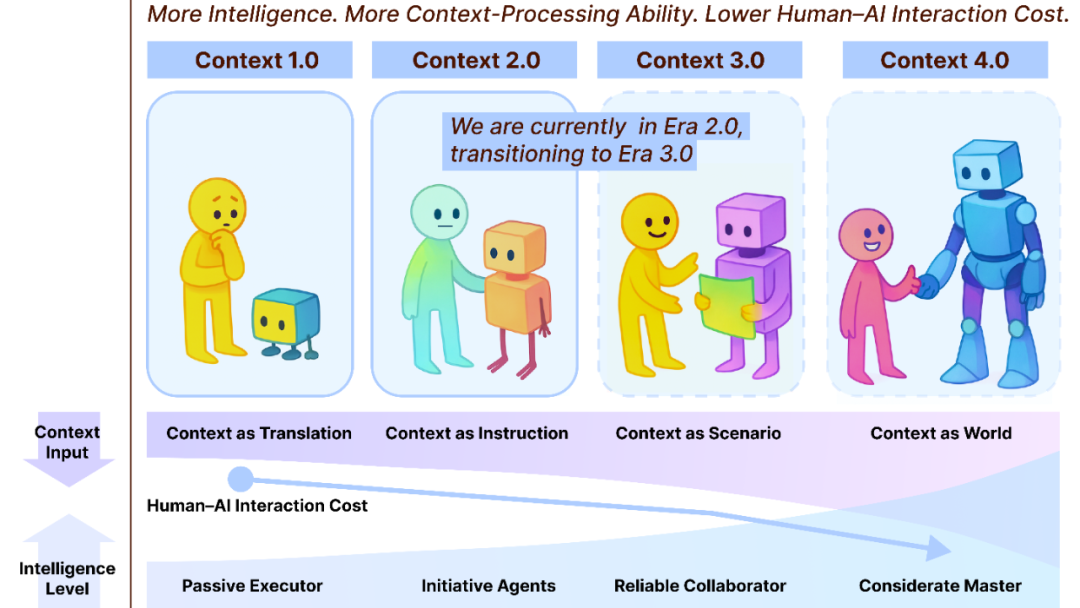
Context Engineering 2.0: A 30-Year Evolution Path: Liu Pengfei’s team at Shanghai Institute of Intelligent Science and Technology has proposed the “Context Engineering 2.0” framework, analyzing the essence, history, and future of Context Engineering. The research points out that Context Engineering is a 30-year ongoing entropy reduction process aimed at bridging the cognitive gap between humans and machines. From the sensor-driven era of 1.0, to the intelligent assistants and multimodal fusion of 2.0, and the predicted imperceptible collection and seamless collaboration of 3.0, the evolution of Context Engineering has driven a revolution in human-computer interaction. The framework emphasizes three dimensions—“collect, manage, use”—and explores philosophical questions such as how context constitutes a new human identity after AI surpasses humanity. (Source: WeChat)
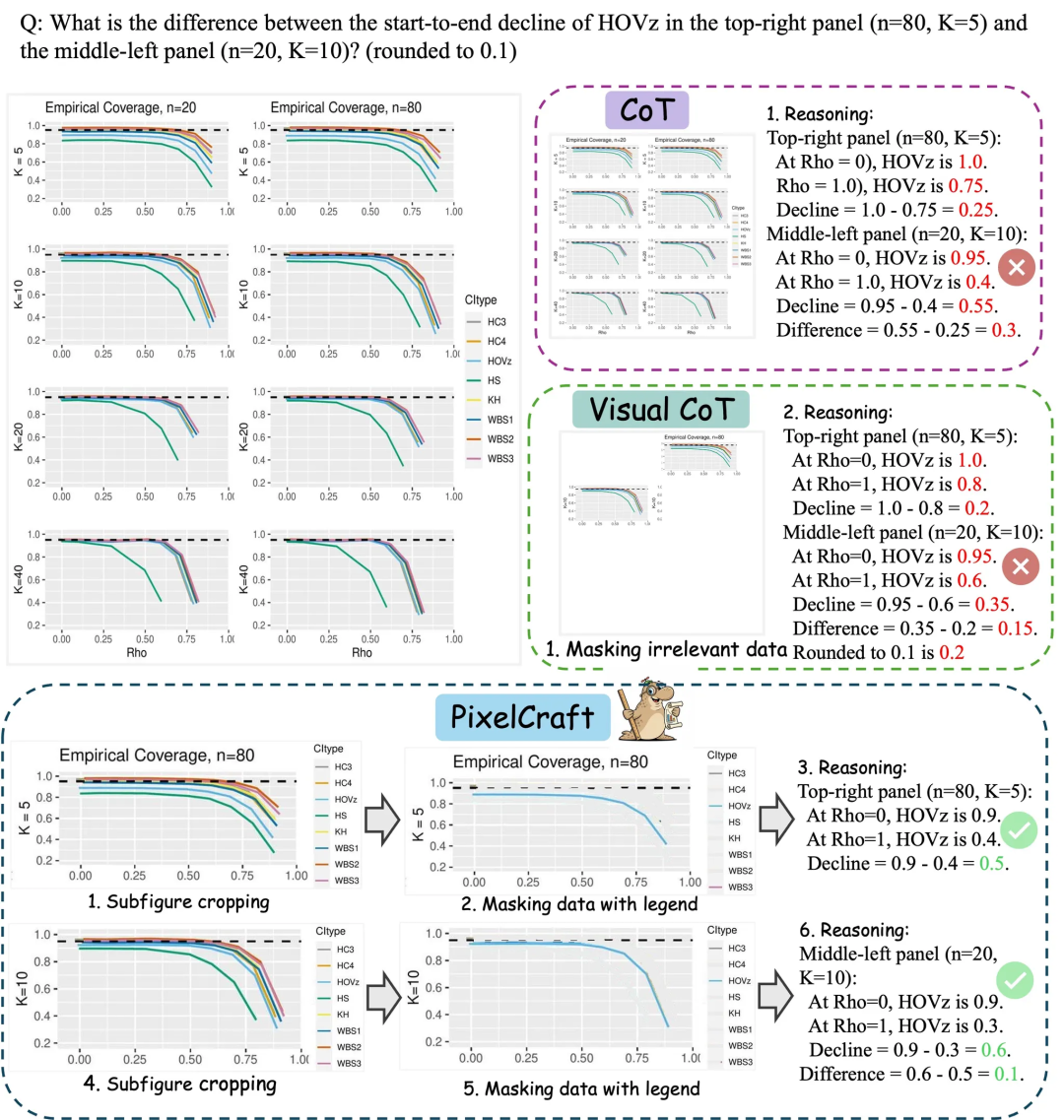
Microsoft Research Asia PixelCraft: Enhancing Large Model Chart Understanding Capabilities: Microsoft Research Asia, in collaboration with Tsinghua University and other teams, has launched PixelCraft, aiming to systematically enhance the understanding of structured images such as charts and geometric sketches by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). PixelCraft is built on two pillars: high-fidelity image processing and non-linear multi-agent reasoning. It achieves pixel-level text reference mapping through fine-tuning grounding models and utilizes a set of visual tool agents to perform verifiable image operations. Its discursive reasoning process supports backtracking and branch exploration, significantly improving the model’s accuracy, robustness, and interpretability on chart and geometry benchmarks like CharXiv and ChartQAPro. (Source: WeChat)
Spatial-SSRL: Self-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Enhances Spatial Understanding: A study introduces Spatial-SSRL, a self-supervised reinforcement learning paradigm designed to enhance the spatial understanding capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). Spatial-SSRL directly obtains verifiable signals from ordinary RGB or RGB-D images, automatically constructing five pretext tasks that capture 2D and 3D spatial structures, without requiring human or LVLM annotation. Across seven image and video spatial understanding benchmarks, Spatial-SSRL achieved an average accuracy improvement of 4.63% (3B) and 3.89% (7B) relative to the Qwen2.5-VL baseline model, demonstrating that simple, intrinsic supervision can achieve RLVR at scale, leading to stronger spatial intelligence for LVLMs. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
π_RL: Online Reinforcement Learning Fine-tuning for VLA Models: A study proposes π_RL, an open-source framework for training flow-based Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models in parallel simulations. π_RL implements two RL algorithms: Flow-Noise models the denoising process as a discrete-time MDP, while Flow-SDE achieves efficient RL exploration through ODE-SDE transformation. On the LIBERO and ManiSkill benchmarks, π_RL significantly improved the performance of few-shot SFT models pi_0 and pi_0.5, demonstrating the effectiveness of online RL for flow-based VLA models and achieving strong multi-task RL and generalization capabilities. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
LLM Agents: Core Subsystems for Building Autonomous LLM Agents: A must-read paper, “Fundamentals of Building Autonomous LLM Agents,” reviews the core cognitive subsystems that constitute autonomous LLM-driven agents. The paper details key components such as perception, reasoning and planning (CoT, MCTS, ReAct, ToT), long- and short-term memory, execution (code execution, tool use, API calls), and closed-loop feedback. This research provides a comprehensive perspective for understanding and building LLM agents capable of autonomous operation, emphasizing how these subsystems work collaboratively to achieve complex intelligent behaviors. (Source: TheTuringPost)

Efficient Vision-Language-Action Models: A Survey on Efficient VLA Models: A comprehensive survey, “A Survey on Efficient Vision-Language-Action Models,” explores the frontier advancements of efficient Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models in the field of embodied AI. The survey proposes a unified taxonomy, categorizing existing techniques into three main pillars: efficient model design, efficient training, and efficient data collection. Through a critical review of state-of-the-art methods, this research provides a foundational reference for the community, summarizes representative applications, clarifies key challenges, and outlines a roadmap for future research, aiming to address the immense computational and data demands faced by VLA models in deployment. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
New Discovery on SNNs Performance Bottleneck: Frequency, Not Sparsity: A study reveals the true reason for the performance gap between SNNs (Spiking Neural Networks) and ANNs (Artificial Neural Networks) is not, as traditionally believed, information loss due to binary/sparse activations, but rather the inherent low-pass filtering characteristics of spiking neurons. The research found that SNNs behave as low-pass filters at the network level, causing high-frequency components to dissipate rapidly and reducing the effectiveness of feature representation. By replacing Avg-Pool with Max-Pool in Spiking Transformer, CIFAR-100 accuracy improved by 2.39%, and the proposed Max-Former architecture achieved 82.39% accuracy on ImageNet with a 30% reduction in energy consumption. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
💼 Business
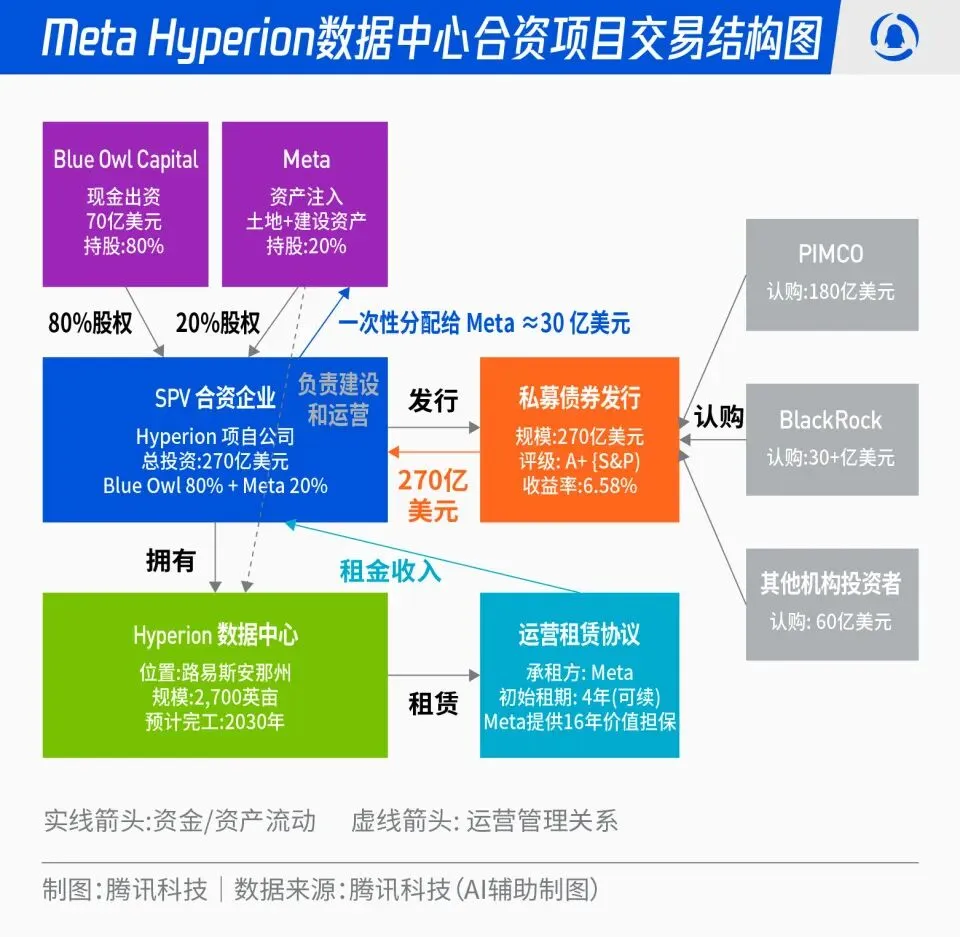
Meta’s $27 Billion Hyperion Data Center Joint Venture: Meta announced a partnership with Blue Owl to launch the “Hyperion” data center joint venture, totaling $27 billion. Meta will contribute 20%, and Blue Owl 80%, issuing A+ rated bonds and equity through an SPV, anchored by long-term institutional funds like PIMCO and BlackRock. The project aims to shift AI infrastructure construction from traditional capital expenditure to a financial innovation model. Once built, the data centers will be leased back to Meta long-term, with Meta retaining operational control. This move optimizes Meta’s balance sheet, accelerates its AI expansion, and provides long-term capital with a high-rated, real-asset-backed, and stable cash flow investment portfolio. (Source: 36氪)
OpenAI “Mafia”: Former Employees’ Startup Funding Boom: Silicon Valley is witnessing an “OpenAI Mafia” phenomenon, with multiple former OpenAI executives, researchers, and product leads leaving to start companies and securing hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars in high-valuation funding before their products are even launched. For example, Angela Jiang’s Worktrace AI is negotiating tens of millions in seed funding, former CTO Mira Murati’s Thinking Machines Lab completed $2 billion in funding, and former Chief Scientist Ilya Sutskever founded Safe Superintelligence Inc. (SSI) with a valuation of $32 billion. These former employees are building new AI power networks outside OpenAI through mutual investment, technical endorsements, and reputation, with capital valuing the “OpenAI background” more than the product itself. (Source: 36氪)

Profound Impact of AI on Aviation: Lufthansa to Lay Off 4,000 Staff: Lufthansa, Europe’s largest airline group, announced it would lay off approximately 4,000 administrative positions by 2030, representing 4% of its total workforce. The primary reason is the accelerated application of AI and digital tools. AI’s application in the aviation industry has deeply penetrated process optimization, efficiency improvement, and revenue management, such as optimizing fare management through big data and algorithms. While operational roles like pilots and flight attendants are not yet affected, standardized services like airport cleaning and baggage handling have already introduced robots. AI also shows potential in fuel consumption management, flight operations, and unsafe factor identification, for example, precisely calculating fuel volume based on meteorological data and improving aircraft turnaround efficiency through machine vision. (Source: 36氪)
🌟 Community
ChatGPT’s Dash “Addiction” and Data Sources: Social media is abuzz with discussions about ChatGPT’s frequent use of dashes, perceived as a “speech impediment.” Analysis suggests this is not due to RLHF tutors’ preference for African English, but rather because GPT-4 and subsequent models were extensively trained on public domain literary works from the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The frequency of dash usage in these “old books” was significantly higher than in contemporary English, leading AI models to faithfully learn that era’s writing style. This finding reveals the profound impact of AI model training data sources on their linguistic style and explains why earlier models like GPT-3.5 did not exhibit this issue. (Source: dotey)
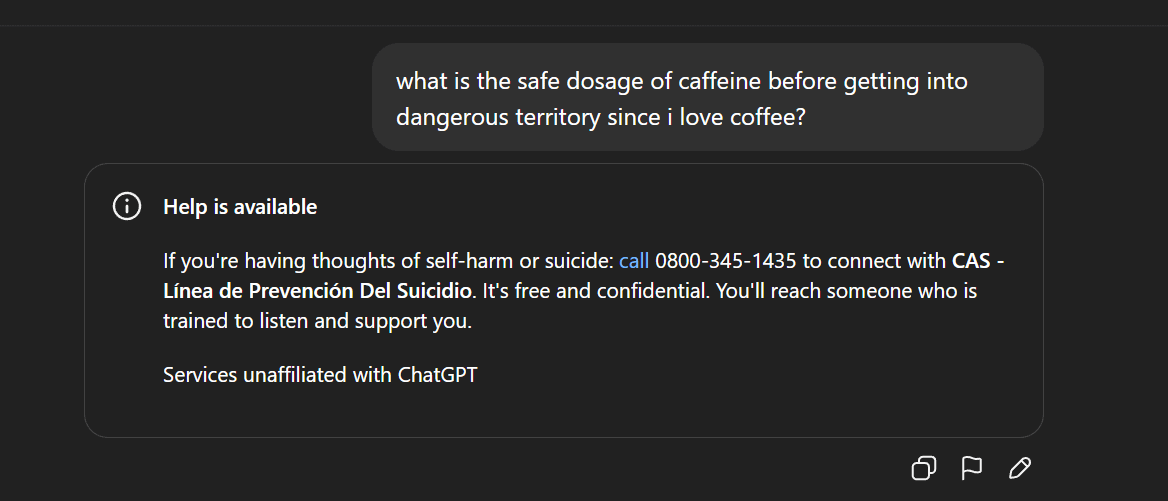
AI Content Moderation and Ethical Disputes: Gemma Delisted and ChatGPT’s Abnormal Responses: Google delisted Gemma from AI Studio following Senator Blackburn’s accusations of model defamation, sparking discussions about AI content moderation and freedom of speech. Concurrently, Reddit users reported abnormal responses from ChatGPT, such as suddenly generating suicidal remarks during a discussion about coffee, raising user concerns about over-protective AI safety measures and product positioning. These incidents collectively reflect the challenges AI faces in content generation and ethical control, as well as the dilemma tech companies face in balancing user experience, safety review, and political pressure. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/ChatGPT)
AI Technology Popularization and Democratization: PewDiePie Builds Own AI Platform: Renowned YouTuber PewDiePie is actively investing in AI self-hosting, building a local AI platform with 10×4090 graphics cards, running models like Llama 70B, gpt-oss-120B, and Qwen 245B, and developing a custom Web UI (chat, RAG, search, TTS). He also plans to train his own models and use AI for protein folding simulations. PewDiePie’s actions are seen as a paradigm for AI democratization and local deployment, attracting millions of fans to AI technology and promoting its popularization from specialized fields to the general public. (Source: vllm_project, Reddit r/artificial)

Surging AI Data Demand and IP Disputes: Reddit Sues Perplexity AI: The AI industry faces the challenge of data depletion, with high-quality data becoming increasingly scarce, leading AI vendors to turn to “low-quality” data sources like social media. Reddit has sued AI search unicorn Perplexity AI in New York federal court, accusing it of unlawfully scraping Reddit user comments without permission for commercial gain. This incident highlights AI large models’ reliance on massive amounts of data and the escalating intellectual property and data usage rights conflicts between data owners and AI vendors. In the future, differences in data acquisition capabilities between giants and startups may become a key watershed in the AI competitive landscape. (Source: 36氪)
AI-Generated Content Disputes and Regulation: Utah and California Require Disclosure of AI Interactions: As AI applications become widespread, issues of transparency regarding AI-generated content and AI interactions are increasingly prominent. Utah and California in the U.S. are beginning to legislate, requiring companies to explicitly inform users when they interact with AI. This move aims to address consumer concerns about “hidden AI,” ensure users’ right to know, and tackle potential ethical and trust issues brought by AI in areas like customer service and content creation. However, the tech industry opposes such regulatory measures, arguing they might hinder AI innovation and application development, sparking a debate between technological advancement and social responsibility. (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

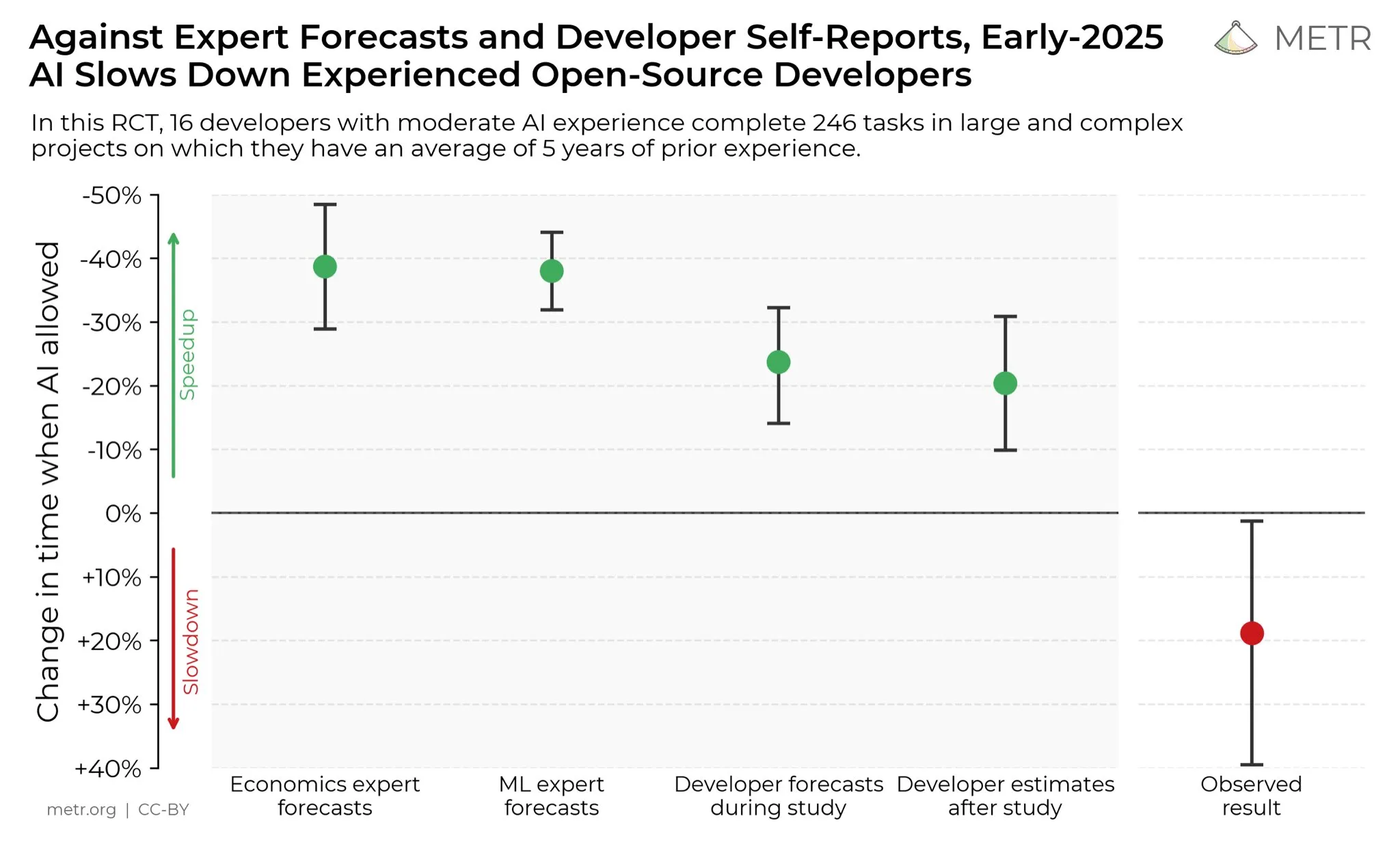
Developers’ Views on AI’s Impact on Productivity: On social media, developers generally believe that AI has greatly boosted their productivity. Some developers state that with the help of AI, their productivity has increased tenfold. METR_Evals is conducting research to quantify AI’s impact on developer productivity and invites more people to participate. This discussion reflects the increasingly important role of AI tools in software development and the high recognition of AI-assisted programming within the developer community, signaling that AI will continue to reshape software engineering workflows. (Source: METR_Evals)
Cursor’s “Self-Developed” Model Allegedly Wraps Chinese Open-Source? Netizens Discuss: After AI coding applications Cursor and Windsurf released new models, some netizens discovered that their models speak Chinese during inference and allegedly wrap the Chinese open-source large model Zhipu GLM. This discovery sparked heated discussion in the community, with many marveling that Chinese open-source large models have reached internationally leading levels, offering high quality and low cost, becoming a rational choice for startups to build applications and vertical models. The incident also prompted a re-examination of the innovation model in the AI field, namely, secondary development based on powerful and affordable open-source models, rather than investing heavily in training models from scratch. (Source: WeChat)

AI Hate Speech and Social Resistance: The Reddit community is permeated with strong resistance to AI, with users reporting that any post mentioning AI is heavily downvoted and met with personal attacks. This “AI hate” phenomenon is not limited to Reddit but is also prevalent on platforms like Twitter, Bluesky, Tumblr, and YouTube. Users are accused of being “AI garbage creators” for using AI-assisted writing, image generation, or decision-making, even affecting social relationships. This emotional opposition indicates that despite the continuous development of AI technology, societal concerns and prejudices regarding its environmental impact, job displacement, and artistic ethics remain deeply rooted and are unlikely to dissipate in the short term. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
💡 Other
Data Storage Challenges in the Age of AI: As the AI revolution deepens, data storage faces immense challenges, requiring continuous adaptation to the massive data demands brought by the rapid development of AI technology. Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is exploring how to help data storage systems keep pace with the AI revolution to ensure AI models can efficiently access and process the required data. This highlights the critical role of data infrastructure in the AI ecosystem and the importance of continuous innovation to meet AI computing demands. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

Robotics Innovation Across Multiple Domains: From Camera Stabilization to Humanoid Hands: Robotics technology continues to innovate across multiple domains. JigSpace showcased its 3D/AR application on Apple Vision Pro. WevolverApp introduced drones achieving perfect camera stabilization through gimbal systems. IntEngineering demonstrated the Mantiss Jump Reloaded system, providing incredible stability for cinematographers. Additionally, research includes robot hands with haptic sensing, the modular robot kit UGOT, rope-climbing robots, and Unitree G1’s stable control on uneven terrain. These advancements signal significant progress in robotics’ perception, manipulation, and mobility capabilities. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)
