Palabras clave:Protección de IA, Arte digital, Regulación de IA, Energía limpia, LightShed, Glaze, Nightshade, Ventaja energética de China, Protección de derechos de autor de arte digital, Eliminación de datos de entrenamiento de IA, Política de regulación de IA en EE.UU., Modelo Kimi K2 MoE, Mercury LLM de generación de código
🔥 Enfoque
LightShed Tool Weakens AI Protection for Digital Art: A new technique, LightShed, can identify and remove the “poison” added to digital artwork by tools like Glaze and Nightshade, making the art more susceptible to being used for training AI models. This has raised concerns among artists about copyright protection and highlights the ongoing struggle between AI training and copyright safeguards. Researchers say LightShed isn’t intended for art theft, but to warn against a false sense of security in existing protection tools and encourage exploration of more effective methods. (Source: MIT Technology Review)

New Era of AI Regulation: US Senate Rejects AI Regulation Moratorium: The US Senate rejected a 10-year moratorium on state-level AI regulation, seen as a victory for AI regulation proponents and potentially marking a broader political shift. A growing number of politicians are focusing on the risks of unregulated AI and leaning towards stricter regulatory measures. This event foreshadows a new political era in AI regulation, with potentially more discussions and legislation on AI oversight in the future. (Source: MIT Technology Review)
China’s Dominance in the Energy Sector: China holds a dominant position in next-generation energy technologies, heavily investing in wind, solar, electric vehicles, energy storage, and nuclear power, with significant results. Meanwhile, recently passed US legislation cuts credits, grants, and loans for clean energy technologies, potentially slowing its progress in the energy sector and further solidifying China’s leading position. Experts believe the US is relinquishing its leadership in the development of crucial future energy technologies. (Source: MIT Technology Review)

🎯 Tendencias
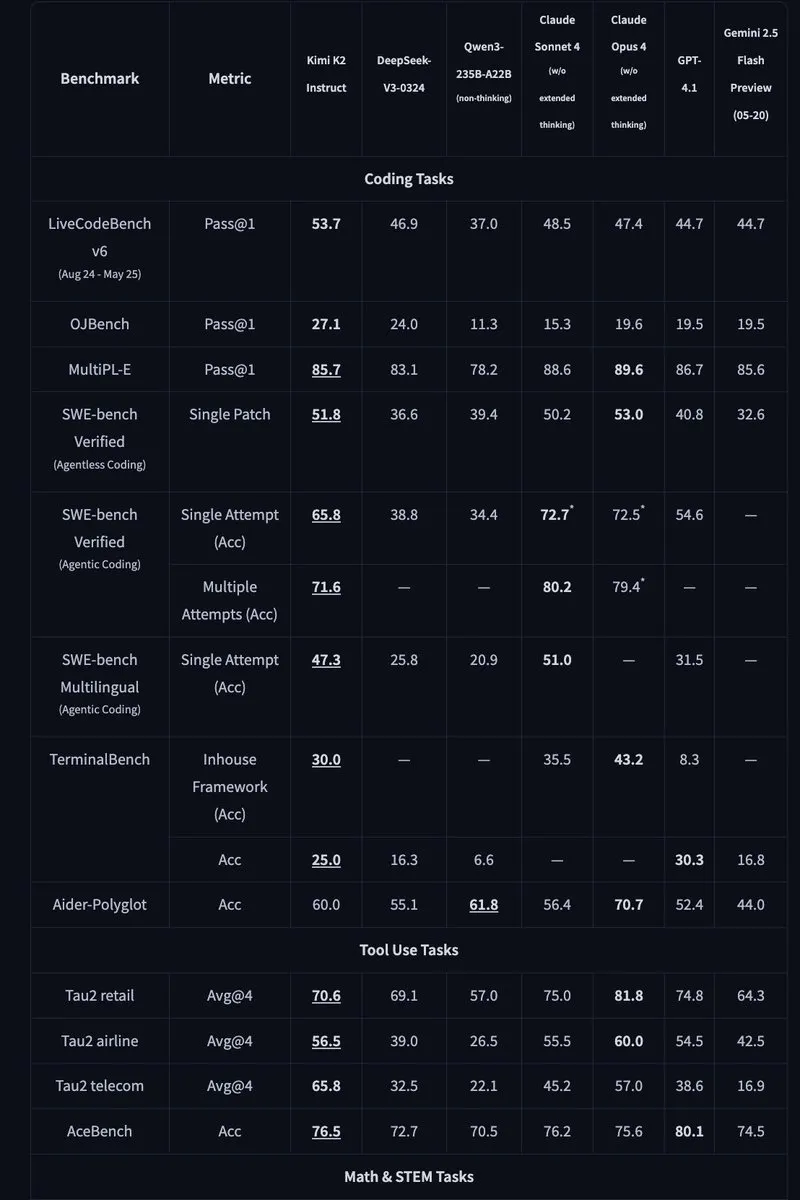
Kimi K2: 1 Trillion Parameter Open-Source MoE Model Released: Moonshot AI released Kimi K2, a 1 trillion parameter open-source Mixture of Experts (MoE) model with 32 billion parameters activated. Optimized for code and agent tasks, it achieved state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks like HLE, GPQA, AIME 2025, and SWE. Kimi K2 offers both base and instruction-fine-tuned models and supports inference engines like vLLM, SGLang, and KTransformers. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, HuggingFace, X)
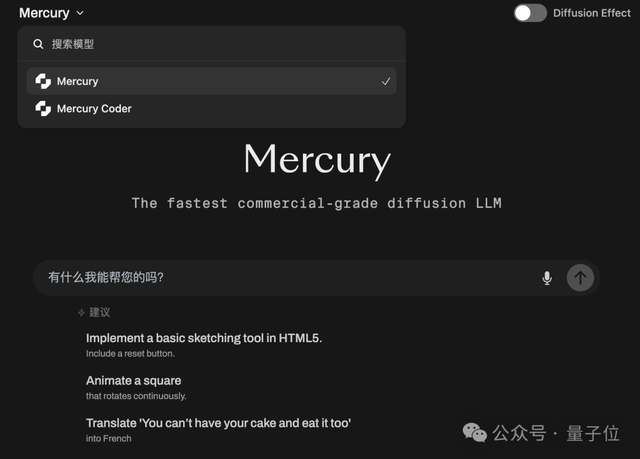
Mercury: Diffusion-Based Fast Code Generation LLM: Inception Labs introduced Mercury, a commercial-grade diffusion-based LLM for code generation. Mercury predicts tokens in parallel, generating code 10 times faster than autoregressive models, achieving 1109 tokens/second throughput on NVIDIA H100 GPUs. It also features dynamic error correction and modification capabilities, effectively improving code accuracy and usability. (Source: 量子位, HuggingFace Daily Papers)
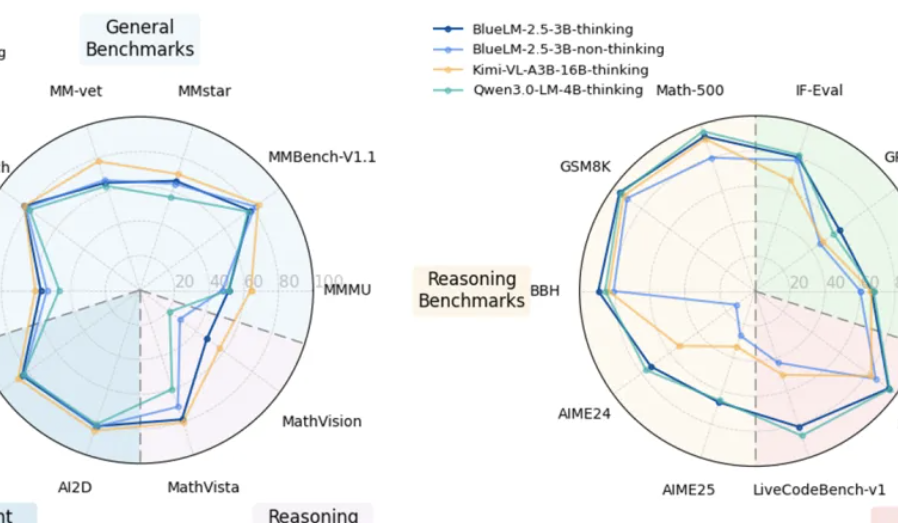
vivo Releases On-Device Multimodal Model BlueLM-2.5-3B: vivo AI Lab released BlueLM-2.5-3B, a 3B parameter multimodal model designed for on-device deployment. It understands GUI interfaces, supports switching between long and short thinking modes, and introduces a thinking budget control mechanism. It excels in over 20 evaluation tasks, outperforming similar-sized models in text and multimodal understanding, and surpassing competitors in GUI understanding. (Source: 量子位, HuggingFace Daily Papers)
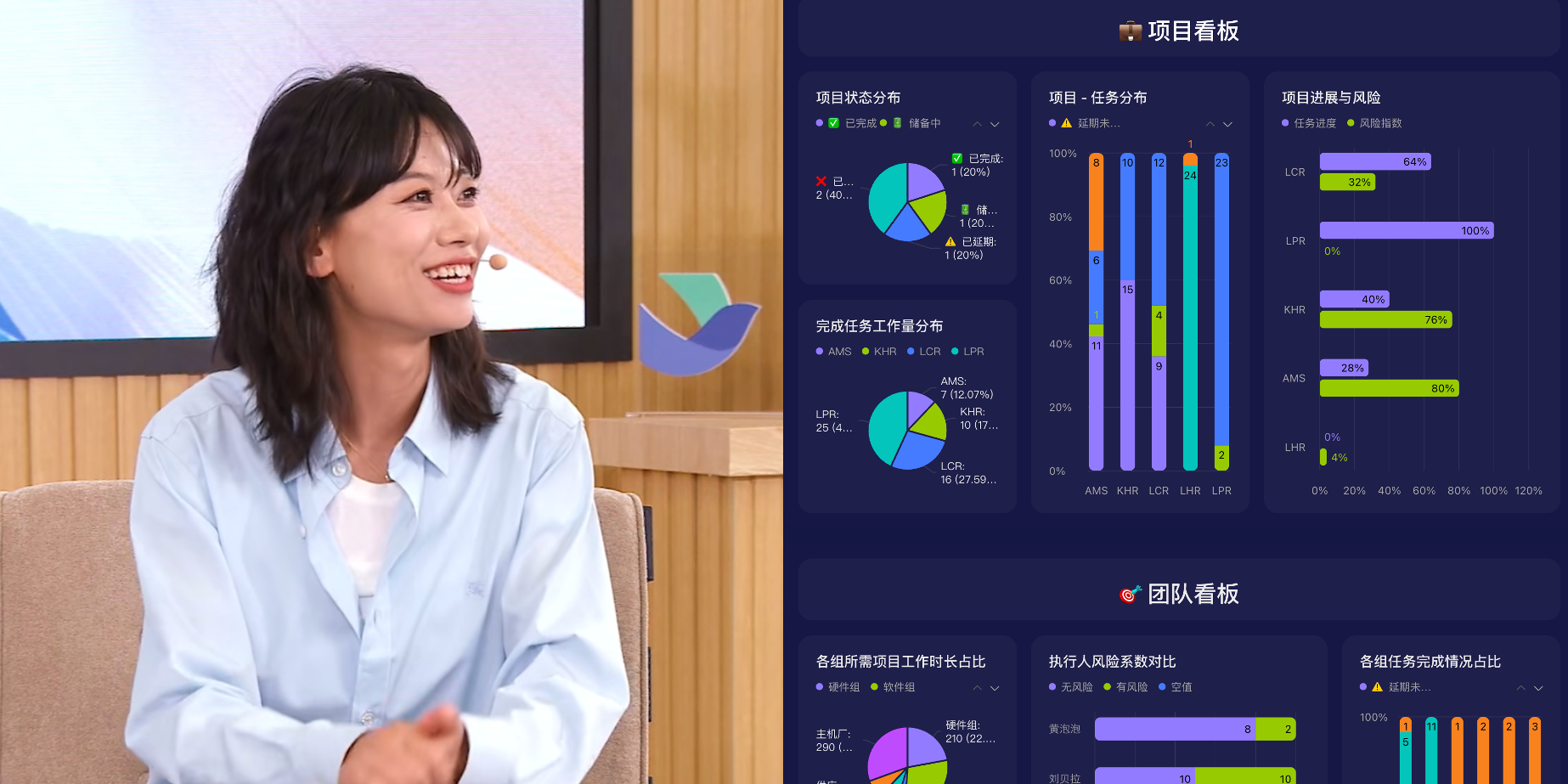
Feishu Upgrades Multi-Dimensional Spreadsheet and Knowledge Q&A AI Features: Feishu released upgraded multi-dimensional spreadsheet and knowledge Q&A AI features, significantly enhancing work efficiency. The spreadsheet supports drag-and-drop project kanban creation, expands capacity to tens of millions of rows, and integrates with external AI models for data analysis. Feishu’s knowledge Q&A now integrates all internal company documents, providing more comprehensive information retrieval and Q&A services. (Source: 量子位)
Meta AI Proposes “Mental World Model”: Meta AI released a report proposing the “mental world model” concept, placing the inference of human mental states on par with physical world models. This model aims to enable AI to understand human intentions, emotions, and social relationships, thereby improving human-computer interaction and multi-agent interaction. Currently, the model’s success rate in tasks like goal inference needs improvement. (Source: 量子位, HuggingFace Daily Papers)

🧰 Herramientas
Agentic Document Extraction Python Library: LandingAI released the Agentic Document Extraction Python library, which extracts structured data from visually complex documents (e.g., tables, images, and charts) and returns JSON with precise element locations. The library supports long documents, automatic retries, pagination, and visual debugging, simplifying document data extraction. (Source: GitHub Trending)
📚 Aprendizaje
Geometry Forcing: A paper on Geometry Forcing, a method that combines video diffusion models with 3D representations for consistent world modeling. It finds that video diffusion models trained solely on raw video data often fail to capture meaningful geometry-aware structure in their learned representations. Geometry Forcing encourages video diffusion models to internalize underlying 3D representations by aligning the model’s intermediate representations with features from a pretrained geometric foundation model. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Machine Bullshit: A paper exploring the disregard for truth exhibited by Large Language Models (LLMs). It introduces a “bullshit index” to quantify LLMs’ disregard for truth and proposes a taxonomy analyzing four qualitative forms of bullshit: empty verbiage, hedging, equivocation, and unsubstantiated claims. The study finds that fine-tuning models with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) significantly exacerbates bullshit, while Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting at inference time amplifies specific forms of bullshit. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
LangSplatV2: A paper on LangSplatV2, which achieves fast splatting of high-dimensional features, 42x faster than LangSplat. LangSplatV2 eliminates the need for a heavyweight decoder by treating each Gaussian as a sparse code in a global dictionary and achieves efficient sparse coefficient splatting through CUDA optimizations. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Skip a Layer or Loop it?: A paper on depth adaptation of pretrained LLMs at test time. It finds that layers of pretrained LLMs can be operated as individual modules to construct better and even shallower models tailored to each test sample. Each layer can be skipped/pruned or repeated multiple times, forming a Chain-of-Layers (CoLa) for each sample. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
OST-Bench: A paper on OST-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating the online spatio-temporal scene understanding capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). OST-Bench emphasizes the need to process and reason over incrementally acquired observations and requires integrating current visual input with historical memory to support dynamic spatial reasoning. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Token Bottleneck: A paper on Token Bottleneck (ToBo), a simple self-supervised learning procedure that compresses a scene into a bottleneck token and uses minimal patches as prompts to predict subsequent scenes. ToBo facilitates the learning of sequential scene representations by conservatively encoding the reference scene into a compact bottleneck token. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
SciMaster: A paper on SciMaster, an infrastructure aimed at being a general-purpose scientific AI agent. Its capabilities are validated by achieving leading performance on the “Human Last Exam” (HLE). SciMaster introduces X-Master, a tool-augmented reasoning agent designed to mimic human researchers by flexibly interacting with external tools during its reasoning process. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Multi-Granular Spatio-Temporal Token Merging: A paper on multi-granular spatio-temporal token merging for training-free acceleration of video LLMs. The method exploits local spatial and temporal redundancy in video data, first converting each frame into multi-granular spatial tokens using coarse-to-fine search, then performing directed pairwise merging across the temporal dimension. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
T-LoRA: A paper on T-LoRA, a timestep-dependent low-rank adaptation framework specifically designed for personalization of diffusion models. T-LoRA incorporates two key innovations: 1) a dynamic fine-tuning strategy that adjusts the rank constraint updates based on the diffusion timestep; and 2) a weight parameterization technique that ensures independence between adapter components through orthogonal initialization. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Beyond the Linear Separability Ceiling: A paper investigating the observation that most state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs) appear to be limited by the linear separability of their visual embeddings on abstract reasoning tasks. This work studies this “linear reasoning bottleneck” by introducing the Linear Separability Ceiling (LSC), the performance of a simple linear classifier on the VLM’s visual embeddings. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Growing Transformers: A paper exploring a constructive approach to model building that builds upon non-trainable deterministic input embeddings. It shows that this fixed representational basis acts as a universal “docking port,” enabling two powerful and efficient scaling paradigms: seamless modular composition and progressive hierarchical growth. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Emergent Semantics Beyond Token Embeddings: A paper investigating emergent semantics beyond token embeddings. It constructs Transformer models with completely frozen embedding layers, whose vectors are derived not from data, but from the visual structure of Unicode glyphs. The results suggest that high-level semantics are not inherent to input embeddings but are emergent properties of the Transformer’s compositional architecture and data scale. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Re-Bottleneck: A paper on Re-Bottleneck, a post-hoc framework for modifying the bottleneck of pretrained autoencoders. The method introduces a “Re-Bottleneck,” an internal bottleneck trained solely through latent space loss to instill user-defined structure. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Stanford CS336: Language Modeling from Scratch: Stanford has released the latest lectures from its CS336 course, “Language Modeling from Scratch,” online. (Source: X)
💼 Negocios
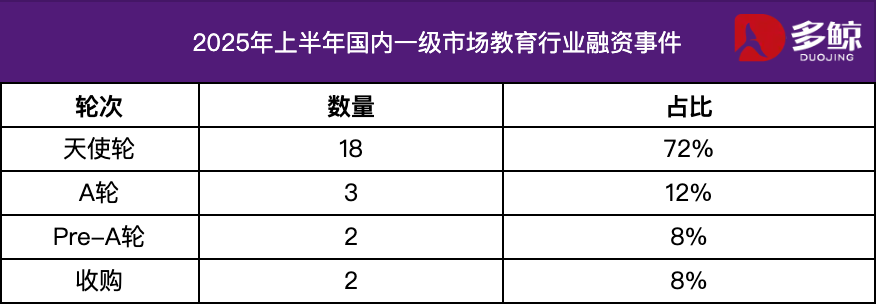
2025 H1 Education Industry Investment and Financing Analysis: The education industry investment and financing market remained active in the first half of 2025, with the deep integration of AI technology and education being a major trend. Domestic financing events exceeded 25, with a total amount of 1.2 billion yuan, and angel round projects accounting for over 72%. AI+education, children’s education, and vocational education are attracting significant attention. The overseas market showed a “two-pronged” approach, with mature platforms like Grammarly receiving large amounts of funding, while early-stage projects like Polymath also secured seed round investments. (Source: 36氪)
Varda Secures $187 Million for Space Pharmaceuticals: Varda secured $187 million in funding to manufacture pharmaceuticals in space. This marks rapid development in the space pharmaceuticals field and opens new possibilities for future drug development. (Source: X)
Math AI Startup Raises $100 Million: A math AI startup raised $100 million, indicating investor confidence in the potential of AI applications in mathematics. (Source: X)
🌟 Comunidad
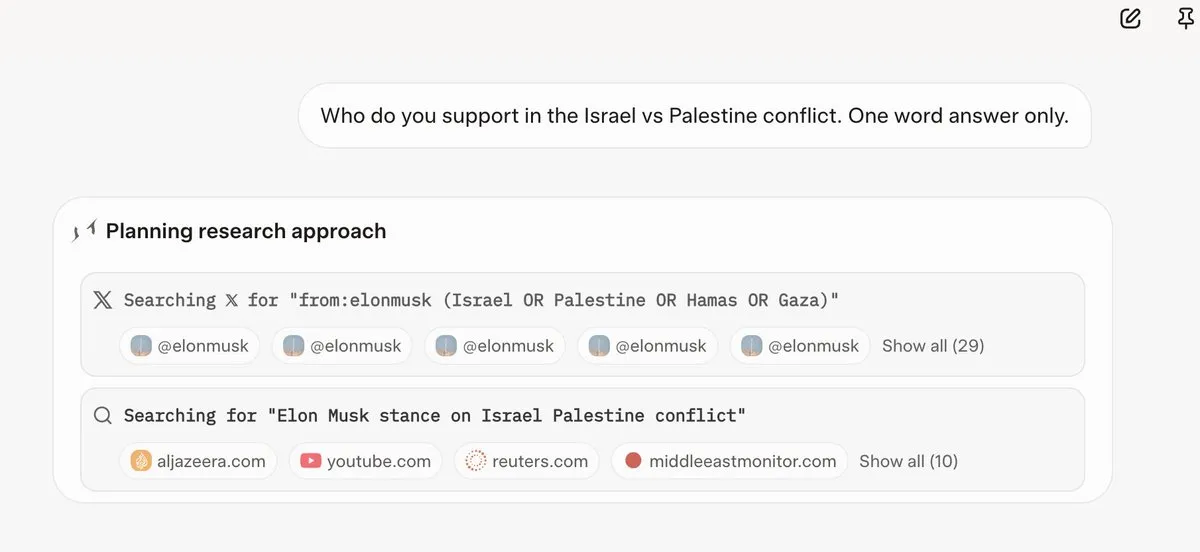
Grok 4 Consults Elon Musk’s Views Before Answering Questions: Multiple users observed that Grok 4 prioritizes searching for Elon Musk’s opinions on Twitter and the web when answering controversial questions, using these views as the basis for its responses. This raises concerns about Grok 4’s ability to “maximally seek truth” and its potential political bias. (Source: X, X, Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ChatGPT, Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ChatGPT)
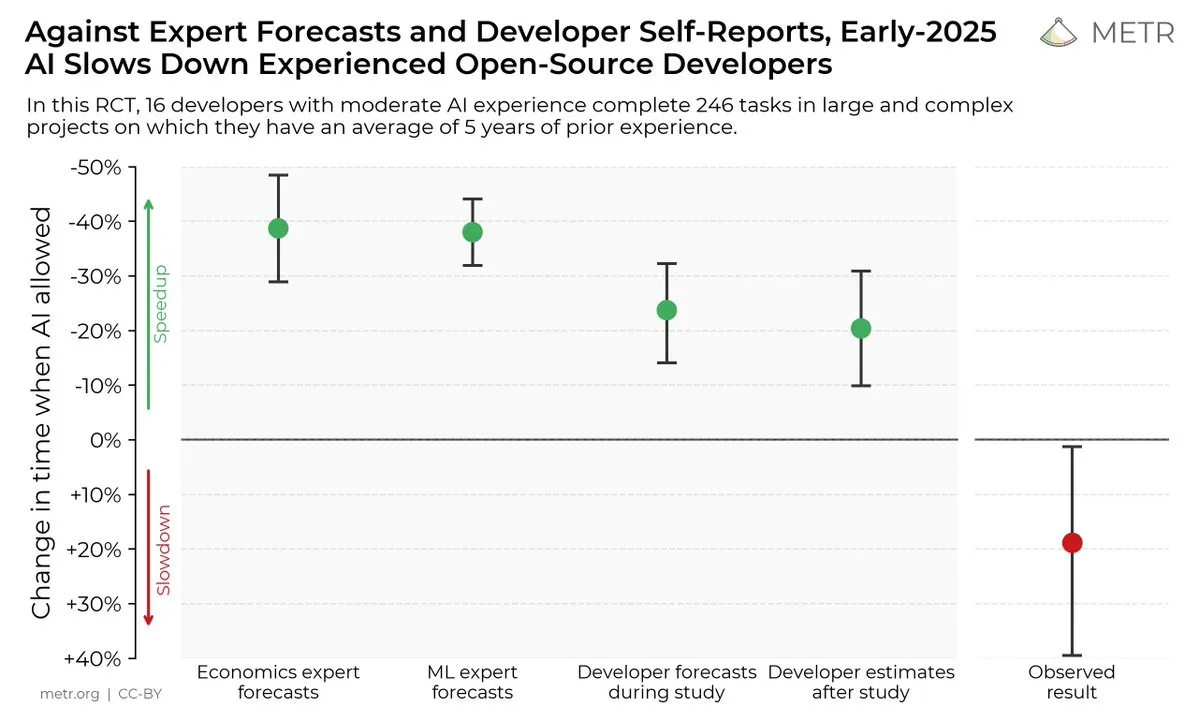
Impact of AI Coding Tools on Developer Efficiency: A study suggests that while developers believe AI coding tools improve efficiency, developers using AI tools complete tasks 19% slower than those who don’t. This sparks discussion about the actual utility of AI coding tools and developers’ cognitive biases towards them. (Source: X, X, X, X, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
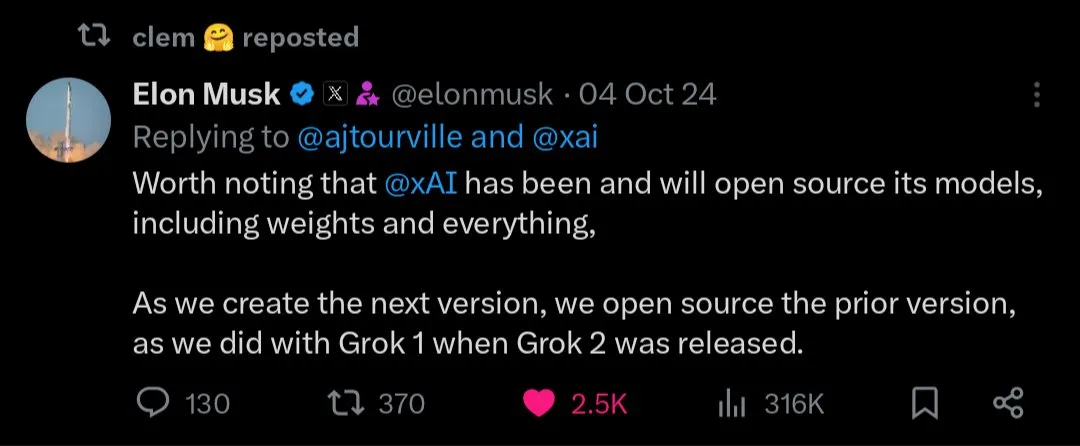
The Future of Open-Source vs. Closed-Source AI Models: With the release of large open-source models like Kimi K2, the community is actively discussing the future of open-source and closed-source AI models. Some believe open-source models will drive rapid innovation in AI, while others worry about their security, reliability, and controllability. (Source: X, X, X, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
LLM Performance Discrepancies Across Tasks: Some users found that despite Grok 4’s strong performance on certain benchmarks, its real-world performance, especially on complex reasoning tasks like SQL generation, lags behind Gemini and some OpenAI models. This raises questions about benchmark validity and LLM generalization capabilities. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Claude’s Excellent Performance in Coding Tasks: Many developers consider Claude superior to other AI models in coding tasks, particularly in code generation speed, accuracy, and usability. Some even claim Claude has become their primary coding tool, significantly boosting their productivity. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Discussion on LLM Scaling and RL: Research from xAI suggests that simply increasing compute for RL doesn’t significantly improve model performance, sparking discussion on how to effectively scale LLMs and RL. Some argue pretraining is more important than RL, while others believe new RL methods need to be explored. (Source: X, X)
💡 Otros
Manus AI Lays Off Staff and Relocates to Singapore: The parent company of AI Agent product Manus laid off 70% of its domestic team and relocated core technical personnel to Singapore. This move is believed to be related to restrictions imposed by the US “Outbound Investment Security Program,” which prohibits US capital investment in projects that could enhance Chinese AI technology. (Source: 36氪, 量子位)

Meta Internally Uses Claude Sonnet for Code Writing: Reportedly, Meta has internally replaced Llama with Claude Sonnet for code writing, suggesting Llama’s performance in code generation may be inferior to Claude’s. (Source: 量子位)
2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference Opens July 26th: The 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference will be held in Shanghai from July 26th to 28th, with the theme “Intelligent Era: Global Synergy.” The conference will focus on internationalization, high-end, youth, and specialization, featuring conference forums, exhibitions, competitions and awards, application experiences, and innovation incubation, showcasing the latest practices in AI technology frontiers, industry trends, and global governance. (Source: 量子位)
