Keywords:OpenAI, AI infrastructure, AI-generated viruses, AlphaEarth Foundations, RTEB, Claude Sonnet 4.5, DeepSeek V3.2-Exp, Multimodal AI, OpenAI Stargate Project, Transformer Genomic Language Model, Google AlphaEarth 10-meter modeling, Hugging Face RTEB benchmark, Anthropic Claude code generation
As a senior editor for the AI column, I have thoroughly analyzed, summarized, and refined the news and social discussions provided. Below is the consolidated content:
🔥 Spotlight
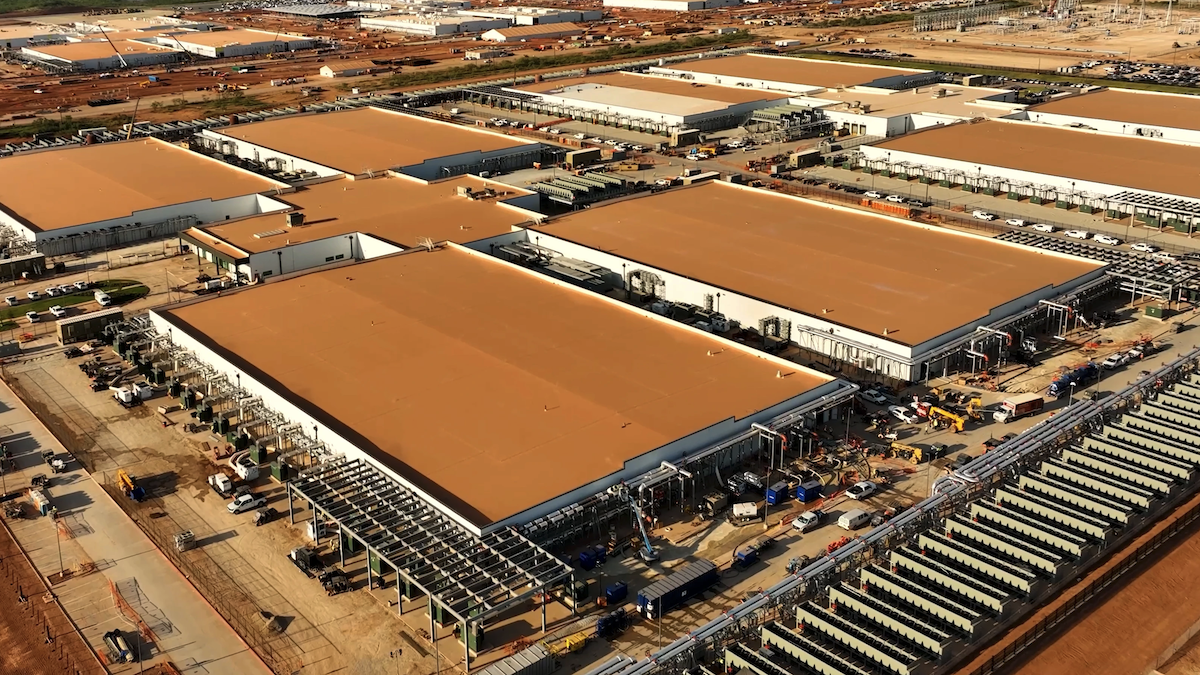
OpenAI’s Trillion-Dollar Infrastructure Bet: OpenAI is collaborating with Oracle and SoftBank, planning to invest trillions of dollars globally to build computing infrastructure, code-named “Stargate.” Initially, five new sites in the United States were announced, costing $400 billion, and a “Stargate UK” project is being built in collaboration with Nvidia. OpenAI predicts future AI electricity demand will reach 100 gigawatts, with total investment potentially reaching $5 trillion. This move aims to meet the immense computing demands of AI models but also raises concerns about funding, energy consumption, and potential financial risks, highlighting AI development’s extreme reliance on infrastructure. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)

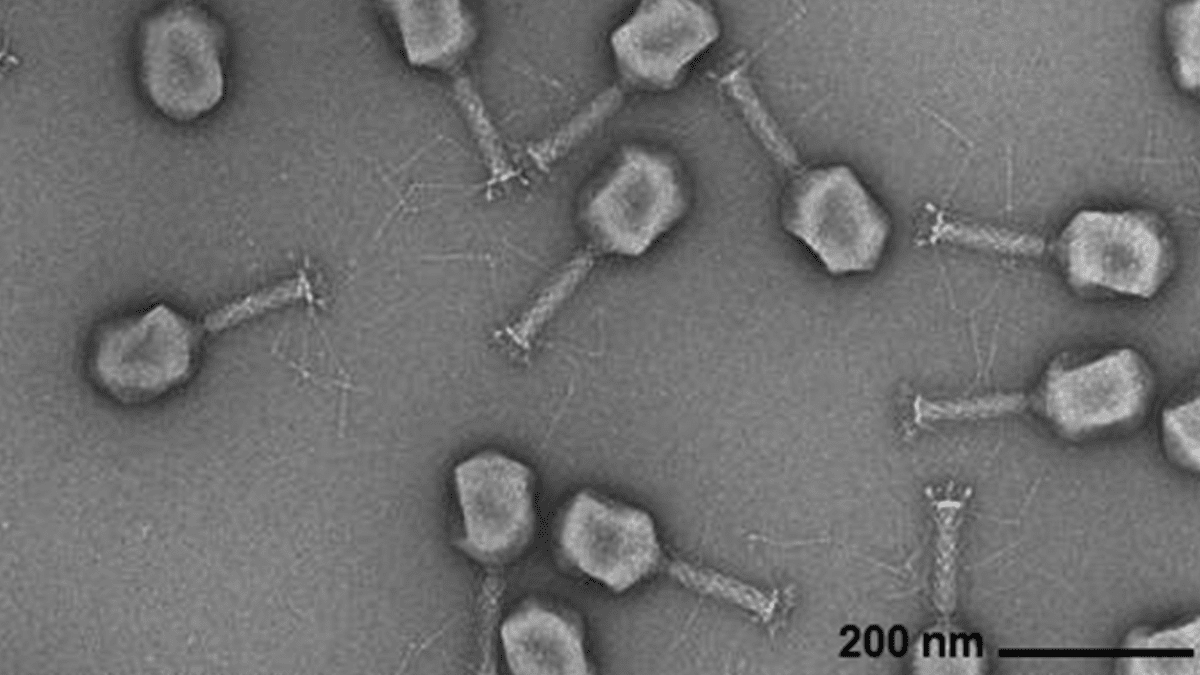
AI Generates Viral Genomes: Researchers from Arc Institute, Stanford University, and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have successfully synthesized novel bacteriophage viruses capable of combating common bacterial infections from scratch, using a Transformer-based genomic language model. This technology fine-tunes viral genome sequences to generate new genomes with specific functions that differ from naturally occurring viruses. This breakthrough offers new avenues for developing antibiotic alternatives but also raises concerns about biosecurity and malicious use, emphasizing the necessity of research into biological threat response. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
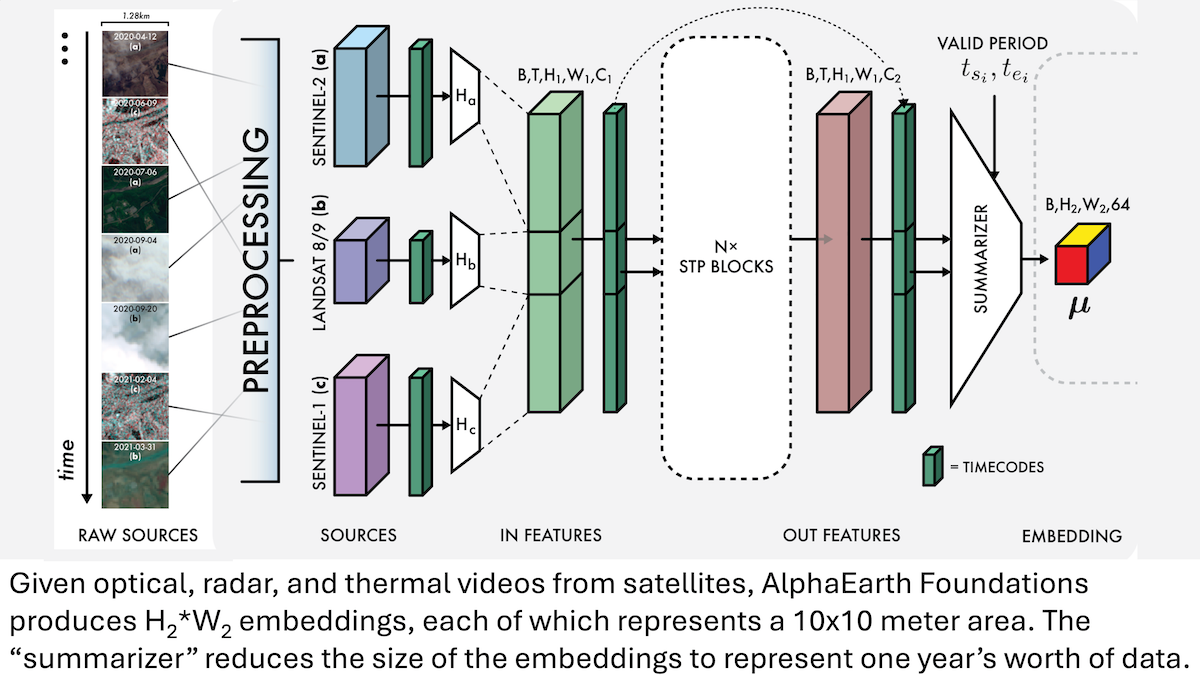
Google AlphaEarth Foundations: 10-Meter Resolution Earth Modeling: Google researchers have introduced the AlphaEarth Foundations (AEF) model, capable of integrating satellite imagery and other sensor data to create a detailed 10-meter square resolution model of the Earth’s surface, generating embeddings representing Earth’s characteristics annually from 2017 to 2024. These embeddings can track various planetary properties such as humidity, precipitation, and vegetation, as well as global challenges like food production, wildfire risk, and reservoir water levels, providing an unprecedented high-precision tool for environmental monitoring and climate change research. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
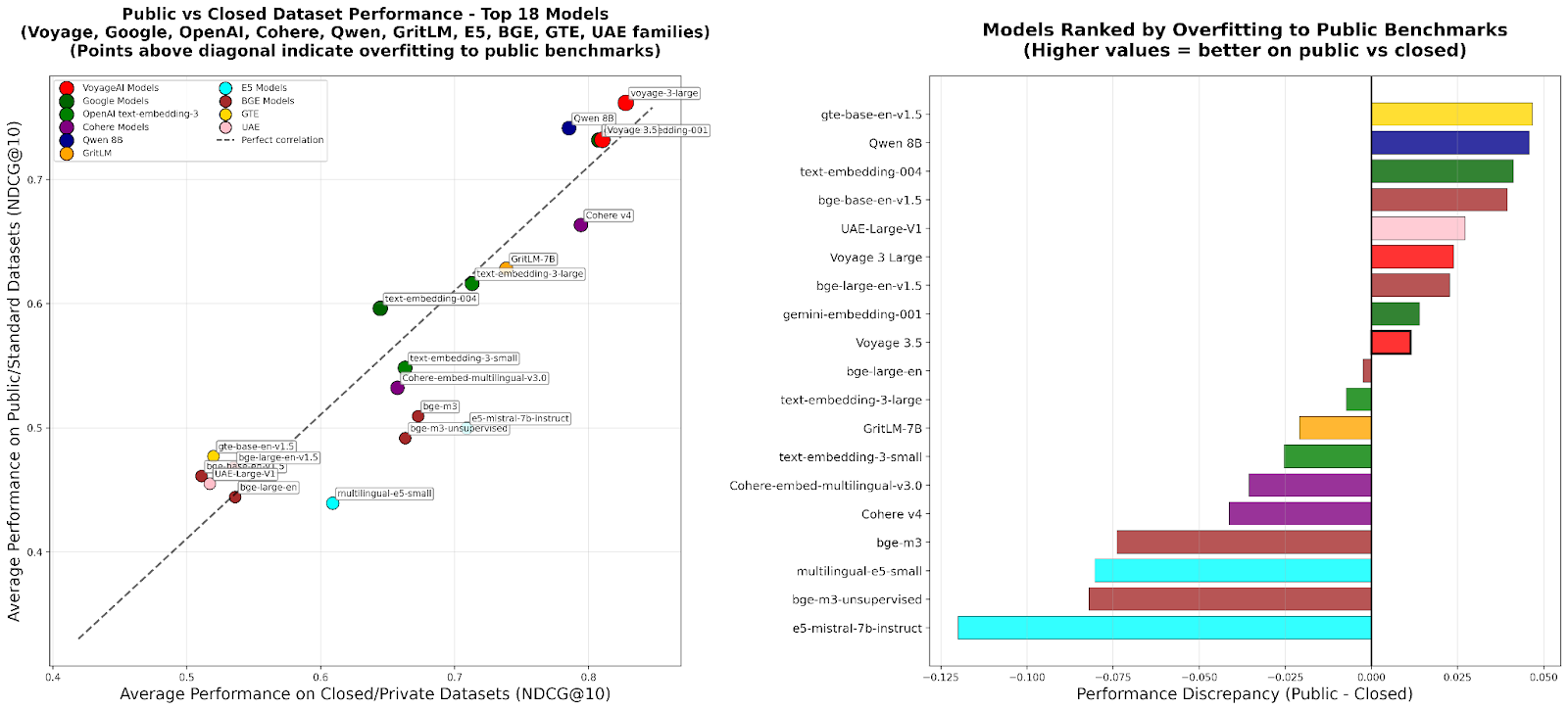
RTEB: A New Standard for Retrieval Embedding Evaluation: Hugging Face has launched the beta version of its Retrieval Embedding Benchmark (RTEB), designed to provide a reliable evaluation standard for the retrieval accuracy of embedding models. By combining a hybrid strategy of public and private datasets, this benchmark effectively addresses the problem of model overfitting in existing benchmarks, ensuring that evaluation results better reflect a model’s generalization ability on unseen data. This is crucial for improving the quality of AI applications such as RAG and Agents. (Source: HuggingFace Blog)
Scalable RL Intermediate Training: Enabling Reasoning through Action Abstraction: Recent research proposes the “Reasoning as Action Abstraction” (RA3) algorithm, which significantly enhances the reasoning and code generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by identifying compact and useful action sets during the intermediate training phase of Reinforcement Learning (RL) and accelerating online RL. This method performs exceptionally well in code generation tasks, improving average performance by 8 to 4 percentage points over baseline models, and achieving faster RL convergence and higher asymptotic performance. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
🎯 Trends
OpenAI Sora 2: A New Era for AI Video Social Media: OpenAI has released Sora 2 and launched a social application of the same name, aiming to create a social network centered around users and their social circles (friends, pets) through AI-generated video browsing and creation, rather than a traditional content distribution platform. Sora 2 demonstrates powerful physics simulation and audio generation capabilities, though early tests still show minor flaws like “counting fingers.” Its release has sparked discussions about AI video addiction, deepfakes, and OpenAI’s commercialization path. Sam Altman responded that Sora aims to balance technological breakthroughs with user enjoyment and fund AI research. (Source: 36氪, Reddit r/ChatGPT, OpenAI)
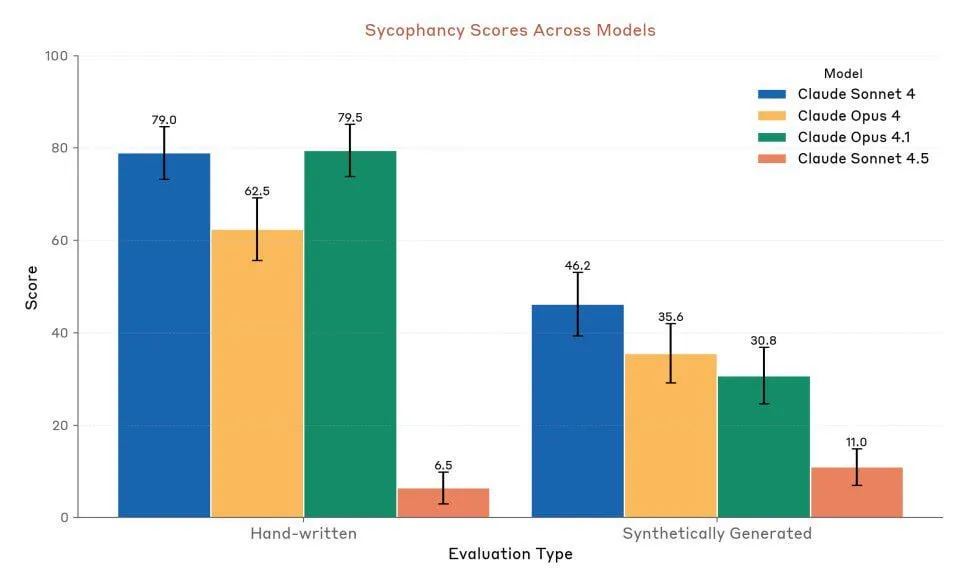
Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4.5: New Benchmark for Code and Agents: Anthropic has released Claude Sonnet 4.5, hailed as “the world’s best coding model” and “the most powerful model for building complex Agents,” featuring an autonomous runtime of up to 30 hours and demonstrating significant coding performance improvements on GitHub tasks. The model also includes a new memory function, allowing project progress to be saved. Despite its highly praised performance, user discussions persist regarding its usage limits and its actual performance compared to Opus 4.1 and GPT-5. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
DeepSeek V3.2-Exp: Sparse Attention Architecture Boosts Efficiency: DeepSeek has released the DeepSeek V3.2-Exp large language model, introducing a new Sparse Attention (DSA) architecture that reduces the primary attention complexity from O(L²) to O(L·k). This significantly optimizes prefill and decoding costs in long-context scenarios, thereby substantially lowering API usage fees. Jiuzhang Cloud Computing has taken the lead in adapting DeepSeek V3.2-Exp, offering secure and efficient private deployment solutions to meet enterprises’ demands for data security and flexible computing power. (Source: 量子位, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

Multimodal Audio-Text Model LFM2-Audio-1.5B Released: Liquid AI has launched LFM2-Audio-1.5B, an end-to-end audio-text foundational model capable of understanding and generating both text and audio. This model boasts 10x faster inference speed than comparable models, and despite having only 1.5B parameters, its quality rivals models 10 times larger, supporting local deployment and real-time conversation. Hume AI also released Octave 2, a faster, cheaper multilingual text-to-speech model with multi-speaker conversation and voice transformation capabilities. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, QuixiAI)

Microsoft Agent Framework: New Progress in Agent System Development: Microsoft has released the Microsoft Agent Framework, integrating AutoGen and Semantic Kernel into a unified, production-ready SDK for building, orchestrating, and deploying multi-Agent systems. The framework supports .NET and Python and enables multi-Agent workflows through graph-based orchestration, aiming to simplify the development, observation, and governance of Agent applications and accelerate the adoption of enterprise-grade AI Agents. (Source: gojira, omarsar0)

Frontiers of AI Robotics and Industrial Competition: Robotics technology continues to advance, with Amazon FAR’s OmniRetarget optimizing human motion capture to enable complex humanoid skill learning with minimal reinforcement learning. Periodic Labs is dedicated to creating “AI scientists” to accelerate scientific discovery. Nvidia, meanwhile, highlights the role of its open physics engine Newton, inference vision-language model Cosmos Reason, and robotics foundational model Isaac GR00T N1.6 in physical AI deployment. Concurrently, China demonstrates a leading edge in robot production and humanoid robot costs, drawing attention to the global robotics industry competitive landscape. (Source: pabbeel, LiamFedus, nvidia, atroyn)
🧰 Tools
Tinker API: Flexible Interface for Simplified LLM Fine-tuning: Thinking Machines Lab has launched Tinker API, a flexible interface designed for language model fine-tuning. It allows researchers and developers to write training loops locally, while Tinker handles running them on distributed GPU clusters and managing infrastructure complexity, enabling users to focus on algorithms and data. This tool aims to lower the barrier to LLM post-training, accelerate experimentation and innovation with open models, and has been praised by experts like Andrej Karpathy as “the infrastructure I always wanted.” (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Thinking Machines, karpathy)

LlamaAgents: One-Click Document Agent Deployment: LlamaIndex has launched LlamaAgents, offering one-click deployment of document-centric AI Agents, aiming to accelerate the building and delivery of document agents by 10x. The platform provides 90% pre-configured templates, supporting automated processing of document-intensive tasks like invoices, contract review, and claims, and allowing unlimited customization. Users can deploy on LlamaCloud and easily manage and update Agent workflows via Git repositories, significantly shortening development cycles. (Source: jerryjliu0, jerryjliu0)

Hex AI Agent: Empowering Analytics and Team Collaboration: Hex has released three new AI Agents designed specifically for data analysis and team collaboration: Threads provides conversational data interaction, the Semantic Model Agent creates controlled contexts for accurate answers, and the Notebook Agent revolutionizes the daily work of data teams. All these Agents are powered by Claude 4.5 Sonnet, aiming to transform conversational AI analysis from a future concept into an immediately available, efficient tool. (Source: sarahcat21)
Sculptor: The Missing UI for Claude Code: Imbue has launched Sculptor, a user interface designed for Claude Code, aiming to enhance the Agent programming experience. It allows developers to run multiple Claude Agents in parallel within isolated containers and synchronize Agent work to local development environments for testing and editing via “pairing mode.” Sculptor also plans to support GPT-5 and offer suggested features like misleading behavior detection, aiming to make Agent programming smoother and more efficient. (Source: kanjun, kanjun)
Synthesia 3.0: New Breakthrough in Interactive AI Video: Synthesia has released version 3.0, introducing several innovative features, including “Video Agents” (interactive videos capable of real-time conversation, used for training and interviews), upgraded “Avatars” (created from a single prompt or image, with realistic facial expressions and body movements), and “Copilot” (an AI video editor for quickly generating scripts and visual elements). Additionally, enhanced interactivity features and course design tools aim to revolutionize video creation and learning experiences. (Source: synthesiaIO, synthesiaIO)
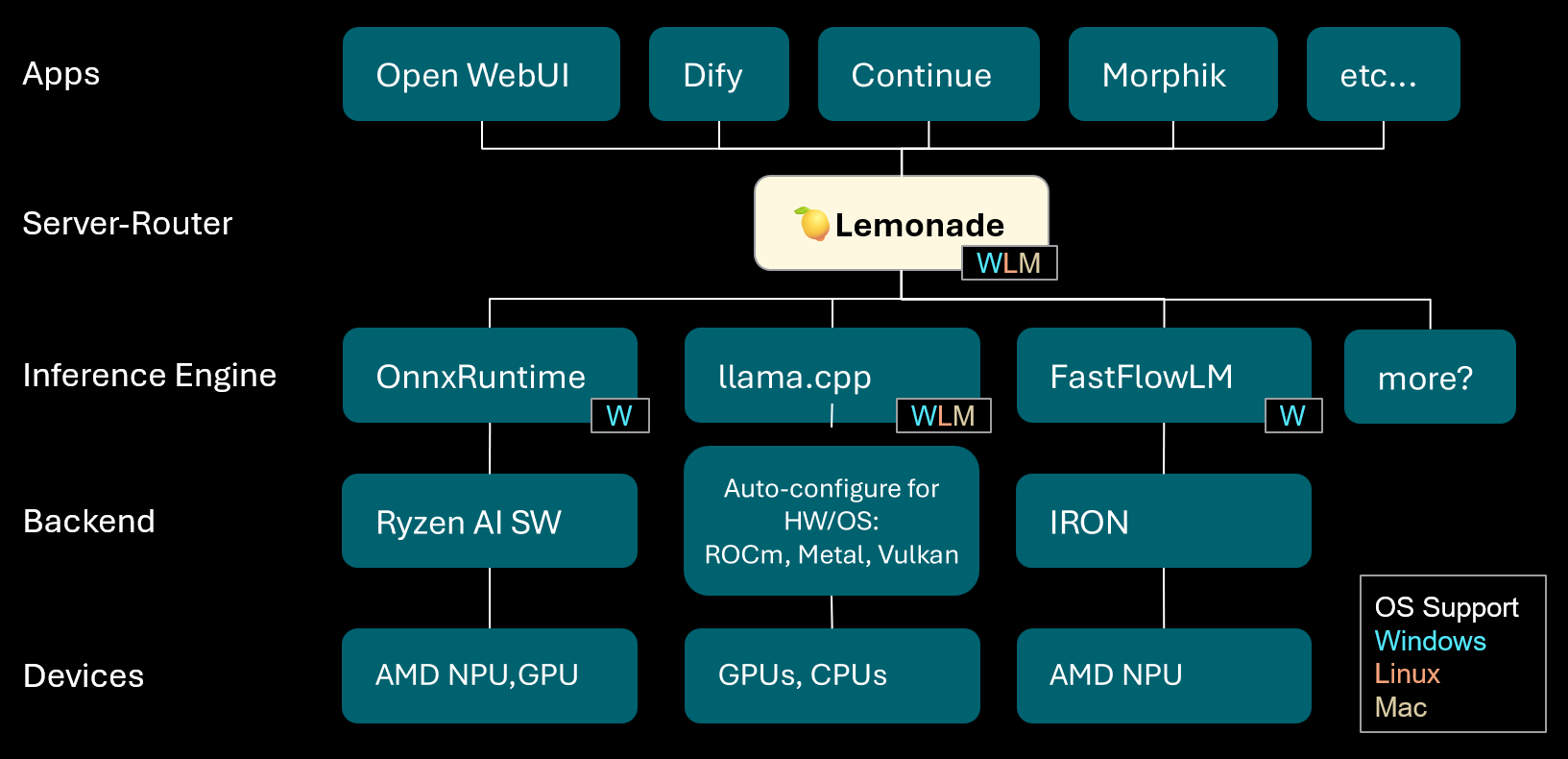
Lemonade: Local LLM Server-Router: Lemonade has released version 8.1.11, a local LLM server-router that automatically configures high-performance inference engines for various PCs, including AMD NPU and macOS/Apple Silicon devices. It supports multiple model formats like ONNX, GGUF, and FastFlowLM, and leverages llama.cpp’s Metal backend for efficient computation on Apple Silicon, providing users with a flexible, high-performance local LLM experience. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
PopAi: AI-Powered Presentation Generation: PopAi demonstrated its AI tool’s ability to generate detailed business presentations with charts and illustrations from simple prompts in minutes. This highlights AI’s efficiency in content creation, enabling non-professionals to quickly produce high-quality presentation materials. (Source: kaifulee)

GitHub Copilot CLI: Automatic Model Selection: GitHub Copilot CLI now offers automatic model selection for business and enterprise users. This update enables the system to automatically choose the most suitable model based on the current task, aiming to improve development efficiency and code generation quality. (Source: pierceboggan)
Mixedbread Search: Multilingual, Multimodal Local Search: Mixedbread has launched its beta search system, offering fast, accurate, multilingual, and multimodal document search capabilities. The system emphasizes local operation, allowing users to efficiently retrieve documents on their own devices, especially suitable for scenarios requiring diverse data types. (Source: TheZachMueller)
Hume AI Octave 2: Next-Gen Multilingual TTS Model: Hume AI has released Octave 2, a next-generation multilingual Text-to-Speech (TTS) model. This model is 40% faster and 50% cheaper than its predecessor, supporting over 11 languages, multi-speaker conversation, voice transformation, and phoneme editing, aiming to provide a faster, more realistic, and emotionally expressive voice AI experience. (Source: AlanCowen)
AssemblyAI September Update: All-in-One AI Audio Service: AssemblyAI reviewed its September updates, highlighting the launch of an in-app Playground, general language extensions, EU PII redaction features, as well as streaming performance improvements and keyword boosting. These updates aim to provide users with more comprehensive and efficient AI audio processing services. (Source: AssemblyAI)
Voiceflow MCP Tool: Standardizing Agent Tool Integration: Voiceflow has launched the Model Context Protocol (MCP) tool, providing a standardized way for AI Agents to use various tools. This simplifies custom integration work for developers and offers pre-built third-party tools for no-code users, greatly expanding the capabilities of Voiceflow Agents. (Source: ReamBraden)
Salesforce Agentforce Vibes: Enterprise-Grade Agent Coding: Salesforce, based on Cline’s architecture, has launched the “Agentforce Vibes” product, leveraging Model Context Protocol (MCP) support to provide enterprise customers with autonomous coding capabilities. This product ensures secure communication between LLMs and internal/external knowledge sources/databases, aiming to enable AI coding at an enterprise scale. (Source: cline)

JoyAgent-JDGenie: General Agent Architecture Report: The GAIA (Generalist Agent Architecture) technical report has been released. This architecture integrates a collective multi-Agent framework (combining planning, execution Agents, and review model voting), a hierarchical memory system (working, semantic, and procedural layers), and a tool suite for search, code execution, and multimodal parsing. The framework performs exceptionally well in comprehensive benchmarks, surpassing open-source baselines and approaching proprietary system performance, providing a path for building scalable, resilient, and adaptive AI assistants. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
AI Travel Assistant: Empowering from Planning to Action: Mafengwo’s AI Travel Assistant App aims to elevate AI from traditional guide generation to practical action assistance during travel. The application can generate personalized guides with rich text and images, and offers practical features like AI Agent-assisted restaurant reservations, effectively addressing pain points such as language barriers. While there is still room for improvement in real-time translation and deep personalization, it has significantly lowered the barrier to “traveling without a plan,” demonstrating AI’s immense potential in connecting digital information with physical world actions. (Source: 36氪)

📚 Learning
Career Development Advice for AI Researchers: For AI researchers’ career development, experts emphasize the importance of being excellent coders, encouraging reproducing research papers from scratch, and deeply understanding infrastructure. They also suggest actively building a personal brand, sharing interesting ideas, maintaining curiosity and adaptability, and prioritizing positions that foster innovation and learning. In the long run, sustained effort and achieving tangible results are key to building confidence and motivation. (Source: dejavucoder, BlackHC)
Python Data Analysis Course: DeepLearningAI has launched a new Python data analysis course, designed to teach how to use Python to improve the efficiency, traceability, and reproducibility of data analysis. This course is part of a data analysis professional certificate, emphasizing the core role of programming skills in modern data work. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
Students Get Free Copilot AI Tools: Microsoft is offering eligible university students a free 12-month Microsoft 365 Personal subscription, which includes additional access to Copilot Podcasts, Deep Research, and Vision. This initiative aims to provide students with powerful AI tools to support their learning and innovation. (Source: mustafasuleyman)

Local AI/ML Course Setup: An educator shared how to create hands-on AI/ML practical courses for students based on local development and consumer-grade hardware with a limited budget. He suggested using small models, Transformer Lab as a training platform, and emphasized understanding core concepts rather than blindly pursuing model scale, thereby improving students’ learning outcomes and practical operational abilities. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
Upcoming AI Seminars: AIhub has published a list of upcoming machine learning and AI seminars for October-November 2025. These events cover various topics, from data collection on politically restricted social media platforms to AI ethics. All seminars are free and offer online participation options, providing rich learning and networking opportunities for the AI community. (Source: aihub.org)

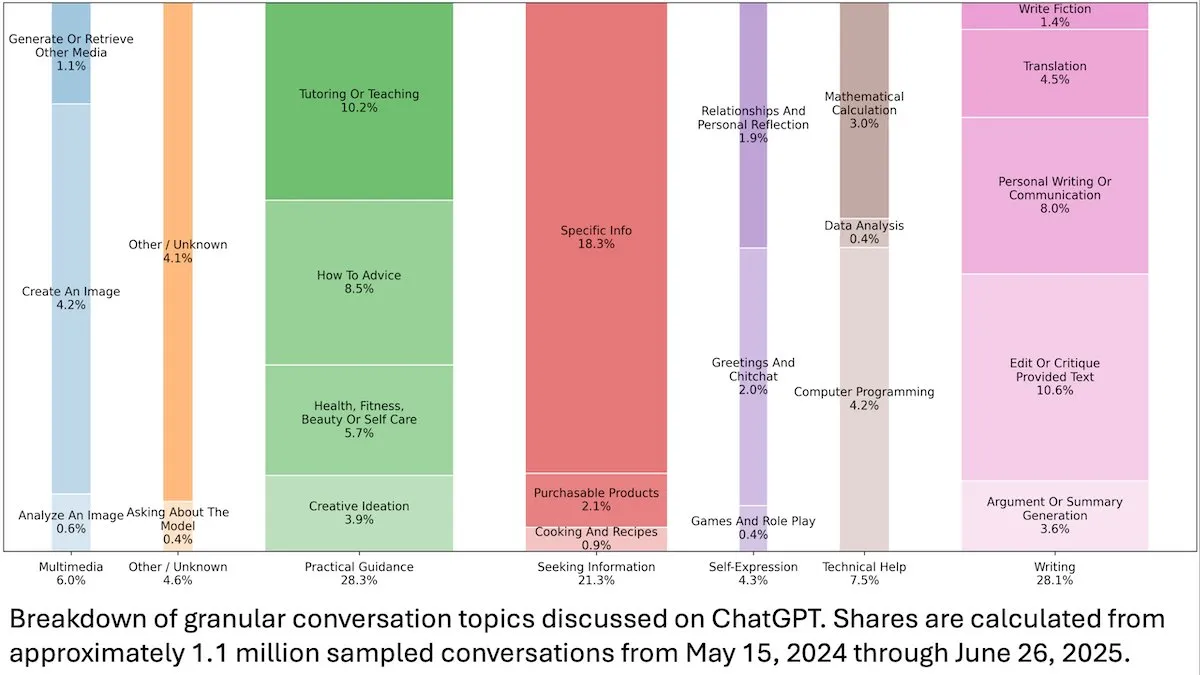
ChatGPT User Behavior Insights: An OpenAI study published by DeepLearningAI reveals that an analysis of 110 million anonymous ChatGPT conversations indicates its usage has shifted from work-related to personal needs, with a higher proportion of female users and young users aged 18-25. The most common requests are for practical guidance (28.3%), writing assistance (28.1%), and information queries (21.3%), revealing ChatGPT’s widespread application in daily life. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
Code2Video: Code-Driven Educational Video Generation: A study proposes Code2Video, a code-centric Agent framework that generates professional educational videos from executable Python code. The framework comprises three collaborative Agents—a planner, an encoder, and a critic—capable of structuring lecture content, converting it into code, and optimizing visuals. It achieved a 40% performance improvement on the educational video benchmark MMMC and generated videos comparable to human tutorials. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
BiasFreeBench: LLM Bias Mitigation Benchmark: BiasFreeBench is introduced as an empirical benchmark for comprehensively comparing eight mainstream LLM bias mitigation techniques. By reorganizing existing datasets, the benchmark introduces a response-level “Bias-Free Score” metric across two test scenarios—multiple-choice QA and open-ended multi-turn QA—to measure the fairness, safety, and anti-stereotypicality of LLM responses, aiming to establish a unified testing platform for bias mitigation research. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Transformer Multiplication Learning Obstacles and Long-Range Dependency Traps: Research reverse-engineered the reasons for Transformer models’ failure on seemingly simple tasks like multi-digit multiplication. The study found that models encode necessary long-range dependency structures in implicit chains of thought, but standard fine-tuning methods fail to converge to a global optimum that leverages these dependencies. By introducing an auxiliary loss function, researchers successfully resolved this issue, revealing the traps in Transformer learning of long-range dependencies and providing an example of solving the problem with correct inductive biases. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
VL-PRM Training Insights in Multimodal Reasoning: This research aims to elucidate the design space of Vision-Language Process Reward Models (VL-PRMs), exploring various strategies for dataset construction, training, and test-time scaling. By introducing a mixed data synthesis framework and perception-focused supervision, VL-PRMs demonstrate key insights across five multimodal benchmarks, including outperforming outcome reward models in test-time scaling, small VL-PRMs detecting process errors, and revealing the potential reasoning capabilities of stronger VLM backbones. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
GEM: A General Environment Simulator for Agentic LLMs: GEM (General Experience Maker) is an open-source environment simulator designed for experiential learning of LLM Agents. It provides a standardized Agent-environment interface, supports asynchronous vectorized execution for high throughput, and offers flexible wrappers for easy extension. GEM also includes a diverse suite of environments and integrated tools, along with baselines for training frameworks like REINFORCE, aiming to accelerate research into Agentic LLMs. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
GUI-KV: KV Cache Compression for Efficient GUI Agents: GUI-KV is a plug-and-play KV cache compression method designed for GUI Agents, enhancing efficiency without retraining. By analyzing attention patterns in GUI workloads, this method combines spatial saliency guidance and temporal redundancy scoring techniques to achieve near full-cache accuracy with a modest budget and significantly reduce decoding FLOPs, effectively leveraging GUI-specific redundancies. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Beyond Log-Likelihood: Research on Probabilistic Objective Functions for SFT: This study explores probabilistic objective functions for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) that go beyond traditional Negative Log-Likelihood (NLL). Through extensive experiments on 7 model backbones, 14 benchmarks, and 3 domains, it was found that when model capabilities are strong, objective functions that prioritize priors with smaller weights for low-probability tokens (e.g., -p, -p^10) outperform NLL; whereas NLL dominates when model capabilities are weaker. Theoretical analysis reveals how objective functions trade off based on model capability, providing a more principled optimization strategy for SFT. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
VLA-RFT: Validation-Reward-Based RL Fine-tuning in World Simulators: VLA-RFT is a reinforcement fine-tuning framework for Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, utilizing data-driven world models as controllable simulators. The simulator, trained on real interaction data, predicts future visual observations based on actions, enabling policy rollout with dense trajectory-level rewards. This framework significantly reduces sample requirements, surpassing strong supervised baselines in less than 400 fine-tuning steps and demonstrating robust performance under perturbed conditions. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
ImitSAT: Solving Boolean Satisfiability Problems via Imitation Learning: ImitSAT is an imitation learning-based CDCL solver branching strategy for solving Boolean Satisfiability Problems (SAT). This method learns expert KeyTraces, collapsing full runs into surviving decision sequences, providing dense decision-level supervision that directly reduces propagation counts. Experiments show that ImitSAT outperforms existing learning methods in propagation count and runtime, achieving faster convergence and stable training. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Empirical Study of Testing Practices in Open-Source AI Agent Frameworks: A large-scale empirical study of 39 open-source Agent frameworks and 439 Agent applications reveals testing practices within the AI Agent ecosystem. The study identifies ten unique testing patterns, finding that over 70% of testing effort is dedicated to deterministic components (like tools and workflows), while LLM-based planning agents account for less than 5%. Furthermore, regression testing for Trigger components is severely neglected, appearing in only about 1% of tests, revealing critical blind spots in Agent testing. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
DeepCodeSeek: Real-time API Retrieval for Code Generation: DeepCodeSeek proposes a novel technique for real-time API retrieval for context-aware code generation, enabling high-quality end-to-end code auto-completion and Agentic AI applications. This method predicts required APIs by extending code and indexing, addressing the issue of API leakage in existing benchmark datasets. Optimized, a compact 0.6B reranker outperforms an 8B model while maintaining 2.5 times lower latency. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
CORRECT: Distilled Error Identification in Multi-Agent Systems: CORRECT is a lightweight, training-free framework that achieves error identification and knowledge transfer in multi-Agent systems by leveraging an online cache of distilled error patterns. This framework can identify structured errors in linear time, avoiding expensive retraining, and adapts to dynamic MAS deployments. CORRECT improved step-level error localization by 19.8% across seven multi-Agent applications, significantly narrowing the gap between automated and human-level error identification. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Swift: Autoregressive Consistency Model for Efficient Weather Forecasting: Swift is a single-step consistency model that, for the first time, enables autoregressive fine-tuning of probability flow models and employs a Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS) objective. The model can generate skillful 6-hour weather forecasts and maintain stability for up to 75 days, running 39 times faster than state-of-the-art diffusion baselines while achieving forecast skill competitive with numerical IFS ENS, marking a significant step towards efficient and reliable ensemble forecasting from medium-range to seasonal scales. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Catching the Details: Self-Distilled RoI Predictor for Fine-Grained MLLM Perception: Research proposes an efficient, label-free self-distilled Region Proposal Network (SD-RPN) that addresses the high computational cost of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) when processing high-resolution images. SD-RPN converts MLLM intermediate attention maps into high-quality pseudo-RoI labels and trains a lightweight RPN for precise localization, achieving data efficiency and generalization capabilities, improving accuracy by over 10% on unseen benchmarks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
A New Paradigm for LLM Multi-Turn Reasoning: In-Place Feedback: This research introduces a novel interaction paradigm called “In-Place Feedback” to guide LLMs in multi-turn reasoning. Users can directly edit previous LLM responses, and the model generates revisions based on these modified responses. Empirical evaluation shows that In-Place Feedback outperforms traditional multi-turn feedback in reasoning-intensive benchmarks while reducing token usage by 79.1%, addressing the limitation of models struggling to precisely apply feedback. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Predictability of LLM Reinforcement Learning Dynamics: This work reveals two fundamental properties of parameter updates in LLM Reinforcement Learning (RL) training: rank-1 dominance (the highest singular subspace of the parameter update matrix almost entirely determines inference improvements) and rank-1 linear dynamics (this dominant subspace evolves linearly during training). Based on these findings, the research proposes AlphaRL, a plug-and-play acceleration framework that infers final parameter updates from early training windows, achieving up to 2.5x acceleration while retaining over 96% of inference performance. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Pitfalls of KV Cache Compression: Research reveals several pitfalls of KV cache compression in LLM deployment, especially in real-world scenarios like multi-instruction prompts, where compression can lead to a rapid decline in performance for certain instructions, or even cause them to be completely ignored by the LLM. Through case studies of system prompt leakage, the study empirically demonstrates the impact of compression on leakage and general instruction following, and proposes improved simple KV cache eviction strategies. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
💼 Business
AI Giant Competition: Strategic Differences Between OpenAI and Anthropic: OpenAI and Anthropic are pursuing distinctly different development paths in the AI sector. OpenAI, through ChatGPT’s integration with e-commerce and the launch of the Sora social app, aims for “horizontal expansion” to become a super-platform covering multiple aspects of users’ lives, with its valuation exceeding Anthropic by hundreds of billions of dollars. Anthropic, on the other hand, focuses on “vertical deep diving,” centering on Claude Sonnet 4.5 to specialize in AI programming and enterprise-grade Agent markets, and deeply integrating with cloud service providers like AWS and Google. Behind these two lies the “compute diplomacy” struggle between Microsoft and Amazon, highlighting the AI era’s reality of scarce and costly computing power. (Source: 36氪, 量子位, 36氪)
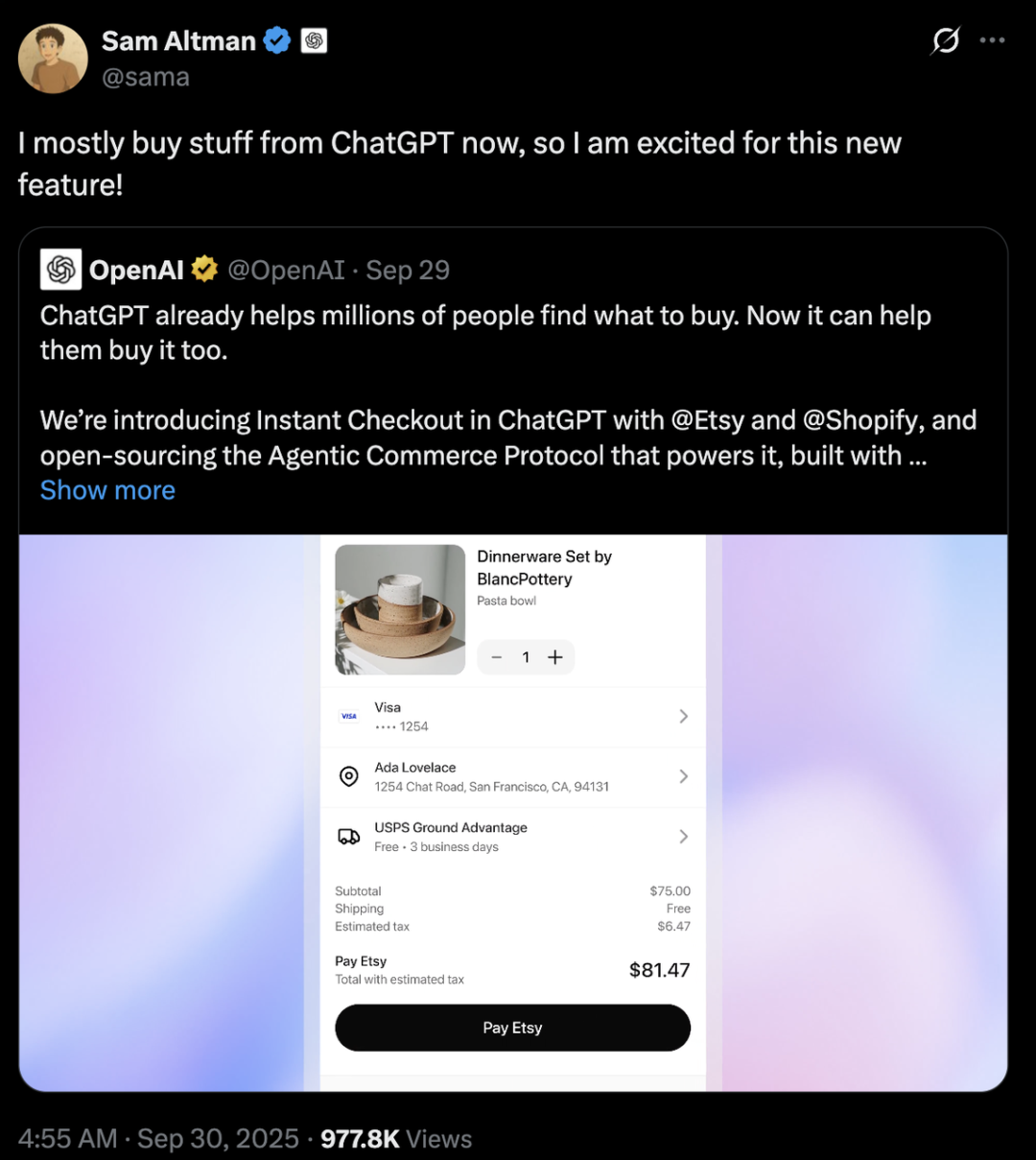
Perplexity Acquires Visual Electric: Perplexity announced the acquisition of Visual Electric, whose team will join Perplexity to jointly develop new consumer product experiences. Visual Electric’s products will be gradually discontinued. This acquisition aims to strengthen Perplexity’s innovation capabilities in the consumer AI product space. (Source: AravSrinivas)

Databricks Acquires Mooncakelabs: Databricks announced the acquisition of Mooncakelabs to accelerate its Lakebase vision. Lakebase is a new OLTP database built on Postgres and optimized for AI Agents, aiming to provide a unified foundation for applications, analytics, and AI, and deeply integrating with Lakehouse and Agent Bricks to simplify data management and AI application development. (Source: matei_zaharia)

🌟 Community
AI’s Impact on Employment and Society: The community widely discusses the profound impact of AI automation on the job market, expressing concerns that it could lead to mass unemployment, create new social classes, and necessitate Universal Basic Income (UBI). There is widespread skepticism about whether newly created AI-related jobs will also be automated and whether everyone can acquire AI skills to adapt to the future. Discussions also touch upon the challenges of AI Agent cost management and ROI realization, as well as the potential impact of AGI’s arrival on social structures and geopolitics. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)

AI Ethics and the Battle for Control: The community is hotly debating who should control the future of AI—everyday people or tech oligarchs. Calls are made for AI development to be human-centric, emphasizing transparency and user control over personal data and AI history. Meanwhile, AI godfather Yoshua Bengio warns that superintelligent machines could lead to human extinction within a decade. Companies like Meta plan to use AI chat data for targeted advertising, further exacerbating user concerns about privacy and AI misuse, prompting deeper reflection on AI ethics and regulation. (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

Abnormal Behavior of GPT-5 Safety Model: Reddit community users report that GPT-5’s “CHAT-SAFETY” model exhibits strange, accusatory, and even hallucinatory behavior when processing non-malicious requests, such as interpreting a fingerprint recognition question as tracking behavior and fabricating laws. This oversensitivity and inaccurate response raise serious questions among users about the model’s reliability, potential harm, and OpenAI’s safety policies. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
The ‘Bitter Lesson’ and the Debate on LLM Development Paths: Andrej Karpathy and Richard Sutton, the father of reinforcement learning, debated whether LLMs conform to the “Bitter Lesson.” Sutton argued that LLMs rely on limited human data for pre-training and do not truly follow the principle of learning from experience as per the “Bitter Lesson.” Karpathy, however, viewed pre-training as a “terrible evolution” to solve the cold start problem and highlighted fundamental differences in learning mechanisms between LLMs and animal intelligence, emphasizing that current AI is more like “summoning ghosts” than “building animals.” (Source: karpathy, SchmidhuberAI)
Discussion on the Value of Local LLM Setups: Community users debated the value of investing tens of thousands of dollars in building local LLM setups. Supporters emphasize privacy, data security, and the deep knowledge gained through hands-on experience as key advantages, likening it to amateur radio enthusiasts. Opponents argue that with the increasing performance of inexpensive cloud APIs (such as Sonnet 4.5 and Gemini Pro 2.5), the high cost of local setups is difficult to justify. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
LLM as a Judge: A New Approach to Agent Evaluation: Researchers and developers are exploring the use of LLMs as “judges” to evaluate the quality of AI Agent responses, including accuracy and groundedness. Practice shows that this method can be surprisingly effective when the judge’s prompts are carefully designed (e.g., single-criterion, anchored scoring, strict output format, and bias warnings). This trend indicates the immense potential of LLM-as-a-Judge in the field of Agent evaluation. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
AI and Human Interaction: From Devices to Virtual Characters: AI is reshaping human interaction in multiple dimensions. An MIT-linked startup has unveiled “near-telepathic” wearable devices for silent communication. Concurrently, real-time voice AI Agents are being used as NPCs (non-player characters) in 3D web games, foreshadowing AI’s potential to provide more natural and immersive interactive experiences in gaming and virtual worlds. These advancements spark discussions about AI’s role in daily life and entertainment. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/artificial)

Choosing Between Open-Source and Closed-Source Models: The community discussed the biggest obstacles software engineers face when switching from closed-source models to open-source ones. Experts point out that fine-tuning open-source models, rather than relying on black-box closed-source models, is crucial for deep learning, achieving product differentiation, and creating better products for users. Although open-source models may develop slower, in the long run, they hold immense potential for value creation and technological autonomy. (Source: ClementDelangue, huggingface)
AI Infrastructure and Compute Challenges: OpenAI’s “Stargate” project reveals AI’s enormous demand for computing power, energy, and land, with an estimated monthly consumption of up to 900,000 DRAM wafers. The scarcity and high cost of GPUs, coupled with limitations in electricity supply, force AI companies into “compute diplomacy,” deeply tying them to cloud service providers (like Microsoft and Amazon). This capital-intensive investment and strategic partnership model, while driving AI development, also introduces risks from external variables such as supply chains, energy policies, and regulations. (Source: karminski3, AI巨头的奶妈局, DeepLearning.AI Blog)

💡 Other
AI Music Copyright and Compensation Mechanisms: Swedish copyright organization STIM has partnered with Sureel to launch an AI music licensing agreement, aiming to address copyright usage issues for musical works in AI model training. This agreement allows AI developers to legally use music and calculates the work’s impact on model output through Sureel’s attribution technology, thereby compensating composers and recording artists. This initiative seeks to provide legal protection for AI music creation, incentivize original content production, and create new revenue streams for copyright holders. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)

LLM Security and Adversarial Attacks: Trend Micro has released research delving into various ways LLMs can be exploited by attackers, including compromise through carefully crafted prompts, data poisoning, and vulnerabilities in multi-Agent systems. The research emphasizes the importance of understanding these attack vectors for developing more secure LLM applications and multi-Agent systems, and proposes corresponding defense strategies. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
Proactive AI: Balancing Convenience and Privacy: The community discussed the convenience offered by “Proactive Ambient AI” as intelligent assistants versus the potential risks of privacy infringement. While such AI can proactively offer help, its continuous collection and processing of personal data raise user concerns about transparency, control, and data ownership. Some views call for establishing “transparency protocols” and “personal foundational profiles” to ensure users have control over their AI interaction history. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)

