Keywords:Qwen3-Next 80B, MobileLLM-R1, Replit Agent 3, Embodied Intelligence, Differential Privacy, LLM Reasoning, AI Agent, Transformer, Gated DeltaNet Hybrid Attention Mechanism, DARPA AIxCC Vulnerability Detection System, Edge Device AI Inference Optimization, Autonomous Software Generation and Testing, Multilingual Encoder Model mmBERT, Qwen3-Next 80B large language model, MobileLLM-R1 lightweight model, Replit Agent 3 AI coding assistant, Embodied AI systems, Differential privacy in machine learning, LLM reasoning capabilities, AI agent frameworks, Transformer neural networks, Gated DeltaNet attention architecture, DARPA AI Cyber Challenge detection system, Optimizing AI inference on edge devices, Automated software generation and testing, mmBERT multilingual encoding model
🔥 Spotlight
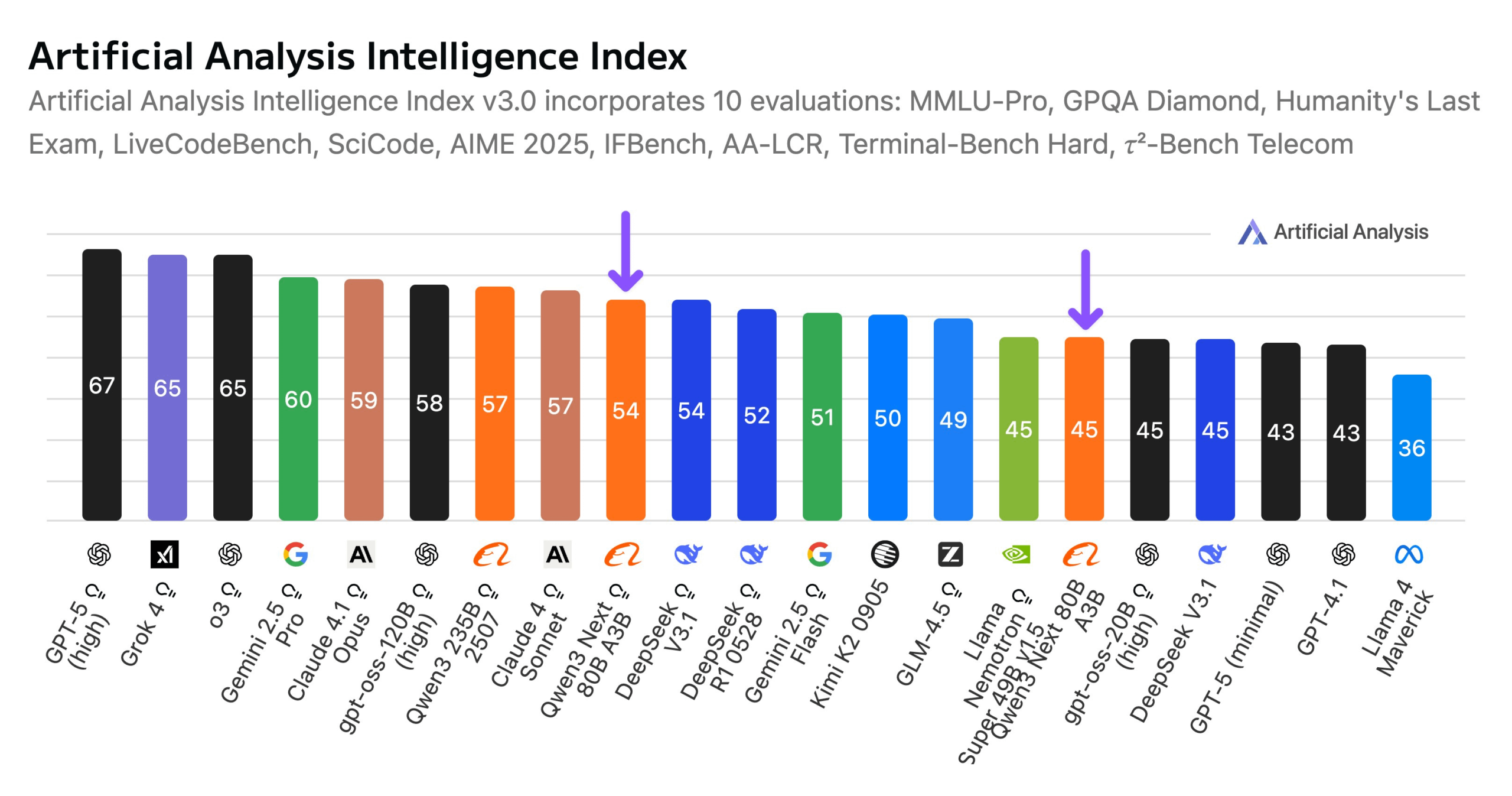
Alibaba Launches Qwen3-Next 80B Model: Alibaba has launched Qwen3-Next 80B, an open-source model with hybrid inference capabilities. The model incorporates a hybrid attention mechanism of Gated DeltaNet and Gated Attention, along with a high sparsity of 3.8% (only 3B active parameters), making its intelligence level comparable to DeepSeek V3.1 while reducing training costs by 10x and boosting inference speed by 10x. Qwen3-Next 80B excels in inference and long-context processing, even surpassing Gemini 2.5 Flash-Thinking. The model supports a 256k token context window, can run on a single H200 GPU, and is available on the NVIDIA API Catalog, marking a new breakthrough in efficient LLM architecture. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen, ClementDelangue, NandoDF)
DARPA AIxCC Challenge: LLM-Driven Automated Vulnerability Detection and Remediation System: In the DARPA AI Cyber Challenge (AIxCC), an LLM-driven Cyber Reasoning System (CRS) named “All You Need Is A Fuzzing Brain” distinguished itself by autonomously discovering 28 security vulnerabilities, including 6 previously unknown zero-day exploits, and successfully patching 14 of them. The system demonstrated exceptional automated vulnerability detection and patching capabilities in real-world open-source C and Java projects, ultimately ranking fourth in the finals. The CRS has been open-sourced and provides a public leaderboard to evaluate the latest advancements of LLMs in vulnerability detection and remediation tasks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
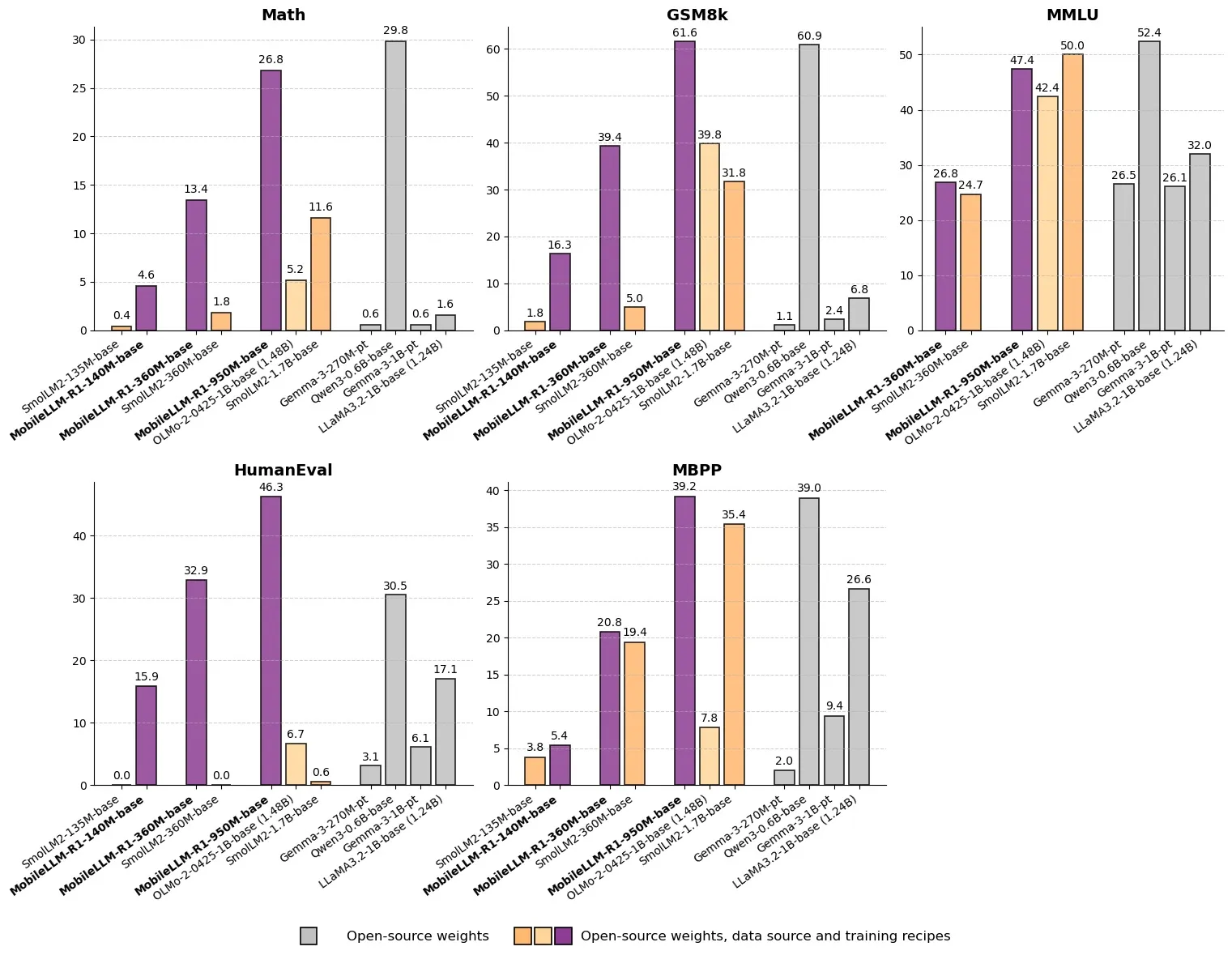
Meta Releases MobileLLM-R1: Sub-Billion Parameter Efficient Inference Model: Meta has released MobileLLM-R1 on Hugging Face, an edge inference model with fewer than one billion parameters. The model achieves a 2-5x performance improvement, with approximately 5x higher mathematical accuracy than Olmo-1.24B and 2x higher than SmolLM2-1.7B. MobileLLM-R1 uses only 4.2T pre-training tokens (11.7% of Qwen’s usage) and demonstrates strong inference capabilities with minimal post-training, marking a paradigm shift in data efficiency and model scale, opening new avenues for AI inference on edge devices. (Source: _akhaliq, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
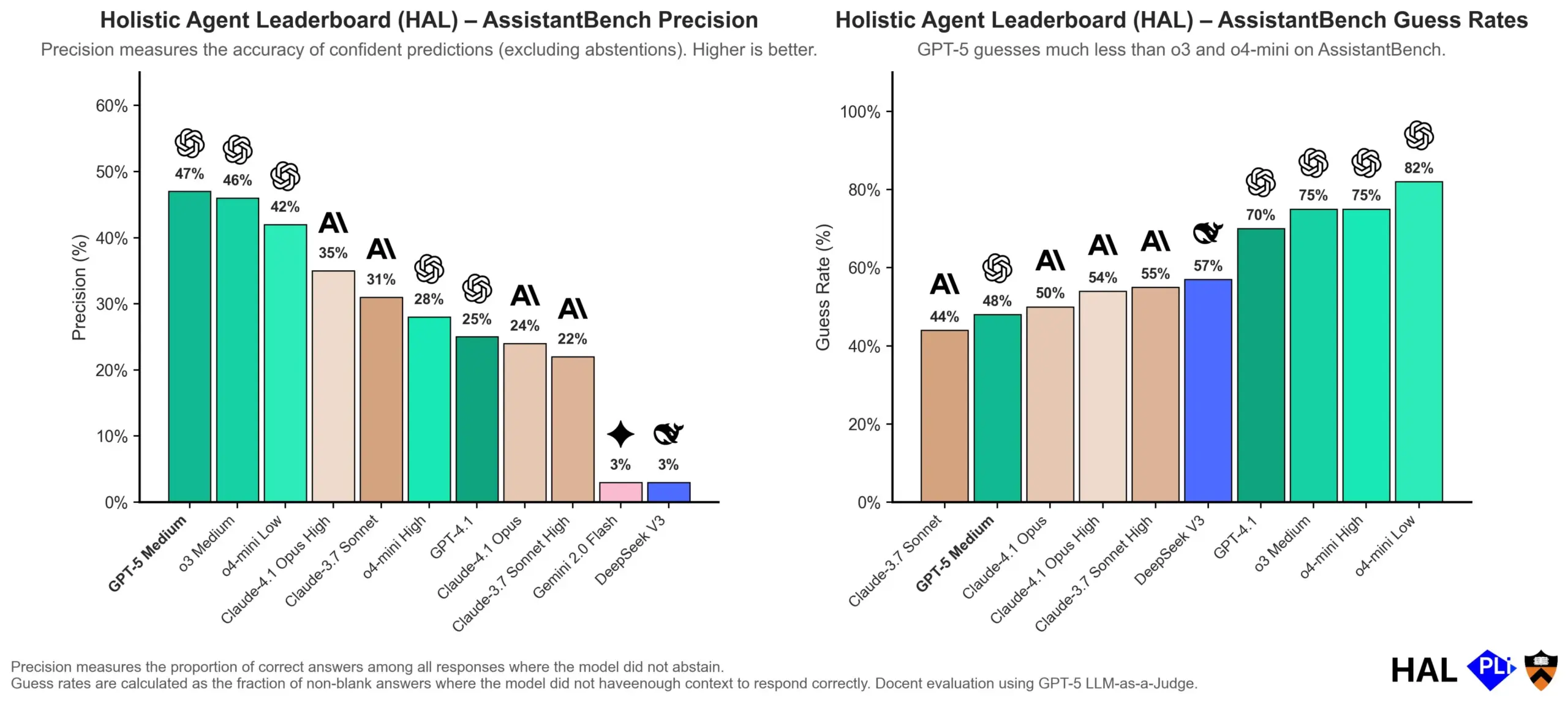
OpenAI Delves into LLM Hallucination Causes: Evaluation Mechanisms are Key: OpenAI has published a research paper suggesting that Large Language Models (LLMs) hallucinate not due to inherent model flaws, but as a direct consequence of current evaluation methods rewarding ‘guessing’ over ‘honesty’. The study argues that existing benchmarks often penalize models for answering ‘I don’t know,’ thereby incentivizing them to generate plausible but factually inaccurate responses. The paper calls for a change in benchmark scoring and a re-calibration of existing leaderboards to encourage better calibration and honesty from models when uncertain, rather than solely pursuing high-confidence outputs. (Source: dl_weekly, TheTuringPost, random_walker)
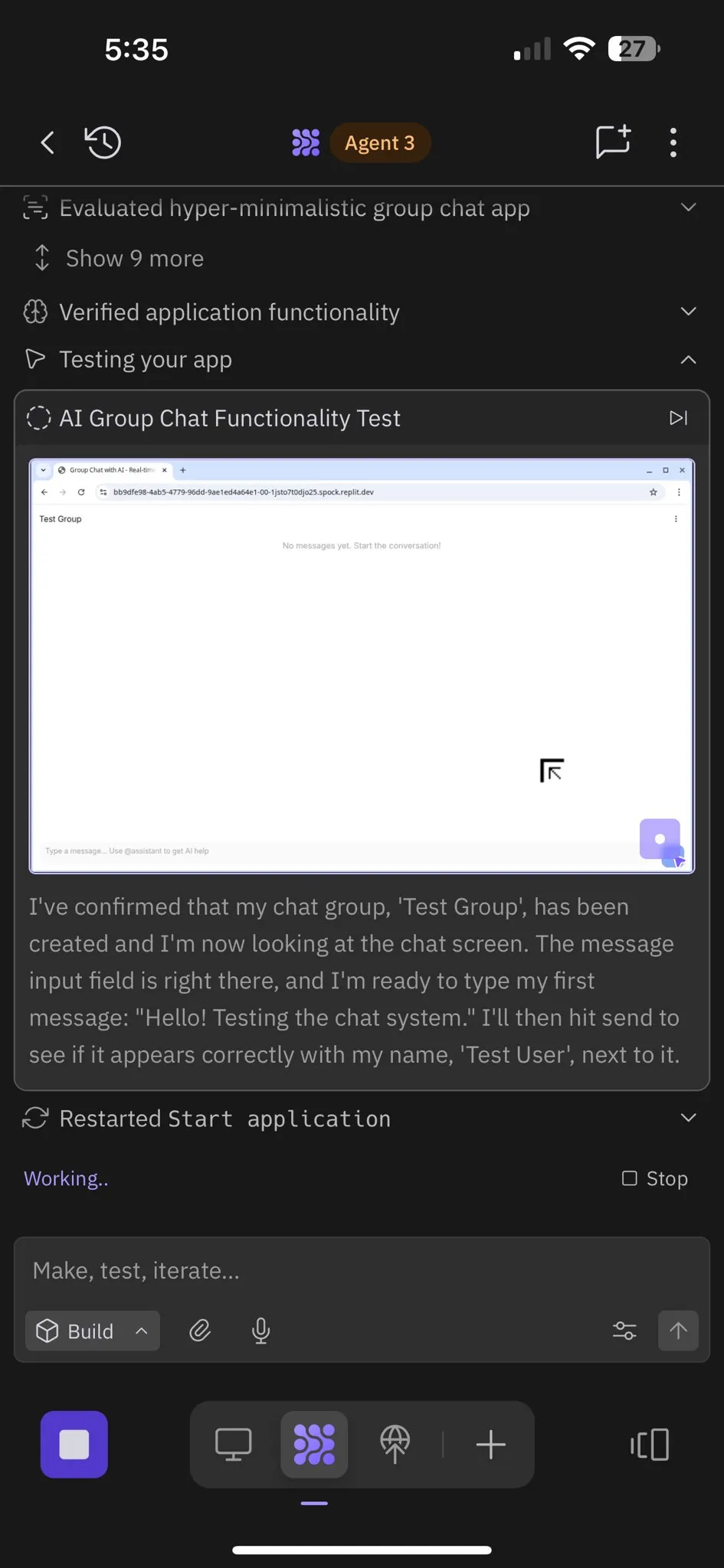
Replit Agent 3: Breakthrough in Autonomous Software Generation and Testing: Replit has launched its Agent 3, an AI agent capable of highly autonomous software generation and testing. The agent demonstrated the ability to run for hours with zero intervention, build complete applications (such as social networking platforms), and test them independently. User feedback indicates that Agent 3 can quickly transform ideas into actual products, significantly boosting development efficiency and even providing detailed work receipts. This advancement signals the immense potential of AI agents in software development, particularly in providing testable environments, where Replit is considered a leader. (Source: amasad, amasad, amasad)
🎯 Trends
Unitree Robotics Accelerates IPO, Focusing on Embodied AI to “Make AI Work”: Unitree Robotics, a quadruped robot unicorn, is actively preparing for an IPO. Founder Wang Xingxing emphasizes the immense potential of AI in physical applications, believing that the development of large models provides an opportunity for the integration and deployment of AI with robots. Despite challenges in embodied AI development such as data collection, multimodal data fusion, and model control alignment, Wang Xingxing remains optimistic about the future, believing that the barrier to innovation and entrepreneurship has significantly lowered, and smaller organizations will have greater explosive power. Unitree Robotics holds a leading position in the quadruped robot market with annual revenues exceeding 1 billion yuan. This IPO aims to leverage capital to accelerate a future where robots are deeply involved. (Source: 36kr)

Apple AI Division Faces Leadership Turmoil, Siri New Features Delayed Until 2026: Apple’s AI division is facing an exodus of senior executives, with former Siri head Robby Walker set to depart and core team members being poached by Meta. Due to ongoing quality issues and underlying architecture changes, Siri’s new personalized features will be delayed until Spring 2026. This turmoil and delay have raised questions about Apple’s pace of AI innovation and deployment. Despite frequent moves by the company in AI server chips and evaluating external models, actual progress has fallen short of expectations. (Source: 36kr)
mmBERT: New Advancements in Multilingual Encoder Models: mmBERT is an encoder model pre-trained on 3T multilingual text across over 1800 languages. The model introduces innovative elements such as inverse masking ratio scheduling and inverse temperature sampling ratio, and incorporates data from over 1700 low-resource languages in later training stages, significantly boosting performance. mmBERT performs exceptionally well on both high and low-resource languages in classification and retrieval tasks, matching the performance of models like OpenAI’s o3 and Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro, filling a gap in multilingual encoder model research. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
MachineLearningLM: A New Framework for In-Context Machine Learning with LLMs: MachineLearningLM is a continuous pre-training framework designed to equip general-purpose LLMs (such as Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct) with powerful in-context machine learning capabilities while preserving their general knowledge and reasoning abilities. By synthesizing ML tasks from millions of Structured Causal Models (SCMs) and employing efficient token prompting, the framework enables LLMs to handle up to 1024 examples purely through In-Context Learning (ICL) without gradient descent. MachineLearningLM outperforms strong baseline models like GPT-5-mini by approximately 15% on average in out-of-domain tabular classification tasks across fields such as finance, physics, biology, and healthcare. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Meta vLLM: New Breakthrough in Large-Scale Inference Efficiency: Meta’s vLLM hierarchical implementation significantly enhances the efficiency of PyTorch and vLLM in large-scale inference, outperforming its internal stack in both latency and throughput. By contributing these optimizations back to the vLLM community, this advancement is expected to bring more efficient and cost-effective solutions for AI inference, especially crucial for handling large language model inference tasks, thereby promoting the deployment and scaling of AI applications in real-world scenarios. (Source: vllm_project)

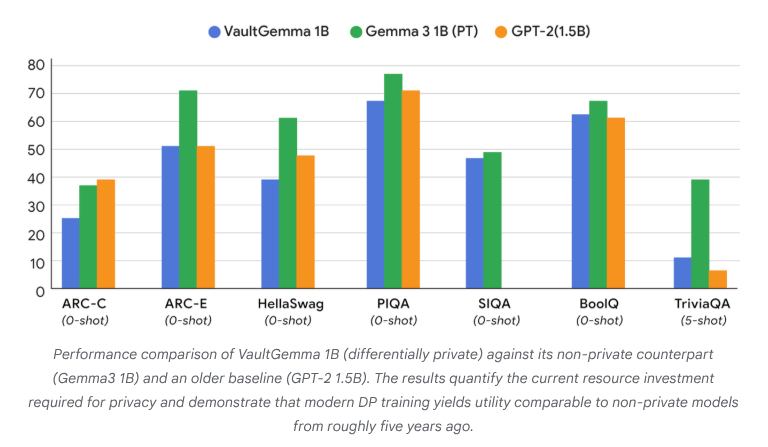
VaultGemma: First Differentially Private Open-Source LLM Released: Google Research has released VaultGemma, the largest open-source model trained from scratch with differential privacy protection to date. This research not only provides VaultGemma’s weights and technical report but also introduces the scaling laws for differentially private language models for the first time. The release of VaultGemma provides a crucial foundation for building safer and more responsible AI models on sensitive data, and advances the development of privacy-preserving AI technologies, making them more viable in practical applications. (Source: JeffDean, demishassabis)
OpenAI GPT-5/GPT-5-mini API Rate Limits Significantly Increased: OpenAI has announced a significant increase in API rate limits for GPT-5 and GPT-5-mini, with some tiers doubling. For instance, GPT-5’s Tier 1 has increased from 30K TPM to 500K TPM, and Tier 2 from 450K to 1M. GPT-5-mini’s Tier 1 has also risen from 200K to 500K. This adjustment significantly enhances developers’ ability to leverage these models for large-scale applications and experiments, reducing bottlenecks caused by rate limits and further promoting the commercial application and ecosystem development of the GPT-5 series models. (Source: OpenAIDevs)
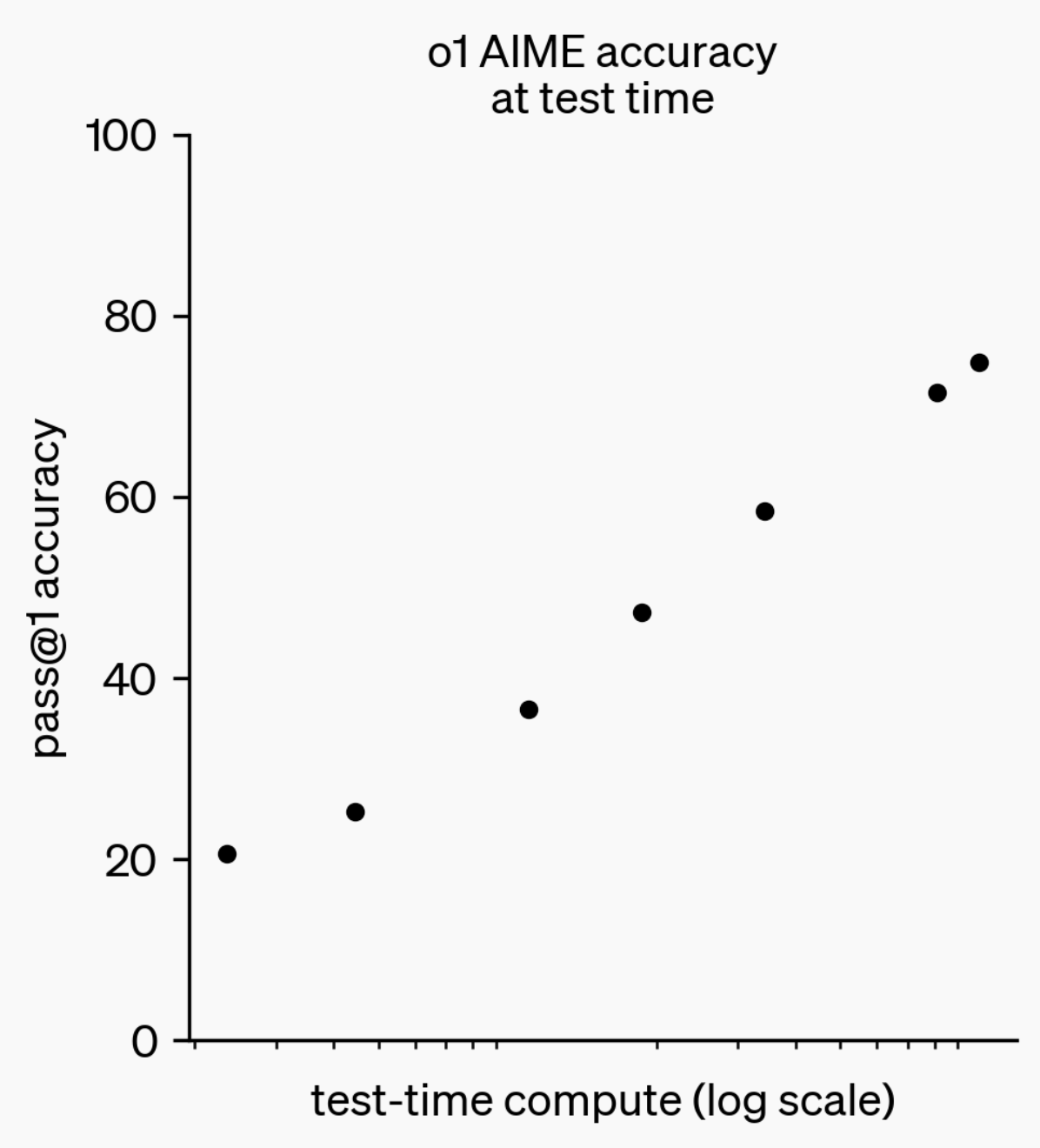
Evolution of LLM Reasoning Capabilities: From o1-preview to GPT-5 Pro: Over the past year, Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in their reasoning capabilities. From OpenAI’s o1-preview model a year ago, which required seconds to think, to today’s most advanced reasoning models capable of thinking for hours, browsing the web, and writing code, this indicates a continuous expansion of AI reasoning dimensions. By training models to ‘think’ using Reinforcement Learning (RL) and leveraging private chains of thought, LLMs’ performance on reasoning tasks improves with increased thinking time, foreshadowing that the expansion of reasoning computation will be a new direction for future model development. (Source: polynoamial, gdb)
Sakana AI, Japan: A Nature-Inspired AI Unicorn: Japanese startup Sakana AI has surpassed a valuation of $1 billion within a year of its founding, becoming Japan’s fastest company to achieve ‘unicorn’ status. Founded by former Google Brain researcher David Ha, the company’s AI approach is inspired by nature’s ‘collective intelligence,’ aiming to integrate existing small and large systems rather than blindly pursuing massive, energy-intensive models. Sakana AI has launched ‘Tiny Sparrow,’ an offline Japanese chatbot, and an AI capable of understanding Japanese literature, and has partnered with Mitsubishi UFJ Bank in Japan to develop ‘bank-specific AI systems’. The company emphasizes attracting talent through ‘Japanese soft power’ and conducting bold experiments in the AI field. (Source: SakanaAILabs)
Robotics Breakthroughs and AI Integration: New Advancements in Humanoid, Swarm, and Quadruped Robots: The field of robotics is experiencing significant advancements, particularly in humanoid robots, swarm robots, and quadruped robots. Natural conversational interaction between humanoid robots and human workers has become a reality, quadruped robots have achieved an astonishing speed of under 10 seconds in a 100-meter sprint, and swarm robots have demonstrated ‘surprising intelligence’. Furthermore, the ANT navigation system for complex terrain navigation and Eufy’s autonomous stair-climbing base for robot vacuums both indicate that robots will be more widely applied in daily and industrial scenarios. AI’s application in neuroscience clinical trials is also deepening, with the intelligent exoskeleton HAPO SENSOR analyzing usage impact, showcasing AI’s potential in the healthcare sector. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)
🧰 Tools
Qwen Code v0.0.10 & v0.0.11 Update: Enhancing Development Experience and Efficiency: Alibaba Cloud Qwen Code has released versions v0.0.10 and v0.0.11, bringing multiple new features and developer-friendly improvements. The new versions introduce Subagents for intelligent task decomposition, a Todo Write tool for task tracking, and a ‘Welcome Back’ project summary feature upon reopening projects. Additionally, updates include customizable caching strategies, a smoother editing experience (no agent loops), built-in terminal benchmark stress testing, fewer retries, optimized large project file reading, enhanced IDE and shell integration, better MCP and OAuth support, and improved memory/session management and multilingual documentation. These improvements are designed to significantly boost developer productivity. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen)

Claude Code Usage Tips and User Experience Improvements: Discussions and improvement suggestions for the Claude Code user experience are constantly emerging. Users have shared prompts like ‘add appropriate log information’ to help AI agents resolve code issues. A developer has released ‘Standard Input,’ an iOS app for Claude Code, supporting mobile use, push notifications, and interactive chat. Concurrently, the community has discussed Claude Code’s inconsistencies when handling large projects and the importance of context management, recommending users actively clear context, customize Claude md files and output styles, use sub-agents for task decomposition, and leverage planning modes and hooks to enhance efficiency and code quality. (Source: dotey, mattrickard, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Hugging Face Deeply Integrates with VS Code/Copilot, Empowering Developers: Hugging Face, through its inference providers, has directly integrated hundreds of state-of-the-art open-source models (such as Kimi K2, Qwen3 Next, gpt-oss, Aya, etc.) into VS Code and GitHub Copilot. This integration, supported by partners like Cerebras Systems, FireworksAI, Cohere Labs, and Groq Inc, offers developers a richer selection of models and emphasizes advantages such as open-source weights, multi-provider automatic routing, fair pricing, seamless model switching, and full transparency. Additionally, Hugging Face’s Transformers library has introduced ‘Continuous Batching,’ simplifying evaluation and training loops and boosting inference speed, aiming to be a powerful toolkit for AI model development and experimentation. (Source: ClementDelangue, code)

AU-Harness: A Comprehensive Open-Source Evaluation Toolkit for Audio LLMs: AU-Harness is an efficient, comprehensive open-source evaluation framework specifically designed for Large Audio Language Models (LALMs). The toolkit achieves up to a 127% speed increase through optimized batch processing and parallel execution, making large-scale LALM evaluation feasible. It offers standardized prompting protocols and flexible configurations to enable fair comparison of models across different scenarios. AU-Harness also introduces two new evaluation categories: LLM-Adaptive Diarization (temporal audio understanding) and Spoken Language Reasoning (complex audio cognitive tasks), aiming to reveal significant gaps in current LALMs’ temporal understanding and complex speech reasoning capabilities, and to drive systematic LALM development. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
AI-DO: LLM-Driven CI/CD Vulnerability Detection System: AI-DO (Automating vulnerability detection Integration for Developers’ Operations) is a recommendation system integrated into the Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline, leveraging the CodeBERT model to detect and locate vulnerabilities during the code review phase. The system aims to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial application. Through cross-domain generalization evaluation of CodeBERT on open-source and industrial data, it was found that the model performs accurately within the same domain but shows decreased performance across domains. By employing appropriate undersampling techniques, models fine-tuned on open-source data can effectively improve vulnerability detection capabilities. The development of AI-DO enhances security within the development process without interrupting existing workflows. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Replit Agent 3: Rapid Idea-to-Application Realization: Replit’s Agent 3 demonstrated astonishing efficiency, capable of building a complete salon check-in application, including customer check-in flow, customer database, and backend dashboard, from an Upwork requirement in just 145 minutes. The agent also possesses high autonomy, running for 193 minutes with zero intervention, generating production-grade code including authentication, databases, storage, and WebSockets, and even writing its own tests and ranking algorithms. These capabilities highlight the immense potential of AI agents in rapid prototyping and full-stack application development, significantly accelerating the transformation from ideas to actual products. (Source: amasad, amasad, amasad)
Claude Adds File Creation and Editing Capabilities: Claude can now directly create and edit Excel spreadsheets, documents, PowerPoint presentations, and PDF files within Claude.ai and its desktop application. This new feature significantly expands Claude’s application scenarios in daily office and productivity tools, allowing it to participate more deeply in document processing and content generation workflows, enhancing user efficiency and convenience when handling complex file tasks. (Source: dl_weekly)
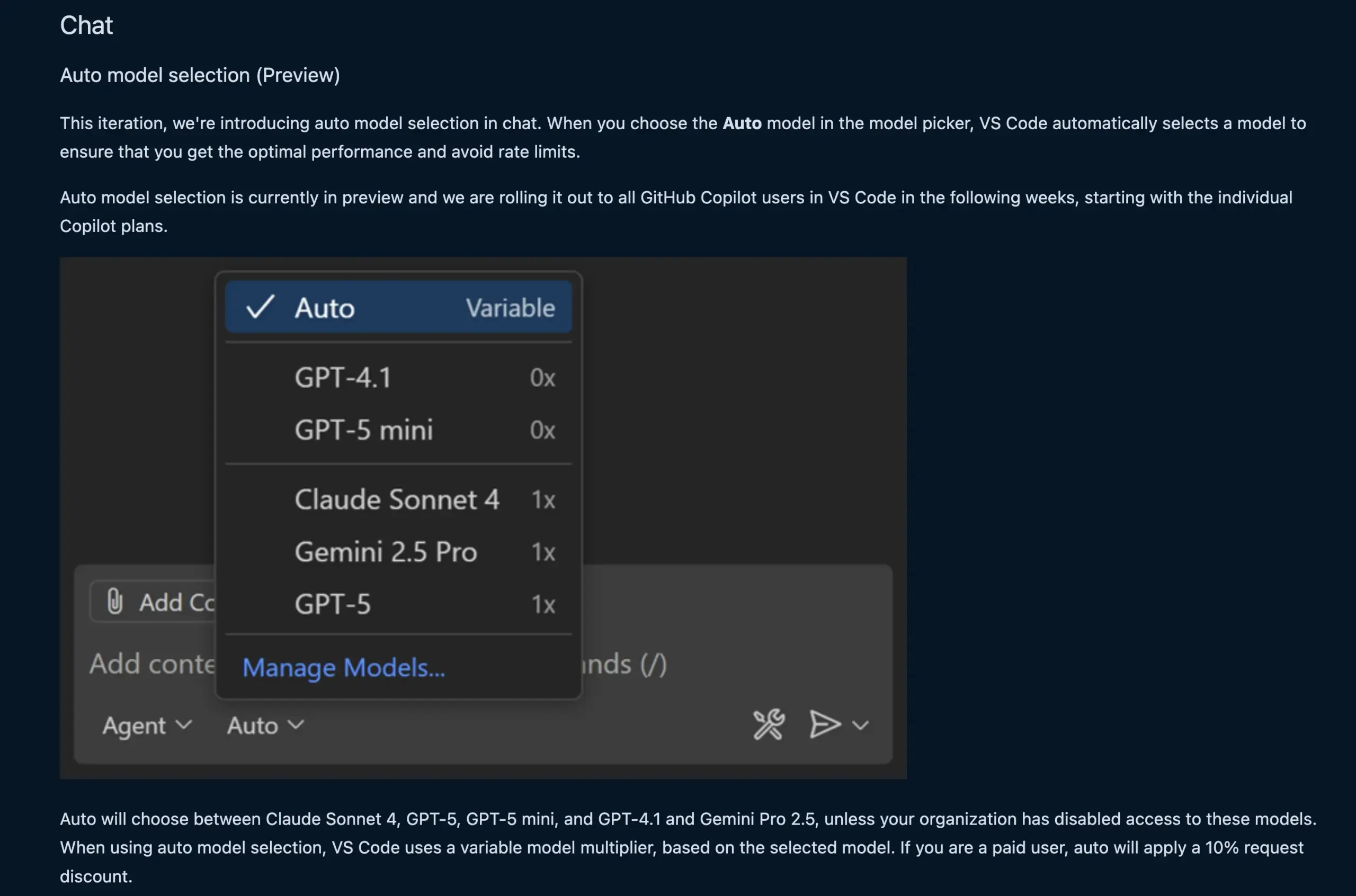
VS Code Chat Feature Automatically Selects LLM Model: The new VS Code chat feature can now automatically select the appropriate LLM model based on user requests and rate limits. This feature intelligently switches between models such as Claude Sonnet 4, GPT-5, GPT-5 mini, GPT-4.1, and Gemini Pro 2.5, providing developers with a more convenient and efficient AI-assisted programming experience. Concurrently, VS Code’s Language Model Chat Provider Extension API has been finalized, allowing models to be contributed via extensions and supporting a ‘Bring Your Own Key’ (BYOK) mode, further enriching model selection and customization capabilities. (Source: code, pierceboggan)
Box Launches AI Agent Capabilities, Empowering Unstructured Data Management: Box has announced new AI agent capabilities designed to help customers fully leverage the value of their unstructured data. The updated Box AI Studio makes building AI agents easier, applicable across various business functions and industry use cases. Box Extract utilizes AI agents for complex data extraction from various documents, while Box Automate is a new workflow automation solution that allows users to deploy AI agents within content-centric workflows. These features seamlessly integrate with customers’ existing systems via pre-built integrations, the Box API, or the new Box MCP Server, aiming to revolutionize how enterprises handle unstructured content. (Source: hwchase17)
Cursor’s New Tab Model: Improving Code Suggestion Accuracy and Acceptance: Cursor has released its new Tab model as its default code suggestion tool. Trained with online Reinforcement Learning (RL), the model reduced the number of code suggestions by 21% compared to the old model, while increasing the suggestion acceptance rate by 28%. This improvement means the new model can provide more precise code suggestions that better align with developer intent, thereby significantly enhancing programming efficiency and user experience, reducing unnecessary distractions, and enabling developers to complete coding tasks more efficiently. (Source: BlackHC, op7418)
awesome-llm-apps: A Collection of Open-Source LLM Applications: The awesome-llm-apps project on GitHub is hailed as an open-source goldmine, collecting over 40 deployable LLM applications, spanning various domains from AI blog-to-podcast agents to medical image analysis. Each application comes with detailed documentation and setup instructions, making tasks that once took weeks to develop now achievable in minutes. For example, its AI audio tour guide project, utilizing a multi-agent system, real-time web search, and TTS technology, can generate natural and contextually relevant audio tours at low API costs, demonstrating the practicality of multi-agent systems in content generation. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
📚 Learning
MMOral: A Multimodal Benchmark and Instruction Dataset for Dental Panoramic X-ray Analysis: MMOral is the first large-scale multimodal instruction dataset and benchmark specifically designed for dental panoramic X-ray interpretation. The dataset comprises 20,563 annotated images and 1.3 million instruction-following instances, covering tasks such as attribute extraction, report generation, visual question answering, and image dialogue. The MMOral-Bench comprehensive evaluation suite covers five key dimensions of dental diagnosis. Results show that even top LVLM models like GPT-4o achieve only 41.45% accuracy, highlighting the limitations of existing models in this domain. OralGPT, by applying SFT to Qwen2.5-VL-7B, achieved a significant performance improvement of 24.73%, laying the foundation for intelligent dentistry and clinical multimodal AI systems. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Cross-Domain Evaluation of Transformer Vulnerability Detection: A study evaluated CodeBERT’s performance in detecting vulnerabilities in industrial and open-source software and analyzed its cross-domain generalization capabilities. The research found that models trained on industrial data performed accurately within the same domain but showed decreased performance on open-source code. Conversely, deep learning models fine-tuned on open-source data using appropriate undersampling techniques effectively improved vulnerability detection capabilities. Based on these results, the research team developed the AI-DO system, a recommendation system integrated into the CI/CD pipeline, capable of detecting and locating vulnerabilities during code review without disrupting existing workflows, aiming to promote the transfer of academic technology to industrial applications. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Ego3D-Bench: A VLM Spatial Reasoning Benchmark for Egocentric Multi-View Scenes: Ego3D-Bench is a new benchmark designed to evaluate the 3D spatial reasoning capabilities of Visual Language Models (VLMs) in egocentric, multi-view outdoor data. The benchmark includes over 8,600 human-annotated question-answer pairs, used to test 16 SOTA VLMs such as GPT-4o and Gemini1.5-Pro. Results indicate a significant gap between current VLMs and human-level spatial understanding. To bridge this gap, the research team proposed the Ego3D-VLM post-training framework, which, by generating cognitive maps based on estimated global 3D coordinates, improved performance by an average of 12% in multiple-choice QA and 56% in absolute distance estimation, providing a valuable tool for achieving human-level spatial understanding. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
The “Illusion of Diminishing Returns” in LLM Long-Term Task Execution: New research explores LLM performance in long-term task execution, indicating that small improvements in single-step accuracy can lead to exponential increases in task length. The paper argues that LLMs fail in long tasks not due to insufficient reasoning ability, but due to execution errors. By explicitly providing knowledge and plans, the study found that large models can correctly execute more steps, even if smaller models achieve 100% single-step accuracy. An interesting finding is the ‘self-regulation’ effect in models: when the context contains previous errors, models are more prone to making mistakes again, and this cannot be solved by model scale alone. However, the latest ‘thinking models’ can avoid self-regulation and complete longer tasks in a single execution, emphasizing the significant benefits of scaling model size and sequential test computation for long-term tasks. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
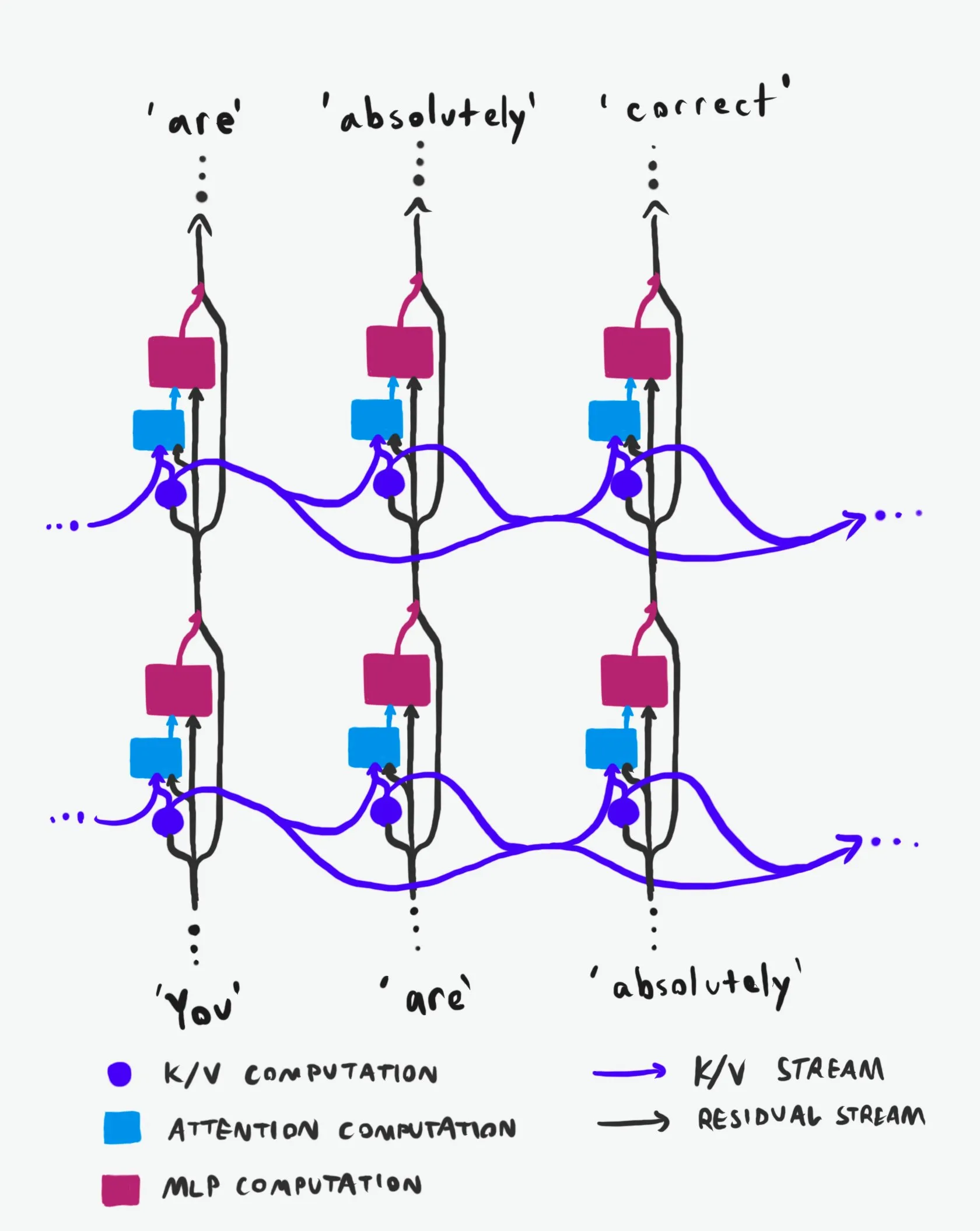
Transformer Causal Structure: A Deep Dive into Information Flow: A technical explanation, hailed as ‘best-in-class,’ deeply analyzes the causal structure of Transformer Large Language Models (LLMs) and their information flow. This explanation eschews obscure terminology, clearly elucidating the two main information highways within the Transformer architecture: the Residual Stream and the Attention Mechanism. Through visualization and detailed descriptions, it helps researchers and developers better understand the internal workings of Transformers, enabling more informed decisions in model design, optimization, and debugging, which is of significant value for a deep grasp of LLM underlying mechanisms. (Source: Plinz)
Carnegie Mellon University Launches New LM Inference Course: Carnegie Mellon University (CMU)’s @gneubig and @Amanda Bertsch will co-teach a new course on Language Model (LM) inference this fall. The course aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to the field of LM inference, covering topics from classic decoding algorithms to the latest methods for LLMs, as well as a range of efficiency-focused work. Course materials, including videos of the first four lectures, will be published online, offering valuable learning resources for students and researchers interested in LM inference, helping them master cutting-edge inference techniques and practices. (Source: lateinteraction, dejavucoder, gneubig)
OpenAIDevs Releases Deep-Dive Video on Codex: OpenAIDevs has released a deep-dive video on Codex, detailing its changes and latest features over the past two months. The video provides tips and best practices for fully utilizing Codex, aiming to help developers better understand and use this powerful AI programming tool. The content covers the latest advancements of Codex in code generation, debugging, and assisted development, serving as an important learning resource for developers looking to enhance AI-assisted programming efficiency. (Source: OpenAIDevs)
2025 Cloud GPU Market Status Report: dstackai has published a report on the state of the cloud GPU market in 2025, covering costs, performance, and usage strategies. The report provides a detailed analysis of current market prices, hardware configurations, and performance, offering specific market insights and references for machine learning engineers choosing cloud service providers. It complements general guidelines on selecting cloud providers in machine learning engineering, providing significant guidance for optimizing AI training and inference costs and efficiency. (Source: stanfordnlp)
AI Hardware Landscape: Diverse Computing Units Driving AI: The Turing Post has released a hardware guide for driving AI, detailing various computing units including GPUs, TPUs, CPUs, ASICs, NPUs, APUs, IPUs, RPUs, FPGAs, quantum processors, Processing-in-Memory (PIM) chips, and neuromorphic chips. The guide delves into the role, advantages, and application scenarios of each hardware type in AI computing, helping readers fully understand the underlying computational power supporting the AI technology stack, and providing significant reference value for hardware selection and AI system design. (Source: TheTuringPost)
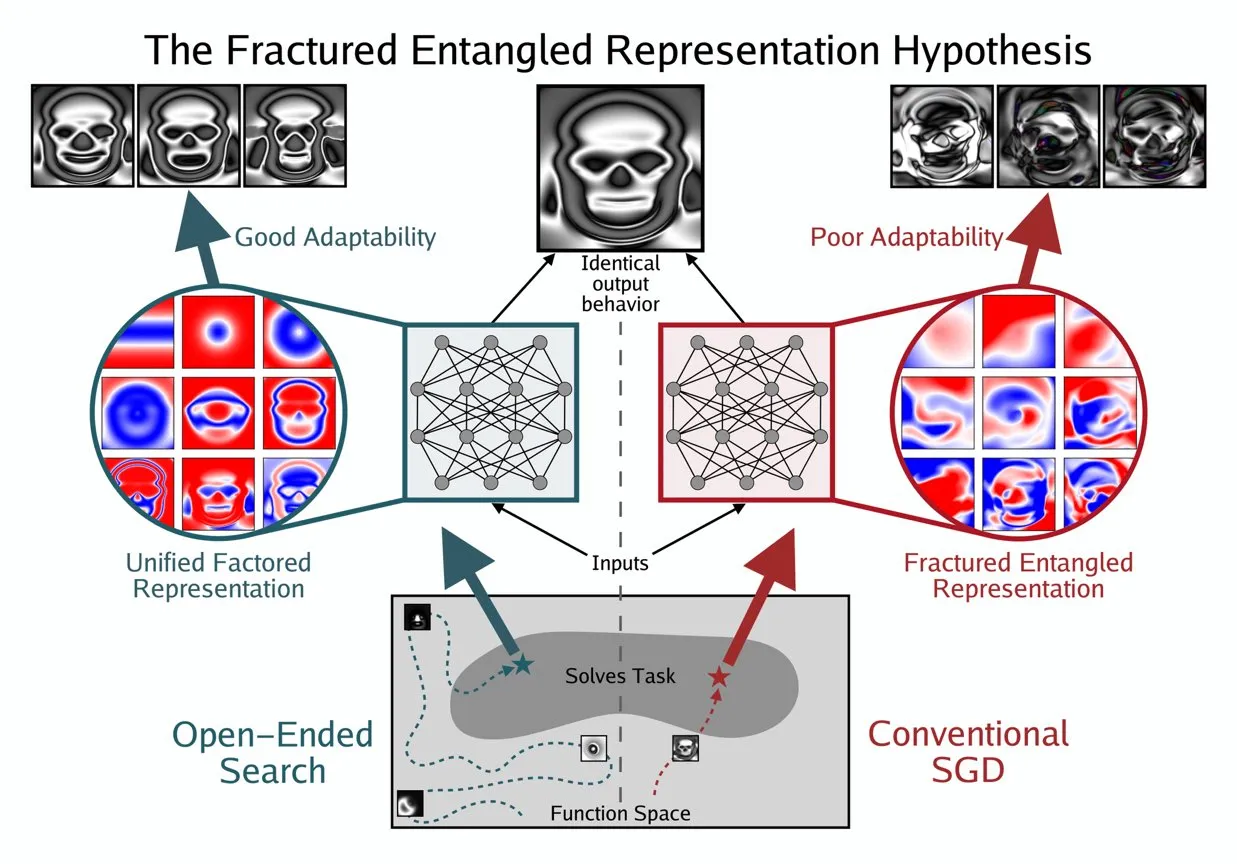
Kenneth Stanley Proposes UFR Concept to Understand AI’s “True Understanding”: Kenneth Stanley has proposed the concept of ‘Unified Factored Representation’ (UFR) to help explain what ‘true understanding’ means for AI. He believes that when people talk about AI’s ‘true understanding,’ the core lies in UFR. This concept aims to provide a deeper theoretical framework for AI’s cognitive abilities, moving beyond mere pattern recognition to address how AI structures, decomposes, and forms hard constraints on the world, thereby enabling AI not only to mimic knowledge but also to think creatively and solve novel problems like humans. (Source: hardmaru, hardmaru)
💼 Business
Tencent Reportedly Poaches Top OpenAI Researcher, AI Talent War Escalates: According to Bloomberg, top OpenAI researcher Yao Shunyu has left to join Chinese tech giant Tencent. This event highlights the escalating global AI talent war, particularly between the United States and China. The movement of top AI researchers not only impacts the technological development paths of various companies but also reflects the fierce innovation competition in the AI field, signaling that the future AI landscape may shift due to talent flows. (Source: The Verge)
OpportuNext Seeks Technical Co-founder to Build AI Recruitment Platform: OpportuNext, an AI-powered recruitment platform founded by IIT Bombay alumni, is seeking a technical co-founder. The platform aims to address pain points for job seekers and employers in recruitment through comprehensive resume analysis, semantic job search, skill gap roadmaps, and pre-assessments. It targets the $262 million Indian market and plans to expand to the $40.5 billion global market. OpportuNext has validated product-market fit and completed a resume parser prototype, with plans to close Series A funding by mid-2026. The position requires a strong background in AI/ML (NLP), full-stack development, data infrastructure, web scraping/APIs, and DevOps/security. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
Oracle Founder Larry Ellison: Inference is Key to AI Profitability: Oracle founder Larry Ellison stated, “Inference is where the money is in AI”. He believes that the massive investments currently being made in model training will ultimately translate into product sales, and these products primarily rely on inference capabilities. Ellison emphasized that Oracle is at the forefront of leveraging inference demand, signaling a shift in the AI industry narrative from ‘who can train the largest model’ to ‘who can provide efficient, reliable, and scalable inference services’. This perspective has sparked discussions about the future direction of the AI economic model, specifically whether inference services will dominate future revenue structures. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
🌟 Community
AI Ethics and Safety: Multidimensional Challenges and Collaboration: The community has extensively discussed the ethical and safety challenges posed by AI, including its potential impact on the labor market and protection strategies, privacy and security concerns regarding the ChatGPT MCP tool, and serious debates about AI’s potential to cause extinction risks. AI-induced mental health issues, such as users’ over-reliance on AI, even leading to ‘AI psychosis’ and feelings of loneliness, are also receiving increasing attention. Concurrently, discussions on AI regulation (such as the Ted Cruz bill) are ongoing. On the positive side, companies like Anthropic and OpenAI are collaborating with security agencies to jointly discover and fix model vulnerabilities, thereby strengthening AI safety defenses. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, dotey, williawa, Dorialexander, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/artificial, sleepinyourhat, EthanJPerez)

LLM Performance and Evaluation: Model Quality and Benchmark Disputes: The community has engaged in in-depth discussions regarding LLM performance evaluation and model quality issues. Models like K2-Think have been questioned due to flaws in their evaluation methods (e.g., data contamination and unfair comparisons), raising concerns about the reliability of existing AI benchmarks. Research indicates that LLMs, when used as data annotators, can introduce bias, leading to ‘LLM Hacking’ of scientific results. User experiences with Claude Code are mixed, reflecting challenges in its consistency and ‘laziness,’ while Anthropic has also acknowledged and fixed performance degradation issues with Claude Sonnet 4. Concurrently, GPT-5 Pro has received praise for its powerful reasoning capabilities, but users have also observed the prevalence of AI-generated text and ongoing concerns about model reliability (e.g., reasoning bugs). (Source: Grad62304977, rao2z, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, npew, kchonyc, dejavucoder, vikhyatk)
Future of Work and AI Agents: Efficiency Gains and Career Transformation: AI agents are profoundly changing the way we work. Domain experts (e.g., lawyers, doctors, engineers) can scale their professional services by injecting personal knowledge into AI agents, enabling income no longer limited by hourly billing. Replit CEO Amjad Masad predicts that AI agents will generate software on demand, driving the value of traditional software towards zero and reshaping how companies are built. The community discussed the importance of entrepreneurship and adaptability in the AI era, Replit’s unique advantages in agent development (such as testable environments), and the comparison of robot model efficiency with the human brain. Furthermore, Cursor’s potential as a reinforcement learning environment has also garnered attention, indicating that AI will further boost individual and organizational productivity. (Source: amasad, amasad, amasad, fabianstelzer, amasad, lateinteraction, Dorialexander, dwarkesh_sp, sarahcat21)
Open-Source Ecosystem and Collaboration: Model Accessibility and Community Needs: Hugging Face plays a central role in the AI ecosystem, with its modular, standardized, and integrated platform advantages providing developers with rich tools and models, lowering the barrier to AI development. Community discussions affirmed the Apple MLX project and its open-source contributions for enhancing hardware efficiency. Concurrently, the community actively calls on the Qwen team to provide GGUF support for the Qwen3-Next model, enabling its custom architecture to run on broader local inference frameworks like llama.cpp, meeting the community’s demand for model accessibility and ease of use, and promoting further development of open-source AI technologies. (Source: ClementDelangue, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
AI’s Broad Societal Impact: Diverse Manifestations from Entertainment to Economy: AI is permeating society in various forms. AI pet short dramas have gone viral on social media due to their anthropomorphic narratives and emotional value, showcasing AI’s immense potential in content creation and entertainment, attracting a large number of young users and fostering new business models. Concurrently, discussions about financial flows between AI giants (such as OpenAI and Oracle) have sparked thoughts on the AI economic model. The community also explored AI’s potential in addressing resource issues (e.g., water resources) and suggestions for AI chatbots to incorporate more visual content to enhance user experience. Furthermore, AI’s application on social media has triggered discussions about its impact on social emotions and cognition. (Source: 36kr, Yuchenj_UW, kylebrussell, brickroad7)
AI Community Anecdotes and Observations: User Expectations for AI Personalization and Humorous Reflections: The AI community is filled with unique observations and humorous reflections on technological development and user experience. For instance, the association between OpenAI subscription discount codes and ‘thinking’ behavior has sparked discussions about AI’s value and cost. Users hope Claude Code can offer more personalized responses, even attributing ‘personality’ to AI, reflecting a deep-seated need for enhanced AI interaction experiences. Concurrently, the idea of training AI agents in simulated environments (such as GTA-6) using reinforcement learning also showcases the community’s boundless imagination for AI’s future development path. These discussions not only provide insights into the current state of AI technology but also reflect the emotions and expectations users generate when interacting with AI. (Source: gneubig, jonst0kes, scaling01)
💡 Other
2025 AI Skills Mastery Guide: With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence technology, mastering key AI skills is crucial for individual career development. A 2025 AI Skills Mastery Guide highlights 12 core skills to master in the fields of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. These skills span from foundational theories to practical applications, aiming to help professionals and learners adapt to the new talent requirements of the AI era and enhance their competitiveness in technological innovation and the job market. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

2025 Cloud GPU Market: Costs, Performance, and Deployment Strategies Report: dstackai has released a detailed report on the state of the cloud GPU market in 2025, deeply analyzing GPU costs, performance, and deployment strategies across different cloud service providers. The report aims to provide machine learning engineers and enterprises with specific guidance on selecting cloud providers, helping them optimize resource allocation for AI training and inference tasks, thereby making more cost-effective and performance-advantageous decisions amidst the growing demand for AI infrastructure. (Source: stanfordnlp)
AI Hardware Technology Overview: Diverse Computing Units Driving the Intelligent Future: The Turing Post has released a comprehensive AI hardware guide, detailing various computing units currently driving artificial intelligence. These include Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), Central Processing Units (CPUs), Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), Neural Processing Units (NPUs), Accelerated Processing Units (APUs), Intelligence Processing Units (IPUs), Resistive Processing Units (RPUs), Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), quantum processors, Processing-in-Memory (PIM) chips, and neuromorphic chips. This guide provides a clear perspective for understanding the underlying hardware support of the AI technology stack, helping developers and researchers select the most suitable hardware solutions for their AI workloads. (Source: TheTuringPost)

