Keywords:supercomputer, AI hallucination, copyright infringement, large language model, AI chip, JUPITER supercomputer, OpenAI AI hallucination paper, Anthropic copyright settlement case, Qwen3-Max-Preview model, OpenAI self-developed AI chip
🔥 Spotlight
Europe’s First Exascale Supercomputer JUPITER Launched: Europe’s first exascale supercomputer, JUPITER, has been launched, powered by NVIDIA Grace Hopper. The system is the world’s most energy-efficient supercomputer, merging AI with HPC, and aims to achieve breakthroughs in areas such as climate science, neuroscience, and quantum simulation. This marks a significant step for Europe in high-performance computing and AI research, expected to accelerate cutting-edge scientific discoveries. (Source: nvidia)

OpenAI Publishes Paper Revealing Root Cause of AI Hallucinations: OpenAI has published a paper titled “Why Language Models Hallucinate,” pointing out that the fundamental reason for AI hallucinations lies in current training and evaluation mechanisms that reward models for guessing rather than admitting uncertainty. During the pre-training phase, models struggle to distinguish valid from invalid information due to a lack of “true/false” labels, making them especially prone to fabrication when dealing with low-frequency facts. OpenAI calls for updated evaluation metrics, penalizing confident errors and rewarding expressions of uncertainty, to encourage models to be more “honest.” (Source: source, source, source, source, source)

Anthropic Reaches $1.5 Billion Settlement in AI Copyright Infringement Case: Anthropic has reached a settlement with book authors in an AI copyright infringement case, agreeing to pay at least $1.5 billion. The settlement involves approximately 500,000 copyrighted works, averaging about $3,000 per work (before legal fees), and pledges to destroy pirated datasets. This case is the first AI-related class-action settlement in the US concerning copyright and could set a precedent for the legal definition of generative AI and intellectual property. (Source: source, source, source, source, source, source, source)

🎯 Trends
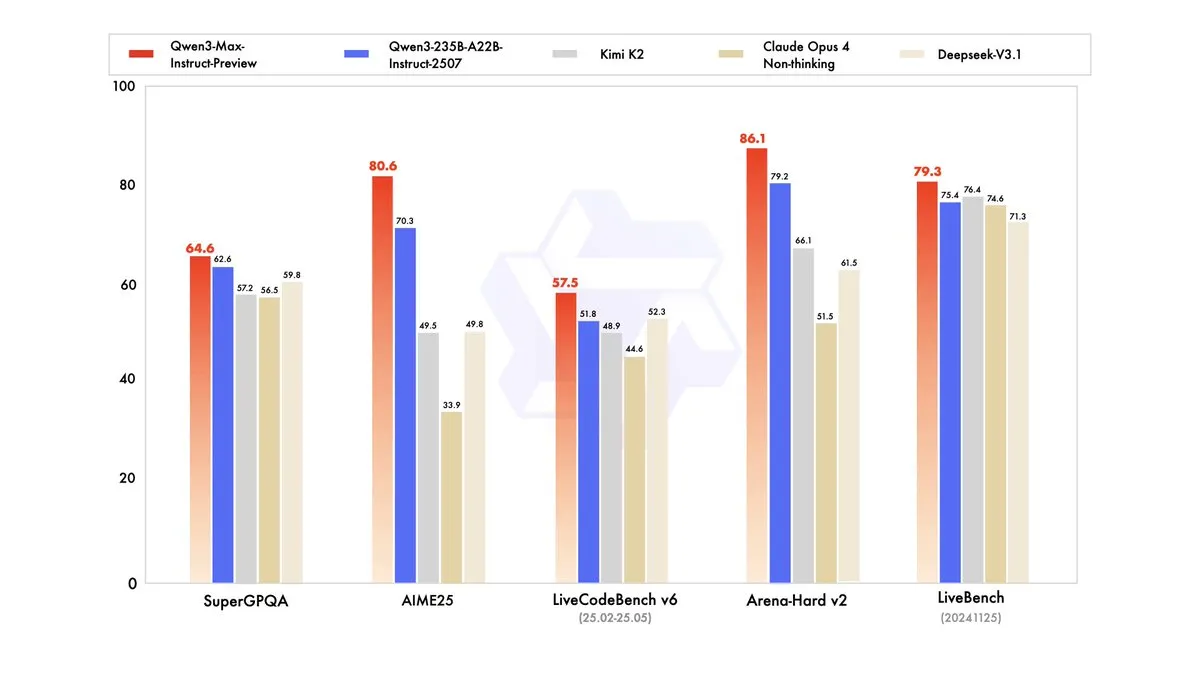
Qwen3-Max-Preview Released with Over a Trillion Parameters: Alibaba Cloud’s Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen) has released its largest model to date, Qwen3-Max-Preview (Instruct), with over a trillion parameters. The model is available via Qwen Chat and Alibaba Cloud API, surpassing previous models like Qwen3-235B-A22B-2507 in benchmark tests. Internal tests and early user feedback indicate significant improvements in performance, knowledge breadth, conversational ability, Agent tasks, and instruction following. The model has also launched on OpenRouter, sparking community discussion about its potential open-sourcing. (Source: source, source, source, source, source, source, source, source)
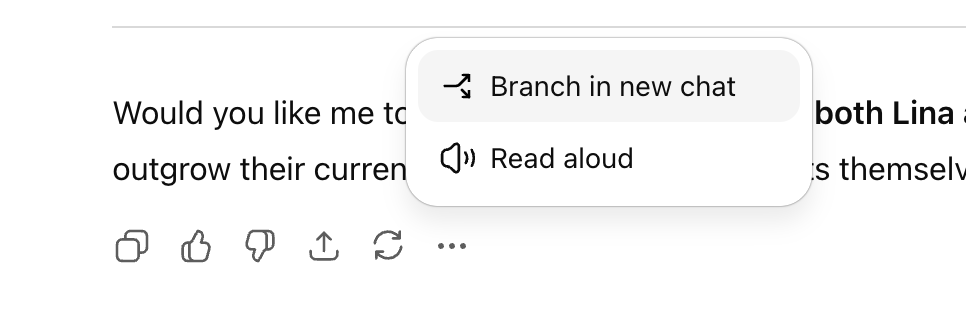
ChatGPT Adds Branching Conversations Feature, Enhancing Multi-threaded Exploration: OpenAI has introduced a new “branching conversations” feature for the ChatGPT web version, allowing users to create new branches at any response for multi-threaded exploration. This eliminates the need to start a new conversation or worry about excessively long contexts. Combined with memory features, this makes conversations more continuous and flexible, transforming them from linear to tree-like structures, helping users retain different ideas and improving the collaborative efficiency of AI assistants. (Source: source, source, source)
OpenAI Plans to Launch AI Recruitment Platform and Develop Own AI Chips: OpenAI plans to launch an AI-powered recruitment platform by mid-2026, competing with LinkedIn and offering “AI fluency” certification. Additionally, to reduce its reliance on Nvidia, OpenAI will begin producing its self-designed AI chips next year. These initiatives demonstrate OpenAI’s ambition in expanding its AI application ecosystem and optimizing hardware infrastructure. (Source: source, source, source, source, source)

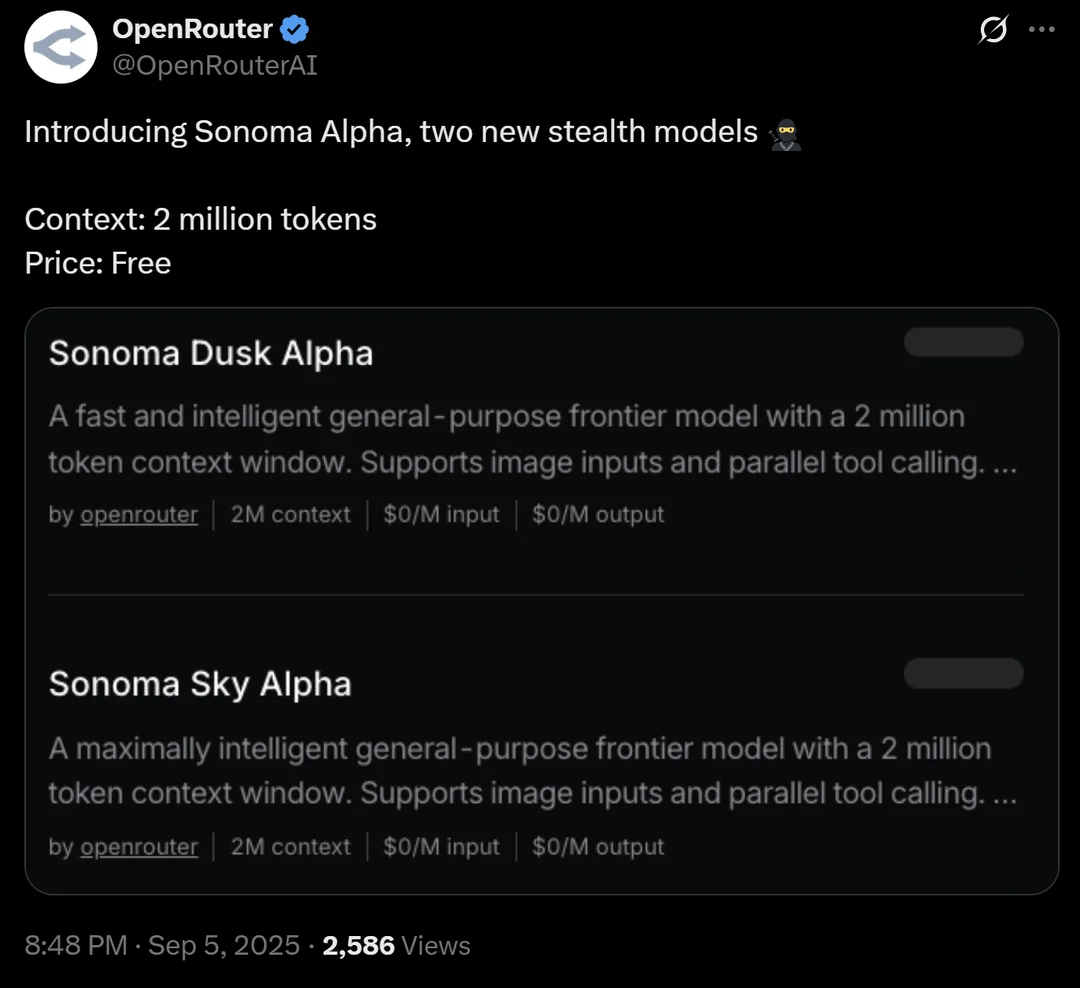
OpenRouter Introduces Sonoma Alpha, a Stealth Model with a 2 Million Context Window: OpenRouter platform has launched a “stealth” model called Sonoma Alpha, whose key highlight is its support for a 2 million context window and free availability. The community widely speculates that this model is from xAI’s Grok series, due to its “maximum truth-seeking” characteristic aligning with Elon Musk’s philosophy. The model excels in code generation, logic, and scientific tasks, foreshadowing the potential of ultra-long context models in practical applications. (Source: source, source, source)
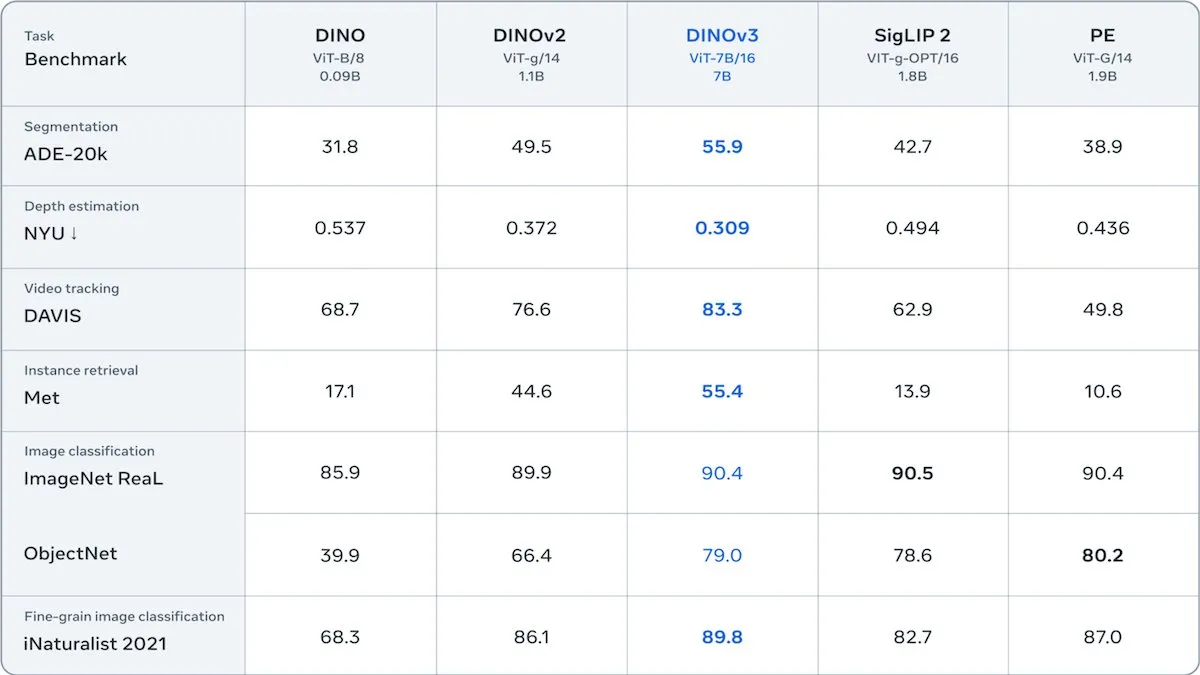
Meta Releases DINOv3 Self-Supervised Vision Transformer: Meta has released DINOv3, a 6.7 billion-parameter self-supervised vision Transformer model that significantly improves image embedding quality in tasks like image segmentation and depth estimation. Trained on 1.7 billion Instagram images, the model introduces a new loss term to maintain patch-level diversity, overcoming the limitations of unlabeled data. DINOv3 is released under a license allowing commercial use but prohibiting military applications, providing a powerful self-supervised backbone for downstream vision applications. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
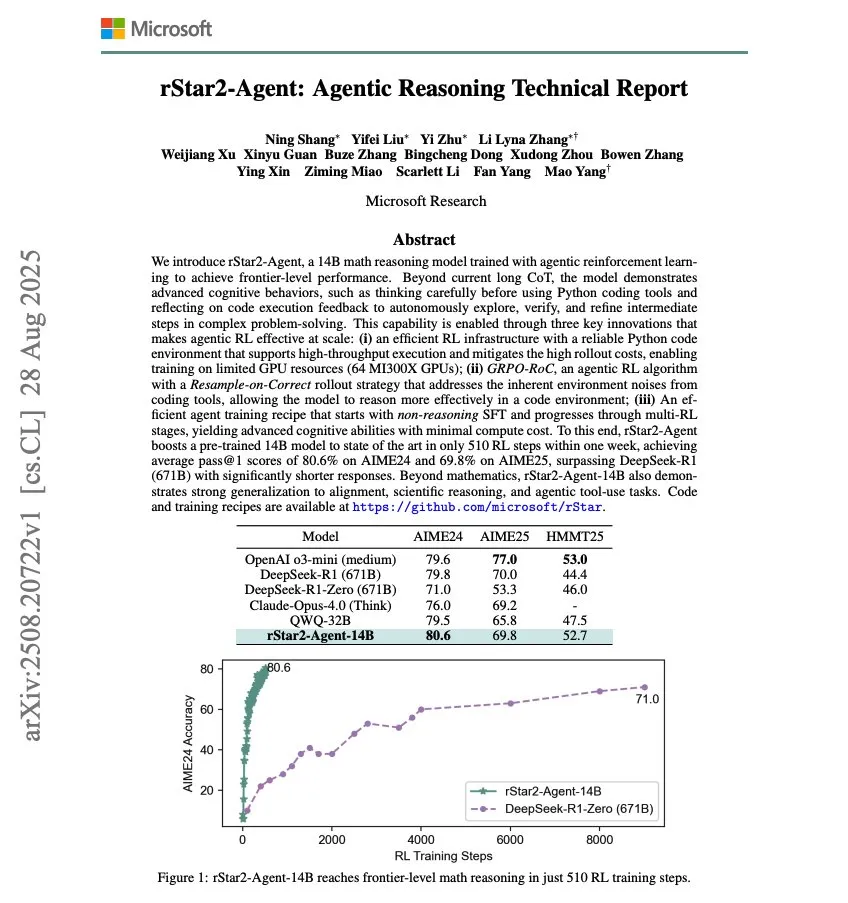
Microsoft Releases rStar2-Agent, a 14B Mathematical Reasoning Model: Microsoft has released rStar2-Agent, a 14B mathematical reasoning model trained via Agentic RL, achieving state-of-the-art mathematical reasoning capabilities with just 510 RL training steps. This research demonstrates the potential to rapidly enhance AI model performance in specific domains through reinforcement learning. (Source: dair_ai)
OpenAI Establishes oai Labs to Explore New Human-AI Collaboration Interfaces: OpenAI announced the establishment of oai Labs, led by Joanne Jang, focusing on researching and prototyping new interfaces for human-AI collaboration. The team aims to move beyond existing chat and agent paradigms, exploring new paradigms and tools to improve how people interact, think, create, learn, and connect with AI. (Source: source, source)
IFA 2025 Exhibition: AI Hardware and Robotics Trends: At IFA 2025 in Berlin, Chinese manufacturers are fully dominating the AI glasses market, with brands like Rokid and LeiBird Innovation showcasing multiple products and actively exploring overseas ecosystems. In the robotics sector, Unitree Technology exhibited its humanoid robot G1 and robot dog Go 2, attracting significant attention; Midea and Ubtech also exhibited home service robots. Functional robots like smart cleaning robots, lawn mowers, and pool robots are flourishing, with upgraded technology that is closer to daily life scenarios. AI has been deeply integrated into consumer electronics products like home appliances, mobile phones, and PCs, emphasizing practical implementation and a “seamless” experience. (Source: 36氪)

OpenBMB Releases MiniCPM 4.1-8B, the First Open-Source Trainable Sparse Attention LLM: OpenBMB has released the MiniCPM 4.1-8B model, the first open-source inference LLM to employ trainable sparse attention. The model outperforms models of similar size across 15 tasks, with a 3x increase in inference speed, and adopts an efficient architecture. This marks significant progress for open-source models in inference capabilities and efficiency, providing researchers with a powerful new tool. (Source: teortaxesTex)

🧰 Tools
Open Instruct: High-Performance RL Research Codebase: Open Instruct, maintained by AllenAI, is a high-performance Reinforcement Learning (RL) research codebase designed to provide easily modifiable and high-performing RL implementations. Led by Finbarr and others, the project is continuously undergoing improvements, providing researchers with a foundational platform for RL experimentation and development. (Source: source, source)
Grok: PDF Reading Comprehension and Summarization: xAI’s Grok introduces a PDF reader feature, allowing users to highlight any section and click “Explain” to understand the content, or click “Cite” to ask specific questions. This significantly enhances user efficiency and depth of understanding when processing lengthy PDF documents. (Source: source, source)
Devin AI: Data Analyst for EightSleep: Cognition’s Devin AI is being used by the EightSleep team as a data analyst, handling tasks ranging from “numerical anomalies” to ad-hoc data queries, reducing analysis/dashboard completion time from days to hours and significantly improving data insight efficiency. This demonstrates the powerful application potential of AI agents in enterprise data analysis. (Source: cognition)
Claude Code Sub-Agent Functionality Explained: Claude Code, through its Task tool, allows users to create three types of specialized sub-agents: general-purpose, status line configuration, and output style configuration. These sub-agents have their own toolsets, capable of handling complex tasks, configuring settings, or creating output styles. Sub-agents are stateless, execute once, and return results, making them suitable for delegating complex searches, analyses, or specialized configurations to maintain the focus of the main conversation. (Source: Vtrivedy10)
LlamaIndex SemTools: Document Search and Analysis Tool for Command-line Agents: LlamaIndex has released SemTools, a CLI toolkit for parsing and semantic search. Combining Unix tools with semantic search capabilities, Agents can efficiently process complex documents, providing more detailed and accurate answers, covering tasks such as search, cross-referencing, and temporal analysis. This indicates that combining existing Unix tools with semantic search can create powerful knowledge workers. (Source: source, source)
Replit Agent: AI Coding Assistant from Prompt to Production Application: Replit Agent celebrates its first anniversary, having evolved from initial AI code completion and chat editing to being able to transform prompts directly into production-ready applications. Replit highlights its ability to automate development environment setup, package installation, database configuration, and deployment, aiming to revolutionize the software development process. (Source: source, source)

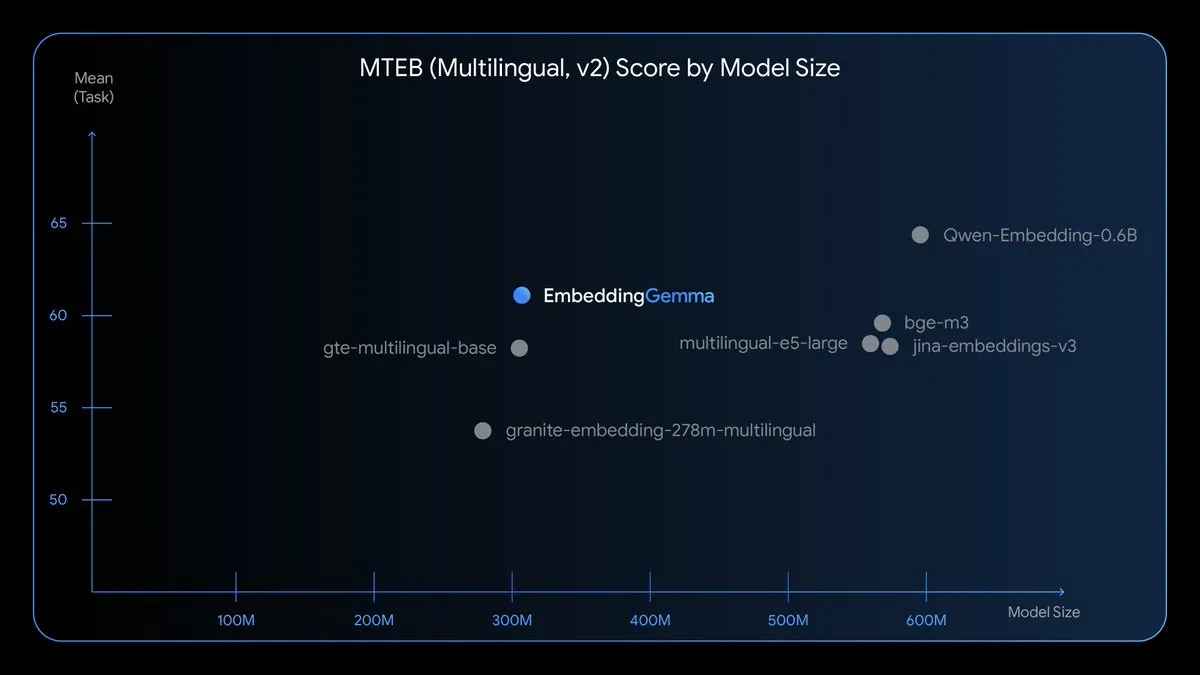
EmbeddingGemma: On-Device Multilingual Embedding Model: EmbeddingGemma is a new open-source multilingual embedding model with 308M parameters, trained on Gemma 3, supporting over 100 languages. Optimized for speed, privacy, and efficiency, the model can run offline with less than 200MB memory footprint and inference time under 15ms, making on-device RAG, semantic search, and classification possible. (Source: TheTuringPost)
Nano Banana Hackathon: Generative AI Challenge: Kaggle will host the Nano Banana Hackathon, offering $400,000 in prizes and making the Gemini API freely available with Gemini 2.5 Flash Image. Participants will create using generative AI technologies within 48 hours, with the competition evaluating innovation, technical execution, impact, and presentation. (Source: source, source, source)

📚 Learning
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch: Python_Dv shared tutorials and guides on building AI Agents from scratch, covering key technologies such as LLM, generative AI, and machine learning. This resource provides developers with an entry path to practical AI Agent development. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

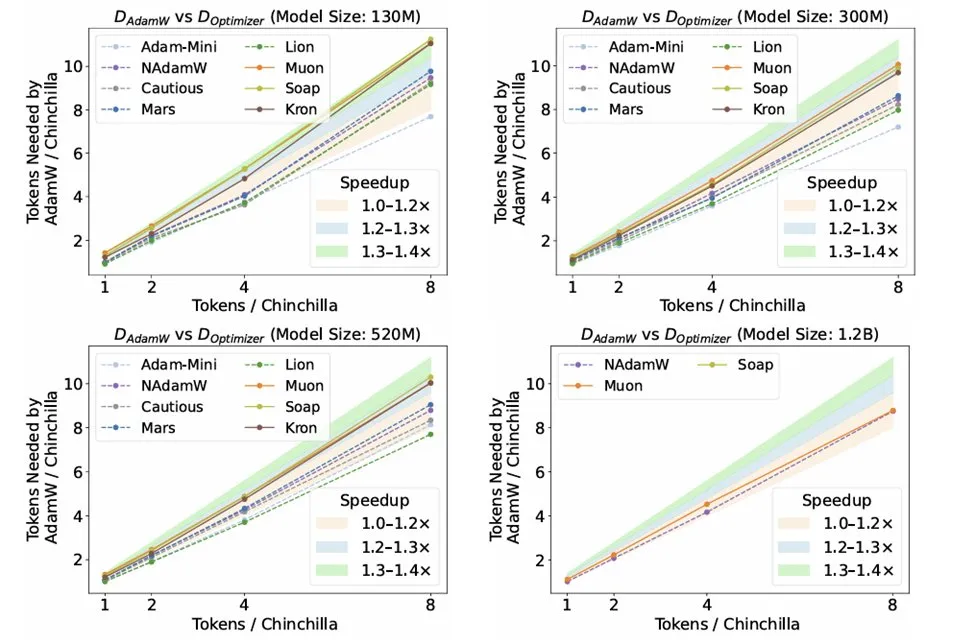
Research on Optimizers in LLM Inference: A research paper titled “Fantastic Pretraining Optimizers and Where to Find Them” by Kaiyue Wen et al. conducted rigorous benchmark tests on 10 optimizers. The study found that despite the attention given to optimizers like Muon and Mars, their acceleration effect relative to AdamW was only about 10% after rigorously tuning hyperparameters and scaling up. This highlights the need to be cautious of insufficient baseline tuning or limited scale when evaluating new optimizers. (Source: source, source, source)
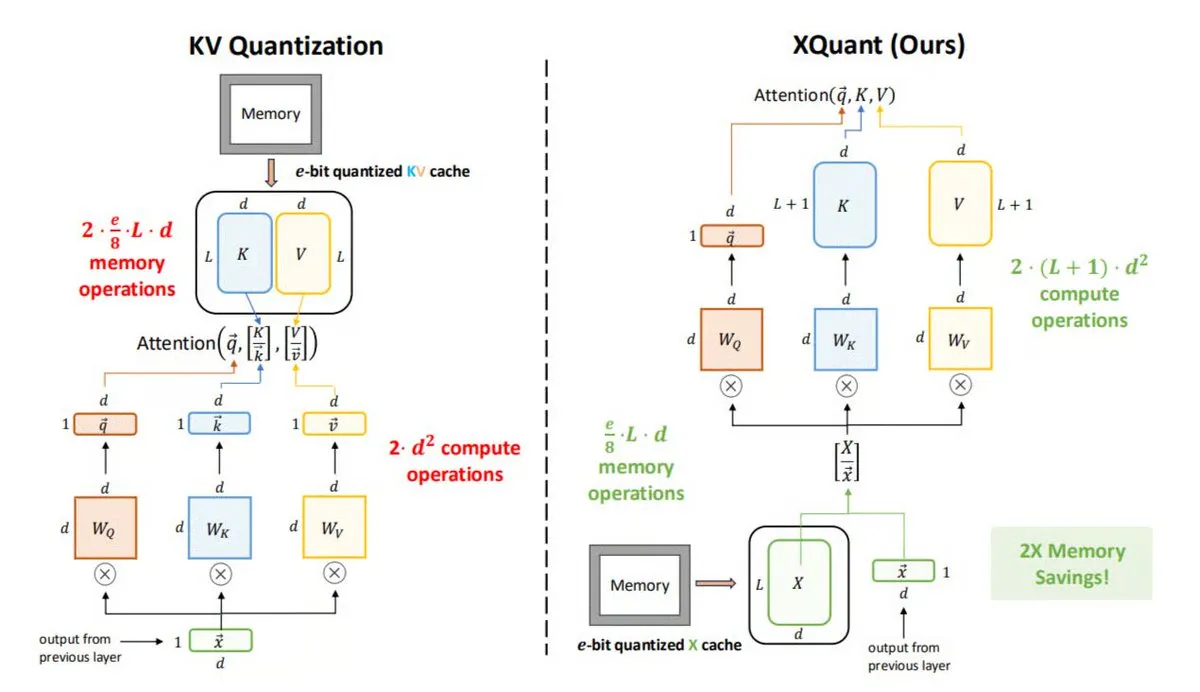
XQuant: Memory Optimization Technique for LLM Inference: UC Berkeley proposes XQuant, a new LLM memory optimization method that can reduce memory usage by up to 12x. Instead of storing traditional KV caches, XQuant quantizes and stores layer input activations (X), regenerating Keys and Values from X on demand during inference. This technique achieves faster, more efficient inference by adding a small amount of computation, without sacrificing accuracy. (Source: TheTuringPost)
LLM Prompt Design: The Mom Test Methodology: Tz shared a methodology for applying the user research principles from “The Mom Test” to LLM prompt design, emphasizing avoiding questions that would elicit “nice platitudes” from the model. Instead, prompts should be constructed to elicit verifiable, fact-based, or clearly constrained responses. The core is to avoid opinions, future assumptions, and vagueness, and to ask for specifics, behavior-driven responses, and verification rather than praise. (Source: dotey)

AI Compression Technology 300x Better Than Traditional Methods: The YouTube channel Two Minute Papers points out that AI compression technology is 300 times more efficient than traditional compression methods but is not yet widely adopted. The video likely explores physics engine technologies like NVIDIA’s WaveBlender, showcasing AI’s immense potential in data compression and its applications in areas like audio simulation. (Source: , source)
NeurIPS 2025 Grand Challenge on Multimodal Superintelligence: Lambda Research invites researchers, engineers, and AI enthusiasts to participate in the NeurIPS 2025 Grand Challenge on Multimodal Superintelligence, aimed at advancing open-source multimodal machine learning. Participating teams will have the opportunity to receive up to $20,000 in compute credits to collectively build the future of open-source multimodal AI. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)

Fully Annotated Guide to Diffusion Models: The Reddit community shared a comprehensive annotated guide on “What are Diffusion Models?”. This guide provides learners with resources for a deep understanding of diffusion model principles and applications, helping them master this cutting-edge generative AI technology. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
LoRA/QLoRA Application in Multi-GPU Training for Visual LLMs: The community discussed the challenges and practices of using LoRA/QLoRA for training large visual LLMs (such as Llama 3.2 90B Visual Instruct) in multi-GPU environments. Due to the massive scale of the models, they cannot run on a single GPU, and developers are seeking frameworks/packages that support multi-GPU training. LoRA/QLoRA is highly anticipated due to its efficient fine-tuning capabilities, but its applicability in specific scenarios still requires further exploration. (Source: source, source)
💼 Business
OpenAI Acquires Y Combinator-Backed Alex Team: OpenAI has acquired the team behind Alex, a Y Combinator-backed startup. The team will join OpenAI’s Codex team, dedicated to AI coding assistants. Alex founder Daniel Edrisian stated that they successfully built top-tier coding agents for iOS and macOS applications, and this acquisition will allow their work to continue on a larger scale. (Source: The Verge)
Baseten Completes $150 Million Series D Funding, Focusing on the Future of AI Inference: Baseten has completed a $150 million Series D funding round. Its CEO, Tuhin One, pointed out that as token prices decrease, inference costs will continue to fall, signaling a larger scale growth in the AI inference market. Baseten is committed to building ubiquitous AI inference infrastructure to support the widespread application of AI across various industries. (Source: basetenco)
RecallAI Completes $38 Million Series B Funding, Accelerating AI Meeting Transcription Services: RecallAI announced the completion of a $38 million Series B funding round, led by BessemerVP, with follow-on investments from HubSpot Ventures and SalesforceVC. RecallAI provides meeting recording API services, already serving over 2,000 companies. This funding will accelerate its expansion in the AI meeting transcription sector, further solidifying its market position. (Source: blader)
🌟 Community
The Value and Controversy of AI Evaluations (Evals): The community engaged in intense discussions surrounding the necessity and methodology of AI evaluations (Evals), exploring their role in enterprise-level applications, their complementarity with A/B testing, and the importance of data science in AI engineering. Some believe Evals are crucial for understanding AI system performance and iterative optimization, while others argue that over-reliance on Evals could lead to “pseudoscience.” (Source: source, source)

AI Coding Quality and the Limitations of “Vibe Coding”: Developers discussed the pros and cons of AI-generated code, pointing out that AI excels at rapid prototyping, handling boilerplate code, and writing tests. However, the generated code is often criticized for being verbose, overly defensive, and lacking refactoring capabilities. Many developers believe that for code requiring long-term maintenance, human-written code is still superior to AI-generated “Vibe Coding.” (Source: source, source)
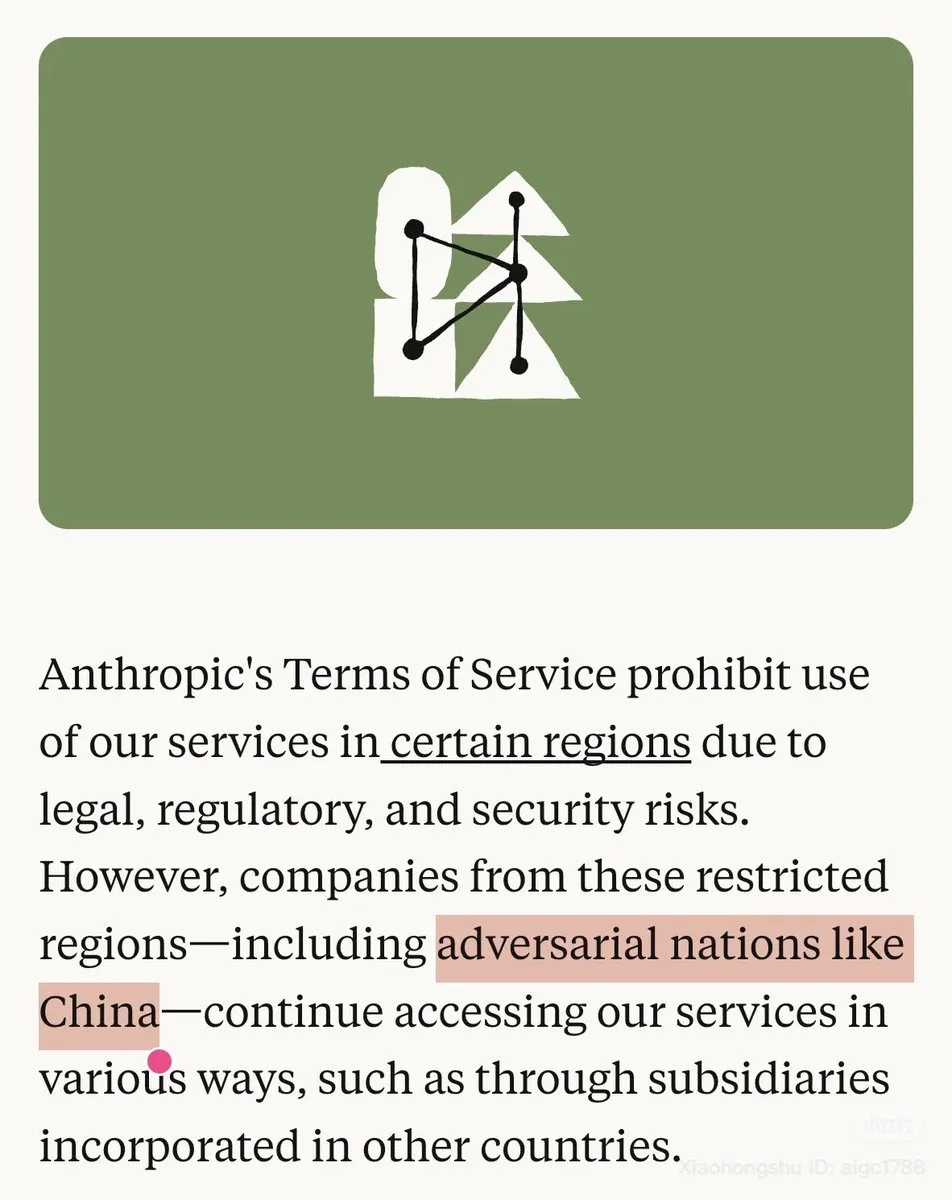
Anthropic’s China Policy and Model Availability Controversy: Anthropic explicitly labeled China as a “hostile nation” in its blog and restricted Claude’s use in certain regions, sparking strong dissatisfaction within the community. Concurrently, Claude.ai’s Opus 4.1 model was temporarily taken offline, exacerbating user concerns about model stability and company policies. Many Chinese users stated they would switch to OpenAI Codex. (Source: source, source)
AI and Political Interaction & Regulatory Concerns: Tech leaders like Sam Altman and Lisa Su praised the Trump administration’s pro-business and pro-innovation policies at a White House dinner, sparking discussions about the interaction between AI companies and political power, and the prospects of AI applications in education. Meanwhile, the FTC will investigate the impact of AI companies on children, reflecting regulators’ concerns about the potential social risks of AI technology. (Source: source, source)

AI Agent Capabilities and Development Challenges: The community discussed the core capabilities required for AI Agents, including the need for ultra-long contexts and Agent interpretability. AI engineers reported that during processes like AI agents generating code, evaluating runs, and model thinking, workflows become highly fragmented, leading to significant time spent waiting, which is becoming one of the most frustrating experiences in the age of AI. (Source: source, source)

AI’s Impact on Employment, UBI, and Social Wealth Distribution: The community hotly debated AI’s impact on the job market, the necessity of Universal Basic Income (UBI), and concerns that AI might exacerbate wealth inequality. Computer scientists like Geoffrey Hinton and other experts believe AI will make a few people richer and most people poorer, triggering deep discussions on AI technology’s social equity, employment impact, and wealth redistribution. (Source: source, source)

AI Model Performance and Declining User Experience: Many users complained about a significant decline in ChatGPT’s recent performance, manifesting as increased hallucinations, refusal to answer specific questions, lack of genuine empathy, and content censorship restrictions. Concurrently, the issue of AI chatbots “playing dumb” also sparked dissatisfaction, with users believing it might be due to corporate policy restrictions rather than a genuine lack of capability, leading to a poor user experience. (Source: source, source)
AI-Generated Content Quality and Public Perception: The community discussed negative public perceptions of AI-generated content, often referred to as “AI Slop,” reflecting concerns about AI misuse, inconsistent quality, and the devaluation of human creativity. Meanwhile, AI generation technology also challenges the era of photography as reliable evidence, sparking discussions on deepfakes and information authenticity. (Source: source, source)

AI Ethics and User Behavior: Being Kind to AI: The community discussed whether users become more unkind when interacting with AI assistants due to their unconditional “compliance,” and whether this interaction pattern negatively impacts communication with humans. Many believe that even if AI lacks emotions, maintaining politeness is for one’s own mental well-being and to prevent bad habits from spreading to real-life human relationships. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
AI Consciousness and the Philosophical Boundaries of Intelligence: The community explored the philosophical question of whether AI possesses consciousness or “life,” citing the example of robot Johnny 5 in the movie “Short Circuit” being deemed “alive” through its understanding of humor. Most views suggest that AI understanding humor is a display of intelligence, but not evidence of life or consciousness. The limitation of the Turing Test lies in its inability to verify AI’s “inner experience.” (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
LocalLLaMA Community Management and AI Generalization Controversy: Reddit’s LocalLLaMA community introduced a new “local only” flair, requiring posts related to local LLM technology to use this tag to filter out “noise” such as non-local models and API costs. This move sparked strong backlash from the community, with many users believing it goes against the community’s original “local-first” intention. Concurrently, discussions about “generalized AI systems being a lie” also reflect skepticism about AI’s generalization capabilities and reliability. (Source: source, source)

GPU Computing Market Competition and AI Development Path: The community discussed the fierce competition in the GPU computing market, with emerging cloud service providers needing to enhance their competitiveness. Meanwhile, AI progress is not solely driven by computational power; learning efficiency and non-Transformer architectures could bring the next exponential leap, sparking thoughts on the future development path of AI. Some also point out that AI progress is not solely driven by computational power, and learning efficiency and non-Transformer architectures could bring the next exponential leap. (Source: source, source)
💡 Others
India Uses Robots to Clean Sewers, Addressing Manual Scavenging Dilemma: The Delhi government in India is promoting the use of robots to replace manual sewer cleaning, aiming to address the long-standing issue of “manual scavenging.” Although the practice has been banned since 1993, it remains widespread and dangerous. Several companies have offered technological alternatives, including robots of varying complexity, aiming to improve operational safety and dignity. (Source: MIT Technology Review)
Researchers Use “Rat Robots” to Simulate Real Rat Behavior: Researchers are developing a “rat robot” aimed at simulating real rat behavior to deeply study biology and neuroscience. This project combines robotics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, providing a new experimental platform for understanding animal behavior. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
AI Reconstructs Orson Welles’ Lost Film “The Magnificent Ambersons”: The Fable Simulation team is using AI technology to non-commercially and academically reconstruct the lost 43 minutes from Orson Welles’ lost masterpiece, “The Magnificent Ambersons.” This project demonstrates AI’s potential in film restoration and artistic heritage preservation, with the potential to allow audiences to re-experience this unfinished classic work. (Source: source, source)

