Keywords:GPT-5, AI self-improvement, embodied intelligence, multimodal models, large language models, reinforcement learning, AI Agent, GPT-5 performance enhancement, Genie Envisioner robotics platform, LLM recruitment assessment bias, Qwen3 ultra-long context, CompassVerifier answer validation
🔥 Focus
GPT-5 Release: Productization and Performance Enhancement : OpenAI has officially released GPT-5, marking the latest iteration of its flagship model. This release focuses on improving user experience by automatically scheduling base models and deep inference models via a real-time router, balancing speed and intelligence. GPT-5 shows significant improvements in reducing hallucinations, enhancing instruction following, and programming capabilities, setting new records in multiple benchmarks. Sam Altman likens it to a “Retina display,” emphasizing its practicality as a “PhD-level AI” rather than merely a breakthrough in intelligence limits. Although not yet AGI technically, its faster inference speed and lower operating costs are expected to drive wider AI adoption. (Source: MIT Technology Review)

Progress in AI Self-Improvement Research : Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg stated that the company is committed to building AI systems capable of self-improvement. AI has already demonstrated self-improvement capabilities in various aspects, such as continuously optimizing its performance through automatic data augmentation, model architecture search, and reinforcement learning. This trend suggests that future AI systems will be able to learn autonomously and surpass human-defined performance boundaries, which is a critical path to achieving higher levels of AI. (Source: MIT Technology Review)

Genie Envisioner: Unified World Model Platform for Robot Manipulation : Researchers have introduced Genie Envisioner (GE), a unified world foundation platform for robot manipulation. GE-Base is an instruction-conditioned video diffusion model that captures the spatial, temporal, and semantic dynamics of real robot interactions. GE-Act maps latent representations to executable action trajectories, enabling precise and generalizable policy inference. GE-Sim, an action-conditioned neural simulator, supports closed-loop policy development. This platform is expected to provide a scalable and practical foundation for instruction-driven general embodied intelligence. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
ISEval: An Evaluation Framework for LMMs’ Ability to Identify Erroneous Inputs : To address the question of whether Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) can proactively identify erroneous inputs, researchers proposed the ISEval evaluation framework. This framework covers seven types of flawed premises and three evaluation metrics. The study found that most LMMs struggle to proactively detect textual flaws without explicit guidance, and their performance varies across different error types. For instance, they are good at identifying logical fallacies but perform poorly on surface language errors and specific conditional flaws. This highlights the urgent need for LMMs to actively validate input validity. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Study on Language Bias in LLM Hiring Assessments : A study introduced a benchmark to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs)’ responses to linguistic discriminatory markers in hiring assessments. Through carefully designed interview simulations, the study found that LLMs systematically penalize certain language patterns, especially vague language, even when content quality is identical. This reveals demographic biases in automated assessment systems and provides a foundational framework for detecting and measuring linguistic discrimination in AI systems, with broad implications for the fairness of automated decision-making. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
🎯 Trends
Qwen3 Series Models Support Million-Token Ultra-Long Context : Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen3-30B-A3B-2507 and Qwen3-235B-A22B-2507 models now support an ultra-long context of up to 1 million tokens. This is made possible by Dual Chunk Attention (DCA) and MInference sparse attention technologies, which not only improve generation quality but also boost inference speed for near-million-token sequences by up to 3 times. This significantly expands the application potential of LLMs in handling complex tasks such as long documents and codebases, and is compatible with vLLM and SGLang for efficient deployment. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen)

Anthropic Claude Opus 4.1 and Sonnet 4 Upgrades : Anthropic has released Claude Opus 4.1 and Sonnet 4, focusing on enhancing Agentic tasks, real-world coding, and reasoning capabilities. The new models feature a “deep thinking” function, allowing flexible switching between instant response and deep inference modes, compressing complex tasks that would take hours into minutes. This further strengthens Claude’s position in multi-model collaboration scenarios, particularly excelling in complex code review and advanced reasoning tasks. (Source: dl_weekly)
Microsoft Launches Copilot 3D Feature : Microsoft has launched a free Copilot 3D feature that can convert 2D images into GLB format 3D models, compatible with various 3D viewers, design tools, and game engines. While currently less effective for animal and human images, this feature provides users with convenient 2D-to-3D conversion capabilities, expected to play a role in product design, virtual reality, and other fields, further lowering the barrier to 3D content creation. (Source: The Verge)
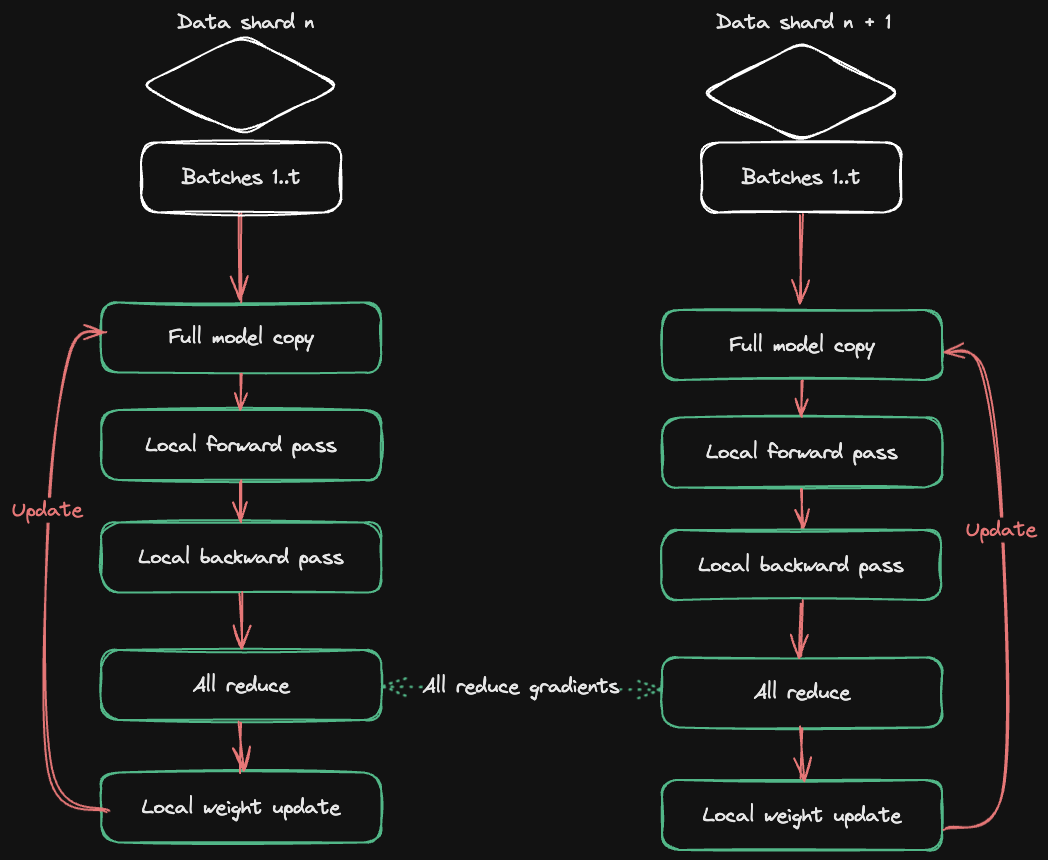
HuggingFace Accelerate Releases Multi-GPU Training Guide : HuggingFace, in collaboration with Axolotl, has released the Accelerate ND-Parallel guide, aiming to simplify the combination and application of parallel strategies in multi-GPU training. The guide details strategies such as Data Parallelism (DP), Sharded Data Parallelism (FSDP), Tensor Parallelism (TP), and Context Parallelism (CP), and provides examples of mixed parallel configurations. This helps developers optimize memory usage and throughput when training large models, effectively addressing communication overhead challenges in multi-node training. (Source: HuggingFace Blog)
🧰 Tools
OpenAI Codex CLI: Local Coding Agent in Terminal : OpenAI has released Codex CLI, a lightweight coding agent that runs locally in the terminal. Users can install it via npm install -g @openai/codex or brew install codex. It supports binding with ChatGPT Plus/Pro/Team accounts for free use of the latest models like GPT-5, or pay-as-you-go via API Key. Codex CLI offers various sandbox modes, including read-write and read-only, and supports custom configurations, aiming to provide developers with efficient and secure local programming assistance. (Source: openai/codex – GitHub Trending)

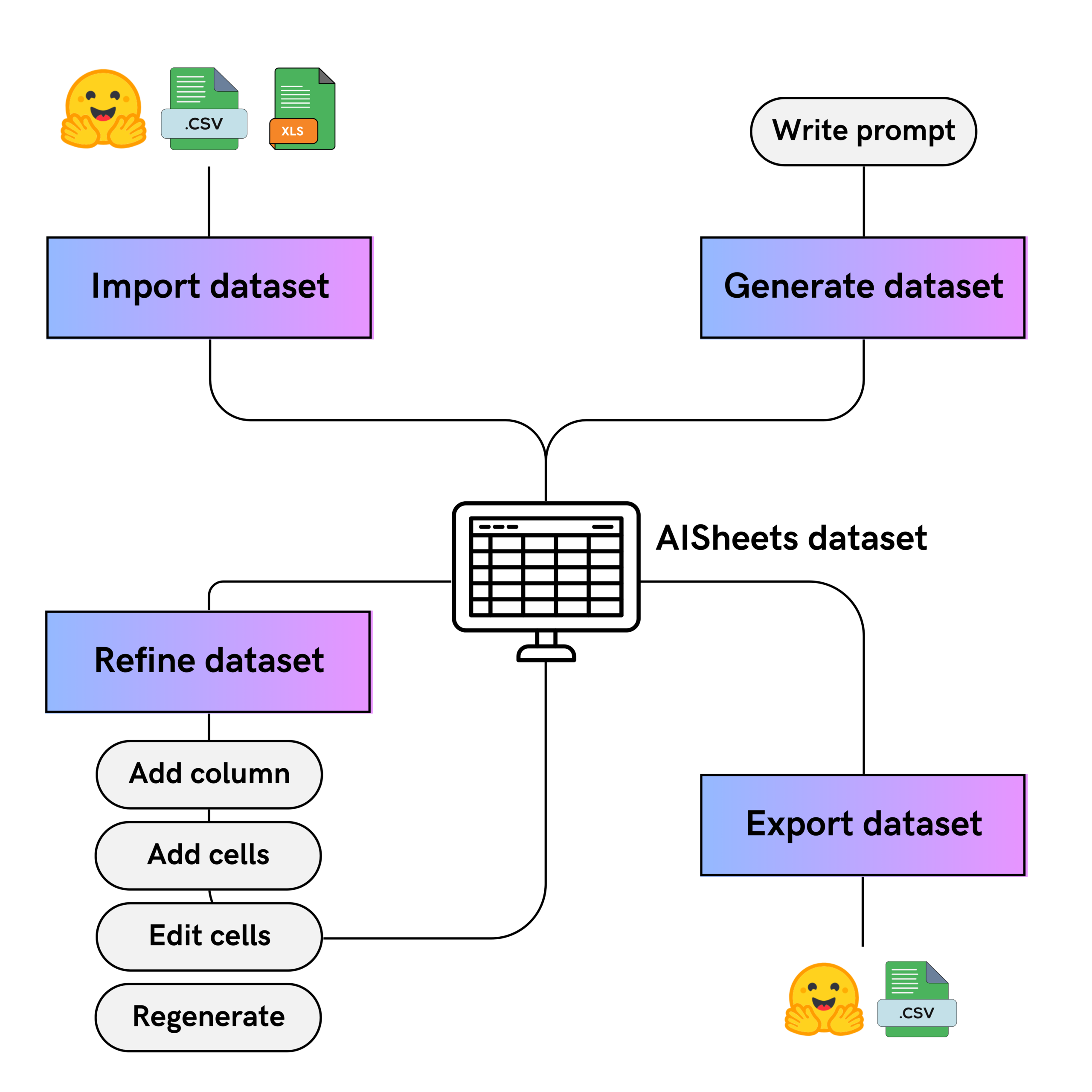
HuggingFace AI Sheets: No-Code Dataset Tool : HuggingFace has launched AI Sheets, an open-source, no-code tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models. The tool features a spreadsheet-like interface and can be deployed locally or run on the Hugging Face Hub. Users can leverage thousands of open models (including gpt-oss) for model comparison, prompt optimization, data cleaning, classification, analysis, and synthetic data generation. It allows iterative improvement of AI-generated results through manual editing and upvote feedback, and can be exported to the Hub. (Source: HuggingFace Blog)
Google Agent Development Kit (ADK) and Examples : Google has released the Agent Development Kit (ADK), an open-source, code-first Python toolkit for building, evaluating, and deploying complex AI Agents. ADK supports a rich tool ecosystem, modular multi-agent systems, and flexible deployment. Its sample library adk-samples provides various agent examples, from conversational bots to multi-agent workflows, aiming to accelerate the agent development process and integrate with the A2A protocol for remote inter-agent communication. (Source: google/adk-python – GitHub Trending & google/adk-samples – GitHub Trending)
Qwen Code CLI: Free Code Execution Tool : Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen Code CLI offers 2000 free code executions daily, easily launched with the command npx @qwen-code/qwen-code@latest. This tool supports Qwen OAuth and aims to provide developers with a convenient and efficient code writing and testing experience. The Qwen team stated they will continue to optimize this CLI tool and the Qwen-Coder model, striving to achieve Claude Code’s performance while remaining open-source. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen)
📚 Learning
OpenAI Python Library Update : The official OpenAI Python library provides convenient access to the OpenAI REST API, supporting Python 3.8+. The library includes type definitions for all request parameters and response fields, and offers both synchronous and asynchronous clients. Recent updates include beta support for the Realtime API, for building low-latency, multimodal conversational experiences, as well as detailed explanations for webhook validation, error handling, request IDs, and retry mechanisms, enhancing development efficiency and robustness. (Source: openai/openai-python – GitHub Trending)
Curated List of AI Agents : e2b-dev/awesome-ai-agents is a GitHub repository that collects numerous examples and resources for autonomous AI agents. This list aims to provide developers with a centralized resource to understand and learn about different types of AI agents, covering various application scenarios from simple to complex, serving as an important learning material for exploring and building AI agents. (Source: e2b-dev/awesome-ai-agents – GitHub Trending)
MeanFlow: A New Paradigm for One-Step Generative Diffusion Models : Scientific Space has proposed MeanFlow, a new method poised to become the standard for accelerating generative diffusion models. This method aims to achieve one-step generation by modeling “average velocity” instead of “instantaneous velocity,” overcoming the slow generation speed of traditional diffusion models. MeanFlow boasts clear mathematical principles, can be trained from scratch with a single objective, and its single-step generation performance is close to SOTA, offering a new theoretical and practical direction for accelerating generative AI models. (Source: WeChat)

Full Lifecycle Optimization of Long-Context KV Cache : Microsoft Research Asia shared its practices for full lifecycle optimization of KV Cache, aiming to address latency and storage challenges in long-context Large Language Model inference. Through the SCBench benchmark and proposing methods like MInference and RetrievalAttention, it significantly reduces Prefilling phase latency and alleviates KV Cache memory pressure. The research emphasizes system-level cross-request optimization and Prefix Caching reuse, providing optimization solutions for the scalability and cost-effectiveness of long-context LLM inference. (Source: WeChat)

Reinforcement Learning Framework FR3E Enhances LLM Exploration Capability : ByteDance, MAP, and the University of Manchester jointly proposed FR3E (First Return, Entropy-Eliciting Explore), a novel structured exploration framework designed to address the insufficient exploration problem in LLMs for reinforcement learning. FR3E identifies high-uncertainty tokens in reasoning trajectories to guide diverse expansions, systematically reconstructing the LLM exploration mechanism to achieve a dynamic balance between exploitation and exploration, significantly outperforming existing methods on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks. (Source: WeChat)

Research on Maxima in Self-Attention Mechanism and Context Understanding : A new study at ICML 2025 reveals the existence of highly concentrated maxima in the Query (Q) and Key (K) representations of large language models’ self-attention mechanisms, which are crucial for understanding contextual knowledge. The study found that this phenomenon is common in models using Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) and appears in early layers. Disrupting these maxima leads to a sharp decline in model performance on tasks requiring contextual understanding, providing new directions for LLM design, optimization, and quantization. (Source: WeChat)

C3 Benchmark: A Chinese-English Bilingual Speech Dialogue Model Test Benchmark : Peking University and Tencent jointly released C3 Benchmark, the first comprehensive evaluation benchmark for spoken dialogue models that examines complex phenomena such as pauses, polyphonic characters, homophones, accents, syntactic ambiguities, and polysemy in both Chinese and English. The benchmark includes 1079 real-world scenarios and 1586 audio-text pairs, aiming to address the critical weaknesses of current speech dialogue models and promote their progress in understanding human daily conversations. (Source: WeChat)

Chemma: Large Language Model for Organic Chemical Synthesis : Shanghai Jiao Tong University’s AI for Science team released the Baiyulan Chemical Synthesis Large Model (Chemma), which for the first time enables a chemical large language model to accelerate the entire organic synthesis process. Chemma, without quantum computing, relies solely on chemical knowledge understanding and reasoning capabilities, surpassing existing best results in single-step/multi-step retrosynthesis, yield/selectivity prediction, and reaction optimization tasks. Its “Co-Chemist” human-AI collaborative active learning framework has been successfully validated in real reactions, providing a new paradigm for chemical discovery. (Source: WeChat)

Intern-Robotics: Shanghai AI Lab’s Embodied Full-Stack Engine : Shanghai AI Lab has released Intern-Robotics, an embodied full-stack engine aimed at driving the “ChatGPT moment” in embodied AI. This engine is an open and shared infrastructure focused on achieving generalization across embodiments, scenarios, and tasks, emphasizing a near 100% success rate for operations. The team is committed to solving data scarcity issues through the “Real to Sim to Real” technical route and real-world reinforcement learning, gradually achieving zero-shot generalization to accelerate the practical application of embodied intelligence. (Source: WeChat)

SQLM: AI Self-Questioning Reasoning Capability Evolution Framework : A team from Carnegie Mellon University proposed SQLM, a self-questioning framework that requires no external data, designed to enhance AI reasoning capabilities through self-questioning and answering. The framework consists of two roles, a proposer and a solver, both trained via reinforcement learning to maximize expected rewards. SQLM significantly improved model accuracy on arithmetic, algebra, and programming tasks, providing a scalable, self-sustaining process for enhancing large language models’ capabilities in the absence of high-quality human-annotated data. (Source: WeChat)

CompassVerifier: AI Answer Verification Model and Benchmark : Shanghai AI Lab and the University of Macau jointly released CompassVerifier, a general answer verification model, and VerifierBench, an evaluation set, aiming to address the issue of large models’ rapid training capability advancements but lagging answer verification ability. CompassVerifier is a lightweight yet powerful multi-domain general verifier, optimized based on Qwen series models, achieving verification accuracy surpassing general large models in mathematics, knowledge, and scientific reasoning. It can also serve as a reinforcement learning reward model, providing precise feedback for LLM iterative optimization. (Source: WeChat)

CoAct-1: Coding as Action for Computer Usage Agents : Researchers proposed CoAct-1, a multi-agent system that enhances computer usage through coding as action, aiming to solve the efficiency and reliability issues of GUI operation agents in complex tasks. CoAct-1’s Orchestrator can dynamically delegate subtasks to either a GUI Operator or a Programmer Agent (which can write and execute Python/Bash scripts), thereby bypassing inefficient GUI operations. This method achieved SOTA success rates on the OSWorld benchmark and significantly improved efficiency, offering a more powerful path towards general computer automation. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
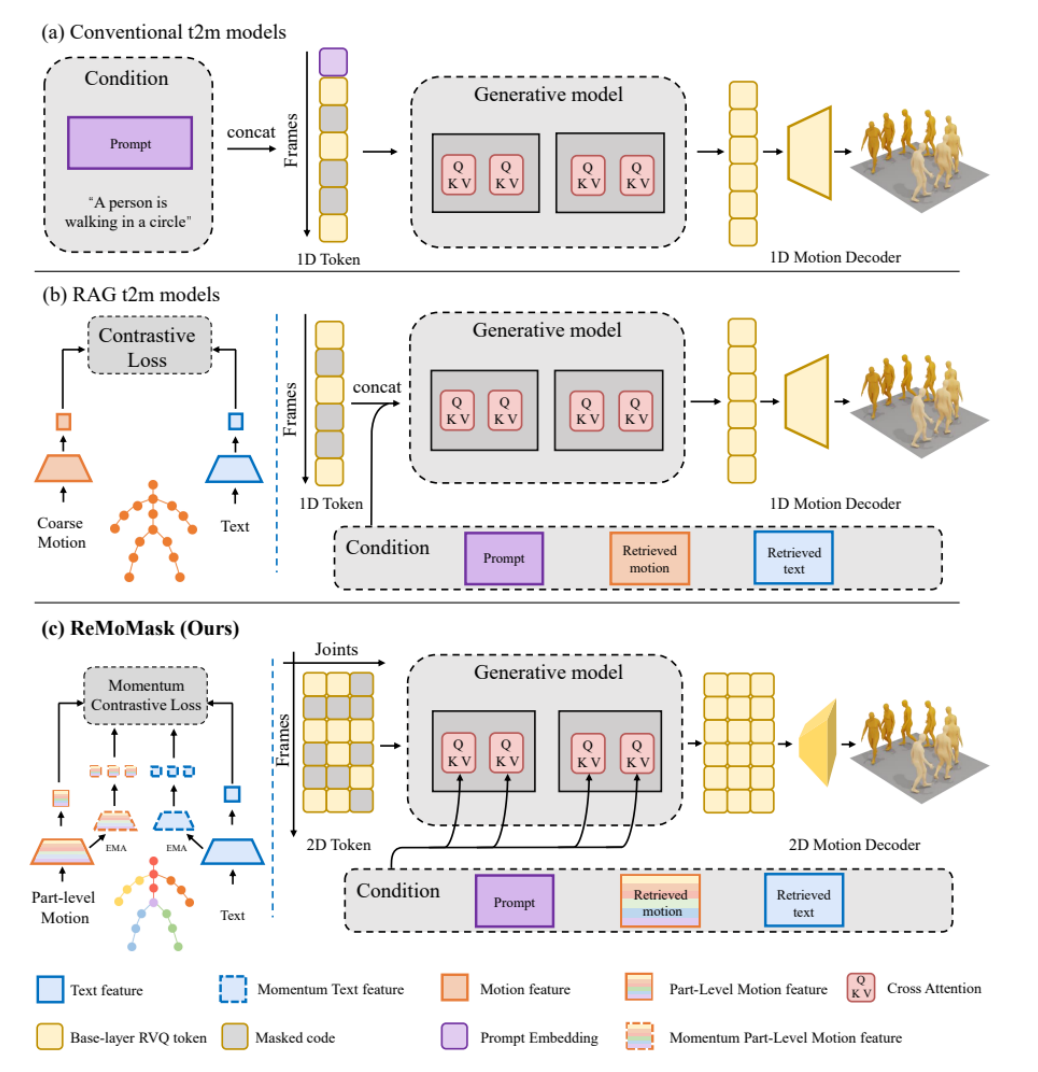
ReMoMask: A New Method for High-Quality Game 3D Motion Generation : Peking University proposed ReMoMask, a retrieval-augmented generation-based Text-to-Motion framework designed to generate smooth and realistic 3D motions from a single instruction with high quality. ReMoMask integrates a momentum bidirectional text-to-motion model, semantic spatio-temporal attention mechanism, and RAG-classifier-free guidance to efficiently generate temporally coherent motions. This method has set new SOTA performance records on standard benchmarks like HumanML3D and KIT-ML, promising to revolutionize game and animation production workflows. (Source: WeChat)
WebAgents Survey: Large Models Empowering Web Automation : Researchers from Hong Kong Polytechnic University published the first comprehensive survey on WebAgents, thoroughly reviewing the research progress of large models empowering AI agents to achieve next-generation web automation. The survey summarizes representative WebAgents methods from perspectives such as architecture (perception, planning and reasoning, execution), training (data, policy), and trustworthiness (security, privacy, generalization), and discusses future research directions, including fairness, interpretability, datasets, and personalized WebAgents, providing guidance for building more intelligent and secure web automation systems. (Source: WeChat)

InfiAlign: An Alignment Framework for LLM Reasoning Capabilities : InfiAlign is a scalable and sample-efficient post-training framework that aligns LLMs to enhance reasoning capabilities by combining SFT and DPO. The core of this framework is a powerful data selection pipeline that automatically filters high-quality alignment data from open-source reasoning datasets. InfiAlign achieved performance comparable to DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B on the Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Base model, but used only about 12% of the training data, and significantly improved mathematical reasoning tasks, providing a practical solution for aligning large reasoning models. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
💼 Business
OpenAI Employee Stock Option Liquidation Program to Retain Talent : To counter talent outflow, OpenAI has launched a new employee stock option liquidation program, valuing the company at $500 billion, aiming to retain talent with substantial financial incentives. This move is expected to push OpenAI’s valuation to new heights. Meanwhile, ChatGPT’s weekly active users have reached 700 million, paid enterprise users have grown to 5 million, and annual recurring revenue is projected to exceed $20 billion, indicating strong product and commercial development for OpenAI. (Source: 量子位)

AWS Builds Largest AI Model Aggregation Platform : Amazon Web Services (AWS) announced that OpenAI’s gpt-oss model is now accessible via Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker for the first time, further enriching its “Choice Matters” strategy for the model ecosystem. AWS now offers over 400 mainstream commercial and open-source large models, aiming to enable enterprises to choose the most suitable model based on performance, cost, and task requirements, rather than pursuing a single “strongest” model, thereby promoting multi-model synergy. (Source: 量子位)

Ant Group Invests in Embodied AI Dexterous Hand Company : Ant Group led a multi-hundred-million yuan angel round investment in Lingxin Qiaoshou, an embodied AI company. Lingxin Qiaoshou is the only company globally to achieve mass production of thousands of high-DOF dexterous hands, holding an 80% market share. Its Linker Hand series of dexterous hands boasts high degrees of freedom, multi-sensor systems, and cost advantages, already deployed in industrial, medical, and other scenarios. This funding will be used for technology reserves and data collection facility construction, accelerating the deployment of dexterous hands in practical applications. (Source: 量子位)

🌟 Community
GPT-5 User Experience Polarized : After the release of GPT-5, user feedback has been mixed. Some users praised its significant improvements in programming and complex reasoning tasks, finding code generation cleaner and more accurate, and its long-context handling capabilities extremely powerful. However, other users expressed disappointment with the decline in model personalization, creative writing, and emotional support capabilities, finding it “boring” and “soulless.” The model routing mechanism also led to unstable experiences, with some users even canceling their subscriptions as a result. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT & Reddit r/LocalLLaMA & Reddit r/ChatGPT & Reddit r/ChatGPT)

AI in Parenting: Applications and Controversies : Working parents are increasingly using AI tools like ChatGPT as “co-parents,” leveraging them to plan meals, optimize bedtime routines, and even provide emotional support. AI’s non-judgmental space for venting alleviates parents’ psychological burden. However, this emerging technology also sparks controversy, including the potential for inaccurate advice, privacy leakage risks (such as ChatGPT data breaches), and excessive reliance on AI possibly leading to interpersonal isolation and potential environmental impacts. (Source: 36氪)
Airbnb User Compensation Incident Due to AI-Generated Images : An incident occurred at Airbnb where a host used AI-generated images to defraud a user for compensation, highlighting the risks of AI in customer service. AI customer service failed to identify the AI-generated images, leading to the user being wrongly ordered to pay compensation. Although OpenAI had previously launched an image detector, AI’s ability to identify AI remains limited, especially against “localized forgery” techniques. This incident raises concerns about the reliability of AI content detection tools and C2C platforms’ ability to cope with the impact of deepfake content. (Source: 36氪)

Silicon Valley AI Leaders Building Doomsday Bunkers Sparks Debate : Silicon Valley AI leaders like Mark Zuckerberg and Sam Altman are reportedly building or owning doomsday bunkers, sparking public concern about the future development and potential risks of AI. Although they deny any AI connection, these actions are interpreted as precautions against emergencies such as pandemics, cyber warfare, and climate disasters. Community discussions speculate whether those most knowledgeable about AI technology see signs unknown to the general public, and whether AI development has brought unpredictable risks. (Source: 量子位)

Kaggle AI Chess Championship: o3 Crowned Champion : In the final of the inaugural Google Kaggle AI Chess Championship, OpenAI’s o3 swept Elon Musk’s Grok 4 with a 4-0 victory, claiming the championship. This match was seen as a “proxy war” between OpenAI and xAI, aiming to test large models’ critical thinking, strategic planning, and on-the-fly adaptability. Although Grok 4 had strong momentum previously, it made frequent errors in the final, while o3 demonstrated systematically stable strategies, remaining undefeated throughout the tournament. (Source: WeChat)

Discussion: AI Enters the “Trough of Disillusionment” : Extensive discussions on social media suggest that AI has entered the “Trough of Disillusionment,” especially after the GPT-5 release. Users point out that AI’s limitations have not been effectively overcome, and the benefits from increased model scale and computing power are diminishing. This view suggests that AI’s progress has become “less obvious,” primarily manifesting in expert domains rather than at a level perceptible to average users, indicating that AI development might be entering a plateau phase requiring entirely new architectural breakthroughs. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

💡 Other
Docker Warns of Security Risks in MCP Toolchains : Docker issued a warning about severe security vulnerabilities in AI-driven development toolchains built on the Model Context Protocol (MCP), including credential leakage, unauthorized file access, and remote code execution, with real-world cases already observed. These tools embed LLMs into development environments, granting them autonomous operational permissions but lacking isolation and supervision. Docker advises against installing MCP servers from npm, recommending signed containers instead, and emphasizes the importance of container isolation and zero-trust networks. (Source: WeChat)

Huawei HarmonyOS Application Developer Incentive Program 2025 : Huawei announced that the number of HarmonyOS 5 devices has exceeded 10 million and launched the “HarmonyOS Application Developer Incentive Program 2025,” investing over 100 million yuan in subsidies, with individual developers eligible for up to 6 million yuan in awards. This program aims to accelerate the development of the HarmonyOS ecosystem and attract developers to create applications for AI and multi-device deployment, achieving “develop once, deploy everywhere.” Huawei provides full-stack development support, including technical empowerment, rapid testing, efficient listing, and operations, aiming to build a robust developer ecosystem. (Source: WeChat)

Domestic AI Supernode Server Yuanbrain SD200 Released : Inspur Information released the supernode AI server “Yuanbrain SD200,” designed to address the computing power challenges of running trillion-parameter large models. This server adopts an innovatively developed multi-host low-latency memory semantic communication architecture, capable of aggregating 64 local GPU chips, providing a maximum of 4TB unified VRAM and 64GB unified memory, supporting trillion-scale ultra-long sequence models. Tests show that SD200 achieves excellent computing power scaling efficiency on models like DeepSeek R1, providing strong support for AI4 Science and industrial applications. (Source: WeChat)

