Keywords:AI research, computer science, reinforcement learning, drug discovery, autonomous driving, language models, multimodal processing, virtual cells, Laude Institute, Reinforcement Learning Teachers (RLTs), BioNeMo platform, Tesla Robotaxi, Kimi VL A3B Thinking model
🔥 Focus
Laude Institute Launched with $100 Million Initial Funding to Advance Public Interest Computer Science Research: Andy Konwinski announced the launch of the Laude Institute, a non-profit organization aimed at funding non-commercial computer science research that has a significant impact on the world. Prominent figures such as Jeff Dean, Joyia Pineau, and Dave Patterson have joined the board. The institute has secured an initial commitment of $100 million in funding and will support researchers in translating ideas into real-world impact through funding, resource sharing, and community building, with a special focus on open and impact-oriented research. (Source: JeffDean, matei_zaharia, lschmidt3, Tim_Dettmers, andrew_n_carr, gneubig, lateinteraction, sarahookr, jefrankle)

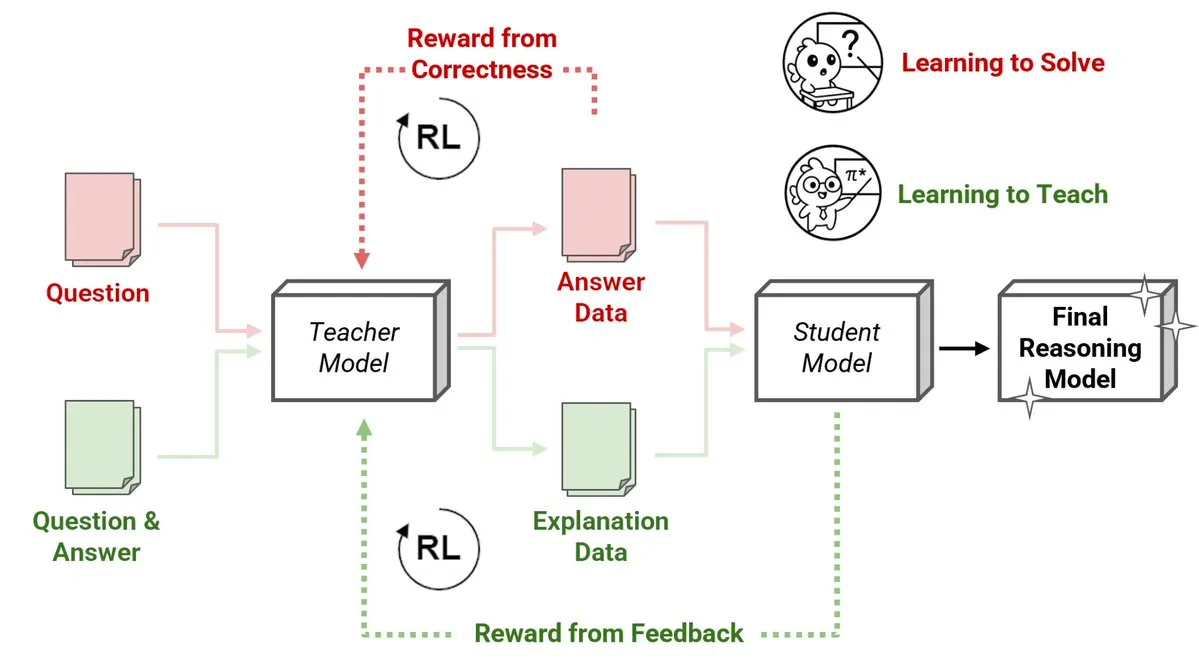
Sakana AI Releases New Reinforcement Learning Teachers (RLTs) Method, Small Models Teach Large Models Reasoning: Sakana AI has introduced a new method for Reinforcement Learning Teachers (RLTs), transforming how Large Language Models (LLMs) are taught reasoning through Reinforcement Learning (RL). While traditional RL focuses on “learning to solve” problems, RLTs are trained to generate clear, step-by-step “explanations” to teach student models. An RLT with only 7B parameters, when teaching a 32B parameter student model, outperformed LLMs many times its size on competitive and graduate-level reasoning tasks. This approach sets a new efficiency standard for developing reasoning language models with RL. (Source: cognitivecompai, AndrewLampinen)
NVIDIA Collaborates with Novo Nordisk, Leveraging AI Supercomputer to Accelerate Drug Discovery: NVIDIA announced a collaboration with Danish pharmaceutical giant Novo Nordisk and the Danish National AI Innovation Centre to jointly utilize AI technology and Denmark’s latest Gefion supercomputer to accelerate new drug discovery. This partnership will employ NVIDIA’s BioNeMo platform and advanced AI workflows, aiming to revolutionize drug research and development models. The Gefion supercomputer, built with technology from Eviden and NVIDIA, will provide powerful computing support for research in fields like life sciences, driving personalized medicine and the discovery of new therapies. (Source: nvidia)

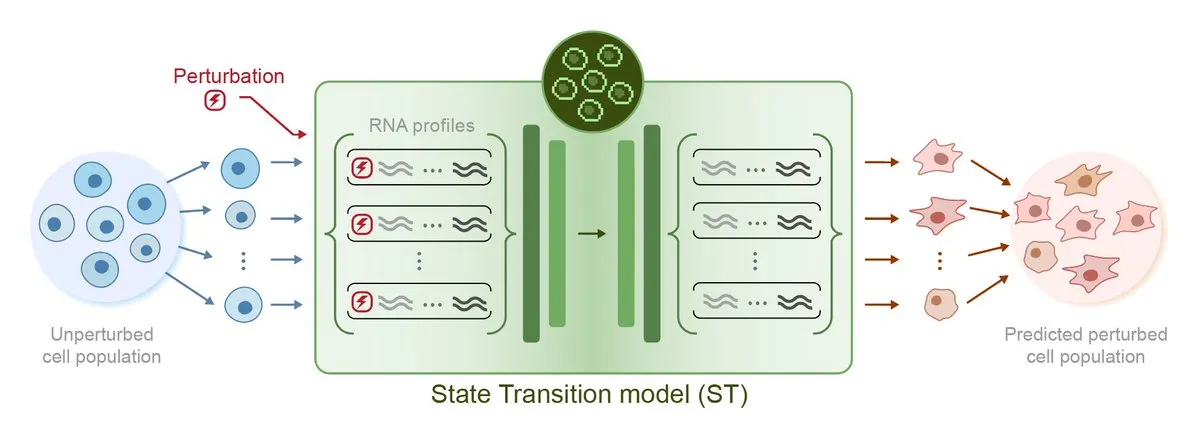
Arc Institute Releases First Perturbation Prediction AI Model STATE, Moving Towards Virtual Cell Goal: Arc Institute has released its first perturbation prediction AI model, STATE, a significant step towards its goal of creating virtual cells. The STATE model is designed to learn how to use drugs, cytokines, or genetic perturbations to alter cell states (e.g., from “diseased” to “healthy”). The release of this model marks new progress in AI’s ability to understand and predict cellular behavior, opening new avenues for disease treatment and drug development. The related model has been made available on HuggingFace. (Source: riemannzeta, ClementDelangue)
Tesla Robotaxi Launches Pilot in Austin, Vision-Based Solution Gains Attention, Karpathy’s Legacy Code Significantly Streamlined: Tesla has officially launched its Robotaxi pilot service in Austin, Texas, USA. The first batch of vehicles, based on modified Model Ys, uses a pure vision perception solution and FSD software. Ashok Elluswamy, head of Tesla AI and Autopilot software, led the team in making significant technical changes to the system, streamlining approximately 330,000-340,000 lines of C++ heuristic code left by Andrej Karpathy’s team by nearly 90%, replacing it with a “giant neural network.” This move aims to shift from “human experience coding” to “parameterized training,” autonomously optimizing the model through massive data and simulated driving. The service is currently in an early experience phase, sparking widespread industry discussion about Tesla’s technological path and scaling capabilities. (Source: 36Kr, Ronald_vanLoon, kylebrussell)

🎯 Trends
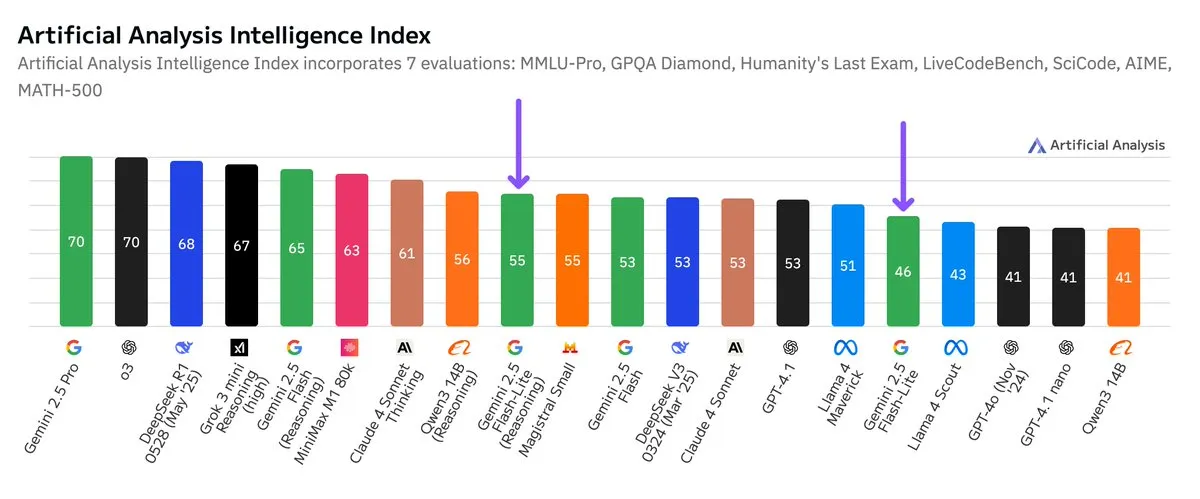
Google Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite Independent Benchmark Released, Price-Performance Improved: According to independent benchmark results released by Artificial Analysis, the Google Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite Preview (06-17) version offers an approximately 5x cost reduction and a 1.7x speed increase compared to the regular Flash version, albeit with a decrease in intelligence. This model is an upgrade to Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite released in February 2025 and is a hybrid model. This update demonstrates Google’s continued efforts in pursuing model efficiency and cost-effectiveness, potentially targeting application scenarios with high demands for cost and speed. (Source: zacharynado)
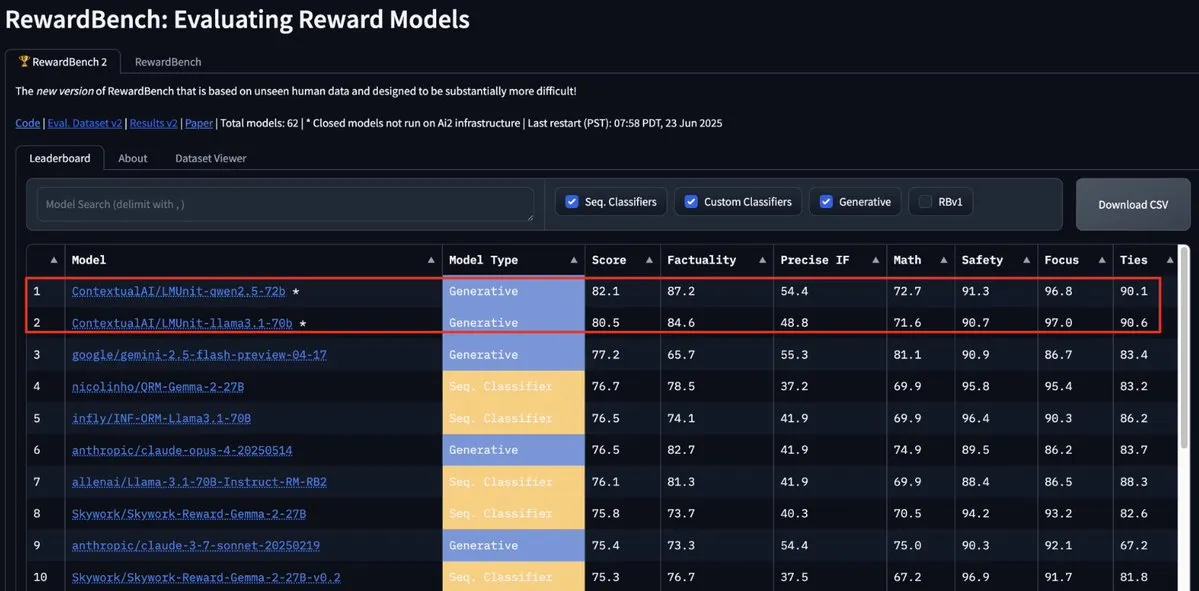
ContextualAI’s LMUnit Model Tops RewardBench2, Surpassing Gemini, Claude 4, and GPT-4.1: ContextualAI’s LMUnit model ranked first on the RewardBench2 benchmark, scoring over 5% higher than well-known models like Gemini, Claude 4, and GPT-4.1. This achievement may be attributed to its unique training method, reportedly similar to the “rubrics” method that OpenAI invested heavily in for o4 and subsequent models. This method helps achieve effective scaling for LLM-as-a-judge during reasoning. (Source: natolambert, menhguin, apsdehal)
Arcee.ai Successfully Extends AFM-4.5B Model Context Length from 4k to 64k: Arcee.ai announced that the context length of its first foundational model, AFM-4.5B, has been successfully extended from 4k to 64k. The team achieved this breakthrough through active experimentation, model merging, distillation, and what they jokingly referred to as “a lot of soup” (referring to model merging techniques). This advancement is crucial for handling long-text tasks. Arcee’s improvements on the GLM-32B-Base model also demonstrate its effectiveness, not only increasing long-context support from 8k to 32k but also improving all base model evaluations (including short context). (Source: eliebakouch, teortaxesTex, nrehiew_, shxf0072, code_star)

Google Gemini API Updated, Enhancing Video and PDF Processing Speed and Capabilities: The Google Gemini API has received significant updates for video and PDF processing. The Time to First Token (TTFT) for cached videos has improved by 3x, and the processing speed for cached PDFs has increased by up to 4x. Additionally, the new version supports batch processing of multiple videos, and the performance of implicit caching is now close to that of explicit caching. These improvements aim to enhance the efficiency and experience for developers using the Gemini API to process multimedia content. (Source: _philschmid)
Moonshot (Kimi) Updates Kimi VL A3B Thinking Model, Enhancing Multimodal Processing Capabilities: Moonshot AI (Kimi) has released an updated version of its small Visual Language Model (VLM), Kimi VL A3B Thinking, which is based on the MIT license. The new version consumes fewer tokens, shortens the thinking trajectory, supports video processing, and can handle higher-resolution images (1792×1792). It achieved a score of 65.2 on VideoMMMU, improved MathVision by 20.1 points to 56.9, MathVista by 8.4 points to 80.1, and MMMU-Pro by 3.2 points to 46.3. It also demonstrates strong performance in visual reasoning, UI Agent localization, video, and PDF processing, and has been open-sourced on Hugging Face. (Source: mervenoyann)

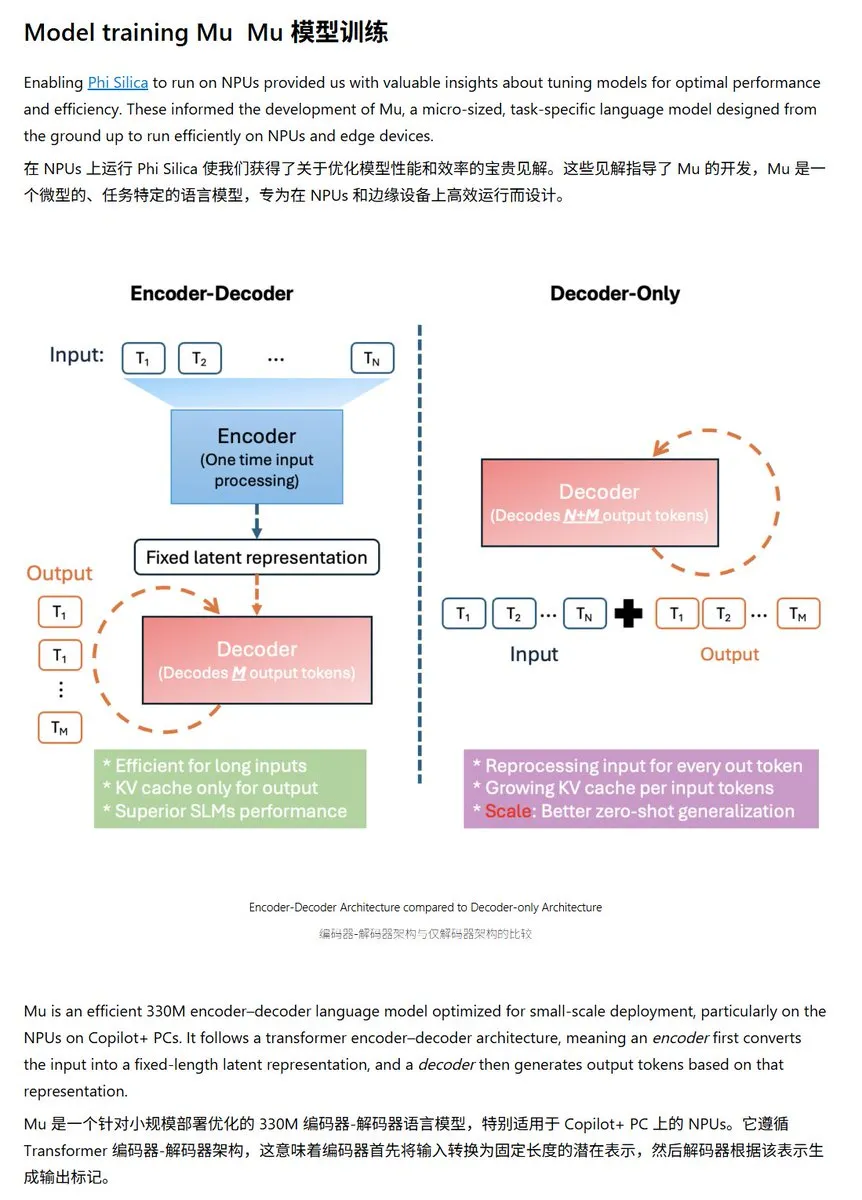
Microsoft Releases Mu-330M Small Language Model, Optimized for Windows NPU: Microsoft has launched a new small language model, Mu-330M, designed to run on the NPU (Neural Processing Unit) of Windows Copilot+ PCs, aiming to support Agent functionalities within the Windows system. The model is optimized for NPUs, employing techniques such as rotary position embeddings, grouped-query attention, and dual-layer LayerNorm to operate efficiently with low performance consumption, marking Microsoft’s further layout in on-device AI capabilities. (Source: karminski3)
DeepMind Releases Mercury Technical Report, Focusing on Diffusion Language Models: Inception Labs (a DeepMind-affiliated team) has released the technical report for its diffusion language model, Mercury. The report details the Mercury model’s architecture, training methods, and experimental results, providing researchers with in-depth insights into this emerging model type. Diffusion models have achieved significant success in image generation, and applying them to language models is a current frontier in AI research. (Source: andriy_mulyar)
Meta Collaborates with Oakley to Expand AI Smart Glasses Series: Meta is collaborating with eyewear brand Oakley to further expand its line of AI smart glasses. The new smart glasses are expected to integrate Meta’s AI technology, offering richer interactive features and user experiences. This collaboration signifies Meta’s continued investment in wearable AI devices, aiming to integrate AI more seamlessly into daily life. (Source: rowancheung, Ronald_vanLoon)
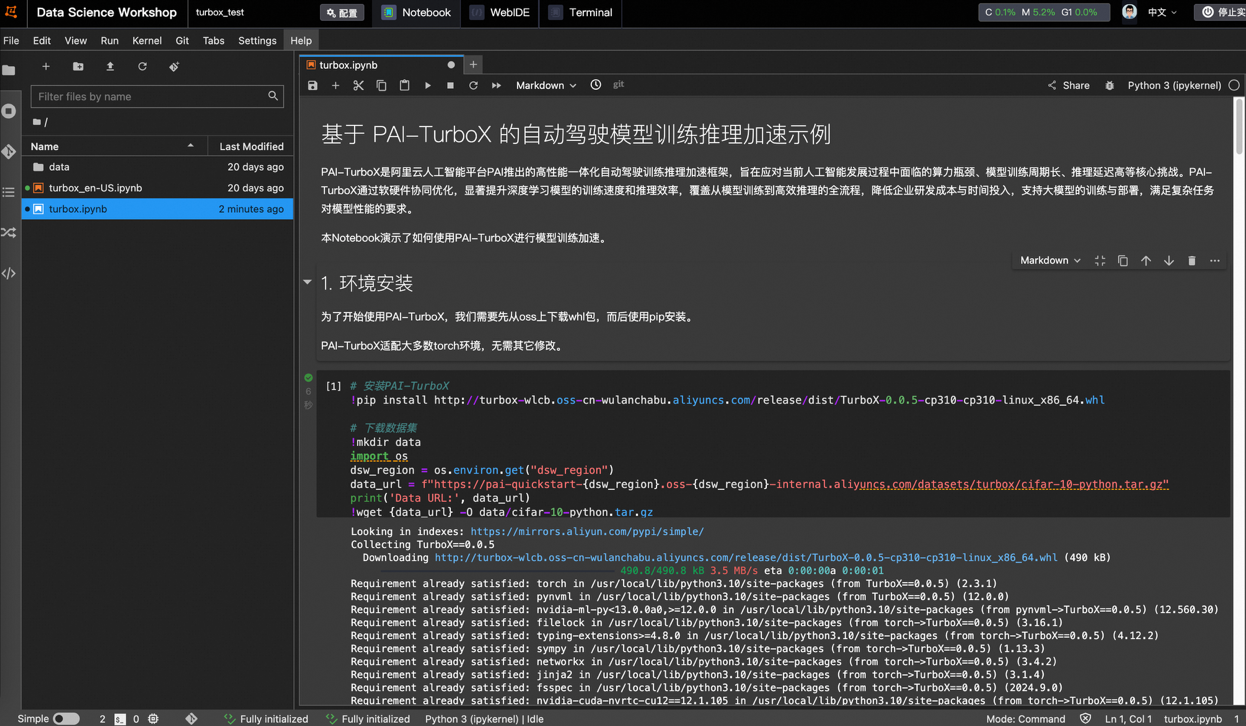
Alibaba Cloud Launches PAI-TurboX, an Autonomous Driving Model Training and Inference Acceleration Framework, Potentially Reducing Training Time by 50%: Alibaba Cloud has released PAI-TurboX, a model training and inference acceleration framework for the autonomous driving sector. The framework aims to enhance the training and inference efficiency of perception, planning control, and even world models. It achieves this by optimizing multimodal data preprocessing, CPU affinity, dynamic compilation, pipeline parallelism, and providing operator optimization and quantization capabilities. Tests show that PAI-TurboX can reduce training time by approximately 50% for several industry models like BEVFusion, MapTR, and SparseDrive. (Source: QbitAI)
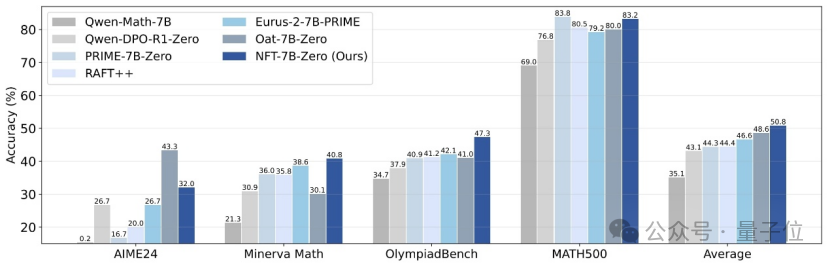
Tsinghua, NVIDIA, and Others Propose NFT Method, Enabling Supervised Learning to “Reflect” on Errors: Researchers from Tsinghua University, NVIDIA, and Stanford University have jointly proposed a new supervised learning scheme called NFT (Negative-aware FineTuning). Building on the RFT (Rejection FineTuning) algorithm, this method utilizes negative data for training by constructing an “implicit negative model,” i.e., an “implicit negative policy.” This policy allows supervised learning to “self-reflect” much like reinforcement learning, bridging some capability gaps between supervised and reinforcement learning. It has demonstrated significant performance improvements in tasks like mathematical reasoning and, under On-Policy conditions, its loss function gradient is equivalent to GRPO. (Source: QbitAI)
OmniGen2 Released: 8B Multipurpose Image Editing Model, Fusing Visual Understanding and Image Generation: A new multipurpose image editing model called OmniGen2 has been released. The model combines visual understanding (based on Qwen-VL-2.5) with image generation (a 4B parameter diffusion model), totaling approximately 8B parameters. OmniGen2 can support various tasks including text-to-image generation, image editing, image understanding, and in-context generation, aiming to provide a unified model capable of solving multiple vision-related problems and suitable for on-device integration. (Source: karminski3)

Chroma-8.9B-v39 Text-to-Image Model Updated, Based on FLUX.1-schnell, Commercially Usable: The text-to-image model Chroma-8.9B-v39 has been updated, improving lighting and task naturalness. The model is based on FLUX.1-schnell, with parameters compressed from 12B to 8.9B, and uses an Apache 2.0 license, allowing commercial use. The model reportedly “reintroduces missing anatomical concepts, completely without content restrictions,” and was post-trained using a dataset containing 5 million anime, furry, art, and photographic works. (Source: karminski3)

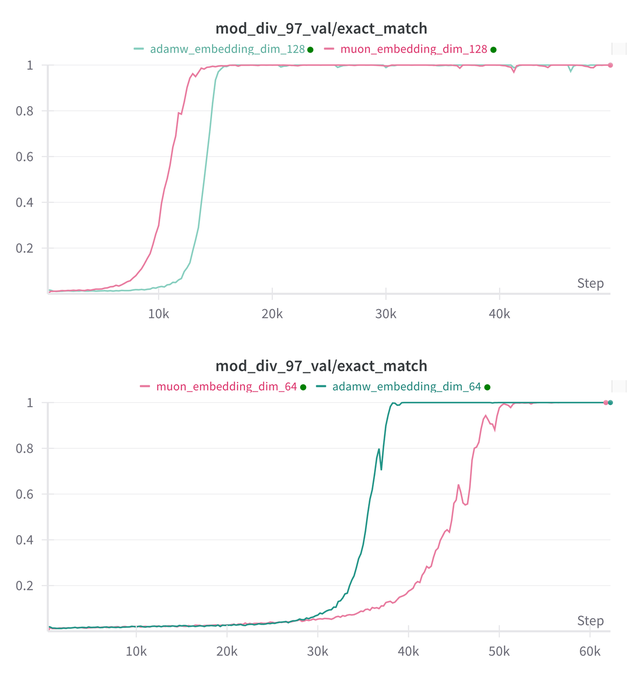
Essential AI Updates Research Findings on Muon and Adam Models’ Grokking Capabilities: Essential AI shared the latest research progress on the Grokking capabilities of its Muon and Adam models (Grokking is a phenomenon where a model performs poorly initially during training, then suddenly understands and generalizes). Initial hypotheses may contradict actual observations. The team disclosed results from internal small-scale research experiments, showing that after expanding the hyperparameter search space, Muon showed no clear universal advantage over AdamW; they performed comparably in different scenarios. This suggests AdamW remains a strong, even SOTA, optimizer in many cases. (Source: eliebakouch, teortaxesTex, nrehiew_)
Ostris AI Image Generation Model Updated, Focusing on No-CFG Version and Optimizing High-Frequency Details: Ostris AI continues to update its image generation model, currently focusing on the development of a no-CFG (Classifier-Free Guidance) version due to its faster convergence. In the latest Day 7 update, the team incorporated new training techniques to better handle high-frequency details and is working to remove high-detail artifacts. The previous Day 4 update had already shown significant improvement in image quality generated by new methods without using CFG. (Source: ostrisai)

Ant Group, CAS, and CUHK Open-Source ViLaSR-7B Model, Achieving “Drawing to Reason in Space” Spatial Reasoning: Ant Technology Research Institute, the Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASIA), and The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) have jointly open-sourced the ViLaSR-7B model. Through a “Drawing to Reason in Space” paradigm, this model enables Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) to draw auxiliary markers (such as reference lines, bounding boxes) in visual space to aid thinking, thereby enhancing spatial perception and reasoning capabilities. ViLaSR employs a three-stage training framework: cold start, reflective rejection sampling, and reinforcement learning. Experiments show that the model achieves an average improvement of 18.4% on 5 benchmarks including maze navigation, image understanding, and video spatial reasoning, and its performance on VSI-Bench is close to Gemini-1.5-Pro. (Source: QbitAI)

🧰 Tools
SGLang Now Supports Hugging Face Transformers as Backend, Enhancing Inference Efficiency: SGLang announced that it now supports Hugging Face Transformers as a backend. This means users can provide fast, production-grade inference services for any Transformers-compatible model without native support, plug-and-play. This integration aims to simplify the deployment process for high-performance language model inference, expanding SGLang’s applicability and ease of use. (Source: TheZachMueller, ClementDelangue)

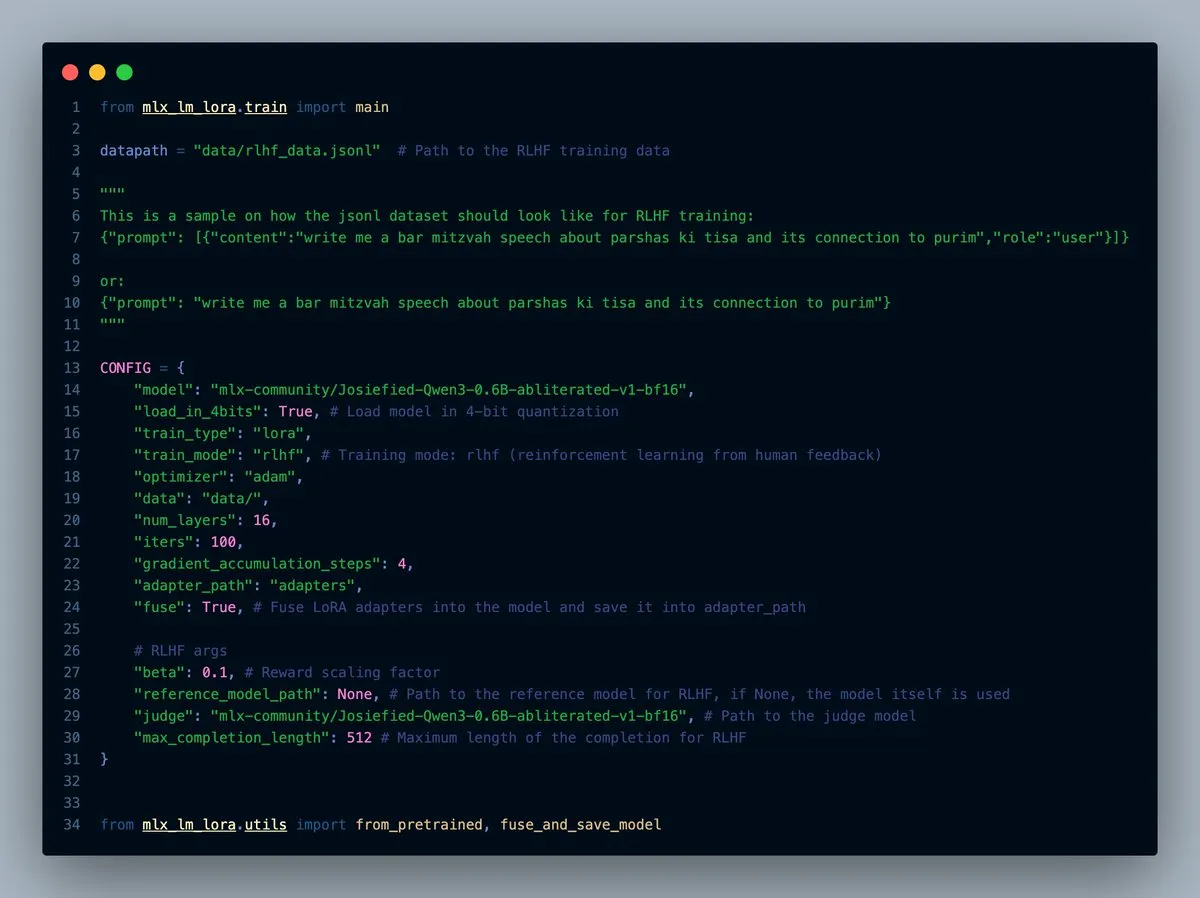
MLX-LM-LORA v0.7.0 Released with Built-in RLHF Functionality: MLX-LM-LORA has released v0.7.0, which includes built-in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) functionality. The tool now supports 4-bit, 6-bit, and 8-bit loading, RLHF training mode, and can directly fuse adapters into base weights. This makes LoRA fine-tuning within the MLX framework smarter and more efficient, especially on Apple Silicon devices. (Source: awnihannun)
LlamaCloud Launched, Providing MCP-Compatible Toolbox for Document Workflows: LlamaCloud is now available, serving as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) compatible toolbox for any document workflow. Users can connect it to models like Claude to perform complex operations such as document extraction and comparison. For example, it can analyze Tesla’s financial performance over the past five quarters and generate a comprehensive report by dynamically creating standardized schemas, running them across all files, and then utilizing code generation for the final result. LlamaCloud can dynamically correct incorrect schemas and supports direct file linking. (Source: jerryjliu0)
Georgi Gerganov Teases LlamaBarn Project: Georgi Gerganov (creator of llama.cpp) posted an image on social media, teasing a new project called “LlamaBarn.” The image shows a dashboard-like interface with elements for model selection, parameter adjustment, etc., suggesting it might be a tool for managing, running, or testing local LLMs. The community has expressed anticipation, believing it could be a strong competitor to existing tools like Ollama. (Source: ClementDelangue, teortaxesTex, jeremyphoward)
Void Editor: A New Open-Source AI Programming Assistant, Supporting MCP and Local Models: Void Editor has emerged as a new open-source AI programming assistant, aiming to be an alternative to tools like Cursor. It supports tab autocompletion, chat mode, Model Context Protocol (MCP), and Agent mode. Users can connect any large language model API or run models locally, providing developers with a flexible AI-assisted programming experience. (Source: karminski3)
Together AI Launches Which LLM Tool to Help Select Suitable Open-Source LLMs: Together AI has released a free tool called “Which LLM,” designed to help users select the most appropriate open-source large language model based on specific use cases, performance requirements, and economic considerations. With the proliferation of open-source LLMs, such tools can provide valuable references for developers and researchers in model selection. (Source: vipulved)
Perplexity Finance Adds Stock Price Timeline Tracking Feature: Perplexity Finance announced that users can now track the price movement timeline for any stock ticker on its platform. This new feature aims to provide users with a more intuitive and convenient tool for analyzing financial market information, potentially bringing a new experience to financial information query and analysis when combined with Perplexity’s AI capabilities. (Source: AravSrinivas)

IdeaWeaver Launches First AI Agent for System Performance Debugging: IdeaWeaver has released what it claims to be the first AI agent specifically designed for debugging system performance issues. The tool utilizes the CrewAI framework and can actually execute system commands to diagnose problems related to CPU, memory, I/O, and networking. It prioritizes using local LLMs (via OLLAMA) to protect privacy, only requesting an OpenAI API key if a local model is unavailable, aiming to apply AI capabilities to the DevOps and system administration fields. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Kling AI Adds Live Photo Support, Allowing Generated Videos to be Saved as Dynamic Wallpapers: Kling AI announced that its video generation feature now supports saving creations as Live Photos. Users can set their favorite Kling-created dynamic content as phone wallpapers, adding to the fun and practicality of AI-generated videos. (Source: Kling_ai)
Cognition AI Open-Sources Blockdiff, Achieving 200x Speedup in VM Snapshotting: Cognition AI announced the open-sourcing of Blockdiff, the VM snapshot file format developed for Devin. Due to the excessive time (30+ minutes) EC2 took to create VM snapshots, the team built their own otterlink hypervisor and Blockdiff file format, increasing snapshot creation speed by 200x. This open-source contribution aims to help developers manage virtual machine environments more efficiently. (Source: karinanguyen_)

📚 Learning
LangChain Blog Post Discusses the Rise of “Context Engineering”: LangChain published a blog post discussing the increasingly popular term “Context Engineering.” The article defines it as “building dynamic systems that provide the right information and tools, in the right format, for an LLM to reasonably accomplish a task.” This is not an entirely new concept, as Agent builders have been practicing it for some time, and tools like LangGraph and LangSmith were created for this purpose. The coining of the term helps draw more attention to the related skills and tools. (Source: hwchase17, Hacubu, yoheinakajima)
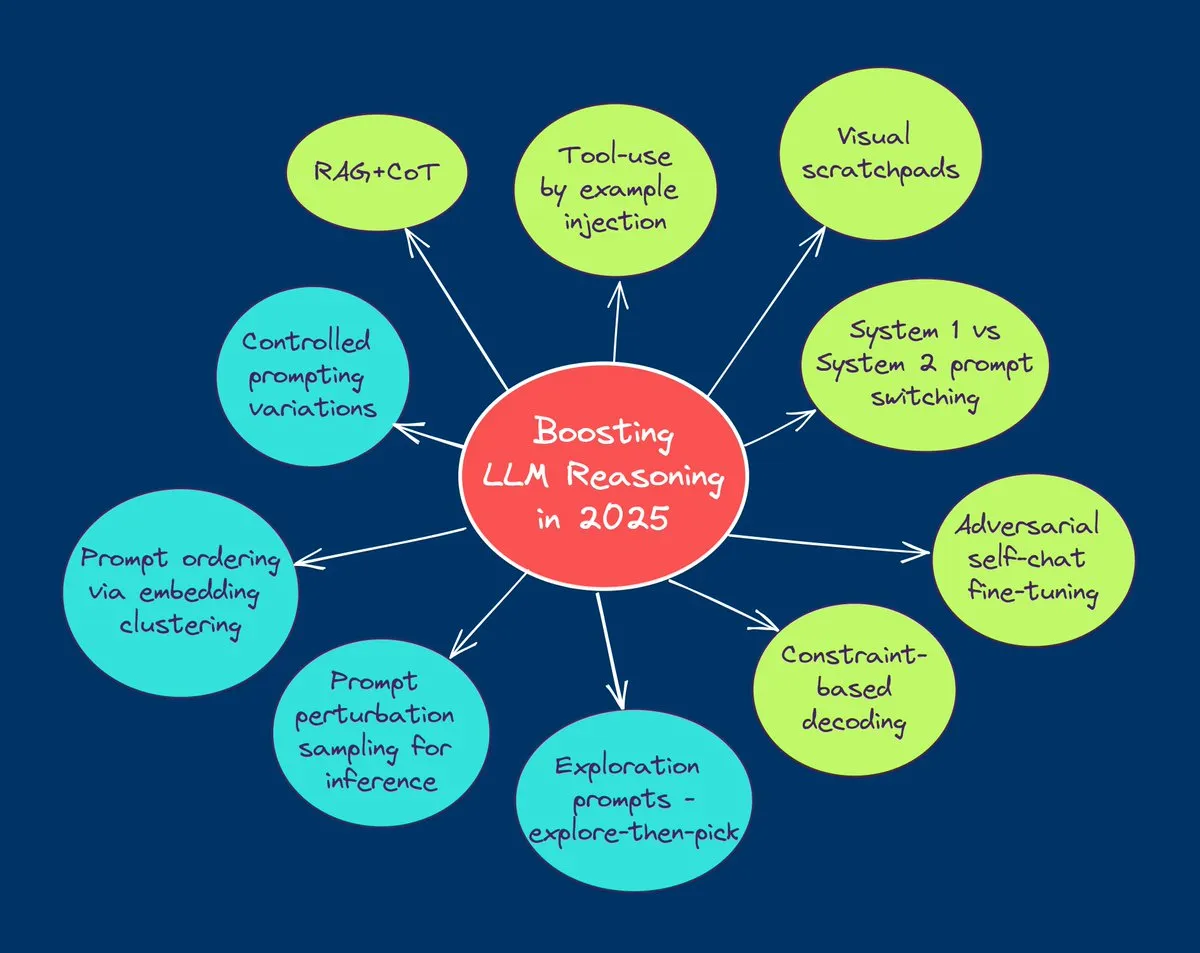
TuringPost Summarizes 10 Key Technologies for Enhancing LLM Reasoning Capabilities in 2025: TuringPost shared 10 key technologies for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in 2025. These include: Retrieval Augmented Generation + Chain of Thought (RAG+CoT), tool use via example injection, visual scratchpad (multimodal reasoning support), System 1 vs. System 2 prompting switch, adversarial self-dialogue finetuning, constraint-based decoding, exploratory prompting (explore then select), prompt perturbation sampling for reasoning, prompt ordering via embedding clustering, and controlled prompt variations. These techniques offer diverse pathways for optimizing LLM performance in complex tasks. (Source: TheTuringPost, TheTuringPost)
Cohere Labs Hosts ML Summer School to Explore the Future of Machine Learning: Cohere Labs’ open science community will host an ML Summer School in July. The event will bring together global community members to discuss the future of machine learning and will feature speakers from the industry. Katrina Lawrence will lead a machine learning math review session on July 2nd, covering core concepts such as calculus, vector calculus, and linear algebra. (Source: sarahookr)

DeepLearning.AI and Meta Collaborate to Launch Free Course “Building with Llama 4”: DeepLearning.AI and Meta have collaborated to launch a free course titled “Building with Llama 4.” The course content includes: hands-on practice with the Llama 4 model series, understanding its Mixture of Experts (MOE) architecture, and how to build applications using the official API; applying Llama 4 for multi-image reasoning, image localization (identifying objects and their bounding boxes), and processing long-context text queries up to 1 million tokens; using Llama 4’s prompt optimization tools to automatically improve system prompts, and utilizing its synthetic data toolkit to create high-quality datasets for fine-tuning. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
EleutherAI YouTube Channel Offers Extensive AI Research Content: EleutherAI’s YouTube channel hosts over 100 hours of recorded videos from its reading groups and lecture series. Topics cover the scalability and performance of machine learning, functional analysis, as well as podcasts and interviews with team members. The channel provides a wealth of learning resources for AI researchers and enthusiasts. EleutherAI has also launched a new lecture series, with the first installment by @linguist_cat discussing tokenizers and their limitations. (Source: BlancheMinerva, BlancheMinerva)
Paper Explores Enhancing Multimodal Reasoning with Latent Visual Tokens (Machine Mental Imagery): A new paper, “Machine Mental Imagery: Empower Multimodal Reasoning with Latent Visual Tokens,” proposes the Mirage framework to enhance multimodal reasoning by incorporating latent visual tokens (rather than generating full images) during VLM decoding, simulating human mental imagery. The method first supervises latent tokens by distilling real image embeddings, then switches to pure text supervision to align latent trajectories with task objectives, and further enhances capabilities through reinforcement learning. Experiments demonstrate that Mirage can achieve stronger multimodal reasoning without generating explicit images. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Proposes Vision as a Dialect Framework, Unifying Visual Understanding and Generation via Text-Aligned Representations: A paper titled “Vision as a Dialect: Unifying Visual Understanding and Generation via Text-Aligned Representations” introduces a multimodal LLM framework called Tar. This framework uses a Text-Aligned Tokenizer (TA-Tok) to convert images into discrete tokens and utilizes a text-aligned codebook projected from the LLM vocabulary, thereby unifying vision and text into a shared discrete semantic representation. Tar enables cross-modal input and output through a shared interface, eliminating the need for modality-specific designs, and employs scale-adaptive encoding/decoding and generative de-tokenization to balance efficiency and visual detail. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Proposes ReasonFlux-PRM: Trajectory-Aware PRMs for Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs: The paper “ReasonFlux-PRM: Trajectory-Aware PRMs for Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs” introduces a novel trajectory-aware Process Reward Model (PRM) specifically designed to evaluate trajectory-response type reasoning traces generated by cutting-edge reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1. ReasonFlux-PRM combines step-level and trajectory-level supervision, achieving fine-grained reward allocation aligned with structured chain-of-thought data, and demonstrates performance improvements in scenarios such as SFT, RL, and Best-of-N test-time scaling. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Studies Evaluation Methods for Large Language Model Jailbreak Guardrails: A paper titled “SoK: Evaluating Jailbreak Guardrails for Large Language Models” provides a systematic knowledge organization of jailbreak attacks on Large Language Models (LLMs) and their guardrails. The paper proposes a new multi-dimensional taxonomy to classify guardrails across six key dimensions and introduces a security-efficiency-utility evaluation framework to assess their practical effectiveness. Through extensive analysis and experiments, the paper identifies the strengths and weaknesses of existing guardrail methods, discusses their universality against different attack types, and offers insights for optimizing defense combinations. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
AAAI 2025 Outstanding Paper Explores Decidable Class of Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs): A paper titled “Revelations: A Decidable Class of POMDP with Omega-Regular Objectives” has received an AAAI 2025 Outstanding Paper Award. The research identifies a decidable class of MDPs (Markov Decision Processes): decision problems with “strong revelations,” where there is a non-zero probability of revealing the exact state of the world at each step. The paper also provides decidability results for “weak revelations,” where the exact state is guaranteed to be eventually revealed, but not necessarily at every step. This research provides a new theoretical foundation for optimal decision-making under incomplete information. (Source: aihub.org)
Paper Proposes CommVQ: Commutative Vector Quantization for KV Cache Compression: The paper “CommVQ: Commutative Vector Quantization for KV Cache Compression” proposes a method called CommVQ that compresses KV caches using additive quantization and lightweight encoders and codebooks to reduce memory footprint in long-context LLM inference. To lower decoding computational costs, the codebook is designed to be commutative with Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE) and is trained using an EM algorithm. Experiments show that this method can reduce FP16 KV cache size by 87.5% with 2-bit quantization and outperforms existing KV cache quantization methods, even achieving 1-bit KV cache quantization with minimal precision loss. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
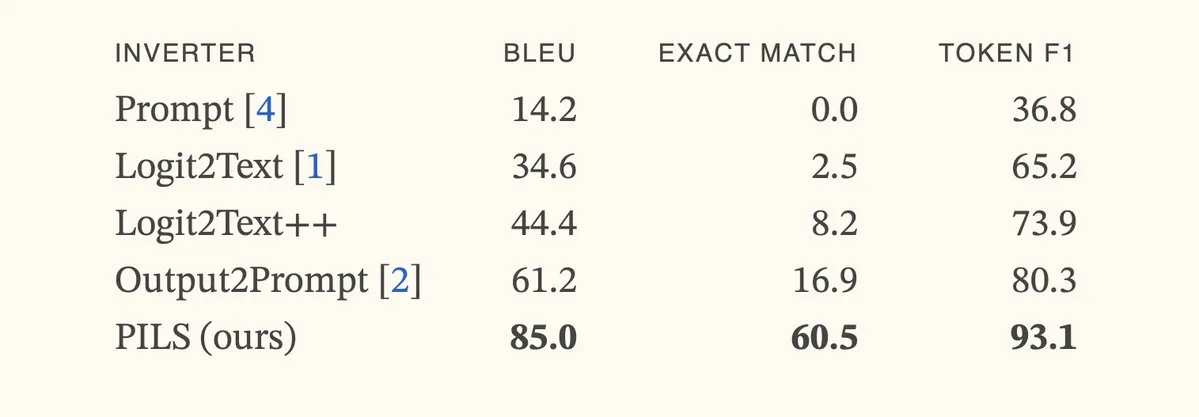
Paper Proposes PILS Method, Improving Language Model Inversion by Compactly Representing Next-Token Distributions: The paper “Better Language Model Inversion by Compactly Representing Next-Token Distributions” proposes a new language model inversion method called PILS (Prompt Inversion from Logprob Sequences). This method recovers hidden prompts by analyzing the model’s next-token probabilities over multiple generation steps. The core idea is the discovery that language model output vectors occupy a low-dimensional subspace, allowing for lossless compression of next-token probability distributions via a linear map, which is then used for more effective inversion. Experiments show that PILS significantly outperforms previous SOTA methods in recovering hidden prompts. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers, jxmnop)
Paper Proposes Phantom-Data: A General Subject-Consistent Video Generation Dataset: The paper “Phantom-Data : Towards a General Subject-Consistent Video Generation Dataset” introduces a new dataset called Phantom-Data, aimed at addressing the prevalent “copy-paste” issue in existing subject-to-video generation models (where subject identity becomes overly entangled with background and contextual attributes). Phantom-Data is the first general cross-paired subject-to-video consistency dataset, containing approximately one million identity-consistent pairs across different categories. The dataset is constructed through a three-stage process involving subject detection, large-scale cross-context subject retrieval, and prior-guided identity verification. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Proposes LongWriter-Zero: Mastering Ultra-Long Text Generation via Reinforcement Learning: The paper “LongWriter-Zero: Mastering Ultra-Long Text Generation via Reinforcement Learning” proposes an incentive-based method to cultivate an LLM’s ability to generate ultra-long, high-quality text from scratch using Reinforcement Learning (RL), without any annotated or synthetic data. The method starts with a base model and guides it through RL to refine its planning and writing processes, using specialized reward models to control length, writing quality, and structural format. Experiments show that LongWriter-Zero, trained from Qwen2.5-32B, outperforms traditional SFT methods on long-text writing tasks and achieves SOTA levels on multiple benchmarks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
💼 Business
Legal AI Company Harvey Announces $300 Million Series E Funding, Valued at $5 Billion: Legal AI startup Harvey announced the completion of a $300 million Series E funding round co-led by Kleiner Perkins and Coatue, valuing the company at $5 billion. Other investors include Sequoia Capital, GV, DST Global, Conviction, Elad Gil, OpenAI Startup Fund, Elemental, SV Angel, Kris Fredrickson, and REV. This funding will help Harvey continue to develop and expand its AI applications in the legal field. (Source: saranormous)
Hyperbolic On-Demand GPU Cloud Service Reaches $1 Million ARR in 7 Days: Yuchenj_UW announced that their Hyperbolic on-demand GPU cloud service, launched last week, grew from $0 to $1 million in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) within 7 days, with minimal marketing via a single tweet. They are offering free 8xH100 node trial credits for builders, indicating strong market demand for high-performance GPU cloud services. (Source: Yuchenj_UW)
Replit Announces Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) Surpasses $100 Million: Online integrated development environment (IDE) and cloud computing platform Replit announced its Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) has surpassed $100 million, a significant increase from $10 million at the end of 2024. The company stated it still has over half of its funds in the bank after its last funding round in 2023 at a $1.1 billion valuation. Replit’s growth is driven by enterprise users (such as Zillow, HubSpot) and independent developers using its platform, and it is currently actively hiring. (Source: pirroh, kylebrussell, hwchase17, Hacubu)
🌟 Community
New AI Programming Paradigm: Design First, Then Prompt, Iteratively Optimize Code Generation: dotey and Bao Yu discuss the shift in software development models brought by AI programming. The traditional debate of “design then code” versus “implement then refactor” is converging in the AI era. AI significantly reduces the cost and time from design to coding, allowing developers to quickly implement versions even when the design is not fully clear, and iteratively improve the design and prompts by validating results. Prompts take on the role of previous “detailed design documents” but are more simplified. In this model, developers should focus more on system design, generate code in small batches, utilize source code management, and review and test AI-generated code. For experienced programmers, changing mindsets and development habits is key to embracing AI programming. (Source: dotey)
Claude Code Favored by Developers for its Powerful Large Codebase Handling and Contextual Efficiency: The Reddit r/ClaudeAI community is buzzing about Claude Code’s excellent performance in handling large codebases. Users report it can understand and modify codebases well over 200k tokens. Discussions suggest Claude Code might achieve efficient contextual processing through strategies similar to human reading (reading only key parts), using tools like grep for contextual retrieval (rather than relying solely on RAG’s vectorized compression), and advantages of first-party model integration. Users shared various success stories using Claude Code for system issue fixing, building personal finance trackers, developing Android apps (even without Android development experience), creating Obsidian DataviewJS scripts, significantly boosting work efficiency. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)

“Context Engineering” Concept Gains Attention, Emphasizing Building Dynamic Systems to Empower LLMs: LangChain’s Harrison Chase proposed that “Context Engineering” is the core work of AI engineers in system building. It is defined as “building dynamic systems that provide the right information and tools, in the right format, for an LLM to reasonably accomplish a task.” This concept emphasizes the importance of how effectively contextual information is organized and provided for model performance in LLM applications, forming the foundation for fields like Agent construction. (Source: hwchase17, Hacubu, yoheinakajima)

Meta Founder Zuckerberg Personally Recruiting AI Talent, Sparking Community Attention: Social media reports indicate that Meta founder Mark Zuckerberg is personally involved in talent recruitment for his superintelligence lab, directly contacting hundreds of potential candidates and inviting respondents to dinner. This move is interpreted as a sign of Meta’s determination and investment in the AI field, particularly in Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) or superintelligence, highlighting the fierce competition among top tech companies for top AI talent. (Source: reach_vb, andrew_n_carr)

AI Development Sparks Profound Reflection on Job Market and Economic Structure: Harvard Business School and economist Anton Korinek warn that AGI could be achieved within 2-5 years, potentially leading to economic collapse if the system isn’t radically reformed, emphasizing the necessity of Universal Basic Income. Concurrently, community discussions suggest AI will automate many quantifiable tasks, impacting both blue-collar and white-collar jobs, requiring businesses to restructure to adapt to AI. Yuval Noah Harari likens the AI revolution to an “AI migration wave,” sparking discussions about AI replacing jobs and seeking power. These views collectively point to the disruptive impact of AI on future socio-economic structures. (Source: 36Kr, 36Kr, Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ChatGPT)

AI Excels in Programming Competitions, Sakana AI Agent’s High Score Sparks Debate: Sakana AI’s agent ranked 21st out of over 1000 human programmers in an AtCoder heuristic programming contest, placing in the top 6.8% overall. The AI iterated through about 100 versions in 4 hours, generating thousands of potential solutions, while human contestants typically test around 12. The AI used Gemini 2.5 Pro and combined expert knowledge with systematic search algorithms (like simulated annealing and beam search) to solve practical optimization problems. Community reactions were mixed, with some arguing that competitive programming differs from enterprise-level engineering, and AI’s victory is more like a computer outperforming humans in addition and subtraction. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
💡 Other
Exploration of AI in Vocational Education: Diverse Attempts in Interviews, Teaching, and Learning Devices: Vocational education giants like Huatu, Fenbi, and Zhonggong are actively exploring AI applications, each in different directions. Huatu focuses on AI interview feedback, Fenbi delves into AI grading and AI teachers (its AI-powered question-刷题 system class has already generated over 14 million RMB in sales), while Zhonggong has launched an AI employment learning device. The industry consensus is that AI should enhance learning outcomes and operational efficiency, rather than merely pursuing high premiums. AI applications are also moving from proof-of-concept to deep-seated scenario integration, such as 51CTO using digital humans and 3D modeling to generate courses, and employing AI for test question generation and learning path analysis. However, most education companies do not yet have the capability to build their own large models, preferring to call third-party APIs. (Source: 36Kr)
Disney, Universal Pictures Sue AI Image Generation Unicorn Midjourney for Copyright Infringement: Hollywood giants Disney and Universal Pictures have jointly sued AI image generation company Midjourney, accusing it of using a large amount of copyrighted IP content (such as Iron Man, Minions, etc.) to train its AI model without permission and generating highly similar images. The plaintiffs are seeking an injunction against the infringing activities and up to $150,000 in damages for each willfully infringed work. This case highlights the copyright challenges faced by generative AI, as Midjourney’s founder had previously admitted to using data without authorization. The lawsuit may aim to push for the establishment of copyright licensing mechanisms and content filtering systems. (Source: 36Kr)

Apple Accused of Lagging in AI, May Consider Acquisitions to Catch Up, Former OpenAI CTO’s Company in Focus: Reports suggest Apple is relatively behind in the AI field, with insufficient in-house AI capabilities and a lackluster Siri performance. To bridge the gap, Apple may consider a major acquisition. It is rumored to have had preliminary contact with former OpenAI CTO Mira Murati regarding her new startup, Thinking Machines Lab. Historically, Apple has often enhanced its capabilities by acquiring smaller tech companies (like Siri itself). Currently, Apple lags far behind industry giants in AI model parameter scale, and acquiring companies like Mistral could help it achieve breakthroughs in its proprietary large models. (Source: 36Kr)