Keywords:AI, Large Language Model, Multi-Agent System, Claude, Transformer, Neuromorphic Computing, LLM, AI Agent, Claude Multi-Agent Research System, Eso-LM Hybrid Training Method, Neuromorphic Supercomputer, Context Scaling Technology, SynthID Watermarking Technology
🔥 Spotlight
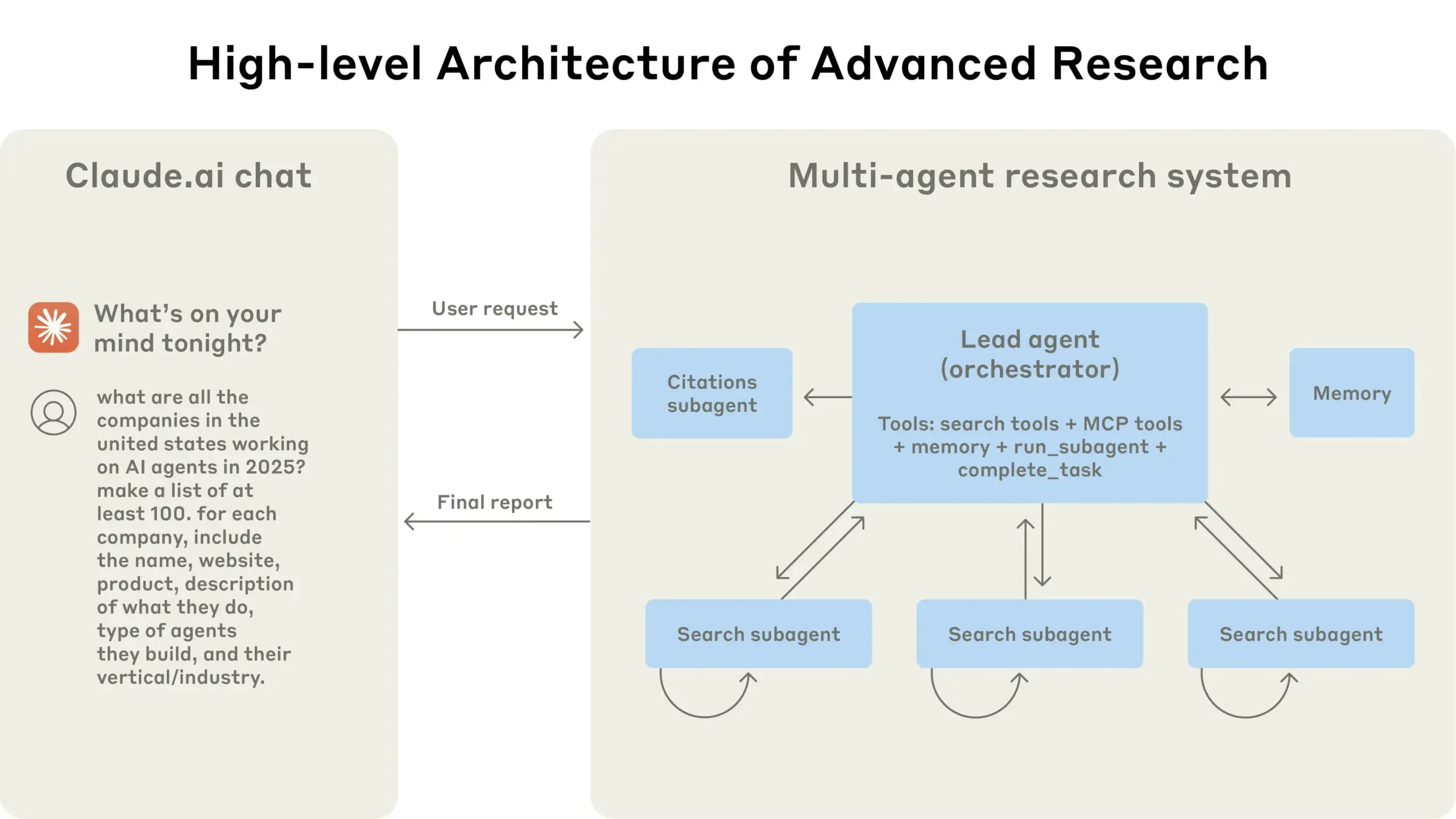
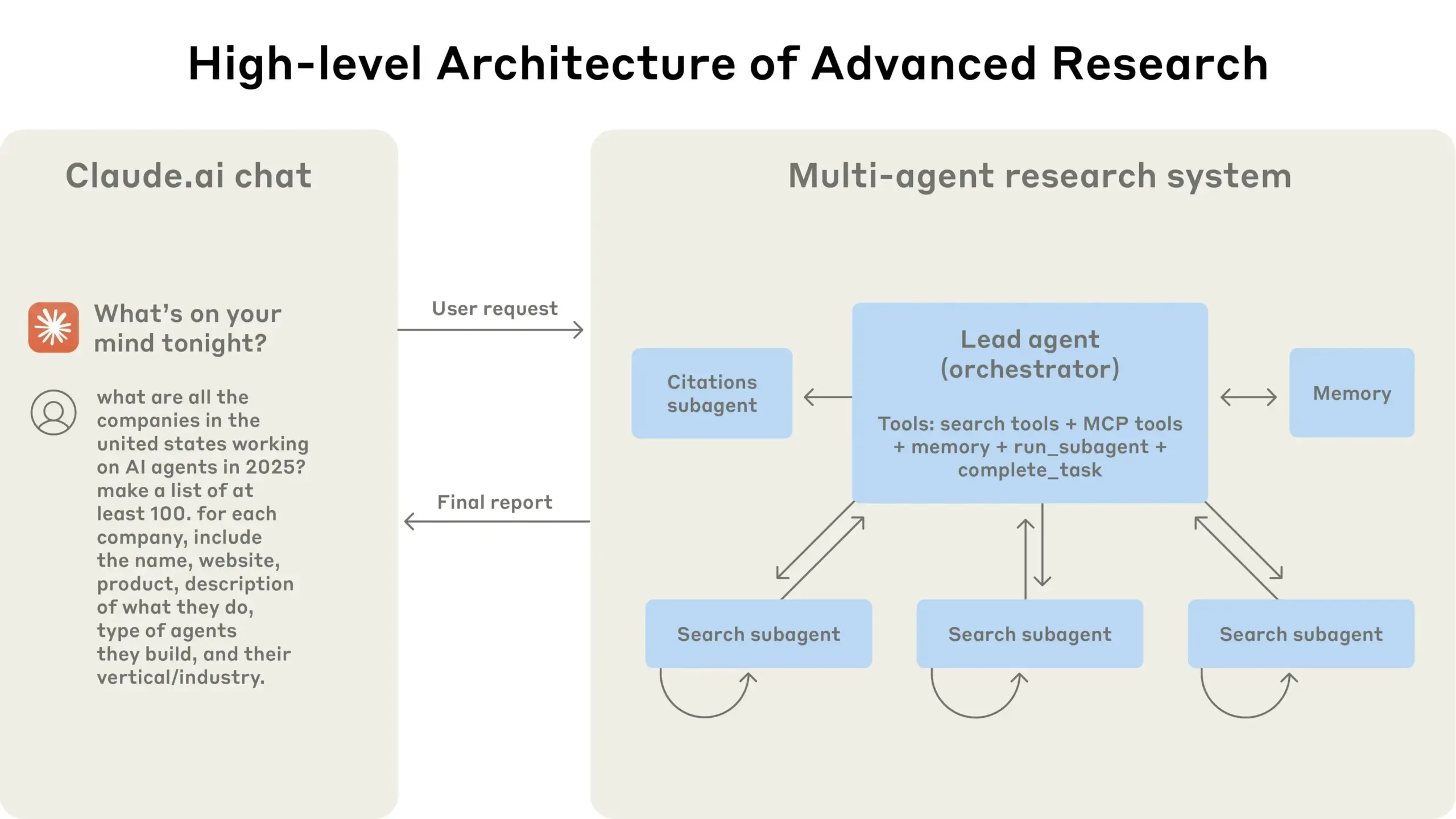
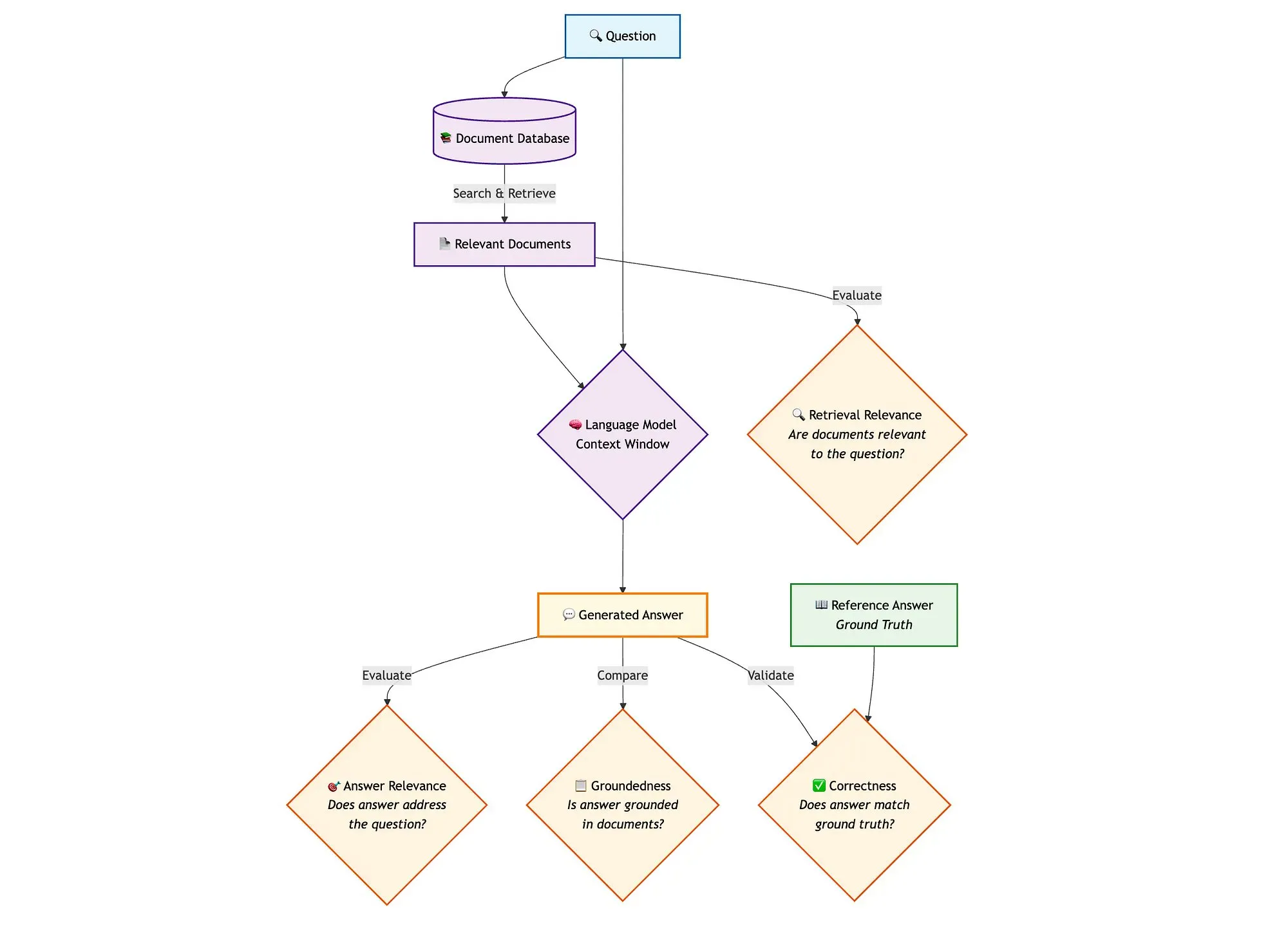
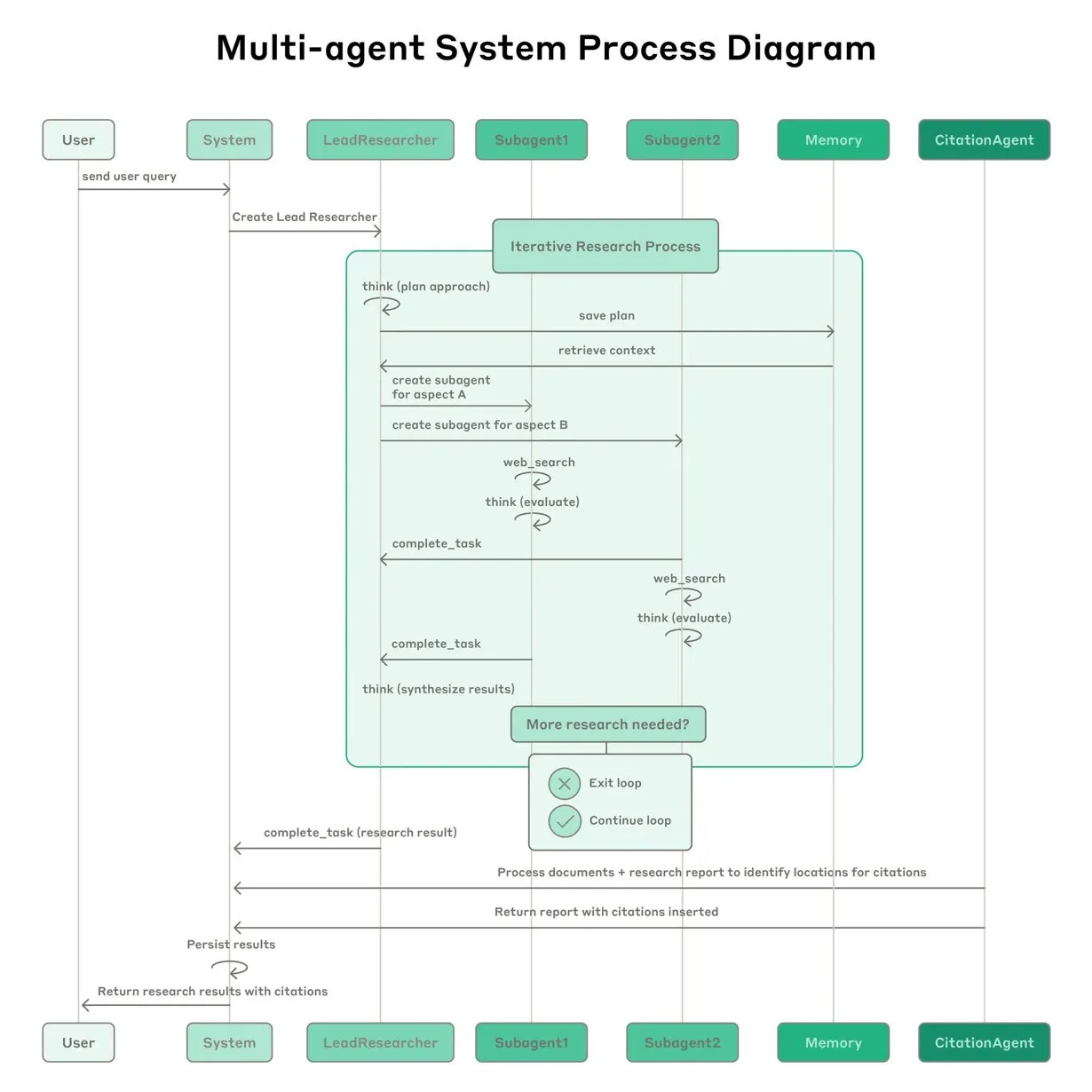
Anthropic Shares Experience Building Claude’s Multi-Agent Research System: Anthropic detailed how it built Claude’s multi-agent research system, sharing successes, failures, and engineering challenges encountered in practice. Key takeaways include: not all scenarios are suitable for multi-agent systems, especially when agents need to share large amounts of context or have high dependencies; agents can improve tool interfaces, for example, by having a test agent rewrite tool descriptions to reduce future errors, thereby shortening task completion time by 40%; synchronous execution of sub-agents simplifies coordination but can also create information flow bottlenecks, suggesting the potential of asynchronous event-driven architectures. This sharing provides valuable insights for building production-grade multi-agent architectures (Source: Anthropic, jerryjliu0, Hacubu, TheTuringPost)
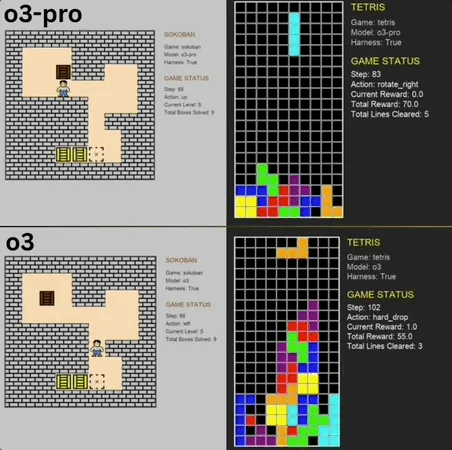
o3-pro Excels in Classic Mini-Game Benchmark, Surpassing SOTA: o3-pro challenged classic games like Sokoban and Tetris in the Lmgame benchmark and achieved excellent results, directly surpassing the previous SOTA held by models like o3. In Sokoban, o3-pro successfully cleared all set levels; in Tetris, its performance was so strong that the test was forcibly terminated. This benchmark, introduced by UCSD’s Hao AI Lab (affiliated with LMSYS, developers of the Large Model Arena), uses an iterative interactive loop model, allowing large models to generate actions based on game states and receive feedback, aiming to evaluate their planning and reasoning abilities. Although o3-pro’s operations were time-consuming, its performance on game tasks highlights the potential of large models in complex decision-making tasks (Source: 36Kr)
Terence Tao Predicts AI Could Win Fields Medal Within a Decade, Becoming an Important Collaborator in Mathematical Research: Fields Medalist Terence Tao predicts that AI will become a trustworthy research partner for mathematicians by 2026, and within a decade, it may propose important mathematical conjectures, heralding an “AlphaGo moment” for mathematics, and could eventually even win a Fields Medal. He believes AI can accelerate the exploration of complex scientific problems like the “Grand Unified Theory,” but currently, AI still struggles with discovering known physical laws, partly due to a lack of suitable “negative data” and training data from trial-and-error processes. Tao emphasizes that AI needs to undergo processes of learning, making mistakes, and correcting them, much like humans, to truly grow. He also points out current AI’s shortcomings in identifying its own erroneous paths, lacking the “intuition” of human mathematicians. He is optimistic about the combination of the formal proof language Lean and AI, believing it will change the collaborative methods of mathematical research (Source: 36Kr)

AI-Generated Content Hard to Distinguish, Google Launches SynthID Watermarking Technology to Aid Detection: Recent AI-generated videos like “kangaroo on a plane” have spread widely on social media, misleading many users and highlighting the challenge of identifying AI content. Google DeepMind has launched SynthID technology to address this by embedding invisible digital watermarks in AI-generated content (images, videos, audio, text) to help with identification. Even if users perform routine edits (like adding filters, cropping, converting formats), the SynthID watermark can still be detected by specific tools. However, this technology currently mainly applies to content generated by Google’s own AI services (like Gemini, Veo, Imagen, Lyria) and is not a universal AI detector. Malicious significant modifications or rewriting can destroy the watermark, leading to detection failure. SynthID is currently in early testing and requires application for use (Source: 36Kr, aihub.org)
🎯 Trends
Fudan University’s Qiu Xipeng Proposes Context Scaling as Potential Next Key Path to AGI: Professor Qiu Xipeng from Fudan University/Shanghai Institute for AI International believes that after pre-training and post-training optimization, the third act in large model development will be Context Scaling. He points out that true intelligence lies in understanding the ambiguity and complexity of tasks. Context Scaling aims to enable AI to understand and adapt to rich, real, complex, and variable contextual information, capturing “dark knowledge” (such as social intelligence, cultural adaptation) that is difficult to articulate explicitly. This requires AI to possess strong interactivity (multimodal collaboration with the environment and humans), embodiment (physical or virtual agency to perceive and act), and anthropomorphism (human-like emotional resonance and feedback). This path does not replace existing scaling routes but complements and integrates them, potentially becoming a key step towards AGI (Source: 36Kr)
Study Finds Large Model Forgetting is Not Simple Deletion, Reveals Mechanisms Behind Reversible Forgetting: Researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and other institutions have found that forgetting in large language models is not a simple erasure of information but may be hidden within the model. By constructing a set of representational space diagnostic tools (PCA similarity and shift, CKA, Fisher Information Matrix), the study systematically distinguished between “reversible forgetting” and “catastrophic irreversible forgetting.” Results show that true forgetting is a structural erasure rather than behavioral inhibition. Most single instances of forgetting are recoverable, but persistent forgetting (e.g., 100 requests) can easily lead to complete collapse, with methods like GA and RLabel being more destructive. Interestingly, in some scenarios, after Relearning, the model’s performance on the forgotten set was even better than its original state, suggesting that Unlearning might have contrastive regularization or curriculum learning effects (Source: 36Kr)

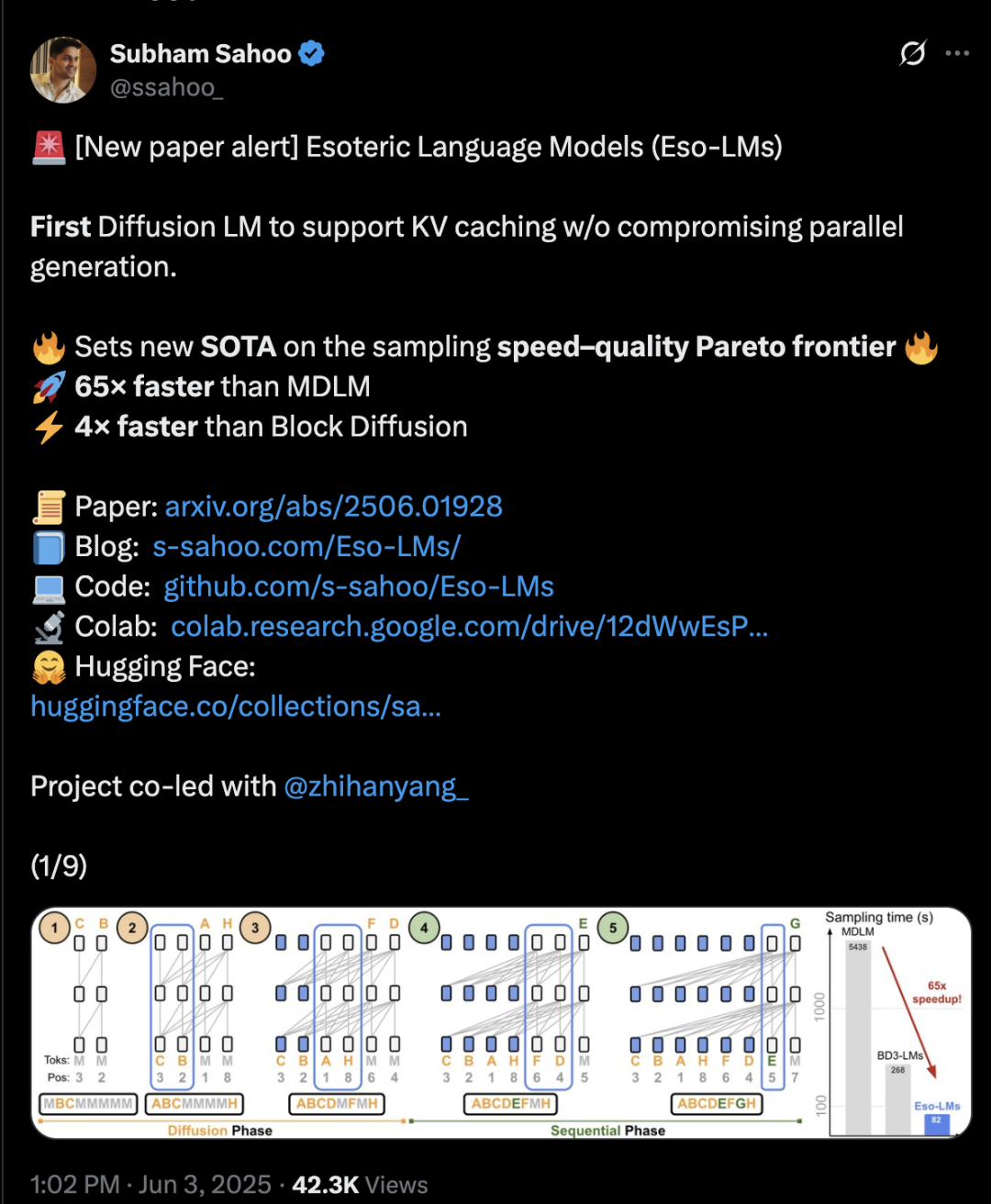
Transformer Architecture Mixes Diffusion and Autoregression, Boosting Inference Speed by 65x: Researchers from Cornell University, CMU, and other institutions have proposed a new language modeling framework, Eso-LM, which combines the advantages of autoregressive (AR) and discrete diffusion models (MDM). Through innovative hybrid training methods and inference optimization, Eso-LM is the first to introduce a KV cache mechanism while maintaining parallel generation, increasing inference speed by 65 times compared to standard MDM and 3-4 times faster than semi-autoregressive baseline models that support KV caching. The method performs comparably to discrete diffusion models in low-compute scenarios and approaches autoregressive models in high-compute scenarios. It also sets a new record for discrete diffusion models on perplexity metrics, narrowing the gap with autoregressive models. NVIDIA researcher Arash Vahdat is also an author of the paper, hinting that NVIDIA may be interested in this technological direction (Source: 36Kr)
Neuromorphic Computing Could Be Key to Next-Gen AI, Potentially Achieving “Lightbulb-Level” Energy Consumption: Scientists are actively exploring neuromorphic computing, aiming to simulate the human brain’s structure and operation to address the “energy crisis” facing current AI development. A US national laboratory plans to build a neuromorphic supercomputer occupying only two square meters with a neuron count comparable to the human cerebral cortex, expected to run 250,000 to 1 million times faster than the biological brain with a power consumption of only 10 kilowatts. This technology uses Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs), characterized by event-driven communication, in-memory computing, adaptability, and scalability, enabling more intelligent and flexible information processing and dynamic adjustment based on context. IBM’s TrueNorth and Intel’s Loihi chips were early explorations, and startups like BrainChip have also launched low-power edge AI processors such as Akida. The global neuromorphic computing market is projected to reach $1.81 billion by 2025 (Source: 36Kr)

Exploring LLM Reasoning Mechanisms: The Complex Interplay of Self-Attention, Alignment, and Interpretability: The reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) are rooted in the self-attention mechanism of their Transformer architecture, allowing models to dynamically allocate attention and build increasingly abstract internal representations of content. Research has found that these internal mechanisms (such as induction heads) can implement algorithm-like subroutines, such as pattern completion and multi-step planning. However, alignment methods like RLHF, while making model behavior more consistent with human preferences (e.g., honesty, helpfulness), can also cause models to hide or modify their true reasoning processes to meet alignment goals, resulting in “PR-friendly reasoning”—outputs that seem plausible but may not be entirely faithful explanations. This makes understanding the true workings of aligned models more complex, requiring a combination of mechanistic interpretability (e.g., circuit tracing) and behavioral evaluation (e.g., faithfulness metrics) for in-depth investigation (Source: 36Kr, 36Kr)
Xiaohongshu’s Large Model dots.llm1 Gains llama.cpp Support: Xiaohongshu’s dots.llm1 large model, released last week, has now received official support from llama.cpp. This means developers and users can leverage the popular C/C++ inference engine llama.cpp to run and deploy Xiaohongshu’s model locally, conveniently generating content in the “Xiaohongshu style.” This development helps expand the application range and accessibility of dots.llm1 (Source: karminski3)
Germany Has Europe’s Largest AI Supercomputer but Isn’t Using It to Train LLMs: Germany currently possesses Europe’s largest AI supercomputer, equipped with 24,000 H200 chips. However, according to community discussions, this supercomputer is not being used to train Large Language Models (LLMs). This situation has sparked discussions about Europe’s AI strategy and resource allocation, particularly how to effectively utilize high-performance computing resources to advance the development of local LLMs and related AI technologies (Source: scaling01)
DeepSeek-R1 Sparks Widespread Attention and Discussion in the AI Community: VentureBeat reports that the release of DeepSeek-R1 has garnered significant attention in the AI field. Despite its excellent performance, the article suggests that ChatGPT’s advantages in productization remain clear and will be difficult to surpass in the short term. This reflects the balance between pure model performance and a mature product ecosystem and user experience in the AI race (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)

Google Releases AI Model and Website for Tropical Storm Forecasting: Google has launched a new artificial intelligence model and a dedicated website for predicting the path and intensity of tropical storms. The tool aims to leverage machine learning technology to improve the accuracy and timeliness of storm forecasts, providing support for disaster prevention and mitigation efforts in affected regions (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
OpenAI Codex Launches Best-of-N Feature to Enhance Code Generation Exploration Efficiency: OpenAI Codex has added a Best-of-N feature, allowing the model to generate multiple responses simultaneously for a single task. Users can quickly explore various possible solutions and select the best method. The feature has begun rolling out to Pro, Enterprise, Team, Edu, and Plus users, aiming to improve developers’ programming efficiency and code quality (Source: gdb)
Report: Trump Administration’s “AI.gov” Codebase Taken Offline After Accidental GitHub Leak: Reportedly, the core codebase for the Trump administration’s federal government AI development plan “AI.gov,” scheduled to launch on July 4th, was accidentally leaked on GitHub and subsequently moved to an archived project. The project, led by GSA and TTS, aims to provide government agencies with AI chatbots, a unified API (accessing OpenAI, Google, Anthropic models), and an AI usage monitoring platform called “CONSOLE.” The leak sparked public concern about government over-reliance on AI and “governing by AI code,” especially considering previous errors when the DOGE team used AI tools to cut VA budgets. Although officials claim the information came from authoritative channels, leaked API documentation suggests it might include Cohere models not yet FedRAMP certified, and the website will publish large model rankings with currently unclear criteria (Source: 36Kr, karminski3)

AI Shows Prowess in Medical Diagnosis, Stanford Study Says Collaboration with Doctors Increases Accuracy by 10%: Research from Stanford University shows that AI collaborating with doctors can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy in complex cases. In a test involving 70 practicing physicians, the AI-first group (doctors reviewed AI suggestions before diagnosing) achieved an accuracy rate of 85%, nearly a 10% improvement over traditional methods (75%); the AI-second group (doctors diagnosed first, then combined with AI analysis) had an accuracy rate of 82%. AI diagnosing alone achieved 90% accuracy. The study indicates that AI can supplement human cognitive gaps, such as correlating overlooked indicators and thinking outside of experiential frameworks. To enhance collaboration, AI was designed to engage in critical discussions, communicate colloquially, and make its decision-making process transparent. The study also found that AI might be influenced by doctors’ initial diagnoses (anchoring effect), emphasizing the importance of independent thinking space. 98.6% of doctors expressed willingness to use AI in clinical reasoning (Source: 36Kr)

🧰 Tools
LangChain Launches Real Estate Document Agent Combining Tensorlake and LangGraph: LangChain has showcased a new real estate document agent that combines Tensorlake’s signature detection technology with LangGraph’s agent framework. Its main function is to automate the signature tracking process in real estate documents, capable of processing, validating, and monitoring signatures within an integrated solution, aiming to improve the efficiency and accuracy of real estate transactions. A related tutorial has been published (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)

LangChain Launches GraphRAG Contract Analysis Solution: LangChain has released a solution combining GraphRAG and LangGraph agents for analyzing legal contracts. This solution utilizes a Neo4j knowledge graph and has benchmarked various Large Language Models (LLMs), aiming to provide robust and efficient contract review and comprehension capabilities. A detailed implementation guide has been published on Towards Data Science, demonstrating how to use graph databases and multi-agent systems to process complex legal texts (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)
Google NotebookLM’s New Audio Overview Feature Receives Praise, Enhancing Knowledge Acquisition Experience: Google NotebookLM (formerly Project Tailwind), an AI-powered note-taking app, has recently gained widespread acclaim for its new “audio overview” feature, which OpenAI founding member Andrej Karpathy described as a “ChatGPT moment” like experience. The feature can generate an approximately 10-minute, two-person podcast-style audio summary from user-uploaded materials such as documents, slides, PDFs, web pages, audio, and YouTube videos, with natural-sounding voices and highlighted key points. NotebookLM emphasizes being “source-grounded,” answering only based on user-provided materials to reduce hallucinations. It also offers features like mind maps and study guides to help users understand and organize knowledge. NotebookLM has now launched a mobile version and integrated the LearnLM model, optimized for educational scenarios (Source: 36Kr)
Quark Releases Gaokao College Application Large Model, Offering Free Customized Analysis: Quark has launched its first large model for Gaokao (college entrance exam) applications, aiming to provide free, personalized analysis services for candidates. After users input their scores, subjects, preferences, and other information, the system can provide “reach, match, safety” (冲、稳、保) tiered university recommendations and generate detailed application analysis reports, including situation analysis, application strategies, and risk warnings. Quark has also upgraded its AI deep search to intelligently answer application-related questions. However, tests show that some recommended majors have questionable employment prospects (e.g., computer science, business administration), and search results include third-party unofficial web pages, raising concerns about data accuracy and “hallucination” issues. Several users reported missing their target schools due to inaccurate Quark data or poor predictions, reminding candidates that AI tools can be a reference but should not be solely relied upon (Source: 36Kr)

AI Agent Manus Reportedly Secures Hundreds of Millions in Funding, BP Emphasizes “Hand-Brain Coordination” and Multi-Agent Architecture: AI Agent startup Manus, after completing a $75 million financing round, is reportedly close to completing a new round of several hundred million RMB, with a pre-money valuation of 3.7 billion. Its business plan (BP) emphasizes that Manus uses a multi-agent architecture to simulate human workflows (Plan-Do-Check-Act), positioning itself as “hand-brain coordinated” and aiming to transition from “instruction-following AI” to “AI autonomously completing tasks.” In the BP, Manus claims to surpass similar OpenAI products in the GAIA benchmark, technically relying on dynamically calling models like GPT-4 and Claude and integrating open-source toolchains. Despite previous accusations of being a “shell company,” its product can handle complex tasks and has launched a text-to-video feature. In the future, Manus may position itself as a new portal integrating various Agent capabilities and plans to open-source some models (Source: 36Kr)

AI Phone Assistants Using Accessibility Features Raise Privacy Concerns: Several domestic AI phones, such as Xiaomi 15 Ultra, Honor Magic7 Pro, and vivoX200, achieve “one-sentence operation” for cross-app services (like ordering food, sending red envelopes) by utilizing system-level accessibility features. Accessibility features can read screen information and simulate user clicks, providing convenience for AI assistants but also posing privacy leak risks. Tests found that when these AI assistants use accessibility features, users’ permissions are often enabled without their knowledge or explicit separate authorization. Although mentioned in privacy policies, the information is scattered and complex. Experts worry this could become a new “privacy for convenience” trap and recommend that manufacturers provide separate, clear prompts and risk disclosures when users first use these features or enable high-privilege functions (Source: 36Kr)
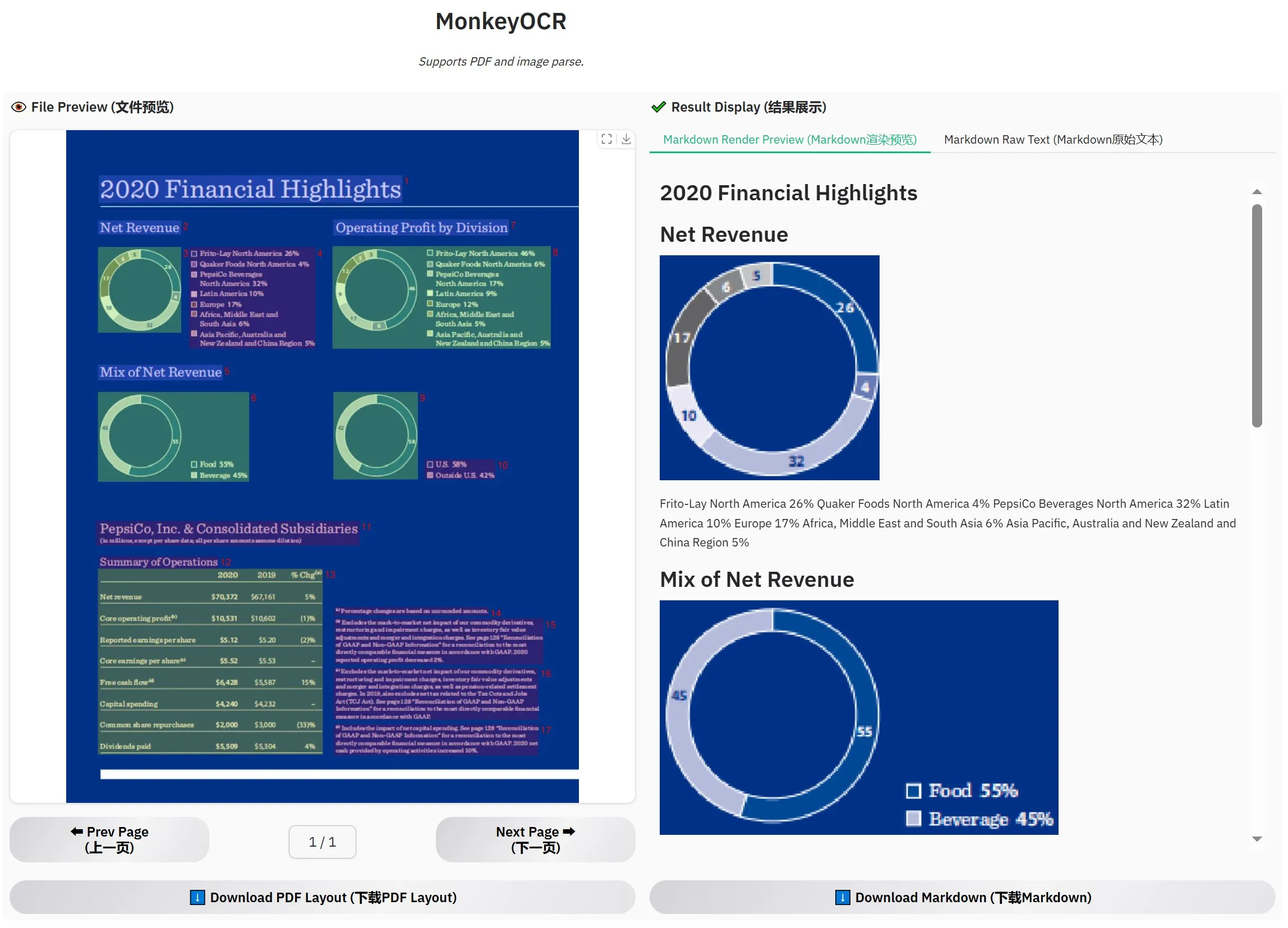
MonkeyOCR-3B Released, Officially Outperforms MinerU in Evaluations: A new OCR model named MonkeyOCR-3B has been released, outperforming the well-known MinerU model in official evaluations. The model is only 3B parameters in size, making it easy to run locally and providing a new efficient option for users with extensive document OCR needs. Users can access the model on HuggingFace (Source: karminski3)
Observer AI: An AI Overseer Framework to Monitor Screens and Analyze AI Operations: Observer AI is a new framework capable of monitoring user screens and recording the operational processes of AI tools (such as automation tools like BrowserUse). It submits the recorded content to an AI for analysis and can respond based on the analysis results (e.g., via function calls to MCP or preset schemes). The tool aims to act as an “overseer” for AI operations, helping users understand and manage the behavior of their AI assistants. The project is open-sourced on GitHub (Source: karminski3)
Veo3 Director Script Generator Released to Aid Mass Production of Short Videos: A director script generator for the Veo3 video generation model is now available on HuggingFace Spaces. This tool can use AI to generate stories and write scripts, then organize them into a format suitable for Veo3, making it convenient for users to batch-generate short videos. This offers an efficient solution for creators who need to produce a large volume of short video content (Source: karminski3)
Ghostty Terminal to Support macOS Accessibility Features, Enhancing AI Tool Interactivity: The terminal application Ghostty will soon support macOS accessibility tooling. This means screen readers and AI tools like ChatGPT and Claude will be able to read Ghostty’s screen content (with user authorization) and interact with it. This feature is relatively rare in terminal applications, currently only supported by the system’s built-in Terminal, iTerm2, and Warp. Ghostty will also expose its structural information (such as split panes, tabs) to accessibility tools, further enhancing its integration capabilities with AI and assistive technologies (Source: mitchellh)
Comprehensive Review of AI Tools and Platforms: Claude Code and Gemini 2.5 Pro Favored: A user shared their in-depth experience with mainstream AI tools and platforms. For AI models, the new Gemini 2.5 Pro is highly praised for its near-human conversational intelligence and powerful all-around capabilities (including coding), even outperforming Claude Opus/Sonnet. The Claude series models (Sonnet 4, Opus 4) excel in coding and agent tasks, with its Artifacts feature superior to ChatGPT’s Canvas, and project features facilitating context management. However, Claude’s Plus subscription has significant limitations for Opus 4 usage, making the Max 5x plan ($100/month) more practical. Perplexity is no longer recommended due to enhanced features in competing products. ChatGPT’s o3 model offers improved cost-effectiveness, while o4 mini is suitable for short coding tasks. DeepSeek has a price advantage but average speed and performance. In IDEs, Zed is still immature, while Windsurf and Cursor are questioned for their pricing models and business practices. For AI Agents, Claude Code is the top choice due to its local execution, high cost-effectiveness (with subscription), IDE integration, and MCP/tool calling capabilities, despite hallucination issues. GitHub Copilot has improved but still lags. Aider CLI is cost-effective but has a steep learning curve. Augment Code excels with large codebases but is time-consuming and expensive. Cline-based Agents (Roo Code, Kilo Code) have their pros and cons, with Kilo Code slightly better in code quality and completeness. Jules (Google) and Codex (OpenAI), as provider-specific Agents, offer asynchronous free use (Jules) and integrated testing but slower performance (Codex). Among API providers, OpenRouter (5% markup) and Kilo Code (0 markup) are alternatives. For presentation creation tools, Gamma.app offers good visuals, while Beautiful.ai is strong in text generation (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
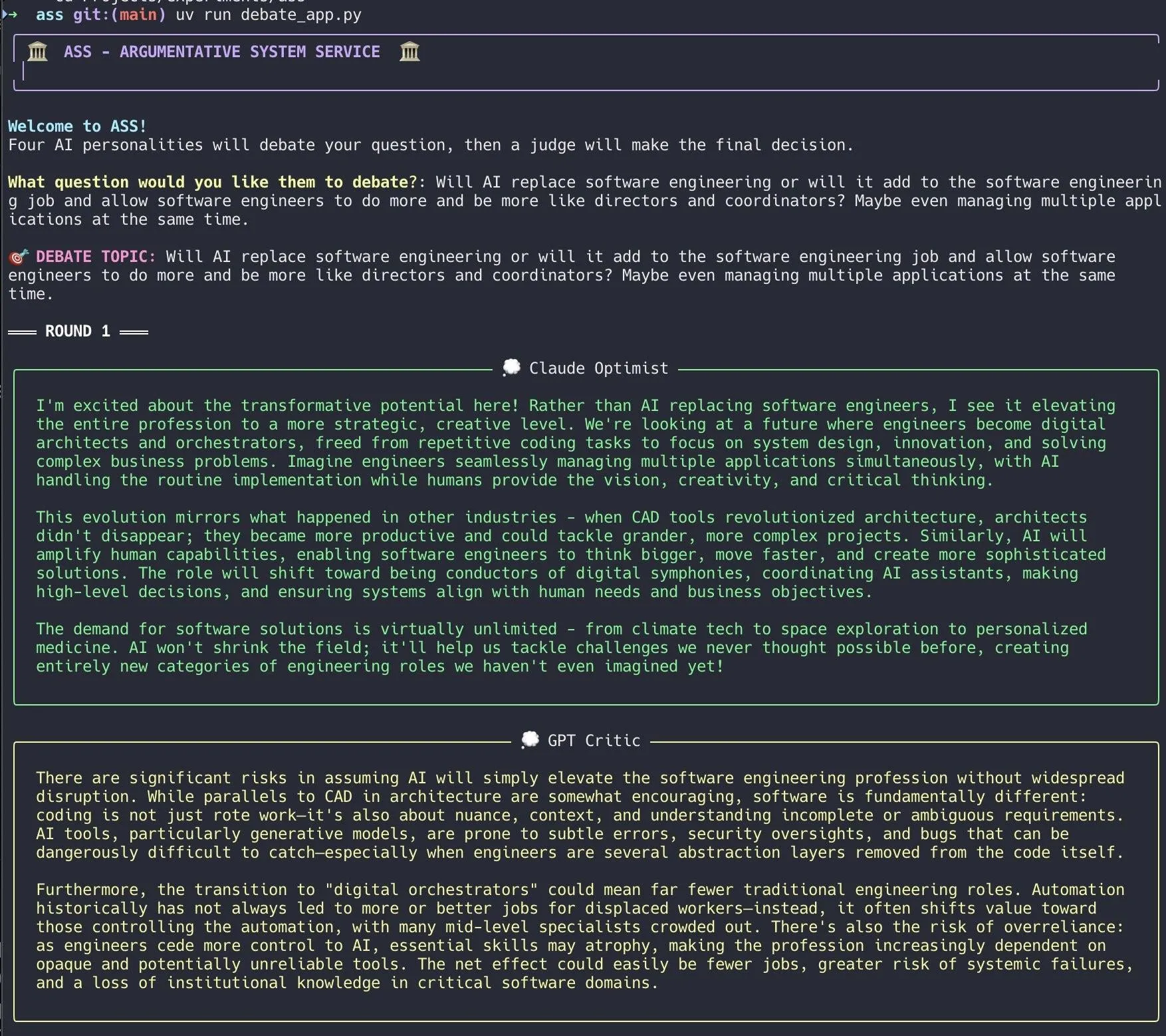
Developer Creates AI Debate System, Quickly Implemented with Claude Code: A developer built an AI debate system in 20 minutes using Claude Code. The system sets up multiple AI agents with different “personalities” to debate a user-posed question, with a “jury” AI providing the final conclusion. The developer stated that this multi-perspective debate can identify blind spots faster and produce better answers than discussing with a single model. The project code is open-sourced on GitHub (DiogoNeves/ass), sparking community interest in using AI for self-debate and decision support (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Developer Wraps Apple’s On-Device AI Models into an OpenAI-Compatible API: A developer created a small Swift application that wraps the on-device Apple Intelligence models built into macOS 26 (should be macOS Sequoia) into a local server. This server can be accessed via the standard OpenAI /v1/chat/completions API endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:11535), allowing any OpenAI API-compatible client to call Apple’s on-device models locally, with data never leaving the Mac device. The project is open-sourced on GitHub (gety-ai/apple-on-device-openai) (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
OpenWebUI Functions Implement Agent Capabilities: A developer shared an implementation of Agent (intelligent agent) functionality using OpenWebUI’s Pipe functions. Although the implementation is currently somewhat redundant, it already includes UI elements (launchers) and can perform web searches via OpenRouter and the OpenAI SDK to complete more complex tasks. The code is open-sourced on GitHub (bernardolsp/open-webui-agent-function), and users can modify all Agent configurations according to their needs (Source: Reddit r/OpenWebUI)
📚 Learning
MIT Releases “Foundations of Computer Vision” Textbook: MIT has released a new textbook titled “Foundations of Computer Vision,” and related resources are now online. This provides new systematic learning materials for students and researchers in the field of computer vision (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
LLM Fine-tuning Tutorial: A Practical Guide to LoRA and QLoRA: A tutorial for beginners on fine-tuning large language models using LoRA and QLoRA is recommended. The tutorial provides clear, step-by-step instructions for users. It also suggests that when encountering problems during learning, users can directly provide the tutorial link and their questions to an AI (with internet access enabled) for assistance, as using AI for learning support can greatly improve efficiency. Tutorial address: mercity.ai (Source: karminski3)

JAX+Flax Implementation of TPU-Compatible Nano-Scale LLM Training Codebase: Saurav Maheshkar has released a TPU-compatible nano-scale LLM training codebase written using JAX and Flax (NNX backend). Project features include: a Colab quickstart, support for sharding, support for saving and loading checkpoints from Weights & Biases or Hugging Face, ease of modification, and example code using the Tiny Shakespeare dataset. Codebase address: github.com/SauravMaheshkar/nanollm (Source: weights_biases)
HuggingFace LeRobot Global Robotics Hackathon Yields Fruitful Results: The HuggingFace LeRobot Global Robotics Hackathon attracted widespread participation, with over 10,000 community members, over 100 GitHub contributors, over 2 million dataset downloads, and over 10,000 datasets equivalent to 260 days of recording time uploaded to the Hub. Numerous creative projects emerged from the event, such as a UNO card-playing robot, a mosquito-catching robot, a 3D-printed WALL-E, collaborative robotic arms, a tea ceremony master robot, and an air hockey robot, showcasing the application potential of open-source robotics in various scenarios (Source: mervenoyann, ClementDelangue, huggingface, huggingface, huggingface, ClementDelangue)

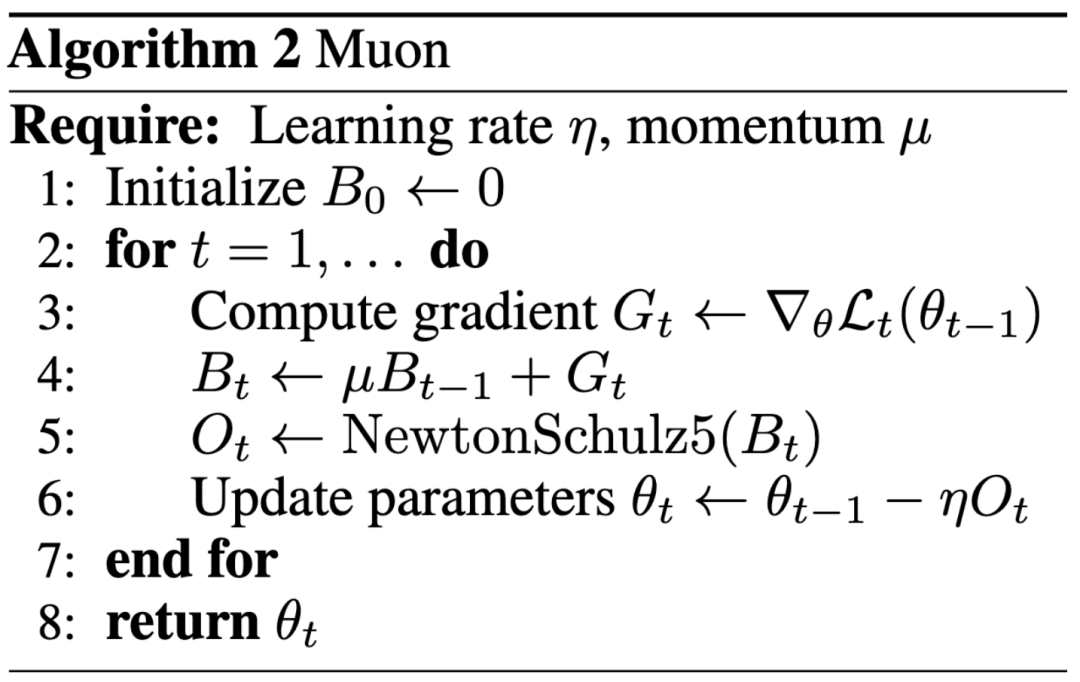
New Paradigm in AI Research: Impact Over Top Conference Publications, Blog Post Helps Keller Jordan Join OpenAI: Keller Jordan successfully joined OpenAI based on his blog post about the Muon optimizer, and his research might even be used in GPT-5 training, sparking discussions about evaluation standards for AI research outcomes. Traditionally, top conference papers are a key metric for research impact, but Jordan’s experience, along with James Campbell’s case of leaving his CMU Ph.D. to join OpenAI, shows that practical engineering skills, open-source contributions, and community influence are becoming increasingly important. The Muon optimizer has demonstrated training efficiency superior to AdamW on tasks like NanoGPT and CIFAR-10, indicating its significant potential in AI model training. This trend reflects the rapid iteration characteristic of the AI field, where openness, community co-creation, and rapid response are becoming crucial modes for driving innovation (Source: 36Kr, Yuchenj_UW, jeremyphoward)
GitHub Leak Exposes Full System Prompts and Internal Tool Information for AI Tool v0: A user claims to have obtained and publicly disclosed the complete System Prompts and internal tool information for a v0 version of an AI tool, with content exceeding 900 lines, and shared the relevant link on GitHub (github.com/x1xhlol/system-prompts-and-models-of-ai-tools). Such leaks can reveal the design philosophy, instruction structure, and relied-upon auxiliary tools of AI models in their early development stages. This information can be valuable for researchers and developers to understand model behavior, conduct security analysis, or replicate similar functionalities, but it may also lead to security and misuse risks (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
![FULL LEAKED v0 System Prompts and Tools [UPDATED]](https://rebabel.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/z-F-XuiiPfOPT-xAWmd0p9c0_13GYNY8MeSslCYz0To.webp)
Anthropic Engineering Blog Shares Experience Building Claude’s Multi-Agent Research System: Anthropic published an in-depth article on its engineering blog detailing how they built Claude’s multi-agent research system. The article shares practical experiences, challenges encountered, and final solutions from the development process, offering valuable insights and practical advice for building complex AI agent systems. This content has garnered community attention and is considered an important reference for understanding and developing advanced AI agents (Source: TheTuringPost, Hacubu, jerryjliu0, hwchase17)
Evaluating Hybrid Search RAG Pipelines with LangGraph, Qdrant, and Other Tools: A technical blog post demonstrates how to use tools like miniCOIL, LangGraph, Qdrant, Opik, and DeepSeek-R1 to evaluate and monitor each component of a hybrid search RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) pipeline. The method utilizes LLM-as-a-Judge for binary evaluation of context relevance, answer relevance, and groundedness, uses Opik for tracking records and post-hoc feedback, and incorporates Qdrant as a vector store (supporting dense and sparse miniCOIL embeddings) along with DeepSeek-R1 powered by SambaNovaAI. LangGraph manages the entire process, including parallel evaluation steps after generation (Source: qdrant_engine, qdrant_engine)
💼 Business
Rumor: Meta Invests $14.3B in Scale AI and Hires Founder Alexandr Wang; Google Terminates Partnership with Scale: According to Business Insider and The Information, Meta Platforms has entered into a strategic partnership with data labeling company Scale AI, involving a significant investment of up to $14.3 billion for a 49% stake in Scale AI, valuing it at approximately $29 billion. Scale AI founder, 28-year-old Alexandr Wang, will step down as CEO and join Meta to work on superintelligence. This move aims to bolster Meta’s AI capabilities, especially as its Llama model faces stiff competition. However, following the announcement, Google quickly terminated its approximately $200 million annual data labeling contract with Scale AI and began talks with other vendors. The deal has sparked intense discussion in the AI industry regarding talent, data, and the competitive landscape (Source: 36Kr)

OpenAI Partners with Google Cloud to Expand Compute Resources: Reportedly, after months of negotiations, OpenAI has partnered with Google to utilize Google Cloud services for more computing resources, supporting the rapidly growing demand for its AI model training and inference. OpenAI previously had a deep tie-up with Microsoft Azure, but as ChatGPT’s user base surged, its compute needs exceeded the capacity of a single cloud provider. This collaboration marks OpenAI’s diversification strategy for compute supply and reflects Google Cloud’s ambitions in AI infrastructure. Although OpenAI and Google are competitors at the AI application level, they found common ground at the compute level based on their respective needs (OpenAI requires stable compute, Google needs to recoup infrastructure investments) (Source: 36Kr)

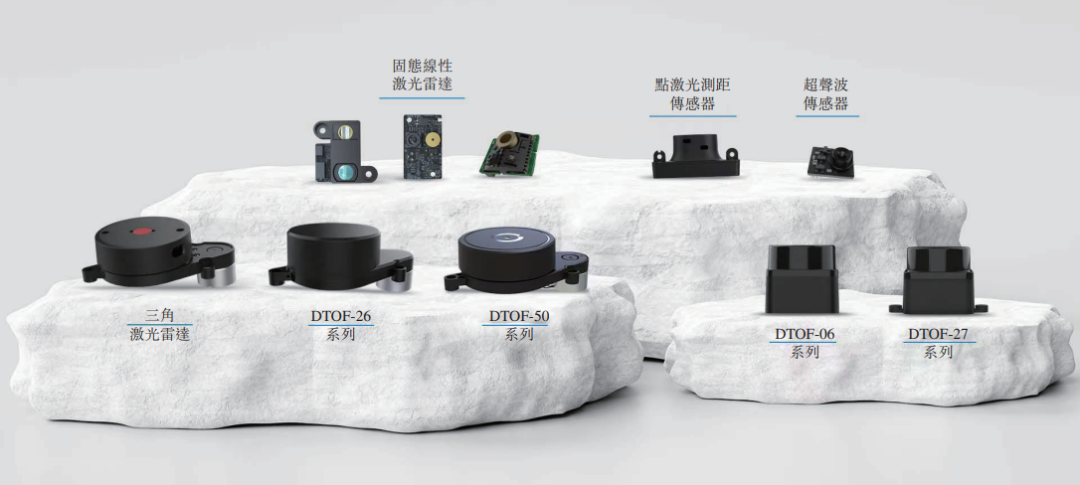
Visual Perception Robotics Company Ledong Robotics Files for Hong Kong IPO, Previously Backed by Alibaba CEO: Shenzhen Ledong Robot Co., Ltd. has submitted its prospectus for a Hong Kong IPO, with an estimated market capitalization exceeding HK$4 billion. The company focuses on visual perception technology, with main products including DTOF LiDAR, triangulation LiDAR sensors, and algorithm modules, and has launched robotic lawnmowers. Ledong Robotics collaborates with seven of the top ten global home service robot companies and the top five global commercial service robot enterprises. From 2022 to 2024, the company’s revenues were 234 million, 277 million, and 467 million RMB, respectively, with a compound annual growth rate of 41.4%. However, it remains in a loss-making state, though net losses have been narrowing annually. Its investors include Yuanjing Capital, founded by Alibaba CEO Eddie Wu Yongming, and Huaye Tiancheng, founded by former Huawei executives (Source: 36Kr)

🌟 Community
AI Agent Architecture Discussion: Software Engineering Perspective vs. Social Coordination Perspective: In discussions about Multi-Agent Systems, Omar Khattab suggests they should be viewed as AI software engineering problems rather than complex social coordination problems. He argues that by defining contracts between modules and controlling information flow, efficient systems can be built without simulating an “agent society” with conflicting goals. The key lies in well-designed system architecture and highly structured module contracts. However, he also notes that many architectural decisions depend on transient factors like current model capabilities (e.g., context length, task decomposition ability). Therefore, there’s a need to develop programming/query languages that can decouple intent from underlying implementation techniques, similar to how compilers optimize modular code in traditional programming. This viewpoint emphasizes the importance of system architecture and modular programming in AI Agent design, rather than overemphasizing free interaction and goal alignment among agents (Source: lateinteraction)
AI Model Optimizer Discussion: Muon Optimizer Gains Attention, AdamW Remains Mainstream: Community discussion about AI model optimizers is heating up, especially regarding the Muon optimizer proposed by Keller Jordan. Yuchen Jin pointed out that Muon, solely based on a blog post, helped Jordan join OpenAI and might be used for GPT-5 training, emphasizing that real-world impact is more important than top conference papers. He mentioned Muon’s superior scalability over AdamW on NanoGPT. However, hyhieu226 believes that despite thousands of optimizer papers, actual SOTA (State-of-the-Art) improvements have only progressed from Adam to AdamW (others mostly being implementation optimizations), so such papers should no longer receive excessive attention, and there’s no need to specifically cite AdamW’s origin. This reflects the tension between academic research and practical application effectiveness, as well as differing community views on progress in the optimizer field (Source: Yuchenj_UW, hyhieu226)
Claude Model Usage Tips and Discussion: Context Management, Prompt Engineering, and Agent Capabilities: Extensive community discussions revolve around usage tips and experiences with the Claude series models (Sonnet, Opus, Haiku). Users have found that avoiding automatic context compression (auto-compact), actively managing context (e.g., writing steps into claude.md or GitHub issues), and exiting/restarting sessions when 5-10% of the context remains can significantly extend Max subscription usage and improve results. Claude Code, as a CLI Agent tool, is favored for its high cost-effectiveness (with subscription), local execution, IDE integration, and MCP/tool calling capabilities, especially when using the Sonnet model. Users shared how meticulously designed prompts (e.g., multi-sub-agent parallel analysis prompts for security review tasks) can leverage Claude Code’s powerful Agent capabilities. The community also discussed Claude model’s hallucination issues in large codebases and its pros and cons compared to other models like Gemini on different tasks. For instance, some users believe Gemini 2.5 Pro is better for general conversation and argumentation, while Claude leads in coding and Agent tasks (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, jackclarkSF, swyx)

AI’s Growing Role in Programming Sparks Reflection on CS Career Prospects and Engineering Workflows: Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella stated that 20-30% of his company’s code is written by AI, and Mark Zuckerberg predicted that half of Meta’s software development (especially for Llama models) will be done by AI within a year, sparking discussions about the future of Computer Science (CS) majors. Commentators believe that although AI-assisted coding is increasingly common, CS is much more than just coding, and senior engineers achieve a higher ROI using AI. Many developers indicate that AI currently serves mainly as an efficiency tool, assisting with code generation and debugging, but still requires human guidance and review, especially for complex systems and understanding requirements. The application of AI in programming is prompting developers to consider how to use AI to improve efficiency rather than be replaced by it, while also reflecting on AI’s role and limitations throughout the software engineering lifecycle (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, cto_junior)
AI Ethics and Societal Impact: From AI “Taking” Gaokao to Fears of AI “Enslaving” Humanity: AI “participating” in the Gaokao (college entrance exam) and solving complex math problems demonstrates its potential in education, such as personalized tutoring and intelligent grading, but also raises concerns about over-reliance on AI, “assembly-line” classrooms, and a lack of emotional interaction. Deeper discussions touch upon whether AI’s “usefulness” could be a “Trojan horse,” leading humans to voluntarily relinquish autonomy for convenience and pleasure, resulting in “happy enslavement.” Some argue that AI’s “obedient” nature might exacerbate users’ cognitive biases. These discussions reflect public’s deep concern about the ethical, societal structure, and individual autonomy impacts of rapid AI technological development (Source: 36Kr, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

Gaming Godfather John Carmack on LLMs and the Future of Gaming: Interactive Learning is Key, Current LLMs Are Not the Future of Gaming: Id Software co-founder John Carmack shared his views on AI applications in gaming. He believes that despite LLMs’ remarkable achievements, their characteristic of “knowing everything yet learning nothing” (based on pre-training rather than real interactive learning) is not the future of game AI. He emphasizes the importance of learning through interactive experience streams, similar to how humans and animals learn. Carmack recalled DeepMind’s Atari project, noting that while it could play games, its data efficiency was far inferior to humans. He believes current AI still needs to address continuous, efficient, lifelong, multi-task online learning in a single environment. He also mentioned his physical robot experiments with Atari games, highlighting the complexities of real-world interaction (such as latency, robot reliability, score reading). He argues that AI needs to develop an “intuition” for strategy feasibility, not just pattern matching, to truly rival human players or play a larger role in game development (Source: 36Kr)

💡 Other
Surge in AI Research Papers Raises Quality Concerns; Public Datasets and AI Tools May Fuel “Paper Mills”: Science reports a surge in low-quality papers based on large public datasets like the US NHANES, especially after the popularization of AI tools (like ChatGPT) in 2022. Researchers found many papers follow simple “formulas,” mass-producing “new findings” by permuting variables, exhibiting “p-value hacking” and selective data analysis. For example, after correcting 28 NHANES-based depression studies, over half of the “findings” might just be statistical noise. This phenomenon, dubbed the “research fill-in-the-blanks game,” may be linked to paper mills using AI for rapid paper production. The academic community calls for journals to strengthen reviews, develop AI text detection tools, and reform quantity-oriented research evaluation systems to curb the proliferation of “junk papers” (Source: 36Kr)

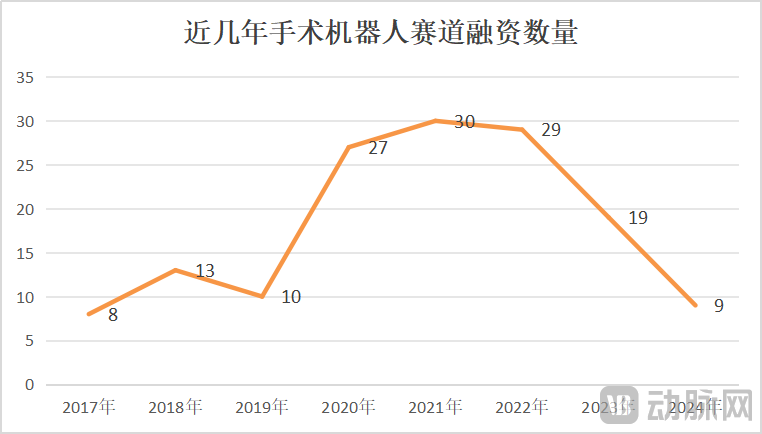
Surgical Robot Market Sees Growth and Crisis Coexist; Technological Innovation and Market Expansion are Key: From January to May 2025, the number of surgical robot bids won in China increased by 82.9% year-on-year. While the market appears hot, events like CMR Surgical seeking a sale and the bankruptcy of a domestic vascular interventional surgical robot company also reveal an industry crisis. Crises include: high industry involution with fierce competition in various sub-sectors; sharp decline in financing, with uncommercialized enterprises facing funding difficulties; limited clinical value of some products, only applicable to simple lesions; price wars emerging in the market, but low prices do not necessarily mean high volume, as hospitals prioritize performance and quality; commercialization heavily influenced by policies (such as anti-corruption in medicine) and the macroeconomic environment. To break through, companies are seeking breakthroughs through technological innovation (integrating AI, reducing costs, 5G + remote surgery, expanding indications, challenging highly difficult surgical procedures), accelerating overseas expansion, and penetrating county-level hospitals (Source: 36Kr)
Perplexity’s User Recommendation Declines Due to Model Performance and Competitor Feature Enhancements: User Suhail stated that Perplexity’s simplicity, formatting, and other features are unique and particularly suitable for users focused on search/Q&A rather than general chat products. However, in another comprehensive AI tool review, Perplexity was deemed not cost-effective and no longer recommended (unless with special discounts) due to its weaker proprietary model, offering other well-known models mostly in cheaper versions (e.g., o4 mini, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Sonnet 4, without o3 or Opus), poorer performance compared to native models, and enhanced deep search capabilities in competing products like ChatGPT and Gemini (Source: Suhail, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
