Keywords:Quantum computing, Autonomous driving, Large language models, 3D generative models, AI tools, Machine learning, Artificial intelligence research, CUDA-Q quantum computing platform, Waymo autonomous driving data research, Claude multi-agent system, Tencent Hunyuan 3D 2.1, AI-generated core performance optimization
🔥 Focus
NVIDIA Launches CUDA-Q Platform for Quantum Computing: NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang announced the launch of CUDA-Q, a quantum-classical accelerated supercomputing platform, during his GTC Paris speech. The platform aims to bridge the gap between current classical computing and future quantum computing, allowing quantum operations to be simulated on classical computers or assisting real quantum computers. CUDA-Q is now available on Grace Blackwell and can accelerate development speeds by 1300 times via the GB200 NVL72 supercomputer. Huang predicted that practical applications of quantum computers will be realized within a few years and emphasized that during this development phase, NVIDIA chips (especially the GB200) are indispensable for simulation computing and assisting QPUs. NVIDIA is collaborating with global quantum computing companies and supercomputing centers to explore the synergistic work of GPUs and QPUs (Source: 量子位)
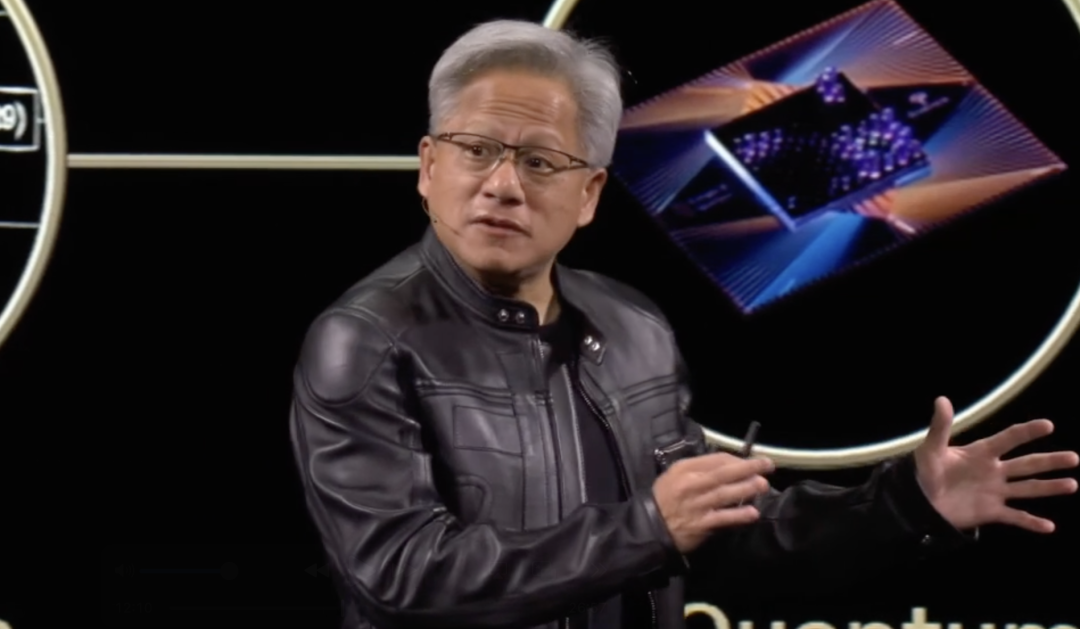
Waymo Releases Large-Scale Autonomous Driving Study, Revealing “Data-Driven” Performance Improvement Patterns: In its latest blog post, Waymo shared comprehensive research findings based on 500,000 hours of driving data, the largest dataset in the autonomous driving field to date. The study shows that, similar to Large Language Models (LLMs), the motion prediction quality of autonomous driving systems also follows a power-law relationship with increasing training computation. Scaling data size is crucial for improving model performance, while expanding inference computation capabilities can also enhance the model’s ability to handle complex driving scenarios. This research, for the first time, confirms that significantly improving real-world autonomous driving performance can be achieved by increasing training data and computational resources, pointing the industry towards a path of capability enhancement through scale (Source: Sawyer Merritt, scaling01)
Anthropic Shares Experience Building Claude’s Multi-Agent Research System: Anthropic detailed in its engineering blog how it built Claude’s research capabilities using multiple agents working in parallel. The article shares successes, problems encountered, and engineering challenges during the development process. This multi-agent system allows Claude to retrieve, analyze, and synthesize information more effectively, thereby enhancing its ability to research and answer complex questions. This sharing is valuable for understanding how large language models can expand their functionality through complex system design (Source: ImazAngel, teortaxesTex)
Meta Introduces V-JEPA 2 World Model for Video Understanding, Prediction, and Robot Control: Meta AI has released V-JEPA 2, a world model trained on video data that has made significant progress in understanding and predicting physical world dynamics. V-JEPA 2 not only performs efficient video feature learning but can also achieve zero-shot planning and robot control in new environments, demonstrating its potential in the field of artificial general intelligence. The model learns world representations from video data through self-supervised learning, providing a new pathway for building smarter AI systems capable of interacting with the real world (Source: dl_weekly)
Paper Explores LLM Weight Self-Updating for Self-Improvement: A paper published on arXiv (2506.10943) proposes that Large Language Models (LLMs) can now achieve self-improvement by updating their own weights. This mechanism could mean LLMs can learn from new data or experiences and dynamically adjust their internal parameters to improve performance or adapt to new tasks without requiring a full retrain. If successful, this research direction would greatly enhance the adaptability and continuous learning capabilities of LLMs, marking an important step towards more autonomous AI systems (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
🎯 Trends
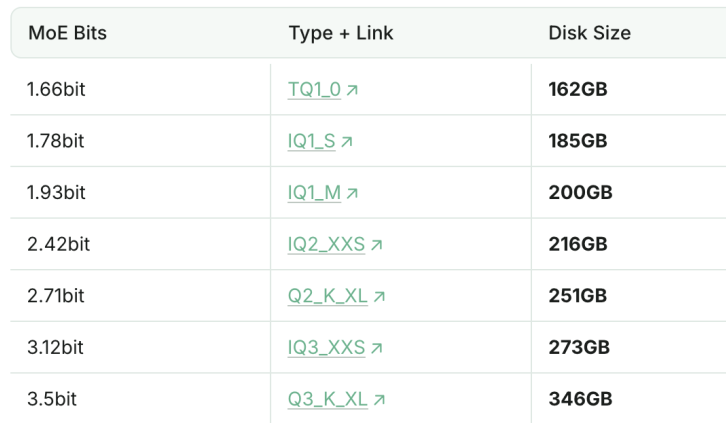
1.93bit Quantized DeepSeek-R1 Surpasses Claude 4 Sonnet in Programming Ability: Unsloth studio successfully quantized DeepSeek-R1 (0528 version) to 1.93bit, achieving a 60% score on the aider programming benchmark, surpassing Claude 4 Sonnet (56.4%) and the January full-precision R1 version. This extremely compressed version reduces file size by over 70% and can even run without a GPU (CPU with sufficient memory). The full-precision R1-0528 scored 71.4% on aider, outperforming Claude 4 Opus without its thinking mode enabled. This demonstrates the potential of model quantization technology to significantly reduce resource requirements while maintaining performance (Source: 量子位)
Tencent Hunyuan Open-Sources First Production-Level PBR 3D Generation Model Hunyuan 3D 2.1: The Tencent Hunyuan team announced the open-sourcing of Hunyuan 3D 2.1, the industry’s first fully open-source, production-level PBR (Physically Based Rendering) 3D generation model. This model utilizes PBR material synthesis technology to generate 3D content with film-grade visual effects, making materials like leather and bronze appear more vivid and realistic under lighting. The project has released model weights, training/inference code, data pipelines, and architecture, and supports running on consumer-grade graphics cards, aiming to promote the development and popularization of 3D content generation technology (Source: op7418, ImazAngel)
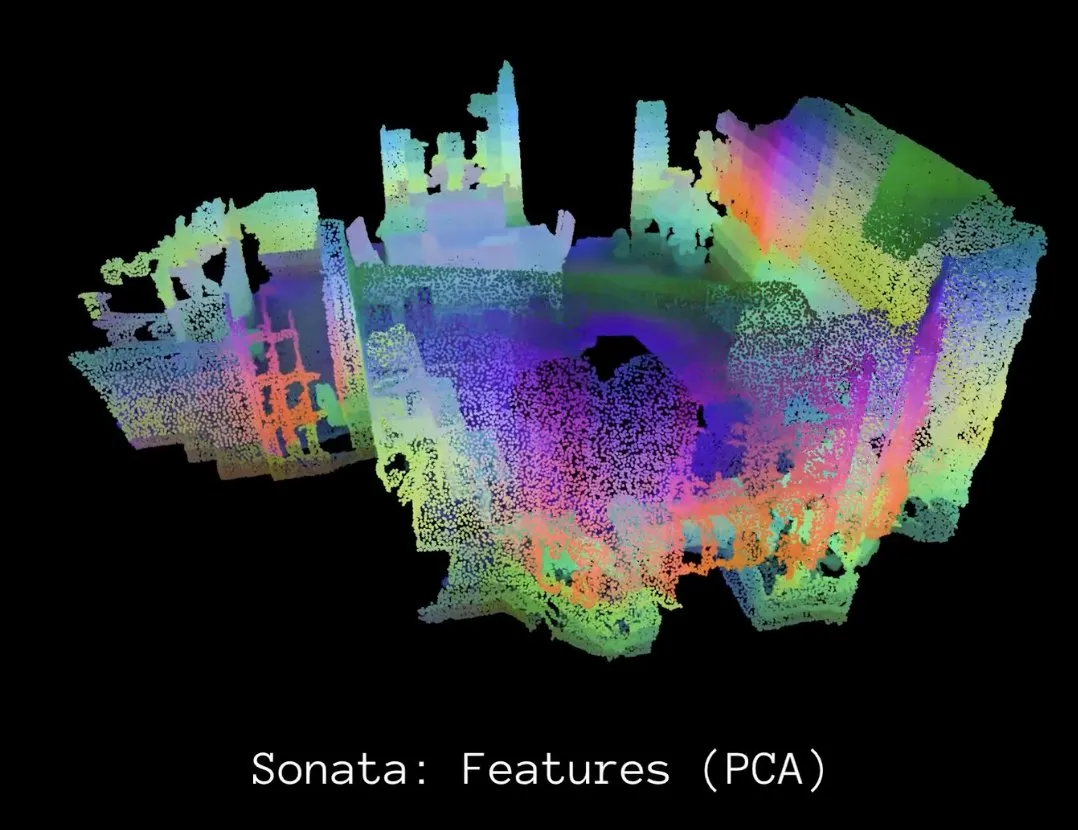
Meta AI Releases Sonata, Advancing Self-Supervised Learning for 3D Point Cloud Representation: Meta AI has introduced Sonata, a study marking significant progress in the field of 3D self-supervised learning. Sonata learns exceptionally robust 3D point cloud representations by identifying and addressing geometric shortcut issues and introducing a flexible and efficient framework. This work elevates the current state of 3D perception technology and lays the foundation for future innovations in 3D perception and its applications (Source: AIatMeta)

Meta AI Releases “Reading Recognition in the Wild Dataset” for Understanding Reading Behavior: Meta AI has publicly released a large multimodal dataset called “Reading Recognition in the Wild,” which includes video, eye-tracking, and head pose sensor outputs. The dataset aims to help solve reading recognition tasks from wearable devices and is the first egocentric dataset to collect eye-tracking data at a high frequency of 60Hz, providing valuable resources for studying human reading behavior (Source: AIatMeta)

Apple Simplifies MLX Swift LLM API, Load Models in Three Lines of Code: Addressing developer feedback about the difficulty of getting started with the MLX Swift LLM API, the Apple team quickly made improvements and launched a new simplified API. Now, developers can load an LLM or VLM and start a chat session in their Swift projects with just three lines of code, significantly lowering the barrier to using large language models within the Apple ecosystem (Source: stablequan)
Google Gemma3 4B Launches GAIA, Optimized for Brazilian Portuguese: Google, in collaboration with several Brazilian institutions (ABRIA, CEIA-UFG, Nama, Amadeus AI) and DeepMind, has released GAIA (Gemma-3-Gaia-PT-BR-4b-it), an open-source language model optimized for Brazilian Portuguese. The model is based on Gemma-3-4b-pt and underwent continued pre-training on 13 billion high-quality Brazilian Portuguese tokens. GAIA employs an innovative “weight merging” technique for instruction following, eliminating the need for traditional SFT, and surpassed the base Gemma model on the ENEM 2024 benchmark. The model is suitable for chat, Q&A, summarization, text generation, and as a base model for fine-tuning in Brazilian Portuguese (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Figure AI Robots Integrate Helix AI and Autonomy to Drive Scalable Deployment: Figure AI showcased how its real-world robots are driving scalable deployment through enhanced Helix AI and autonomy. This indicates that the combination of physical robots and advanced AI models is making robot applications in more complex environments possible, highlighting the importance of engineering and emerging technologies in the robotics field (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
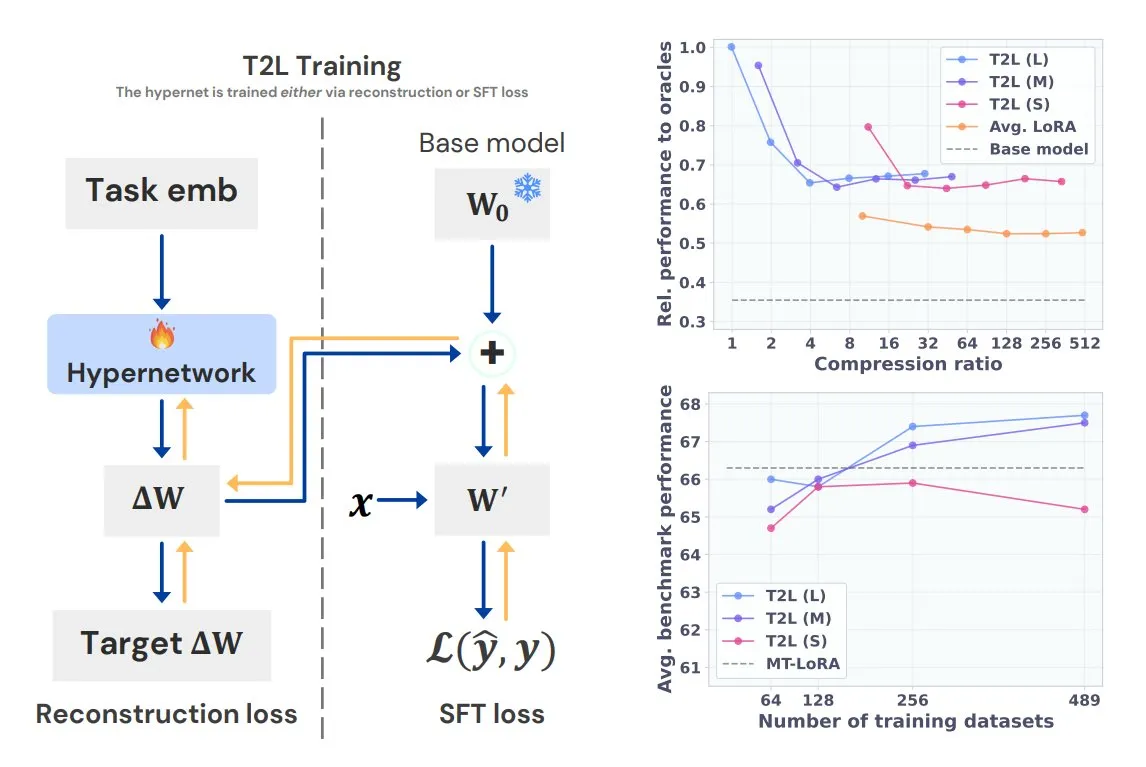
Sakana AI Introduces Text-to-LoRA (T2L) Hypernetwork: Sakana AI has released Text-to-LoRA (T2L), a novel hypernetwork capable of compressing multiple existing LoRAs (Low-Rank Adaptations) into itself and rapidly generating new LoRA adapters for large language models solely from a textual description of the task. Once trained, T2L can create new LoRAs instantly, providing an efficient pathway for rapid customization and deployment of task-specific LLMs. The results will be presented at ICML 2025 (Source: TheTuringPost)
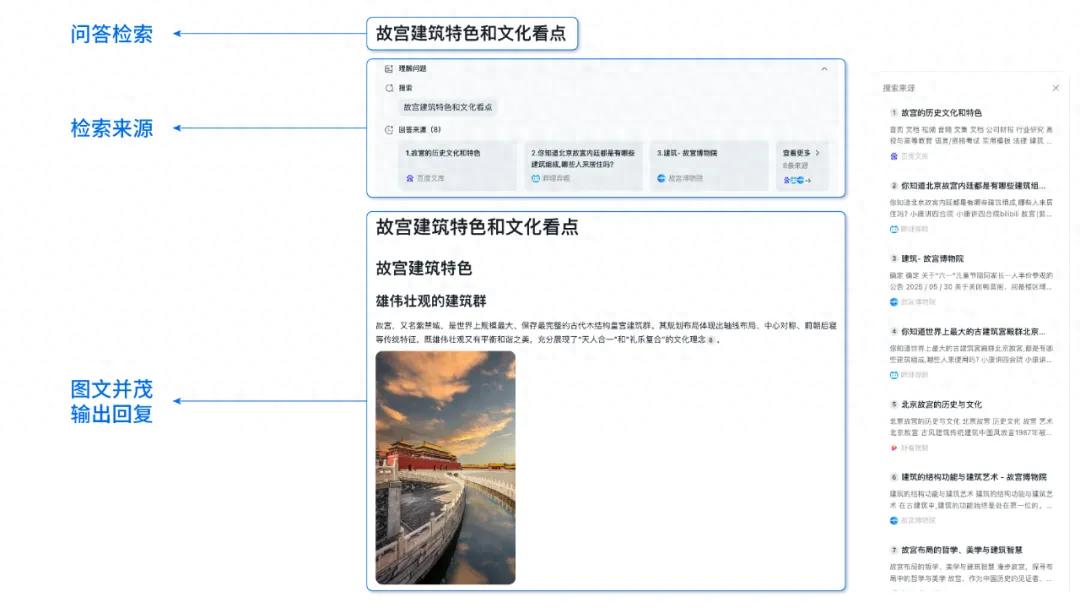
Baidu AI Search Fully Launched on Baidu AI Cloud Qianfan Platform: Baidu AI Cloud’s Qianfan AppBuilder application development platform has officially launched the “Baidu AI Search” service. This service integrates “Baidu Search” and “Intelligent Search Generation,” two core capabilities, to provide enterprises with a full-chain service from information retrieval to intelligent generation. It leverages Baidu’s over 20 years of Chinese search technology and a petabyte-scale database to offer ad-free, multimodal search results, supporting precise filtering, source tracing, and enterprise-level security policies. The intelligent search generation capability, combined with models like Ernie and Deepseek, provides features such as AI summarization and federated search over private knowledge (Source: 量子位)
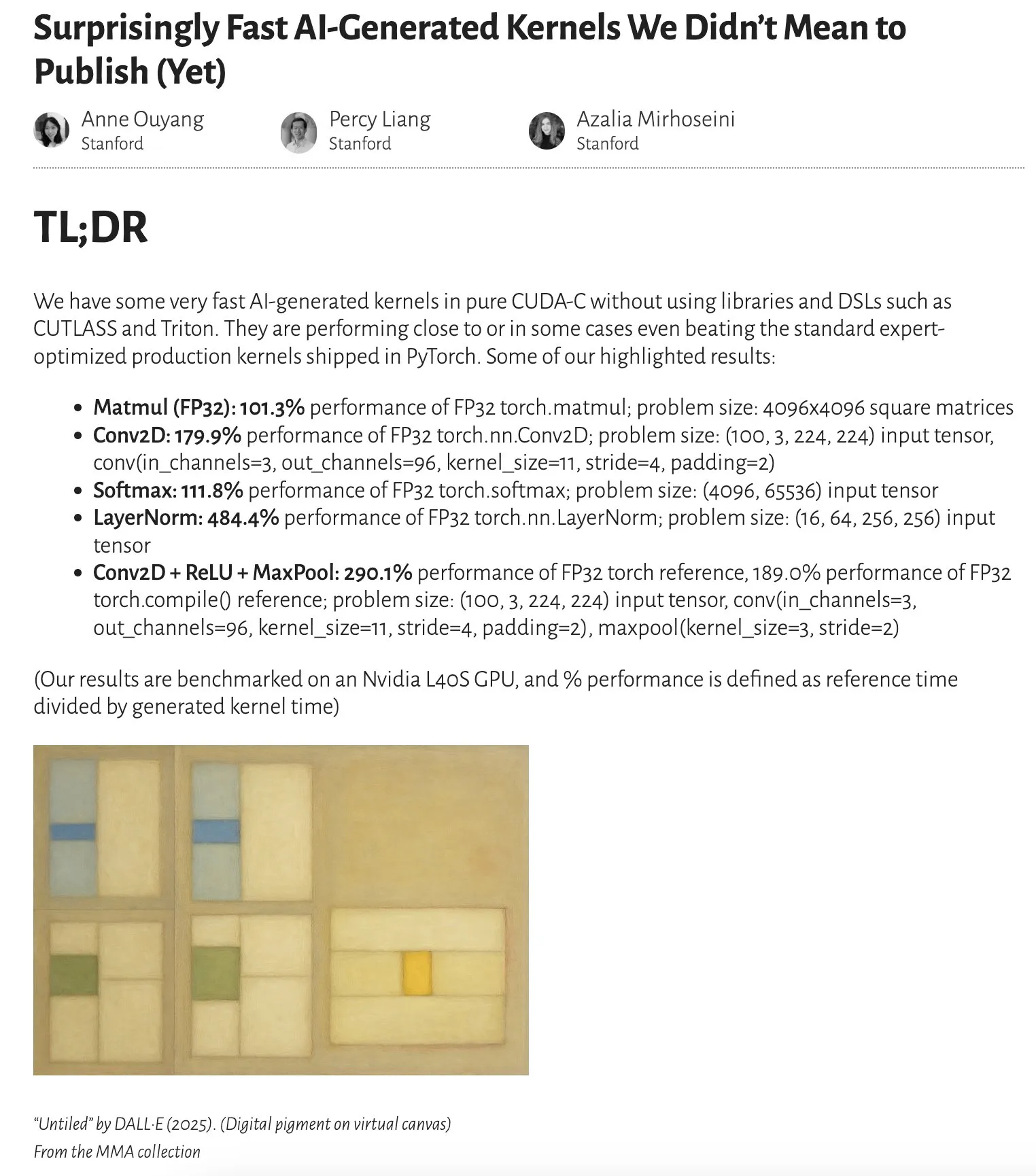
Research Shows AI-Generated Kernels Perform Close to or Even Surpass Expert-Optimized Kernels: Anne Ouyang’s blog post points out that AI-generated kernels, through simple test-time only search, have achieved performance close to, and in some cases surpassing, standard expert-optimized production kernels in PyTorch. This indicates the immense potential of AI in code optimization and performance improvement, suggesting it may play a more significant role in optimizing low-level libraries in the future (Source: jeremyphoward)
“Diffusion Duality” Study Proposes New Method for Few-Step Generation in Discrete Diffusion Language Models: A paper titled “The Diffusion Duality,” presented at ICML 2025, proposes a new method for achieving few-step generation in discrete diffusion language models by leveraging latent Gaussian diffusion. This method outperforms autoregressive (AR) models on 3 out of 7 zero-shot likelihood benchmarks, offering a new approach to improving the generation efficiency of diffusion models (Source: arankomatsuzaki)
New Breakthrough in MLP Layer Interpretability: Decomposing Activations into Interpretable Features: New research by Mor Geva et al. demonstrates a simple method to decompose activations in Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) into interpretable features. This method reveals a hidden conceptual hierarchy where sparse combinations of neurons form increasingly abstract concepts, providing a deeper perspective on understanding the internal workings of neural networks (Source: menhguin)

HeadHunter Framework Enables Fine-Grained Control over Perturbed Attention Guidance: Sayak Paul et al. proposed the HeadHunter framework for a principled analysis of perturbed attention guidance. This framework allows for deep, fine-grained control over generation quality and visual attributes, providing new tools and insights for improving and customizing the output of generative models (Source: huggingface, RisingSayak)

🧰 Tools
Windsurf Paid Plans Now Support Claude Sonnet 4: Windsurf announced that all its paid plans now include the Claude Sonnet 4 model. Users can now leverage the powerful capabilities of Anthropic’s latest model on the Windsurf platform for tasks such as text generation and conversation, further enhancing the performance and experience of AI assistants (Source: op7418)
Anthropic Releases Official Python SDK for Claude Code: Anthropic has officially launched a Python SDK for Claude Code, designed to make it easier for developers to integrate Claude’s code generation and tool use capabilities into their Python projects. The SDK supports tool use, streaming output, synchronous/asynchronous operations, file handling, and has a built-in chat structure, simplifying the development process for interacting with Claude Code (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Claude Task Master VS Code Extension Released: DevDreed has released version 1.0.0 of the Claude Task Master VS Code extension. This extension is designed to complement eyaltoledano’s Claude Task Master AI project by integrating Claude Task Master’s output directly into the VS Code interface, allowing users to seamlessly switch between the editor and console, thereby improving development efficiency (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
SmartSelect AI: In-Browser Text and Image AI Processing Tool: A Chrome extension called SmartSelect AI has been released, allowing users to directly summarize, translate, or chat with selected text, and get AI descriptions for images while browsing the web, without switching tabs or copying/pasting to external applications like ChatGPT. The tool is based on the Gemini model and aims to improve information acquisition and processing efficiency (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)

Unsiloed AI Open-Sources Versatile Data Chunking Tool: Unsiloed AI (EF 2024) has open-sourced part of its data chunker functionality. The tool is designed to help process documents in various formats such as PDF, Excel, and PPT, converting them into a format suitable for large language models. Unsiloed AI has been used by Fortune 100 companies and several startups for multimodal data ingestion (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Claude Superprompt System: Free Tool for Optimizing Claude Prompts: Igor Warzocha developed and shared an online tool called “Claude Superprompt System,” designed to help users transform simple requests into structured, complex prompts containing chains of thought and contextual examples to better leverage Claude’s capabilities. The tool is based on Anthropic’s official documentation and community-discovered best practices, optimizing prompts through XML tag structuring, CoT reasoning blocks, and other methods to improve Claude’s output quality. The project code is open-sourced on GitHub (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Local TTS Firefox Plugin Kokoro-TTS Released: Developer Pinguy has released a Firefox plugin called Kokoro TTS, which uses an 82M parameter locally hosted neural network model (Kokoro TTS model) for text-to-speech. It runs entirely offline, protecting user privacy. It supports multiple voices and accents and runs smoothly even on older hardware, with versions available for Windows, Linux, and macOS (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Spy Search: Open-Source LLM Search Engine Project Update: JasonHonKL has updated his open-source LLM search engine project, Spy Search. The project aims to build an efficient search engine based on large language models, with the latest version capable of searching and responding within 3 seconds. The project code is hosted on GitHub and aims to provide users with a fast and useful daily search tool (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
HandFonted: Handwriting-to-Font Tool Open-Sourced: Resham Gaire developed and open-sourced the HandFonted project, an end-to-end Python application that converts images of handwritten characters into installable .ttf font files. The system utilizes OpenCV for image processing and character segmentation, a custom PyTorch model (ResNet-Inception) for character classification, the Hungarian algorithm for optimal matching, and finally, the fontTools library to generate the font file (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
📚 Learning
Paper by Wei Dongyi et al. Tops Mathematics Journal, Studying Blow-up Phenomenon of Supercritical Defocusing Nonlinear Wave Equation: A paper titled “On blow-up for the supercritical defocusing nonlinear wave equation” by Peking University scholars Wei Dongyi, Zhang Zhifei, and Shao Feng was published in the top mathematics journal “Forum of Mathematics, Pi.” The research explores the blow-up (solution becomes infinite in finite time) problem for a specific defocusing nonlinear wave equation in the supercritical state. They proved the existence of smooth complex-valued solutions that blow up in finite time for spatial dimension d=4 and p≥29, and for d≥5 and p≥17. This achievement fills a gap in the related field, and its proof method provides new ideas for blow-up research in other nonlinear partial differential equations (Source: 量子位)

Paper Explores Universality of Linear Properties in Large Language Model Representations: Research by Emanuele Marconato et al., “All or None: Identifiable Linear Properties of Next-token Predictors in Language Modeling” (published at AISTATS 2025), explores from an identifiability perspective why linear properties are so prevalent in the representations of Large Language Models (LLMs). This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the structure and behavior of internal representations in LLMs (Source: menhguin)
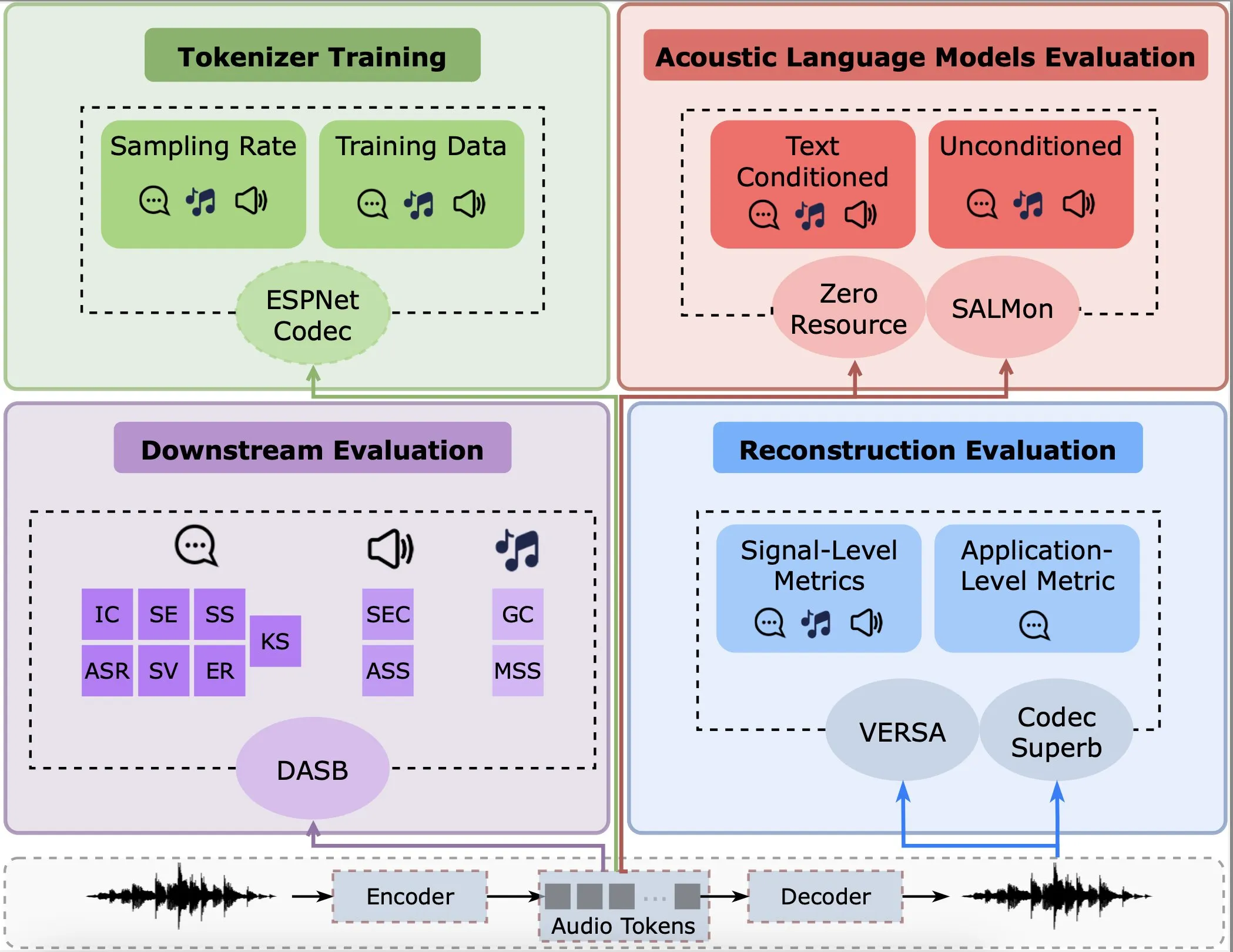
Study Analyzes Performance of Audio Encoders in Reconstruction, Downstream Tasks, and Language Models: Gallil Maimon et al. published new research conducting a comprehensive empirical analysis of existing audio encoders (Audio Tokenisers). The study evaluates these encoders from multiple dimensions, including reconstruction quality, performance in downstream tasks, and integration with language models, providing a reference for selecting and optimizing audio processing models (Source: menhguin)
Paper Discusses “Illusion of Thought”: Understanding Reasoning Model Strengths and Weaknesses from Problem Complexity Perspective: A response paper (arXiv:2506.09250) to Apple’s “Illusion of Thought” research has been submitted, listing Claude Opus as the first author. The paper criticizes the experimental design of Apple’s study and argues that the observed reasoning collapse is actually due to token limitations rather than an inherent lack of logical ability in the models. This has sparked a discussion on how to evaluate the true reasoning capabilities of large language models (Source: NandoDF, BlancheMinerva, teortaxesTex)

Research Explores Adaptive Language Models, but Medium-Term Memory Remains a Challenge: After studying papers on “adaptive language models,” Dorialexander pointed out that while it is a promising research direction, models still have limitations in achieving medium-term memory during reasoning. This indicates that current models still face challenges in processing coherent information that spans longer contexts (Source: Dorialexander)

RLHF Test Quality Research: How Good Are Current Tests? How to Improve Them? How Important is Test Quality?: Recent work by Kexun Zhang et al. explores the importance of validators (tests) in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), especially in the LLM coding domain. The research poses three key questions: How good is the quality of current tests? How can we obtain better tests? How much does test quality affect model performance? The study emphasizes the necessity of high-quality tests for enhancing LLM coding capabilities (Source: StringChaos)
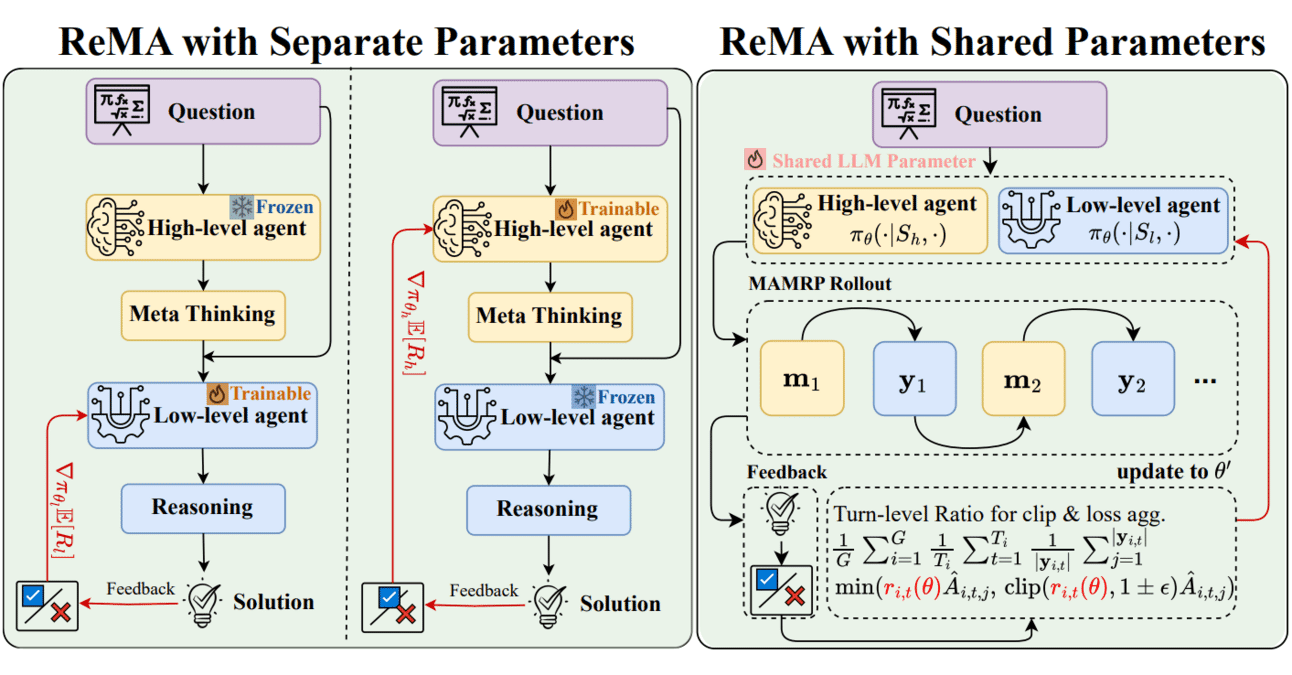
Meta-learning Combined with Reinforcement Learning: ReMA Enhances LLM Collaboration Efficiency: Reinforced Meta-thinking Agents (ReMA) combine Meta-learning and Reinforcement Learning (RL) to improve the efficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs), especially when multiple LLM agents work collaboratively. ReMA divides problem-solving into meta-thinking (planning strategy) and reasoning (executing strategy) and optimizes them through specialized agents and multi-agent reinforcement learning, achieving improvements on both mathematical benchmarks and benchmarks judged by LLMs (Source: TheTuringPost, TheTuringPost)
AI Evaluation Strategy: How to Combine Cheap and Expensive Evaluators Under Budget Constraints to Get the Best Model Quality Estimate: Research by Adam Fisch et al. (arXiv:2506.07949) explores a practical problem: when you have a cheap but noisy evaluator, an expensive but accurate evaluator, and a fixed budget, how should the budget be allocated to obtain the most accurate estimate of model quality? The study provides a cost-benefit analysis framework for AI system evaluation (Source: Ar_Douillard)
“Spurious Rewards” and “Spurious Prompts” Phenomena in LLM Prompting: Research by Stella Li et al. reveals interesting phenomena in LLM training and evaluation. Following the discovery of “spurious rewards” (e.g., random rewards can also improve model performance on certain tasks), they further explored “spurious prompts,” where even nonsensical text like “Lorem ipsum” can lead to significant performance improvements (e.g., 19.4%) in some cases. These findings pose new challenges and considerations for understanding how LLMs respond to prompts and how to design more robust evaluation methods (Source: Tim_Dettmers)

Paper Discusses “Puppet Theatre” Model of AI Interaction: A paper (or draft) titled “The Pig in Yellow: AI Interface as Puppet Theatre” proposes viewing language AI systems (LLMs, AGI, ASI) as performative interfaces that simulate subjectivity rather than possessing it. Using “Miss Piggy” as an analogy, the article analyzes AI’s fluency, coherence, and emotional expression not as indicators of mind, but as products of optimization, emphasizing that interfaces are like puppets, and users co-construct meaning in interaction, with power manifested through performative design (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
💼 Business
SwitchBot, Backed by “DJI Godfather” Li Zexiang, Files for IPO: SwitchBot, a company specializing in AI embodied home robots founded by alumni brothers from Harbin Institute of Technology, has submitted its prospectus for an IPO in Hong Kong. The company received investment and resource support from Li Zexiang, known as the “DJI Godfather,” who holds a 12.98% stake. Over the past decade, SwitchBot has secured seven rounds of financing, with its valuation growing from 20 million to 4 billion RMB. Its products include executive robots that simulate human limb movements and perception-decision systems. It has become the world’s largest supplier of AI embodied home robots, with a market share of 11.9%, and achieved an adjusted net profit of 1.11 million RMB in 2024 (Source: 量子位)

Tencent Launches 2026 “Qingyun Plan,” Opens Topic Resource Pool for the First Time: Tencent announced the launch of its 2026 “Qingyun Plan,” recruiting top global tech students across ten major technical fields, including AI large models, basic infrastructure, and high-performance computing, offering over a hundred technical topics. Unlike previous years, this iteration of the plan opens the Qingyun topic resource pool for the first time and provides a green channel for outstanding talent recruitment, aiming to deepen university-enterprise cooperation and cultivate young tech talent. Tencent will provide top-tier industry mentors, computing resources, and competitive salaries (Source: 量子位)

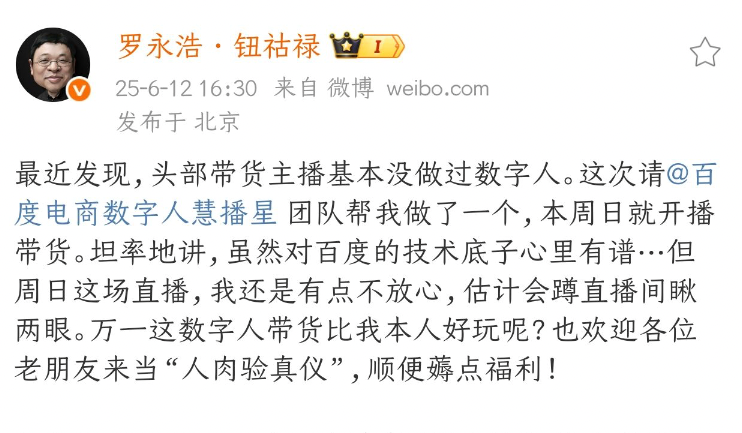
Luo Yonghao’s Digital Human to Debut on Baidu E-commerce on June 15th: Luo Yonghao announced that his AI digital human avatar will make its live streaming debut on the Baidu e-commerce platform on June 15th. This marks the first time a top-tier influencer has used an AI digital human for live commerce, thanks to Baidu’s breakthroughs in key technologies like highly persuasive digital humans. This move is seen as an exploration of a new “AI + Top IP” e-commerce paradigm, expected to drive the live e-commerce industry towards intelligence, efficiency, and lower costs. Baidu e-commerce data shows that over 100,000 digital human streamers are already being used across various industries, significantly reducing merchants’ operational costs and increasing GMV (Source: 量子位)
🌟 Community
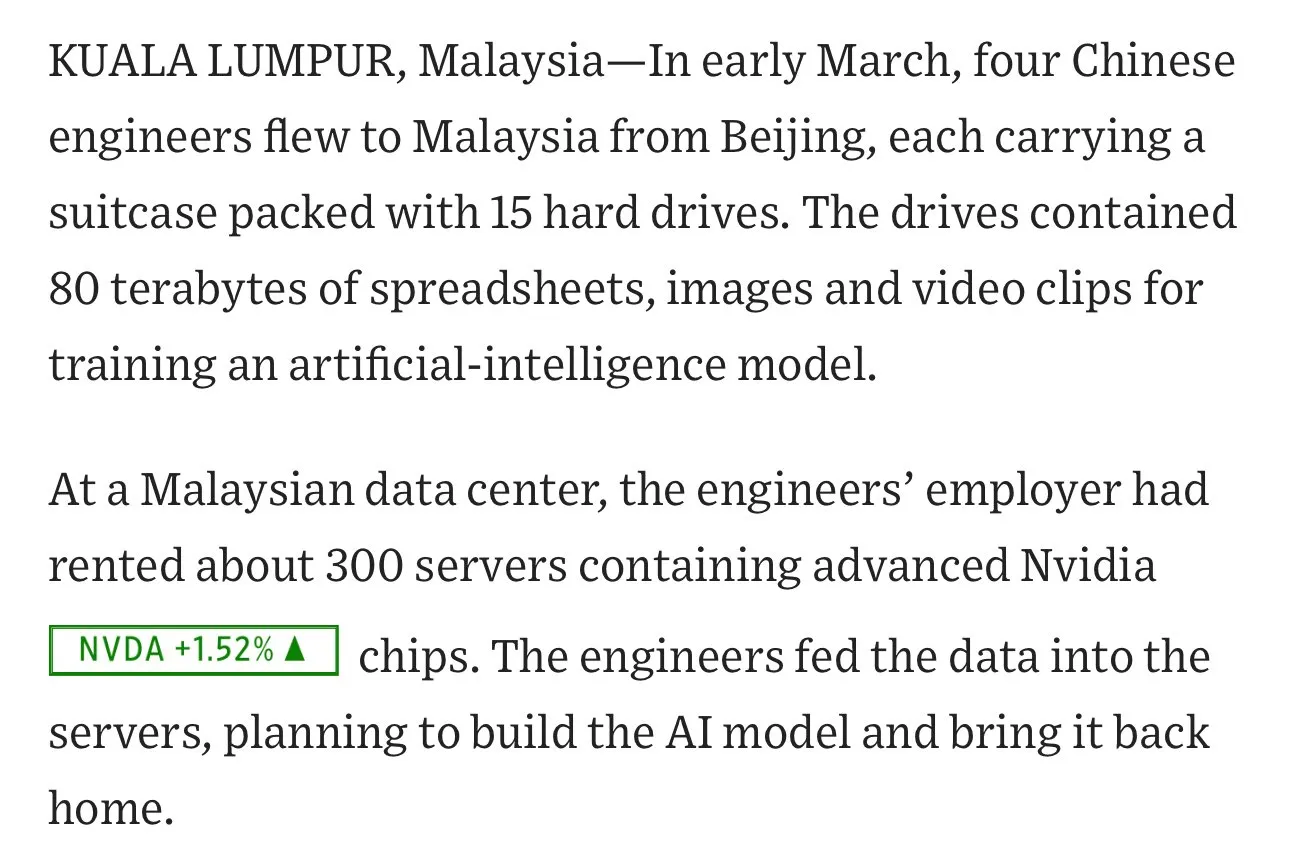
Chinese AI Companies Ship Large Quantities of Data Hard Drives to Malaysia for Model Training: NIKKEI reports that Chinese AI companies, to circumvent chip restrictions and utilize overseas computing resources, have resorted to strategies like “physically carrying” hard drives full of training data to places like Malaysia. For example, an engineer reportedly flew to Malaysia with 15 hard drives containing 80TB of data to rent servers for model training. This phenomenon reflects the intense global competition for AI computing power and the practical challenges of cross-border data flow, while also raising discussions about data security and compliance (Source: jpt401, agihippo, cloneofsimo, fabianstelzer)
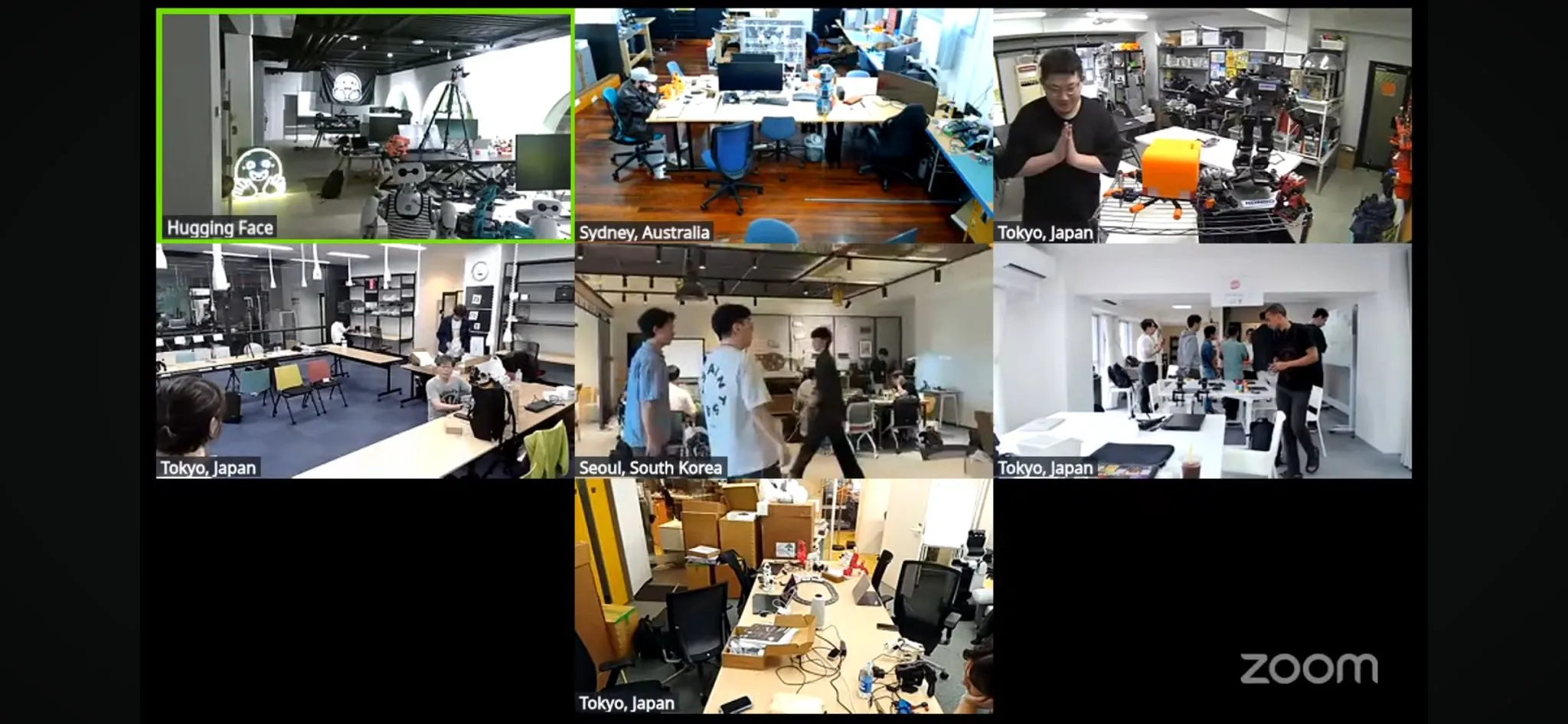
World’s Largest LeRobot Robotics Hackathon Kicks Off: The LeRobot global robotics hackathon, organized by Hugging Face, has officially started, spanning over 100 locations across 5 continents and attracting over 2,300 participants. The event aims to promote the development of open-source AI robotics, with participants engaging in robotics-related building and exploration over 52 hours. Developers and teams from various locations enthusiastically participated, sharing photos from the event and project progress, showcasing the community’s passion and creativity for robotics technology (Source: _akhaliq, eliebakouch, ClementDelangue)
Lovable Hosts AI Web Page Generation Showdown, Claude Receives Positive Feedback: Lovable hosted an event allowing users to freely use top models from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google for an AI web page generation competition. User op7418 shared their experience generating web pages using the same set of prompts across the three models, noting that Claude stood out in terms of content volume and visual appeal. Such events provide developers and users with opportunities to compare the performance of different large models in specific application scenarios (Source: _philschmid, op7418)
Discussion on AI Model Reasoning Abilities: Token Limits vs. True Logic: In response to Apple’s “Illusion of Thinking” paper, counterarguments have emerged within the community. Comments and subsequent research (such as arXiv:2506.09250, which lists Claude Opus as an author) suggest that the observed “collapse” in model reasoning ability is more due to token limitations than an inherent lack of logical capability in the models themselves. When models are allowed to use more compressed answer formats or have sufficient context, they can successfully solve problems. This has sparked an in-depth discussion about how to accurately assess and understand the true reasoning capabilities of large language models, as well as the potential limitations of current evaluation methods (Source: NandoDF, BlancheMinerva, teortaxesTex, rao2z)
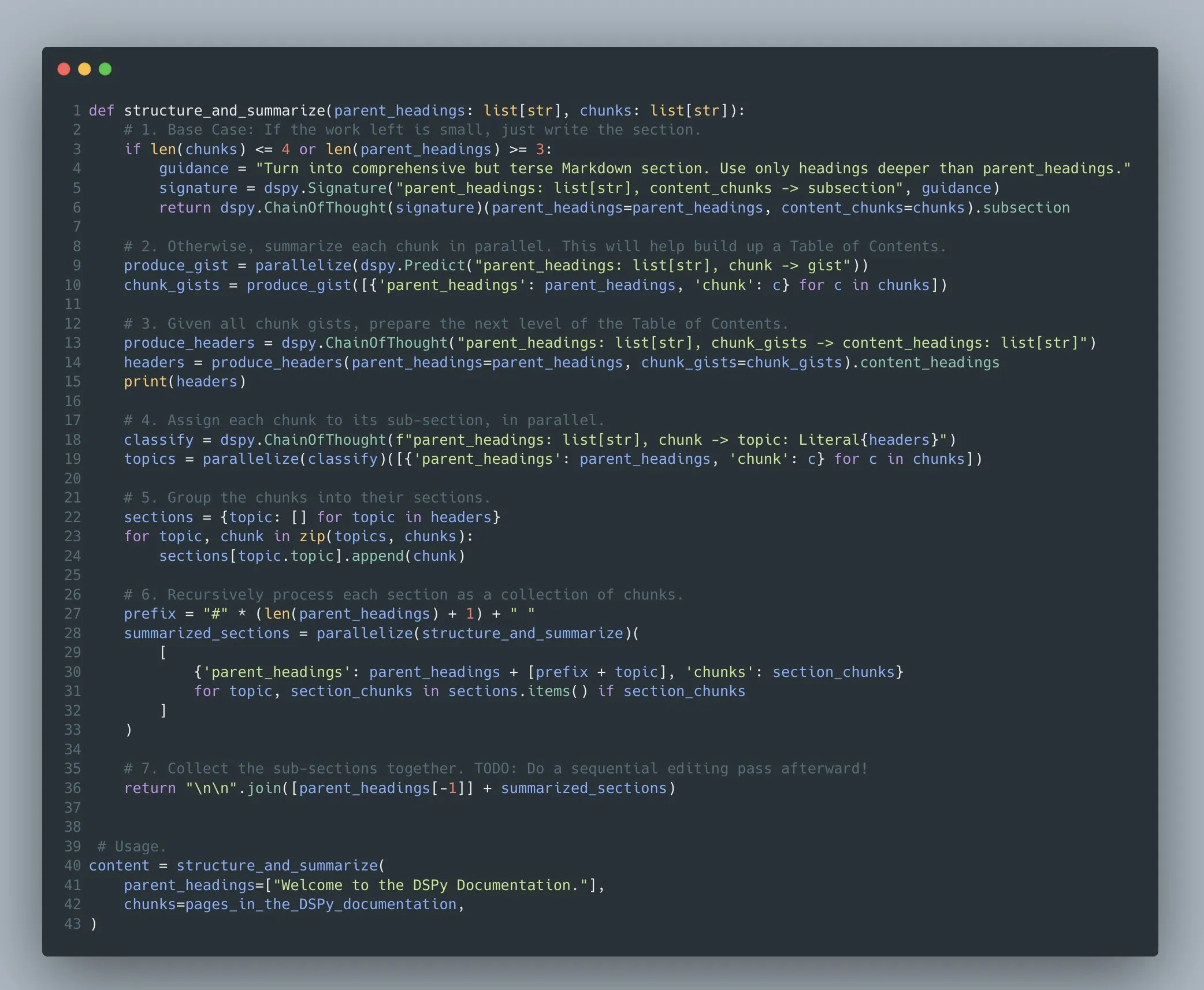
DSPy Framework Supports Optimization of Complex Multi-Stage Language Model Programs: Omar Khattab emphasized that the DSPy framework has supported prompt optimization and reinforcement learning for complex multi-stage language model programs (Compound AI Systems) since 2022/2023. He argues that as AI systems become increasingly complex, it is more appropriate to view them as “programs” rather than simple “models.” DSPy aims to provide support for building and optimizing such programs of arbitrary complexity (including recursion, exception handling, etc.), not just linear “flows” or “chains” (Source: lateinteraction)
Discussion on Whether LLMs Think Similarly to Humans: Geoffrey Hinton believes Large Language Models (LLMs) process language similarly to humans and are our best models for understanding how language works. However, Pedro Domingos questions this, arguing that LLMs being superior to older linguistic theories does not mean they think like humans. This discussion reflects the ongoing debate in the AI field regarding the nature of LLMs and their relationship to human cognition (Source: pmddomingos)
AI Shows Great Potential in Physical Science Research: A researcher in the earth sciences shared a positive experience using o3 Pro (likely referring to an advanced model from OpenAI), describing it as a “very smart postdoc” in their research. The model performed excellently in coding, model development, and idea refinement, able to execute instructions quickly and accurately and assist in research. The researcher believes that while current models do not yet possess the ability to proactively propose research questions (an AGI characteristic), their powerful auxiliary functions have significantly improved research efficiency, and they sense that LLMs with autonomy are not far off (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
💡 Other
AI Comic Generation Tools Make Creative Expression More Accessible: User StriderWriting shared their experience using AI tools to create comics, believing that AI makes it possible to turn “silly ideas” into comics. This reflects the popularization of AI in the field of creative content generation, lowering the barrier to creation and allowing more people to easily express their creativity (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)

Concerns About AI Bias: ChatGPT’s Performance on Gender Stereotypes Dissatisfies User: A female user reported that ChatGPT exhibited negative stereotypes about men in conversation. For example, when discussing work and medical issues, it assumed negative roles were male without prompting and used phrases like “men are just annoying.” The user pointed out that such lazy, gender-based stereotyping is uncomfortable and questioned whether OpenAI has rules to curb such behavior. This once again sparks discussion about biases in AI model training data and how they manifest in interactions (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
Potential and Current Limitations of AI in Objective News Reporting: A user tested OpenAI’s o3 model’s potential as an “unbiased news reporter” by prompting it to comment on the potential “unintended consequences” of various policies from the Trump and Biden administrations since 2017. While AI can generate seemingly objective analysis, its information sources, potential biases, and true depth of understanding of complex political and economic dynamics remain issues to be addressed in the future. This reflects the community’s expectation of using AI to enhance news objectivity and depth, as well as an awareness of current technological limitations (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
