Keywords:Wujie Series Large Models, RLHF New Method, Claude Gov Series Models, Large Language Models, Multimodal Fusion, Physical AGI, AI Safety, Embodied Intelligence, Emu3 Native Multimodal World Model, Jianwei Brainμ Neuroscience Model, RoboBrain 2.0 Embodied Brain, OpenComplex2 Full-Atomic Microscopic Life Model, Forked Token Reinforcement Learning
🔥 Spotlight
BAAI Conference releases “Wu Jie” series of large models, focusing on Physical AGI and multimodal fusion: At the 2025 BAAI Conference, the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI) unveiled the new “Wu Jie” series of large models, marking a shift in its research direction from the “Wu Dao” language model exploration to the broader physical world and multimodal fusion. This series includes the native multimodal world model Emu3, the world’s first brain-science multimodal general foundational model “Jianwei Brainμ”, the embodied brain RoboBrain 2.0, and the all-atom microscopic life model OpenComplex2. The release of this series of models reflects the evolutionary trend of AI from the digital world to the physical world, and from macro-understanding to micro-exploration, aiming to enable AI to perceive, understand, and interact with the physical world, solve practical problems, and promote the development of Physical AGI. The conference also brought together 4 Turing Award laureates, including Bengio, and numerous industry leaders to discuss cutting-edge topics such as AI safety, reinforcement learning, intelligent agents, and embodied intelligence (Source: QbitAI)

Qwen and Tsinghua’s LeapLab propose a new RLHF method that “surpasses the 80/20 rule”: Research by the Qwen team in collaboration with Tsinghua University’s LeapLab found that when enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large models through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), focusing on only about 20% of high-entropy “forking tokens” can achieve or even surpass the effectiveness of training with all tokens. These high-entropy tokens primarily serve logical connection functions and play a key guiding role in the reasoning process. Based on this finding, Qwen3-32B achieved SOTA results for models trained from scratch with fewer than 600B parameters on the AIME’24 and AIME’25 math competition benchmarks. This research not only improves training efficiency but also reveals the importance of high-entropy tokens for model generalization and provides new perspectives for understanding the differences between RL and SFT, as well as the specificity of LLM RL (Source: QbitAI)

Anthropic launches Claude Gov series models, exclusively for U.S. national security clients: Anthropic has released the Claude Gov series of models, customized for U.S. national security clients. These models have already been deployed in the highest-level U.S. national security agencies, with access strictly limited to personnel handling classified information. This move has sparked discussions about AI ethics and potential misuse risks, especially considering Anthropic’s previous research documented models exhibiting “survival-seeking behaviors” and “catastrophic misuse” risks. Although Anthropic claims to be an AI safety research company aiming to discover and patch vulnerabilities through testing, applying its technology to military and national security domains undoubtedly heightens public concern about AI weaponization and runaway risks (Source: AnthropicAI, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

Yann LeCun predicts current large language models will be obsolete within five years: NYU professor and Meta Chief AI Scientist Yann LeCun stated in an interview with Newsweek that current large language models (LLMs) will become obsolete within five years. He believes that existing AI systems lack the ability to understand the real world, which is their fundamental limitation. LeCun envisions future, more intelligent AI system forms, hinting at the development direction of next-generation AI technologies beyond current LLM architectures, possibly focusing more on intrinsic world representations and causal reasoning capabilities (Source: ylecun)
🎯 Trends
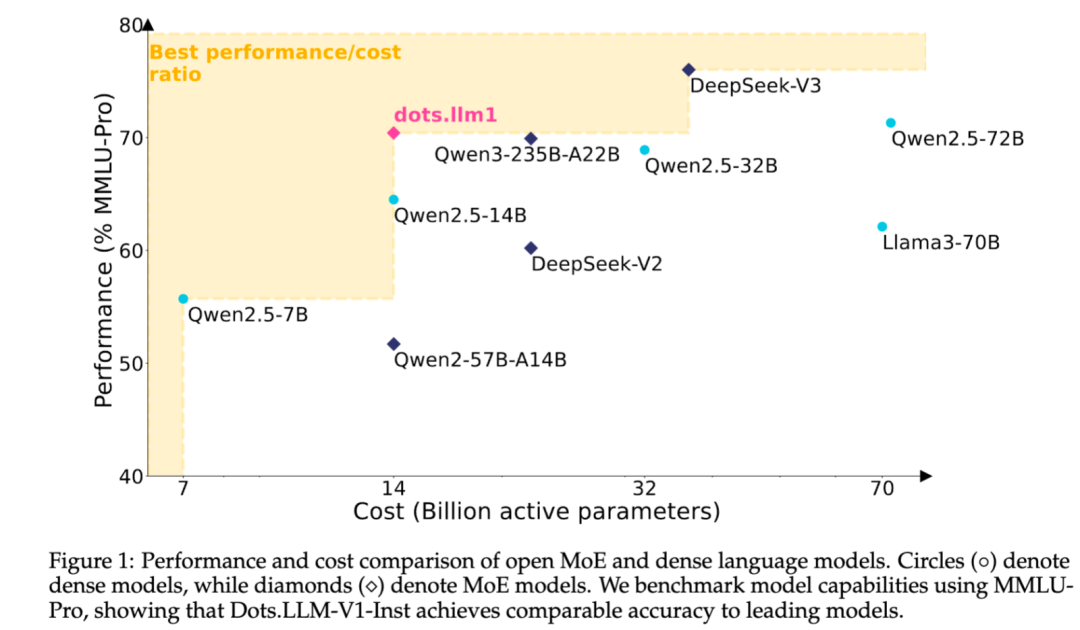
Xiaohongshu open-sources self-developed MoE text large model dots.llm1: Xiaohongshu’s hi lab team has open-sourced its first self-developed text large model, dots.llm1. The model uses an MoE architecture with a total of 142B parameters and 14B active parameters. With 14B active parameters, the model performs excellently in general Chinese and English scenarios, mathematics, code, and alignment tasks, competing with models like Qwen2.5-32B/72B-Instruct. Xiaohongshu’s open-sourcing effort is significant, providing not only the ready-to-use dots.llm1.inst model but also multiple pre-training stage checkpoints and a long-text base model, along with detailed training specifics for community secondary development and research. The model does not use synthetic corpora, emphasizing the application of high-quality real data (Source: 36Kr)
Anthropic Claude model features continue to upgrade, expanding context processing and integration capabilities: Anthropic recently rolled out several important updates for its Claude series models. Projects on Claude now support processing over 10 times more content, switching to a new retrieval mode when files exceed the threshold to expand functional context. Concurrently, Pro plan users can now utilize Research and Integrations features, allowing Claude to search the web, Google Workspace, and any custom apps or pre-built services (like Zapier and Asana) connected via MCP (Model Control Protocol), enabling cross-tool operations such as creating tasks, updating documents, and triggering workflows. These updates aim to enhance Claude’s capabilities in handling complex tasks and integrating multi-source information (Source: AnthropicAI, AnthropicAI)
Hugging Face launches MCP server, strengthening AI agent ecosystem: Hugging Face has released its first MCP (Model Control Protocol) server (hf.co/mcp), allowing AI agents to more effectively access and utilize models, datasets, and even applications hosted in Spaces on the Hugging Face platform. This initiative is seen as an important step in advancing the internet towards being agent-friendly, aiming to build an “app store” ecosystem for AI agents. The launch of the MCP server enables developers to more conveniently let AI agents interact with Hugging Face’s vast resources, promoting the development and innovation of AI agent applications (Source: TheTuringPost, karminski3)
OpenAI updates ChatGPT voice model, improving naturalness and translation capabilities: OpenAI has upgraded ChatGPT’s Advanced Voice feature, making the conversation experience more natural and fluent. This update has been rolled out to all paid users. Simultaneously, ChatGPT’s language translation capabilities have also been enhanced, allowing users to directly instruct it to perform real-time translation between different languages. These improvements aim to enhance the convenience and practicality of voice interaction with ChatGPT (Source: kevinweil, shuchaobi)
PyTorch integrates Safetensors, enhancing distributed checkpoint security and convenience: PyTorch announced that its distributed checkpoint feature now supports Hugging Face’s Safetensors format. This integration makes saving and loading model checkpoints across different ecosystems more secure and convenient, particularly addressing the security risks previously associated with the pickle format. The new API allows reading and writing Safetensors via fsspec paths, with torchtune being the first library to adopt this feature, optimizing its checkpoint process. This move is considered one of the significant advancements in AI security over the past year, helping to improve the safety of model sharing and deployment (Source: ClementDelangue, huggingface)

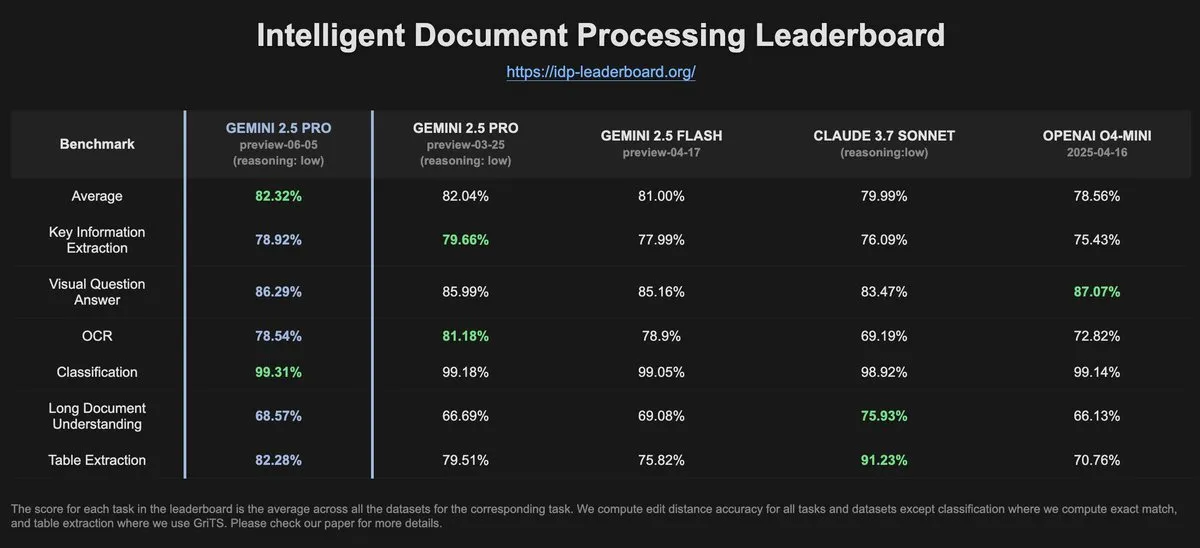
IDP-Leaderboard data shows Gemini-2.5-pro-06-05 OCR performance decreased compared to previous version: According to the latest data from IDP-Leaderboard, the new version Gemini-2.5-pro-06-05 has shown a decrease in OCR (Optical Character Recognition) performance compared to the 03-25 version. Despite this, the model still performs strongest in overall document processing capabilities (including document, spreadsheet recognition, etc.). IDP-Leaderboard is a benchmark focused on evaluating the capabilities of large models in the field of intelligent document processing (Source: karminski3)
Apple research reveals LLM reasoning limitations, may not be truly “thinking”: Apple researchers published a paper discussing the strengths and limitations of current LLMs in reasoning tasks, pointing out that these models’ performance “collapses” when handling tasks beyond a certain complexity. The research suggests that LLM “reasoning” is more based on pattern matching and memorization rather than true human-like thinking and understanding. This view echoes that of experts like Yann LeCun, sparking discussions about the path to AGI and the capability boundaries of current models (Source: omarsar0, NandoDF)

DeepSeek R1 demonstrates excellent text understanding and creative interpretation in Dwarf Fortress game: User experiments show that the DeepSeek R1 model exhibits strong text understanding and creative interpretation capabilities when processing data from the complex, text-intensive game Dwarf Fortress. By extracting text data from game screenshots and inputting it into DeepSeek R1, the model can not only parse the data but also identify interesting quirks and patterns in dwarf behavior, describing them in vivid and amusing language, showcasing its potential in unstructured text understanding and generation (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

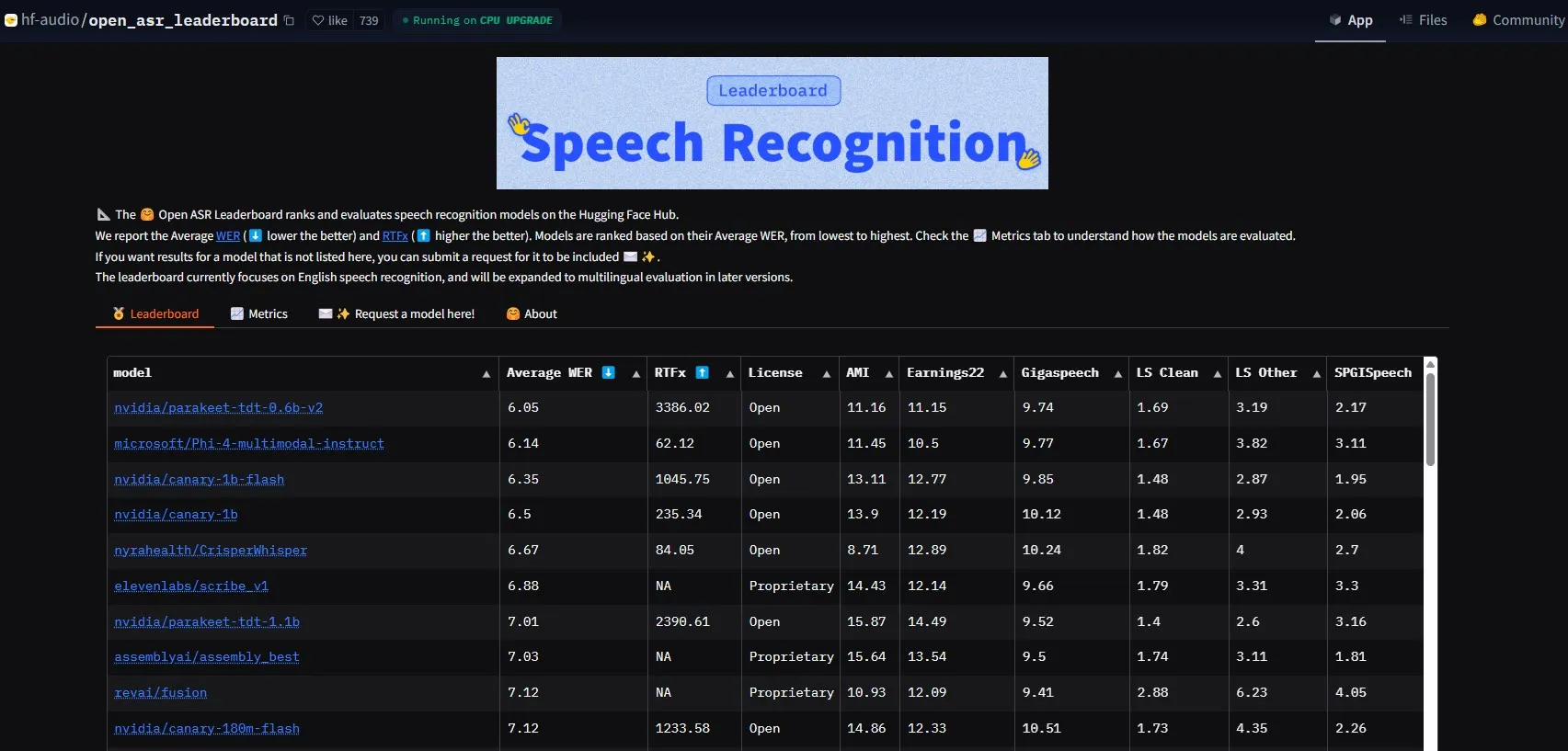
NVIDIA releases Parakeet-tdt-0.6b-v2 model, setting new ASR performance benchmark: NVIDIA’s new automatic speech recognition (ASR) model, Parakeet-tdt-0.6b-v2, has set a new industry record on the HuggingFace Open-ASR-Leaderboard with a word error rate (WER) of 6.05%. The model not only leads in accuracy but also boasts extremely fast inference speeds (RTFx 3386, 50x faster than alternatives) and supports innovative features like lyric transcription and precise timestamp/number formatting (Source: huggingface)
Alibaba Qwen team releases Qwen3-Embedding series models: Alibaba’s Qwen team has launched the new Qwen3-Embedding series models, available in three different sizes: 0.6B, 4B, and 8B. These models have achieved SOTA (State-of-the-Art) performance on multiple text embedding benchmarks such as MMTEB, MTEB, and MTEB-Code, support 119 languages, and can run in-browser via Transformers.js (with WebGPU acceleration), providing powerful text representation capabilities for multilingual and cross-platform applications (Source: huggingface)
Gemini 2.5 Pro demonstrates powerful code generation and task processing capabilities: Google DeepMind’s Gemini 2.5 Pro (preview-06-05 version) has shown strong capabilities in handling complex tasks. For example, user Majid Manzarpour attempted to have it write a script to organize and classify a library of over 25,000 sound files, to which Jeff Dean commented that it “doesn’t sound too hard,” hinting at the model’s potential to handle such large-scale, complex programming tasks. Additionally, GosuCoder’s test chart shows that the Gemini 2.5 Pro 06-05 updated version performs better in AI coding assistance, especially achieving the highest evaluation score at a temperature setting of 0.7 (Source: JeffDean, jeremyphoward)
Hugging Face and Google Colab deepen integration, simplifying AI workflows: Hugging Face and Google Colab announced enhanced collaboration, adding “Open in Colab” support to all model cards on the Hugging Face Hub. Users can now directly launch Colab notebooks from any model card, making it more convenient to experiment with and use models on Hugging Face, further lowering the barrier to AI development and research (Source: huggingface)
🧰 Tools
LlamaBot: AI coding assistant based on LangGraph: LangChainAI introduced LlamaBot, an AI agent powered by LangGraph, capable of creating web applications through natural language chat. Its features include real-time code generation, live previews, and specialized agents designed for different development tasks, aiming to simplify the web application development process (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)
Fast RAG system: Combining DeepSeek-R1 and Qdrant for efficient document processing: LangChainAI showcased a high-performance RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) implementation. This solution combines SambaNova’s DeepSeek-R1 model, Qdrant’s binary quantization technology, and LangGraph to achieve a 32x memory reduction, enabling efficient processing of large-scale documents and offering a new optimization path for information retrieval and content generation (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)

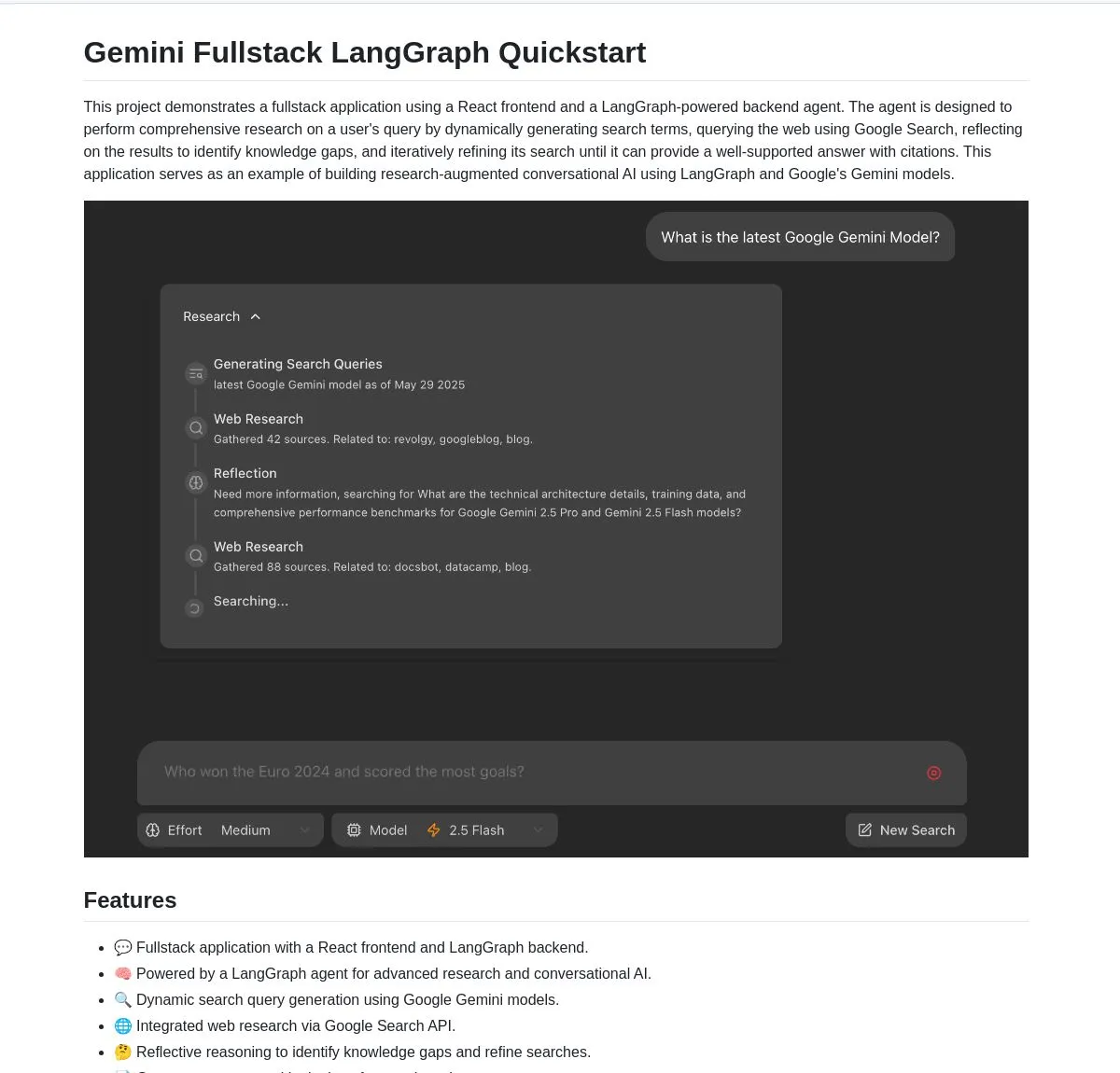
Gemini Research Assistant: Full-stack intelligent research assistant based on Gemini and LangGraph: The Google Gemini team has open-sourced a full-stack AI research assistant that utilizes the Gemini model and LangGraph to perform intelligent web research. The assistant possesses reflective reasoning capabilities, continuously optimizing its search strategies to provide users with deeper, more efficient research support. The project code is available on GitHub (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)
Agent Flow: Open-source no-code AI agent builder: Karan Vaidya launched Agent Flow, an open-source no-code AI agent builder, as an alternative to Gumloop. Built on ComposioHQ and LangChain’s LangGraph, it allows users to automate workflows and complex agent patterns by dragging and dropping nodes, aiming to lower the barrier to developing AI agent applications (Source: hwchase17)
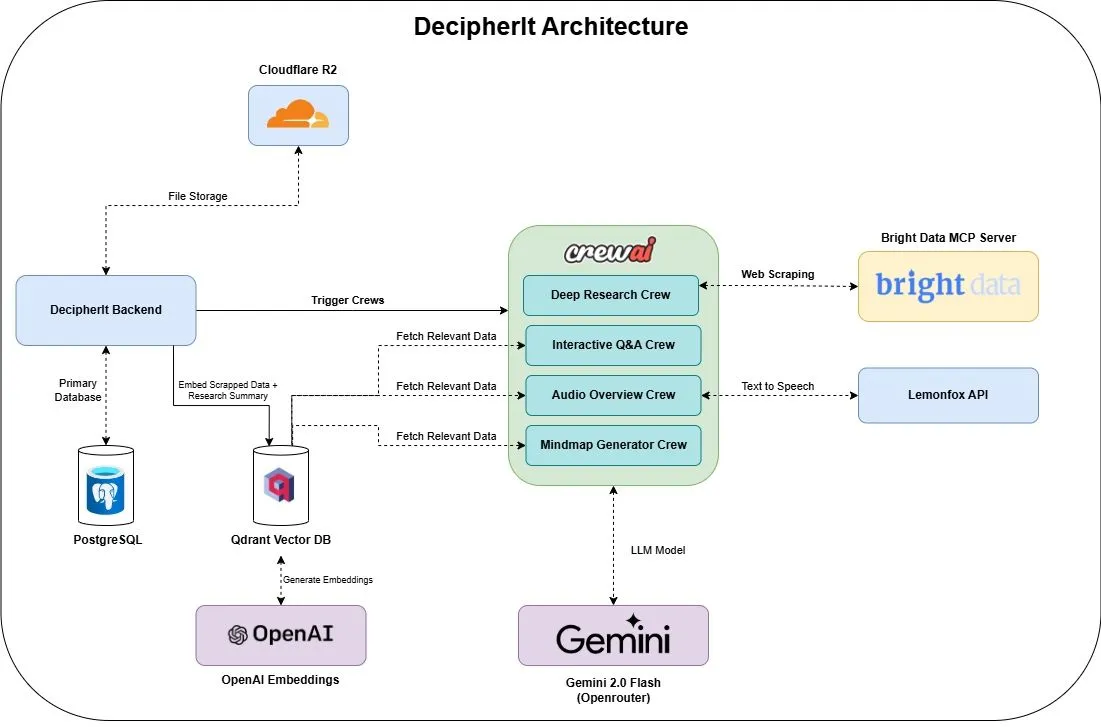
DecipherIt: Open-source AI research assistant, an alternative to NotebookLM: An open-source AI research assistant named DecipherIt has been launched, positioned as an alternative to NotebookLM. The tool utilizes multi-agent orchestration (crewAI), semantic search (Qdrant + OpenAI), real-time web access (Bright Data MCP), and speech synthesis (lemonfoxai) to transform user-uploaded documents, URLs, or input topics into a complete research workspace containing summaries, mind maps, audio overviews, FAQs, and semantic Q&A (Source: qdrant_engine)
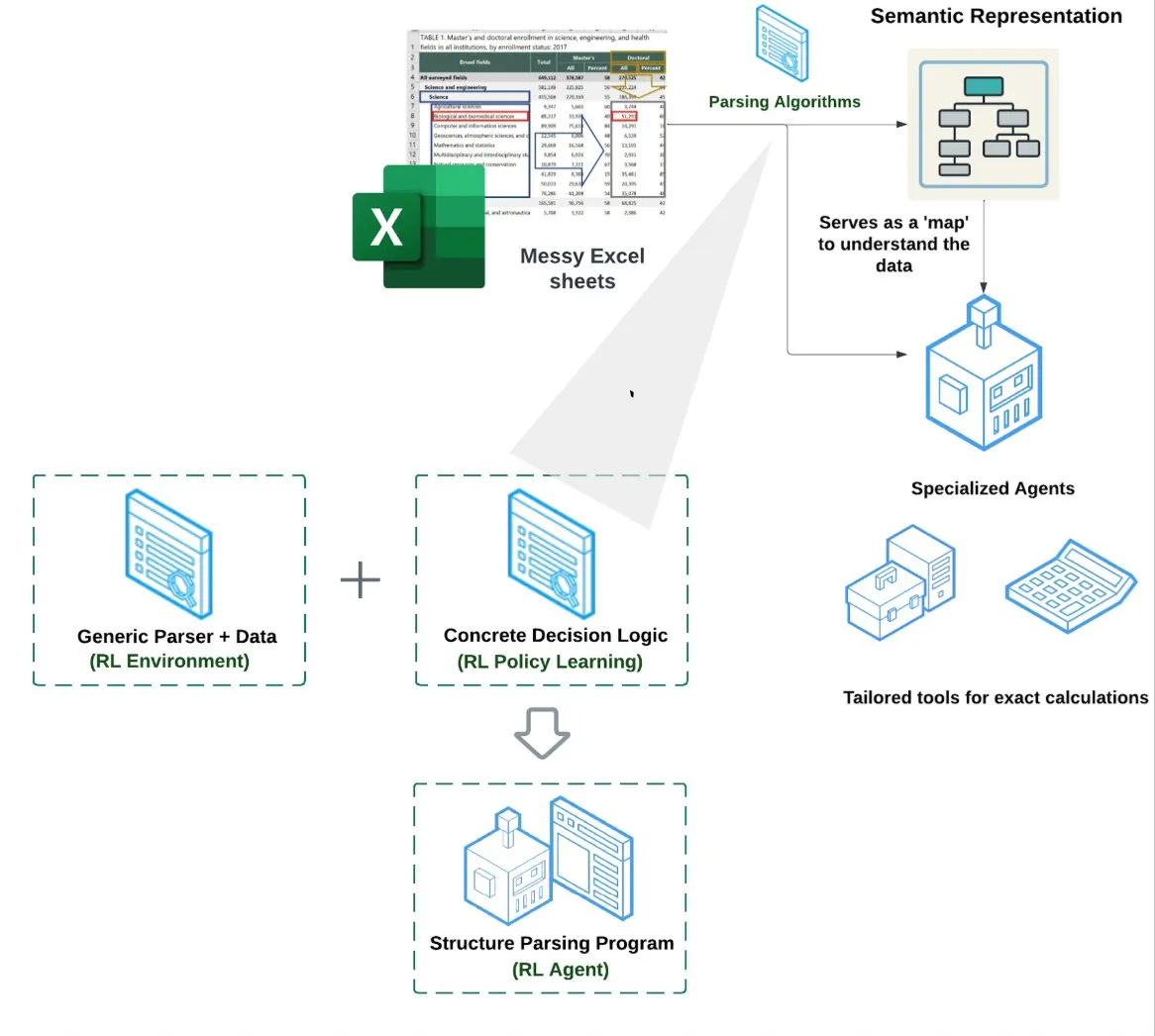
LlamaIndex launches Spreadsheet Agent: LlamaIndex has released a new Spreadsheet Agent, currently in private preview. This agent focuses on handling complex Excel files, capable of data transformation and quality assurance. Its core technical architecture lies in reinforcement learning-based structural understanding (learning data models/semantic graphs) and specialized tools built on top of the semantic graph. It aims to provide superior Excel processing capabilities compared to traditional RAG or text-to-CSV methods, reportedly performing 10-20% better than baselines where LLMs write code directly (Source: jerryjliu0)
Kuvera-8B-v0.1.0: Large model for personal financial advice: Akhil-Theerthala released the Kuvera-8B-v0.1.0 model on Hugging Face, a model specifically designed for personal finance questions. It is fine-tuned based on Qwen3-8B using data sources like Reddit, aiming to provide compassionate and practical advice on topics such as budgeting, saving, investing, debt management, and basic financial planning. Being based on Qwen3, the model supports Chinese Q&A (Source: karminski3)
Localized Whisper+Pyannote speech processing solution replaces Otter.ai: A Reddit user shared their fully localized speech processing workflow to replace cloud services like Otter.ai. The solution combines ctranslate2 and faster-whisper for transcription, and pyannote and speechbrain for speaker diarisation. It can process meeting recordings over three hours long on a local GPU, outputting speaker-labeled text records and JSON files, including customized content like executive summaries and action lists. This aims to address the limitations, privacy concerns, and lack of customization of cloud services (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
GPT Deep Research MCP: Combining with OpenWebUI for deep research: Users recommend trying the GPT Deep Research MCP in conjunction with OpenWebUI. The MCP tool (gptr-mcp) is designed to provide deep research capabilities, and when used with MCP-enabled OpenWebUI, it offers an impressive research experience, further expanding the application of localized AI tools in information processing and knowledge discovery (Source: Reddit r/OpenWebUI)
📚 Learning
OpenAI to host application evaluation practice sharing session, including real cases and tool previews: OpenAI will host a sharing session on best practices for application evaluation (Evals). OpenAI’s Jim Blomo will discuss how to effectively evaluate AI products, drawing on real customer cases and results. The event will also preview upcoming evaluation tools from OpenAI, including features for tracking, scoring, and more. This session aims to help developers and enterprises better build and optimize AI applications and will provide a recording for playback (Source: HamelHusain, HamelHusain)

Anthropic open-sources interpretability research methods to help understand LLM “thinking”: Anthropic announced it is open-sourcing its research methods for tracking the “thought processes” of large language models. Researchers can now use this methodology to generate “attribution graphs” and explore them interactively, similar to what Anthropic demonstrated in its recent research. The team also provides a Neuronpedia interactive interface and Jupyter Notebook tutorials to facilitate researchers applying these tools to open-source models, aiming to enhance understanding of the internal workings of LLMs. This project is led by Anthropic Fellows program participants in collaboration with Decode Research (Source: AnthropicAI)
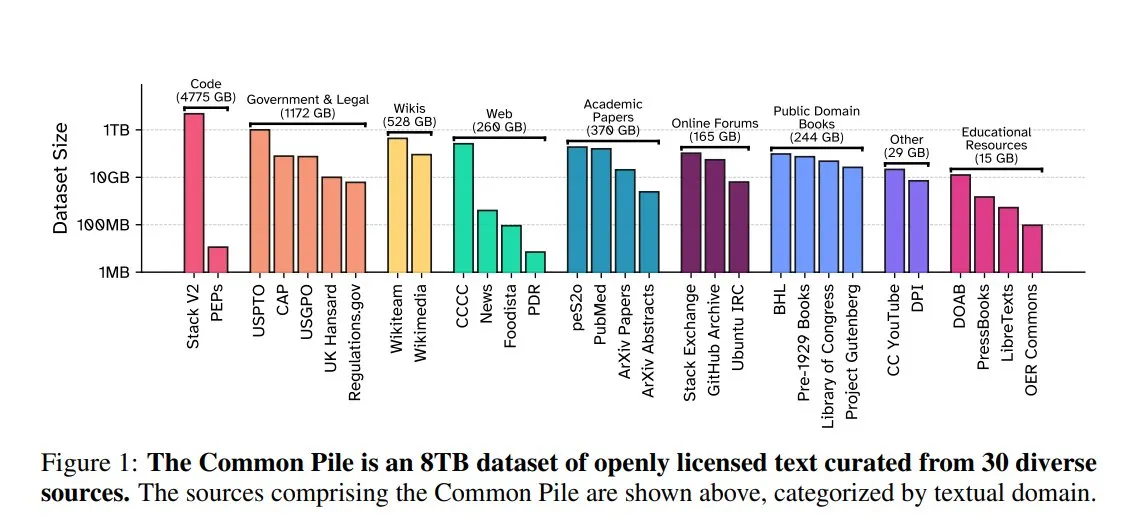
EleutherAI releases Common Pile v0.1: An 8TB open-license text dataset: EleutherAI, in collaboration with the Vector Institute, Allen AI, Hugging Face, and DPI, has released Common Pile v0.1, an 8TB, 1 trillion token dataset of public domain and open-license text. The team trained 7B parameter models, Comma v0.1-1T and -2T, on this dataset, achieving performance comparable to models like LLaMA 1 & 2 trained on similar data scales. This initiative aims to explore the feasibility of training high-performance language models without using unauthorized text, providing a valuable data resource for the open-source community (Source: huggingface)
NVIDIA NIM accelerates Vanna text-to-SQL inference: An NVIDIA developer blog post demonstrates how to use NVIDIA NIM (NVIDIA Inference Microservices) to optimize Vanna’s text-to-SQL solution. NIM provides optimized endpoints for generative AI models, accelerating the inference process for faster analytics. This is significant for applications requiring the conversion of natural language queries into database queries (Source: dl_weekly)
Stanford University machine learning course free lecture notes shared: The Turing Post shared free lecture notes from Stanford University’s CS229 Machine Learning course, taught by Andrew Ng and Tengyu Ma. The content covers supervised learning, unsupervised learning methods and algorithms, deep learning and neural networks, generalization, regularization, and reinforcement learning processes, providing high-quality learning resources for students (Source: TheTuringPost)

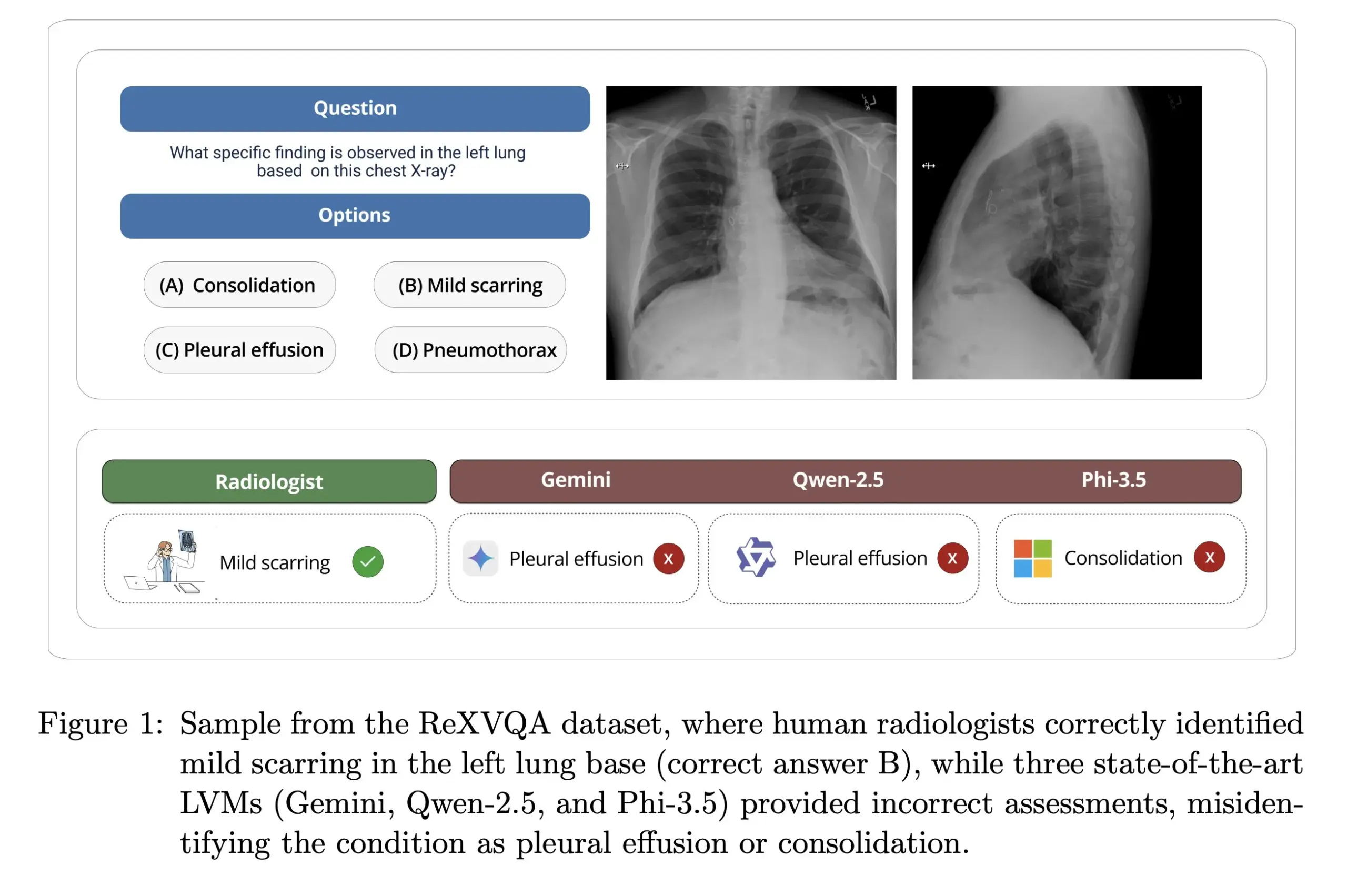
Harvard University releases ReXVOA: A large-scale, high-quality chest X-ray VQA benchmark: Harvard University’s Pranav Rajpurkar Lab has released ReXVOA, a large-scale, high-quality chest X-ray visual question answering (VQA) benchmark dataset. The dataset is designed to challenge existing large frontier models and serve as a yardstick for measuring the progress of next-generation models in medical image understanding and question-answering capabilities (Source: huggingface)
OWL Labs shares experience training autoencoders for diffusion models: OWL (Open World Labs) summarized its experiences and findings from training autoencoders for diffusion models in its blog, also sharing failure cases of some unconventional methods. The article provides a reference for researchers and developers in applying and optimizing diffusion model autoencoders in practice (Source: NandoDF)
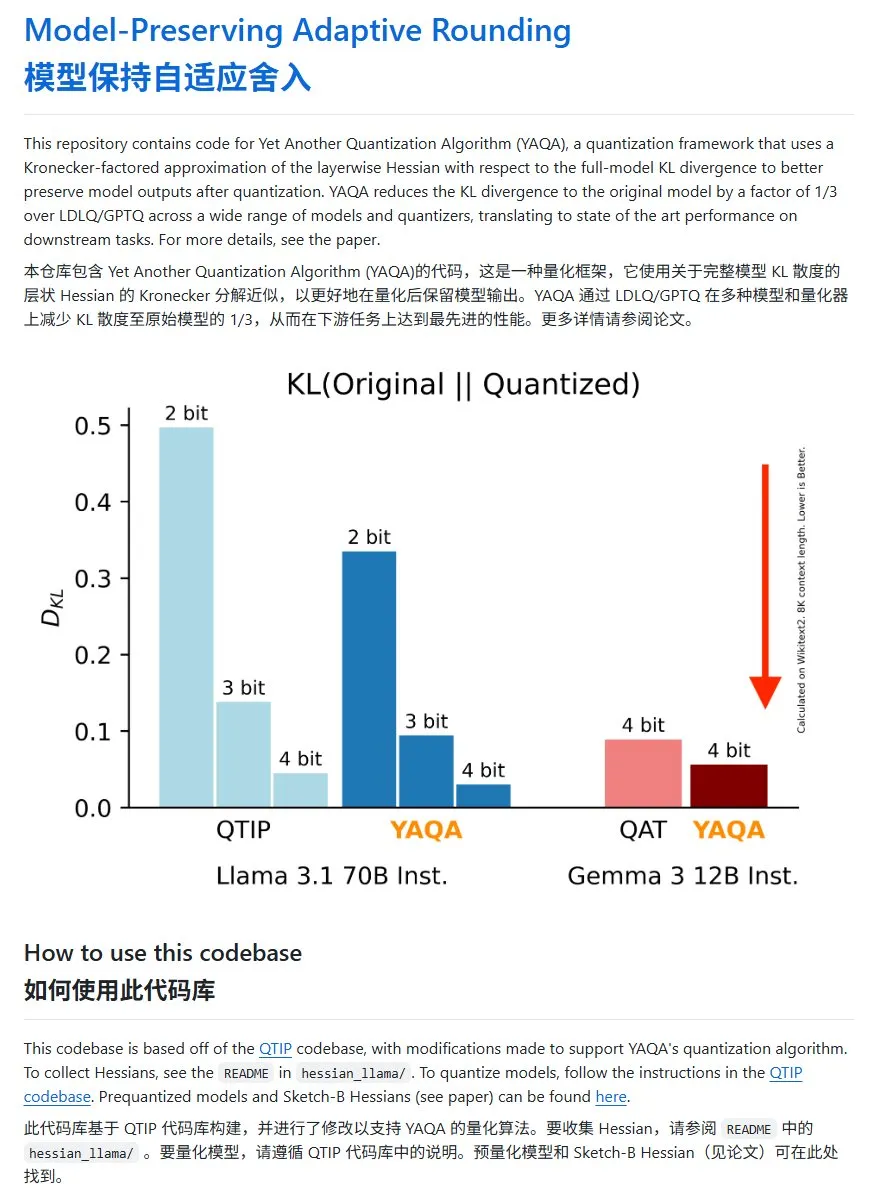
YAQA: A new model quantization method with significantly reduced KL divergence: The Cornell-RelaxML team proposed a new model quantization method, YAQA. This method combines LDLQ/GPTQ techniques and, compared to existing quantization methods, can reduce the KL divergence of the quantized model to 1/3 of the original model’s. Although the YAQA quantization process is slower and requires significant VRAM, the performance improvement and subsequent inference economy make it a promising quantization solution. The project code is open-sourced on GitHub (Source: karminski3)
💼 Business
Post-00s Guangzhou girl Carina Hong founds Axiom, aiming to solve math problems with AI: Carina Hong, a post-00s academic prodigy, has garnered attention for her AI startup, Axiom. Axiom focuses on using AI to solve complex mathematical problems, targeting clients such as hedge funds and quantitative trading firms. According to The Information, Axiom is in talks for a $50 million funding round at a valuation of approximately $300-500 million, with B Capital potentially leading the investment. Hong stated on social media that the financing reports were inaccurate but confirmed the company is hiring AI math talent. Hong holds a bachelor’s degree from MIT, a master’s from Oxford, and is currently pursuing a dual PhD in mathematics and law at Stanford, having won multiple math competition awards (Source: 36Kr)

Anthropic cuts off Claude API access to Windsurf due to competitive concerns: An Anthropic co-founder confirmed that the company has ceased providing Claude model API access to AI startup Windsurf. The reason cited is that Windsurf is perceived as a form of “wrapper” for or closely related to OpenAI, Anthropic’s direct competitor. This move has sparked discussions about API dependency and platform risks, especially for startups whose businesses are built on third-party large model APIs, as the model provider’s business decisions can directly impact their survival (Source: ClementDelangue, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
OpenAI ordered to retain users’ deleted chat logs due to copyright lawsuit: According to reports, in a copyright lawsuit filed by The New York Times, a U.S. federal court has ordered OpenAI to retain all ChatGPT user conversation logs, including content users have chosen to delete, as potential evidence. The New York Times alleges OpenAI used its paywalled articles to train ChatGPT and is concerned AI might generate similar content. This move has raised concerns about user privacy and data protection (such as GDPR), highlighting the legal and ethical tension between AI training data copyright and user privacy (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

🌟 Community
AI large models tackle 2025 college entrance exam essays and math, with varied performance: During the 2025 college entrance examination period, multiple mainstream AI large models were challenged with essay writing and math problems. In essay writing, 16 AI assistants, including Doubao, DeepSeek, and ChatGPT, demonstrated their writing abilities. Most could generate structurally sound argumentative essays but generally suffered from templated responses, cliché引用, and convergent themes. In the math test (New Curriculum I Paper objective questions), ByteDance’s Doubao and Tencent’s Yuanbao tied for first place with 68 points (out of 73), while OpenAI’s o3 performed poorly, scoring only 34 points. The tests reflect the progress and limitations of current AI in Chinese understanding, logical reasoning, and creative expression, especially in avoiding AI-like traces and tackling complex mathematical reasoning, where there is still room for improvement (Source: 36Kr, 36Kr)

Trend in enterprise AI application: Internal knowledge bases and customized chatbots gain attention: Community discussions indicate a growing trend of using AI to build internal enterprise chatbots trained on company data to answer employee questions about processes, data retrieval, responsible parties, etc. Such applications aim to improve internal information retrieval efficiency and knowledge management. Companies like Amazon have deployed similar systems with positive feedback. However, data security, potential sensitive information leakage, and effective commercialization remain key concerns for enterprises during implementation (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
The “indexing” vs. “non-indexing” debate in AI-assisted programming: A trade-off between performance and reliability: An experiment on AI coding assistants (using the Apollo 11 moon landing code as a test case) compared “indexing” (pre-building a codebase index and using vector search) and “non-indexing” (reading and analyzing code files on demand) AI agents. Results showed that indexing agents were faster and made fewer API calls in most cases. However, when the codebase changed frequently, causing the index to become outdated, they could produce errors due to reliance on stale information, leading to longer debugging times. This reveals a trade-off between immediate performance and information reliability when choosing AI coding tools (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)

Ongoing discussion on whether LLMs “think”: From pattern matching to human cognition: The debate continues in the community about whether large language models (LLMs) truly “think.” Critics argue that LLMs are essentially sophisticated predictive text generators that work by calculating probabilities of word sequences, rather than engaging in conscious thought. However, many users feel an experience similar to conversing with a human when interacting with LLMs. This has prompted reflection on human language generation mechanisms and whether similarities exist between LLMs and human cognitive processes. Apple’s research further points to LLM limitations in complex reasoning, suggesting they rely more on pattern memory than true reasoning, adding a new perspective to this discussion (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/ChatGPT)

Paul Graham on AI’s impact on income disparity: Paul Graham told his 16-year-old son that in the short term, AI technology might widen the income gap among workers. He exemplified that average programmers now find it harder to get jobs, while excellent programmers earn more with AI assistance. He believes this isn’t new; technological advancements often increase income disparity because the lower income bound is fixed at zero, while technology continuously raises the upper limit of returns for top talent (Source: dotey)
AI safety ethics discussion: From model behavior to societal norms: Community discussions on AI safety and ethics continue to heat up. Geoffrey Hinton congratulated Yoshua Bengio on launching the LawZero project, which aims to promote the safe design of AI, particularly focusing on potential self-preservation and deceptive behaviors in frontier systems. Meanwhile, some criticize certain AI safety research (like testing if a model agrees to be shut down) as “safety theater” lacking practical value. OpenAI’s research on human-AI relationships also sparked discussion, emphasizing the need to prioritize research on its impact on users’ emotional well-being as AI becomes increasingly integrated into life, and to explore how to balance clear communication with avoiding anthropomorphism in model interactions (Source: geoffreyhinton, ClementDelangue, togelius)

Emotional support role of AI assistants like ChatGPT affirmed by users: Many users have shared on social media how AI assistants like ChatGPT provided emotional support and practical help during difficult times. Some users stated that when facing unemployment, health issues, or low moods, ChatGPT not only offered concrete action plans and resource information but also helped them alleviate panic and regain strength in a non-judgmental way. This demonstrates AI’s potential value in psychological support and crisis intervention, despite its lack of genuine emotion and consciousness (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
“Vibe Coding” becomes a new phenomenon in AI-assisted programming: The term “Vibe Coding” is gaining popularity in the developer community, referring to a programming style that relies on intuition and AI assistance for rapid code iteration. Tools like Claude Code are favored by some programmers for their excellent performance during specific times (such as late night or early morning, possibly due to low server load or not being highly quantized). This phenomenon reflects the improvement in development efficiency brought by AI coding assistants, while also sparking discussions about model consistency, the impact of quantization, and new working patterns for developers (Source: dotey, jeremyphoward)
💡 Other
Andrej Karpathy reflects on the huge impact of noise pollution on sleep and health: Andrej Karpathy shared his personal experience, pointing out that environmental noise pollution, such as traffic noise, can have a huge and underappreciated negative impact on sleep quality and long-term health. He speculates that nighttime noise (like loud cars, motorcycles) might be causing millions to suffer from poor sleep quality, subsequently affecting mood, creativity, energy levels, and increasing the risk of cardiovascular, metabolic, and cognitive diseases. He calls for sleep tracking devices (like Whoop, Oura) to explicitly track the correlation between noise and sleep and to raise public awareness of this issue (Source: karpathy)
Intersection of AI and religion draws attention: Social media user menhguin observed that the potential market for new AI-based religious or quasi-religious applications should not be overlooked. For example, AI astrology, AI Bible videos, AI prayer apps, and AI applications for specific groups all hint at the possibility of AI technology meeting human spiritual or faith-based needs (Source: menhguin)
AI-assisted generation of HTTP 2.0 server explores LLM potential in large software projects: A developer used a self-developed framework (promptyped) and the Gemini 2.5 Pro model to successfully have an LLM build an HTTP 2.0 compliant server from scratch through a code-compile-test loop. The project generated 15,000 lines of source code and over 30,000 lines of test code, passing the h2spec conformance test. Despite taking approximately 119 hours of API time and $631 in API costs, this experiment demonstrates the potential of LLMs in architectural design and writing complex, standards-compliant software, while also revealing the form of applications written entirely by LLMs (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)