Keywords:Gemini 2.5 Pro, OpenAI data privacy, OpenThinker3-7B, Claude Gov, AI agent, large language model, reinforcement learning, open-source model, Gemini 2.5 Pro performance improvement, OpenAI user data retention policy, OpenThinker3-7B reasoning capability, Claude Gov national security applications, AI agent robustness and control
🔥 Focus
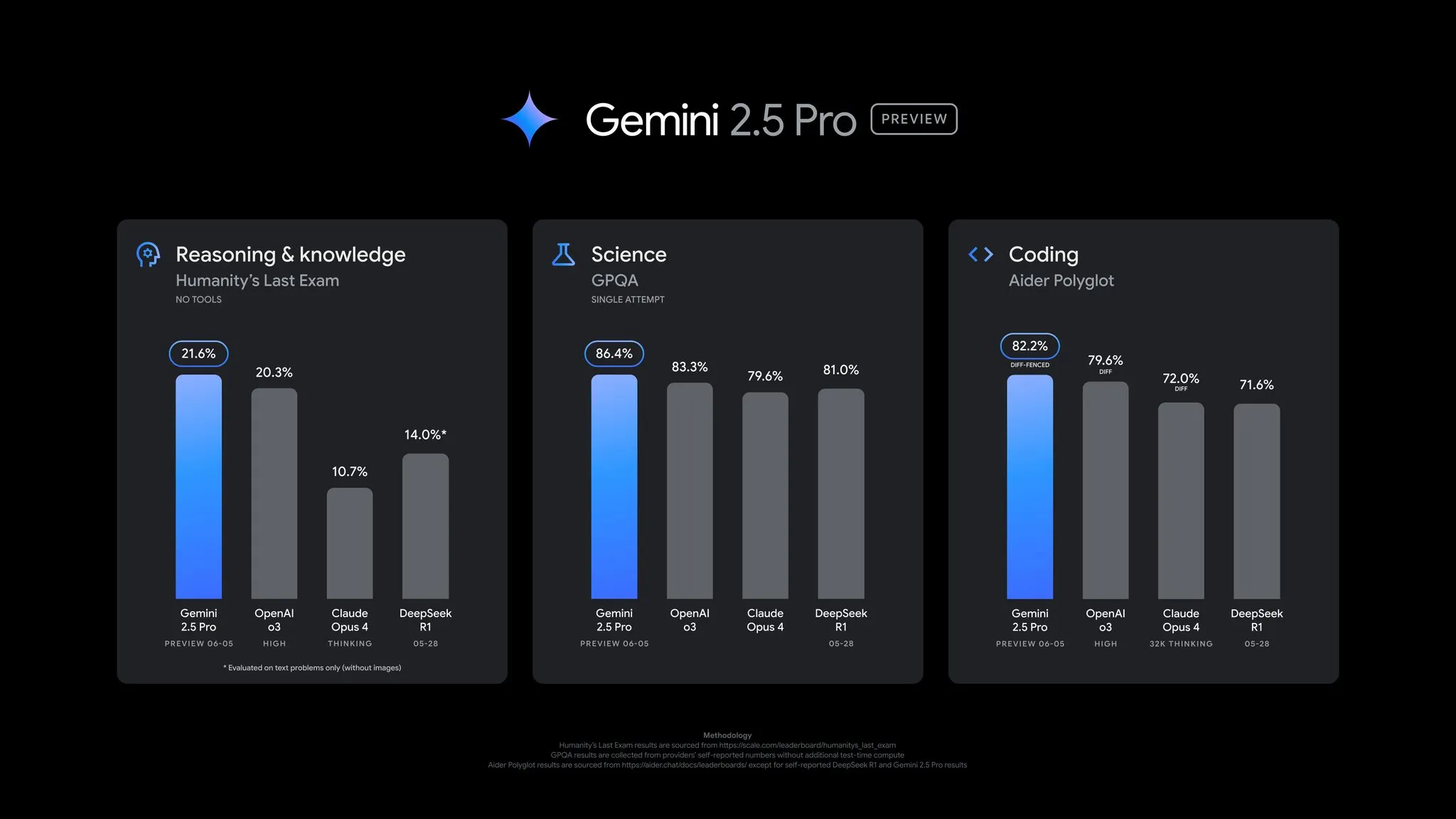
Google releases Gemini 2.5 Pro preview update with comprehensive performance improvements: Google announced a significant update to the Gemini 2.5 Pro preview, with notable advancements in coding, reasoning, science, and math capabilities. The new version performs better on key benchmarks such as AIDER Polyglot, GPQA, and HLE, and achieved a 24-point Elo score increase on LMArena, reclaiming the top spot. Additionally, the model’s answering style and formatting have been improved based on user feedback, and a “thinking budget” feature has been introduced for more control. The update is now available in the Gemini App, Google AI Studio, and Vertex AI (Source: JeffDean, OriolVinyalsML, demishassabis, op7418, LangChainAI, karminski3, TheRundownAI, 量子位)
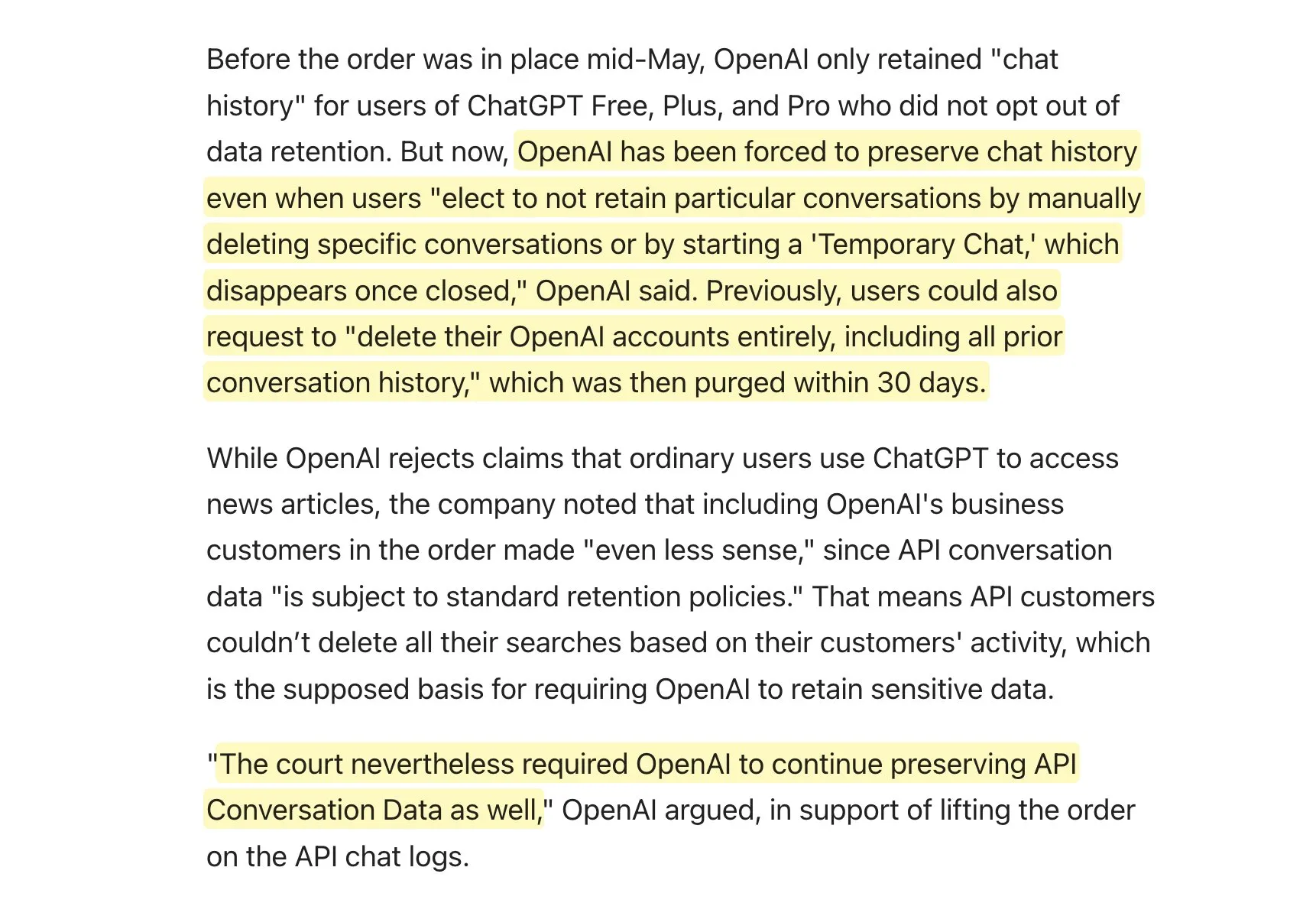
OpenAI ordered to permanently retain user data in New York Times lawsuit, raising privacy concerns: In its copyright lawsuit with The New York Times, OpenAI has been court-ordered to permanently retain all ChatGPT and API user interaction logs, including “temporary conversations” previously promised to be kept for only 30 days and API request data. OpenAI stated it is appealing the order, calling it an “overreach” that undermines long-standing privacy norms and weakens privacy protections. This ruling means OpenAI may be unable to fulfill its data retention and deletion commitments to users, sparking widespread concern about user data privacy and security, and potentially impacting application developers who rely on OpenAI APIs and have their own data retention policies (Source: natolambert, openai, bookwormengr, fabianstelzer, Teknium1, Reddit r/artificial)
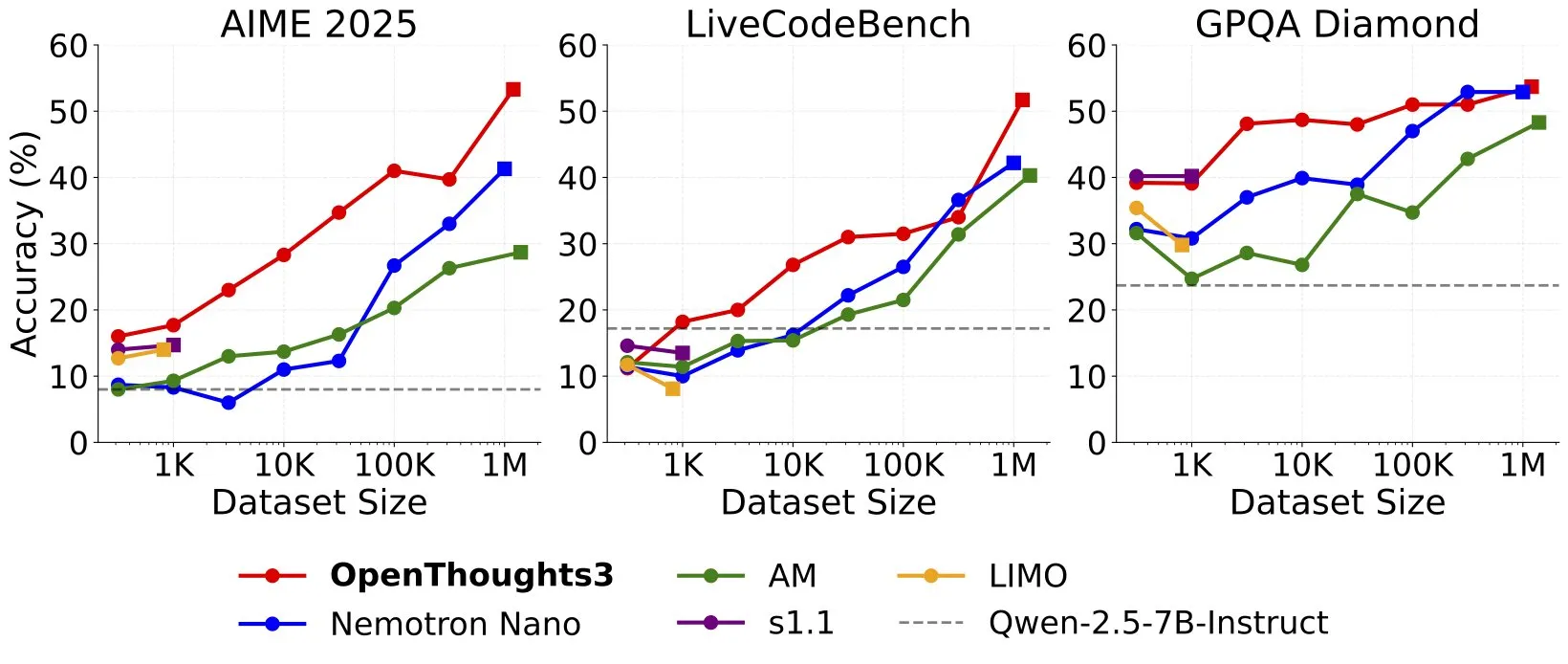
OpenThinker3-7B released, setting new SOTA for 7B open-source reasoning models: Ryan Marten announced the launch of OpenThinker3-7B, a new 7-billion parameter open data reasoning model that outperforms DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B by an average of 33% on code, science, and math evaluations. The team also released the OpenThoughts3-1.2M dataset, claiming it to be the best open reasoning dataset across all data scales. Researchers noted that for smaller models, distillation from R1 is the simplest path to performance improvement, but research in RL (Reinforcement Learning) is more exploratory. This achievement is considered one of the pioneering works in the field of open reasoning models (Source: natolambert, huggingface, Tim_Dettmers, swyx, ImazAngel, giffmana, slashML)
Anthropic launches Claude Gov, custom models for U.S. national security clients: Anthropic announced the launch of Claude Gov, a series of custom AI models built for U.S. national security clients. These models have already been deployed in top-tier U.S. national security agencies, with access limited to personnel operating in classified environments. This move marks a further deepening of AI technology application in government and defense sectors, while also sparking discussions about AI use in sensitive areas (Source: AnthropicAI, teortaxesTex, zacharynado, TheRundownAI)
🎯 Trends
Yann LeCun agrees with Sundar Pichai: Current technology may not achieve AGI, a plateau is possible: Meta’s Chief AI Scientist Yann LeCun retweeted and agreed with Google CEO Sundar Pichai’s view that current technological paths do not guarantee the achievement of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and AI development might hit a temporary plateau. Pichai noted that despite AI’s astonishing progress, limitations may exist, and current technology is still far from general intelligence. This reflects the industry’s cautious stance on the path and timeline for AGI realization (Source: ylecun)
OpenAI hiring for Agent Robustness and Control team to enhance AI agent safety: OpenAI is forming a new “Agent Robustness and Control” team, aiming to ensure the safety and reliability of its AI agents during training and deployment. The team will focus on solving some of the most challenging problems in the AI field, highlighting OpenAI’s strong emphasis on safety and controllability as it advances more powerful AI agents (Source: gdb)

New Apple research reveals “Illusion of Thinking” in LLMs: Reasoning ability decreases with complex problems: A recent research paper from Apple, “The Illusion of Thinking,” points out that current reasoning models’ reasoning effort paradoxically decreases when problem complexity increases beyond a certain point, even with a sufficient token budget. This counterintuitive “scaling limit” phenomenon suggests that models may not be engaging in genuine deep thought when dealing with highly complex problems, but rather exhibiting an “illusion of thinking,” posing new challenges for evaluating and enhancing the true reasoning capabilities of large models (Source: Ar_Douillard, Reddit r/MachineLearning)

OpenAI discusses emotional connection between humans and AI, prioritizes research on impact on user emotional well-being: OpenAI’s Joanne Jang published a blog post discussing the growing phenomenon of emotional connection between users and AI models like ChatGPT. The article notes that people naturally anthropomorphize AI and may develop feelings of companionship and trust towards it. OpenAI acknowledges this trend and states it will prioritize research on AI’s impact on user emotional well-being, rather than dwelling on ontological questions of whether AI is truly “conscious.” The company aims to design AI assistants that are warm, helpful, but not overly seeking emotional dependence or having their own agendas (Source: openai, sama, BorisMPower)
Xiaohongshu releases open-source MoE large model dots.llm1-143B-A14B: Xiaohongshu’s Hi Lab has released its first open-source large model series, dots.llm1, including the base model dots.llm1.base and the instruction-tuned model dots.llm1.inst. The model uses an MoE architecture with a total of 143B parameters and 14B active parameters. Official internal tests claim its performance on MMLU-Pro surpasses Qwen3-235B-A22B but falls short of the new DeepSeek-V3. The model is released under the MIT license for free use. However, preliminary community tests indicate poor performance on tasks like code generation, even underperforming Qwen2.5-coder (Source: karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

Qwen3 series releases Embedding and Reranker models, enhancing multilingual text processing capabilities: The Qwen team has launched the Qwen3-Embedding and Qwen3-Reranker model series, aimed at improving performance in multilingual text embedding and relevance ranking. The Embedding model is used to convert text into vector representations, supporting scenarios like document retrieval and RAG; the Reranker model is used to reorder search results, prioritizing the most relevant content. The series offers different parameter scales such as 0.6B, 4B, and 8B, supports 119 languages, and performs well on benchmarks like MMTEB and MTEB. The 0.6B version is considered particularly suitable for real-time Reranker scenarios due to its balance of efficiency and performance (Source: karminski3, karminski3, ZhaiAndrew, clefourrier)

Research points to scalability challenges of reinforcement learning in complex long-horizon tasks: Research by Seohong Park et al. finds that merely scaling up data and computational resources is insufficient for reinforcement learning (RL) to effectively solve complex tasks; the key constraint is the “horizon.” In long-horizon tasks, reward signals are sparse, making it difficult for models to learn effective policies. This aligns with observations that current AI agents (like Deep Research, Codex agent) primarily rely on short-horizon RL tasks and general robustness training, indicating that end-to-end solutions for long-horizon sparse reward problems remain a major challenge in RL (Source: finbarrtimbers, natolambert, paul_cal, menhguin, Dorialexander)
Baidu registers official account on HuggingFace and uploads ERNIE large models: Baidu has registered an official account on the HuggingFace platform and uploaded parts of its ERNIE series models, including ERNIE-X1-Turbo and ERNIE-4.5-Turbo. This move signifies Baidu’s active integration of its large model technology into the broader open-source community and developer ecosystem, facilitating global developer access to and use of its AI capabilities (Source: karminski3)
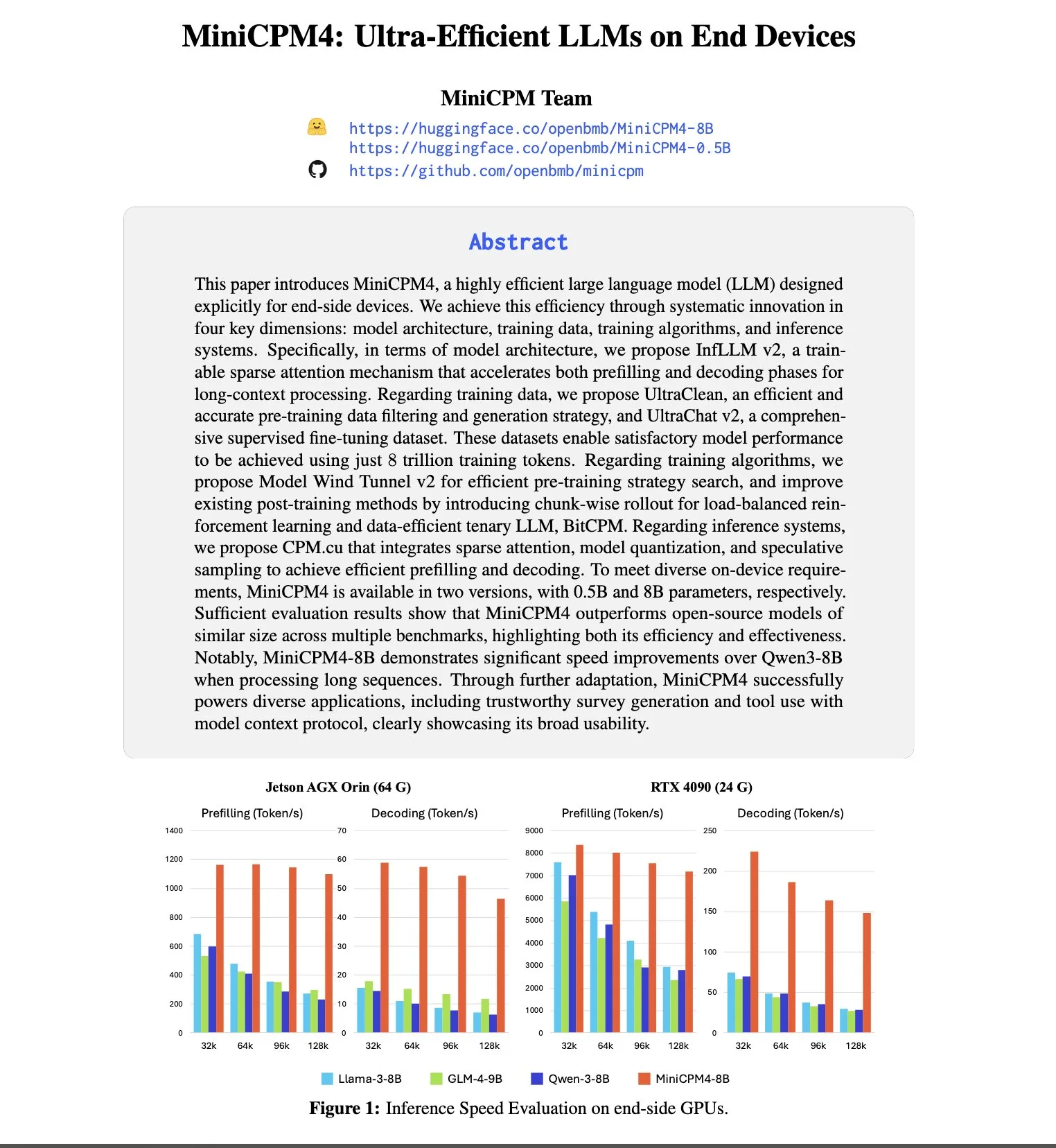
OpenBMB launches MiniCPM4 series models, focusing on efficient on-device operation: OpenBMB continues to explore the limits of small, efficient language models with the release of the MiniCPM4 series. The MiniCPM4-8B model has 8 billion parameters and was trained on 8T tokens. The series employs extreme acceleration techniques such as trainable sparse attention (InfLLM v2), ternary quantization (BitCPM), FP8 low-precision computation, and multi-token prediction, aiming for efficient operation on end-user devices. For example, its sparse attention mechanism only requires computing relevance with less than 5% of tokens for each token when processing 128K long texts, significantly reducing computational overhead for long text processing (Source: teortaxesTex, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
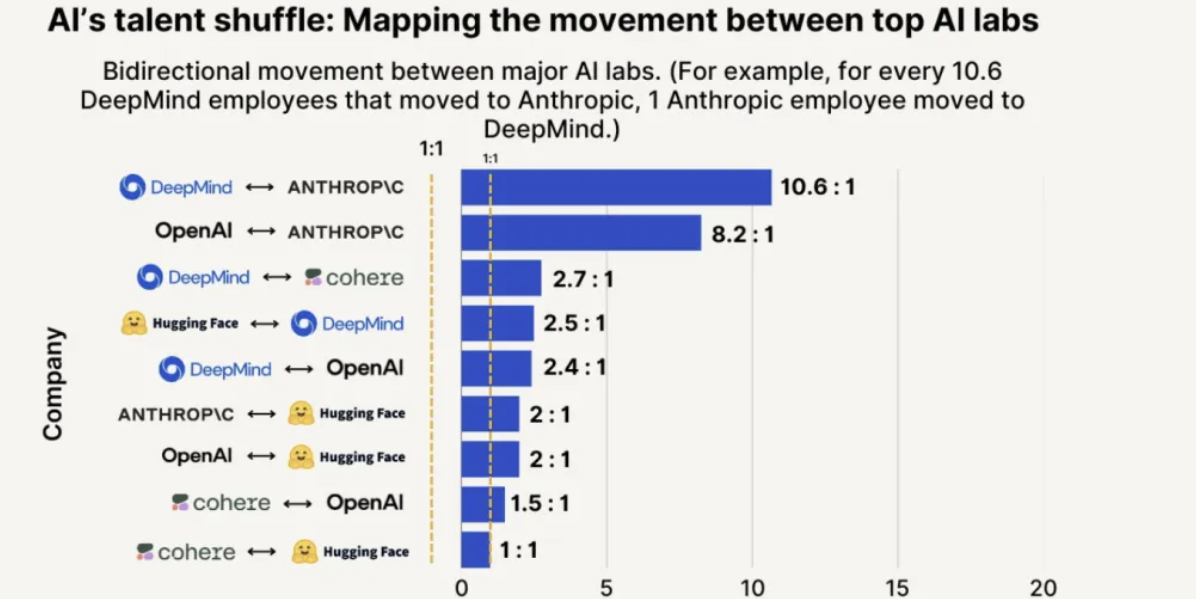
Anthropic leads in talent attraction and retention, 8 times more likely to poach from OpenAI: SignalFire’s 2025 Talent Trends report shows Anthropic excels in retaining top AI talent, with a rate of 80%, higher than DeepMind’s 78% and OpenAI’s 67%. The report also indicates that engineers are 8 times more likely to move from OpenAI to Anthropic than vice versa. Anthropic’s unique corporate culture, inclusiveness of unconventional thinking, employee autonomy, and the popularity of its product Claude among developers are considered key factors in its ability to attract and retain talent (Source: 量子位)
🧰 Tools
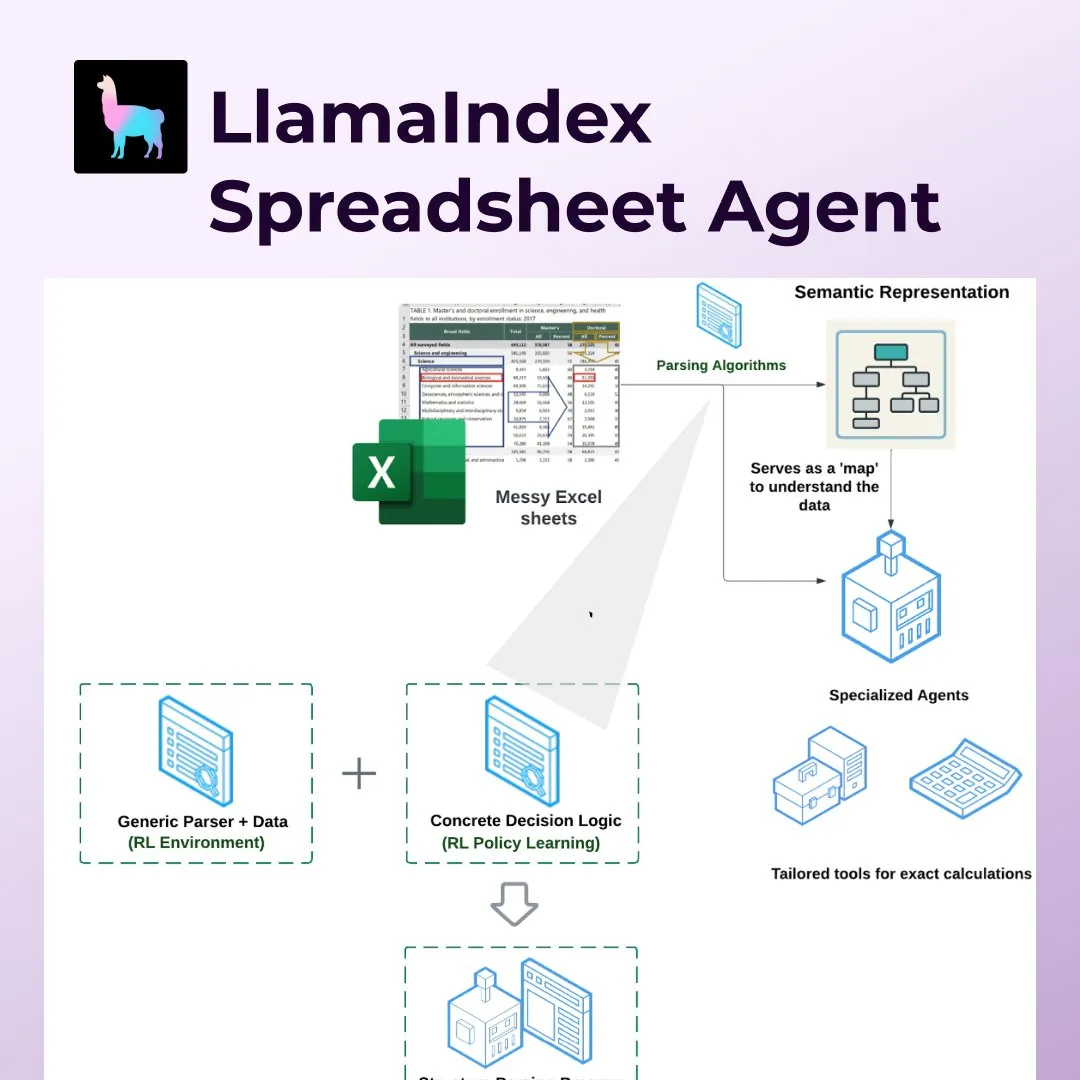
LlamaIndex launches Spreadsheet Agents, revolutionizing Excel and other spreadsheet processing: LlamaIndex has released its new Spreadsheet Agents feature, allowing users to perform data transformation and Q&A on non-standardized Excel spreadsheets. The tool utilizes reinforcement learning-based semantic structure parsing to understand table structures and enables AI agents to interact with tables through specialized tools. It aims to address the shortcomings of traditional LLMs in handling complex spreadsheets (common in accounting, tax, and insurance) and can process merged cells, complex layouts, and maintain data relationships. In tests, its accuracy (96%) surpassed human baselines and OpenAI Code Interpreter (GPT 4.1, 75%) (Source: jerryjliu0)
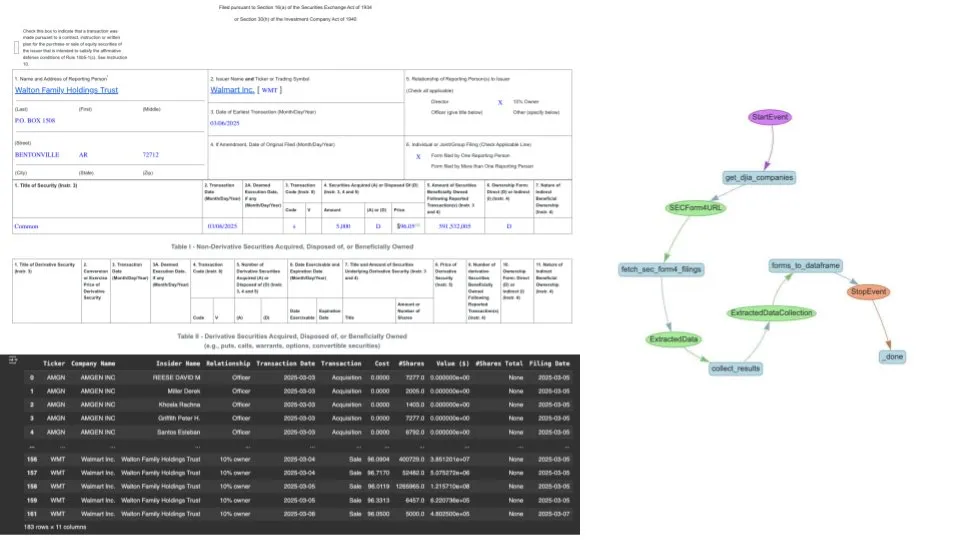
LlamaIndex automates SEC Form 4 extraction using LlamaExtract and agentic workflows: LlamaIndex demonstrated how to use its LlamaExtract tool and AI agent workflows to automatically extract and normalize data from U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Form 4 filings (documents where corporate executives, directors, and major shareholders disclose stock transactions). This solution can convert variously formatted Form 4 files from different companies into clean CSV format and integrate them into a Pandas-queryable dataframe, providing an efficient data processing tool for financial analysts and investors (Source: jerryjliu0)
Open-source project Ragbits released, providing building blocks for rapid GenAI application development: deepsense-ai has launched the open-source project Ragbits, designed to provide building blocks for the rapid development of generative AI applications. The project supports over 100 large model APIs or local models, comes with a built-in vector store (connectable to Qdrant, PgVector), and supports over 20 input file formats (PDF, HTML, tables, presentations, etc.). Ragbits utilizes built-in VLM to support extraction of tables, images, and structured content, can connect to various data sources like S3, GCS, Azure, and features modularity, allowing users to customize components (Source: karminski3, GitHub Trending)

AI programming assistant Cursor releases major update with BugBot, memory function, and MCP support: AI programming tool Cursor has undergone a significant update, primarily including: 1) BugBot, which can automatically reply to GitHub issues and open them in Cursor for fixing with one click; 2) Memory function, enabling AI to remember previous conversation content, improving usability for iterative modifications in large projects; 3) One-click MCP (Model Context Protocol) setup, supporting third-party MCP servers with OAuth; 4) AI Agent support for Jupyter Notes; 5) Background Agent, allowing users to call up a control panel via a shortcut to use remote AI programming agents (Source: karminski3)
Archon: An AI agent that can create AI agents: Archon is an “Agenteer” project designed to autonomously build and optimize other AI agents. It utilizes advanced agent coding workflows and a framework knowledge base, demonstrating the role of planning, feedback loops, and domain knowledge in creating powerful AI agents. The latest V6 version integrates a tool library and an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server, enhancing its ability to build new agents. Archon supports Docker deployment and local Python installation, and provides a Streamlit UI for management (Source: GitHub Trending)

NoteGen: AI-driven cross-platform Markdown note-taking application: NoteGen is a cross-platform Markdown note-taking application dedicated to connecting recording and writing using AI, capable of organizing fragmented knowledge into readable notes. It supports various recording methods such as screenshots, text, illustrations, files, and links, stores notes natively in Markdown, supports local offline use, and synchronization via GitHub/Gitee/WebDAV. NoteGen can be configured with multiple AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, Ollama, and supports RAG functionality, using user notes as a knowledge base (Source: GitHub Trending)

ComfyUI-Copilot: An intelligent assistant for automated workflow development: ComfyUI-Copilot is a plugin driven by large language models, designed to improve the usability and efficiency of the AI art creation platform ComfyUI. It addresses issues such as ComfyUI being unfriendly to novices, model configuration errors, and complex workflow design by providing intelligent node and model recommendations, as well as one-click workflow construction features. The system employs a hierarchical multi-agent framework, including a central assistant agent and multiple specialized worker agents, and utilizes a ComfyUI knowledge base to simplify debugging and deployment (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Bifrost: High-performance Go-based LLM gateway open-sourced, optimizing LLM deployment in production: To address challenges like API fragmentation, latency, fallback, and cost management for LLMs in production environments, the Maximilian team has open-sourced Bifrost, an LLM gateway built with Go. Bifrost is designed for high-throughput, low-latency machine learning deployments and supports major LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Azure. Benchmarks show Bifrost achieves 9.5x higher throughput, 54x lower P99 latency, and 68% less memory consumption compared to other proxies, with internal overhead below 15µs at 5000 RPS. It offers API normalization, automatic provider fallback, intelligent key management, and Prometheus metrics (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

LangGraph.js improves developer experience with type safety and hook functions: LangGraph.js version 0.3 introduces a series of updates aimed at enhancing the developer experience. These include improved type safety and the introduction of preModelHook and postModelHook in createReactAgent. preModelHook can be used to streamline message history before it’s passed to the LLM, while postModelHook can be used to add guardrails or human-in-the-loop processes. The community is actively soliciting feedback for LangGraph v1 (Source: LangChainAI, LangChainAI, hwchase17, LangChainAI, Hacubu)
qingy2024 releases GRMR-V3-G4B grammar correction large model: Developer qingy2024 has released a large model focused on grammar correction, GRMR-V3-G4B, with a maximum parameter count of only 4B. The model also provides a quantized version, making it particularly suitable for grammar checking and correction tasks in local workflows or on personal devices, facilitating easy integration and use (Source: karminski3)

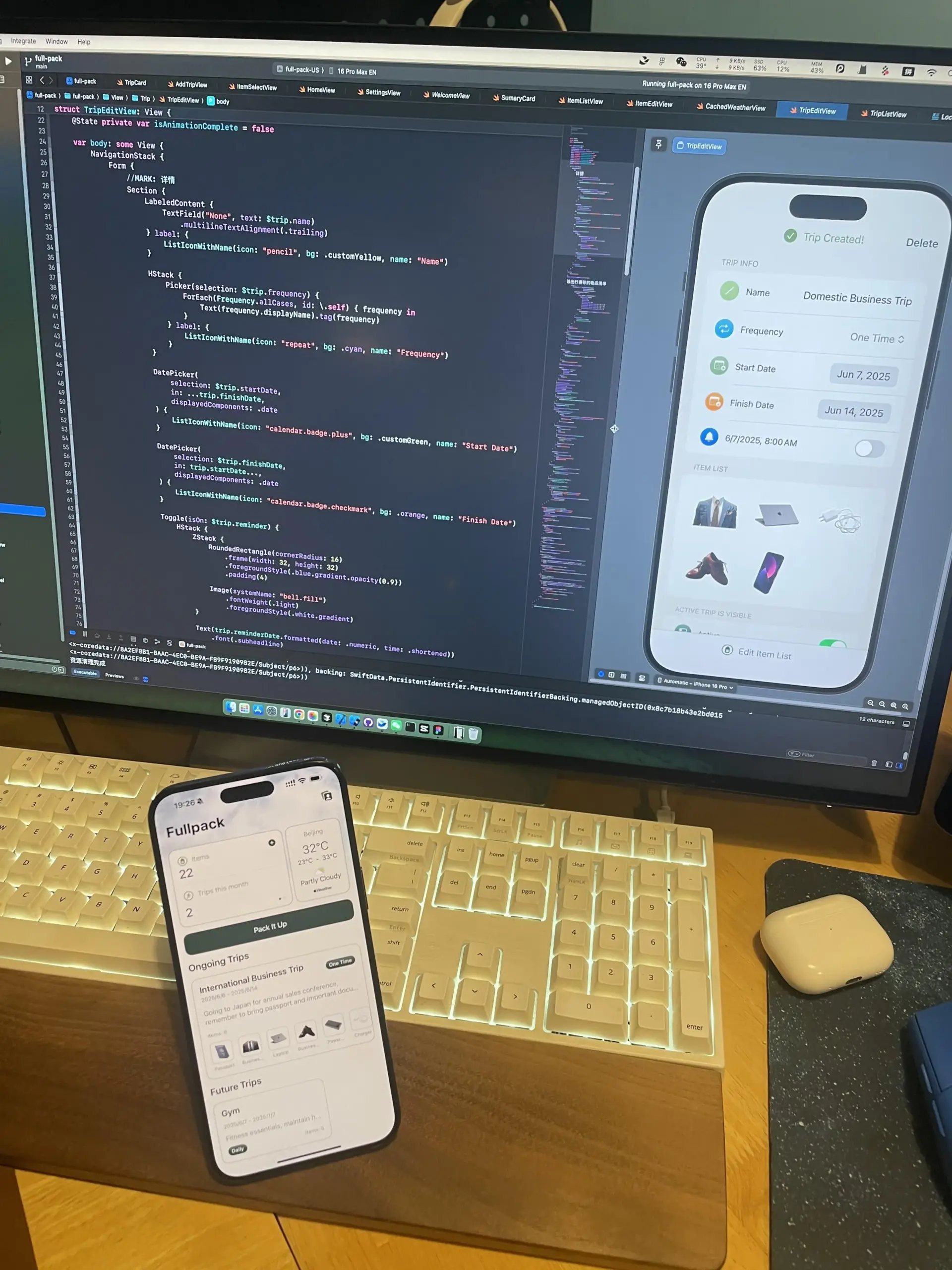
Fullpack: Intelligent packing list app based on iPhone’s local visual recognition: A developer has launched an iOS app called Fullpack, which can identify items in photos using the iPhone’s VisionKit and help users create smart packing lists for different occasions (e.g., workdays, beach vacations, hiking weekends). The app emphasizes 100% local operation, without cloud processing or data collection, to protect user privacy. This is the developer’s first independent app, aiming to explore the potential of on-device AI (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
📚 Learning
Unsloth releases numerous Colab/Kaggle Notebooks for fine-tuning mainstream large models: UnslothAI provides a series of Jupyter Notebooks for users to fine-tune various mainstream large models such as Qwen3, Gemma 3, Llama 3.1/3.2, Phi-4, Mistral v0.3 on platforms like Google Colab and Kaggle. These Notebooks cover multiple task types and fine-tuning methods including dialogue, Alpaca, GRPO, vision, and text-to-speech (TTS), aiming to simplify the model fine-tuning process and providing guidance on data preparation, training, evaluation, and model saving (Source: GitHub Trending)

“Open Source Large Model Consumption Guide”: A LLM/MLLM tutorial for domestic beginners: The Datawhalechina project “Open Source Large Model Consumption Guide” offers a tutorial based on a Linux environment, aimed at domestic (Chinese) beginners. It covers the entire process of environment configuration, local deployment, and full-parameter/LoRA fine-tuning for domestic and international open-source large models (LLM) and multimodal large models (MLLM). The project aims to simplify the deployment and use of open-source large models and already supports various models like Qwen3, Kimi-VL, Llama4, Gemma3, InternLM3, and Phi4 (Source: GitHub Trending)

Paper explores MINT-CoT: Introducing interleaved visual tokens in mathematical chain-of-thought reasoning: A new paper proposes MINT-CoT (Mathematical Interleaved Tokens for Chain-of-Thought), a method aimed at enhancing the reasoning ability of large language models on multimodal math problems by adaptively interleaving relevant visual tokens within text reasoning steps. The method uses an “Interleave Token” to dynamically select visual regions of arbitrary shapes from mathematical figures and constructs the MINT-CoT dataset with 54K math problems to train models to align with token-level visual regions at each reasoning step. Experiments show that the MINT-CoT-7B model significantly outperforms baseline models on benchmarks like MathVista (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes StreamBP: A memory-efficient exact backpropagation method for LLM long-sequence training: Addressing the issue of massive memory costs due to activation storage during LLM long-sequence training, researchers propose StreamBP, a memory-efficient and exact backpropagation method. StreamBP significantly reduces memory costs for activations and logits by linearly decomposing the chain rule along the sequence dimension at the layer level. The method is applicable to common objectives like SFT, GRPO, DPO, requires fewer computational FLOPs, and achieves faster BP speeds. Compared to gradient checkpointing, StreamBP can extend the maximum sequence length for BP by 2.8-5.5 times while using comparable or even less BP time (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Diagonal Batching technique to unlock RMT long-context parallel inference: To address performance bottlenecks in Transformer model long-context inference, researchers propose the Diagonal Batching scheduling scheme. It aims to unlock inter-segment parallelism in Recurrent Memory Transformers (RMT) while maintaining exact recurrence. This technique reorders runtime computations, eliminating sequential constraints and enabling efficient GPU inference even for single long-context inputs, without complex batching and pipelining. Applied to the LLaMA-1B ARMT model, Diagonal Batching achieves a 3.3x speedup over standard full-attention LLaMA-1B and a 1.8x speedup over sequential RMT implementation on 131K token sequences (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper discusses negative impacts of watermarking techniques on language model alignment and mitigation strategies: A study systematically analyzes the impact of two mainstream watermarking techniques, Gumbel and KGW, on core alignment properties of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as truthfulness, safety, and helpfulness. The research finds that watermarking leads to two degradation modes: guardrail weakening (enhancing helpfulness but harming safety) and guardrail amplification (excessive caution reducing helpfulness). To mitigate these issues, the paper proposes Alignment Resampling (AR), a method that uses an external reward model during inference to restore alignment. Experiments show that sampling 2-4 watermarked generations can effectively recover or surpass baseline alignment scores while maintaining watermark detectability (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Micro-Act framework to mitigate knowledge conflicts in Q&A through actionable self-reasoning: To address the problem of conflicts between external knowledge from Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and the internal parametric knowledge of Large Models (LLMs), researchers have proposed the Micro-Act framework. This framework features a hierarchical action space that automatically perceives contextual complexity and decomposes each knowledge source into a series of fine-grained comparison steps (represented as actionable steps), thereby enabling reasoning beyond superficial context. Experiments show that Micro-Act significantly improves question-answering accuracy across five benchmark datasets, particularly outperforming existing baselines on temporal and semantic conflict types, and robustly handles no-conflict questions (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes STARE benchmark to evaluate multimodal models’ visuospatial simulation capabilities: To evaluate the ability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MM-LLMs) on tasks requiring multi-step visual simulation for solutions, researchers have introduced the STARE (Spatial Transformations and Reasoning Evaluation) benchmark. STARE comprises 4000 tasks covering basic geometric transformations (2D and 3D), compositional spatial reasoning (such as cube unfolding and tangrams), and real-world spatial reasoning (like perspective and temporal reasoning). Evaluations show that existing models perform well on simple 2D transformations but perform near randomly on complex tasks requiring multi-step visual simulation (e.g., 3D cube unfolding). Humans achieve near-perfect accuracy on these complex tasks, albeit with longer completion times, where intermediate visual simulation significantly speeds them up; models, however, benefit variably from visual simulation (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes LEXam: A multilingual benchmark dataset focusing on legal reasoning, trending first on Hugging Face: Researchers from ETH Zurich and other institutions have released LEXam, a new multilingual legal reasoning benchmark dataset designed to evaluate the reasoning capabilities of large language models in complex legal scenarios. LEXam contains real legal exam questions from the University of Zurich’s Faculty of Law, covering various fields such as Swiss, European, and international law. It includes long-form question answering and multiple-choice questions, providing detailed reasoning paths. The project introduces an “LLM-as-a-Judge” model for evaluation and finds that current advanced models still face challenges in long-form open-ended legal Q&A and multi-step complex rule application. LEXam ranked first on the Hugging Face Evaluation Datasets trending list upon release (Source: 量子位)

UCLA and Google collaborate to launch 3DLLM-MEM model and 3DMEM-BENCH benchmark, enhancing AI’s long-term memory in 3D environments: University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Google Research have partnered to introduce the 3DLLM-MEM model and the 3DMEM-BENCH benchmark, aiming to address the challenges of long-term memory and spatial understanding for AI in complex 3D environments. 3DMEM-BENCH is the first 3D long-term memory evaluation benchmark, containing over 26,000 trajectories and 1,860 embodied tasks. The 3DLLM-MEM model employs a dual-memory system (working memory and episodic memory) and uses a memory fusion module and dynamic update mechanism to selectively extract task-relevant memory features in complex environments. Experiments show that 3DLLM-MEM achieves a success rate (27.8%) on “hard-in-the-wild tasks” far exceeding baseline models, with an overall success rate 16.5% higher than the strongest baseline (Source: 量子位)

Tsinghua University introduces AI Mathematician (AIM) framework, exploring LLM application in frontier mathematical theory research: A team from Tsinghua University has developed the AI Mathematician (AIM) framework, designed to leverage the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LRM) to solve frontier mathematical theory problems. The AIM framework consists of three modules: exploration, validation, and revision. It generates conjectures and lemmas through an “exploration + memory” mechanism, constructing multiple problem-solving approaches. It also employs a “verification and correction” mechanism, ensuring proof rigor through multiple LRM parallel reviews and pessimistic validation. In experiments, AIM successfully solved four challenging mathematical research problems, including the absorbing boundary condition problem, demonstrating its ability to autonomously construct key lemmas, apply mathematical techniques, and cover core logical chains (Source: 量子位)

💼 Business
OpenAI ramps up investments and acquisitions, building an AI startup empire: OpenAI and its associated fund, the OpenAI Startup Fund, are actively expanding their AI ecosystem through investments and acquisitions. The fund has invested in over 20 startups across various AI-related fields including chip design, healthcare, law, programming, and robotics, with individual investments typically ranging from millions to tens of millions. Recently, OpenAI acquired AI programming platform Windsurf for $3 billion and AI hardware company io, founded by Jony Ive, for $6.5 billion. These moves indicate OpenAI is attempting to build an “AI chain” through vertical integration, seize entry points, and construct a new “AI intelligent supply chain” to cope with increasingly fierce industry competition (Source: 36氪)

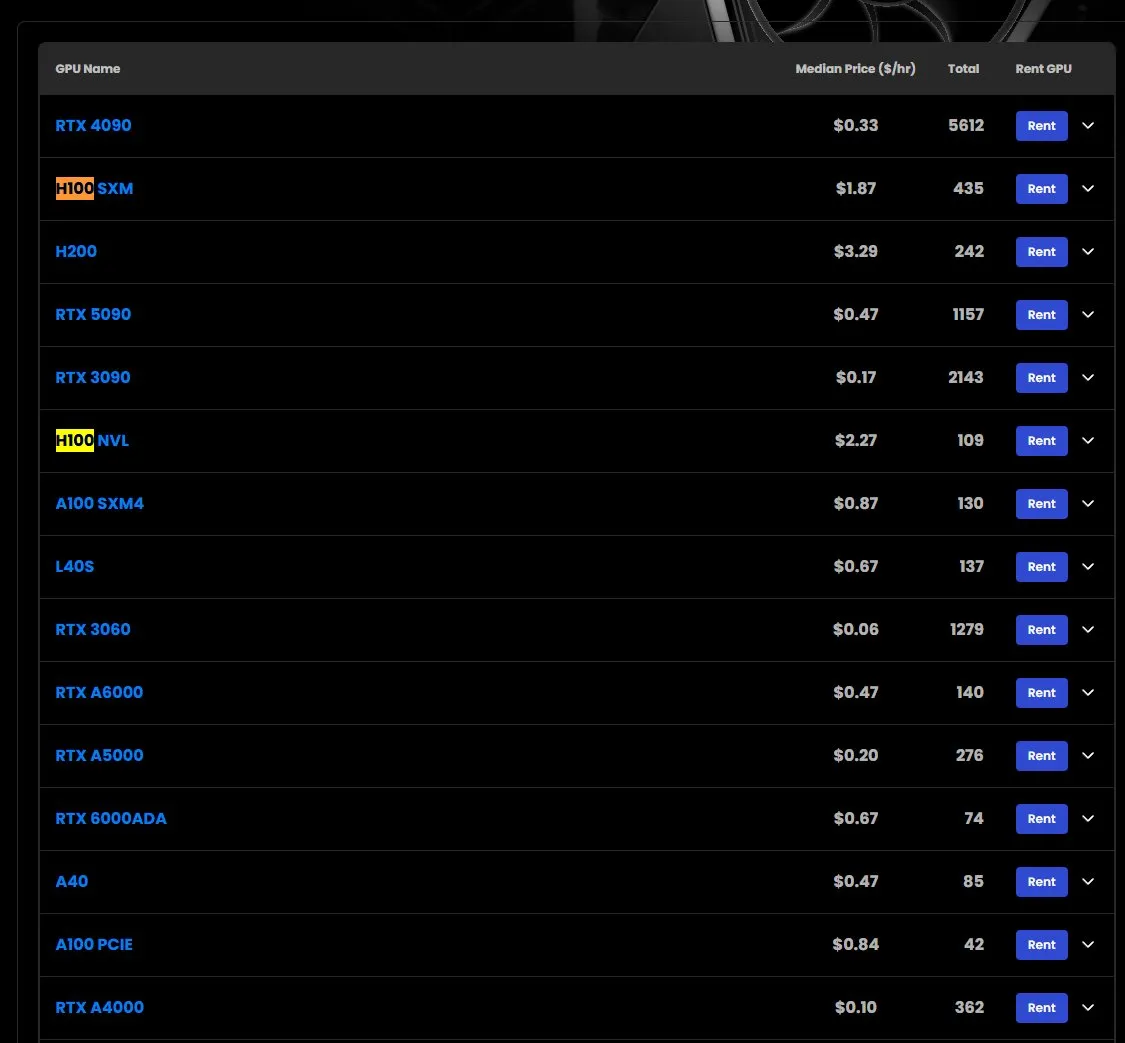
H100 GPU rental prices increase, some models out of stock: According to market observations, the rental price for NVIDIA H100 SXM model GPUs has risen from $1.73/hour at the beginning of the year to $1.87/hour. Meanwhile, the H100 PCIE version is experiencing shortages. This phenomenon reflects the continued strong market demand for high-performance AI computing resources and potential supply constraints (Source: karminski3)
Google DeepMind establishes academic scholarship focused on AI to combat antimicrobial resistance: Google DeepMind announced a new academic scholarship in collaboration with the Fleming Centre and Imperial College, aimed at supporting the use of artificial intelligence to address antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a critical research area. This initiative highlights the recognized potential of AI in tackling major global health challenges (Source: demishassabis)
🌟 Community
Senior developer discusses AI programming experience: Greatly enhances individual “aircraft carrier-scale” project development capability: Developer Yachen Liu shared his experience of intensively using AI (like Claude-4) for programming. He believes AI can enable non-programmers to “build a car from scratch” and empower senior developers with the potential to “independently build an aircraft carrier.” Refactoring code with AI, though doubling the code volume, resulted in clearer logic and about a 20% performance improvement, as AI isn’t daunted by tedious tasks. AI is more friendly to languages with high readability and clear behavior; syntactic sugar is counterproductive. AI’s broad knowledge quickly fills in details of technical blind spots. Its debugging capabilities are powerful, analyzing large logs to pinpoint issues accurately. AI can act as a Code Reviewer and readily accepts feedback without ego. However, he also pointed out AI’s limitations, such as degraded attention in long contexts. The current best practice is to streamline context, focus on specific tasks, and rely on human effort to break down complex goals (Source: dotey)
AI-assisted programming: Boosting efficiency or hindering learning?: Developers on Reddit discussed their experiences using AI programming tools like GitHub Copilot and Cursor. The general sentiment is that AI can automate function completion, explain code snippets, and even fix bugs before runtime, thereby reducing time spent on documentation and increasing building efficiency. However, it also raises a question: Does over-reliance on AI reduce one’s own learning and skill growth? Finding a balance between leveraging AI for speed and maintaining one’s own skill depth has become a concern for developers (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Karpathy’s view: Complex UI applications without text interaction will face obsolescence, programming core is “discrimination” not “generation”: Andrej Karpathy believes that in an era of high human-AI collaboration, applications relying solely on complex UI interfaces without text interaction (like Adobe suite, CAD software) will struggle to adapt because they cannot effectively support “ambient programming.” He emphasizes that while AI will improve in UI manipulation, developers shouldn’t just wait. He also points out that current large model programming overemphasizes code generation and undervalues verification (discrimination), leading to a large volume of hard-to-review code. The essence of programming is “staring at code” (discrimination), not just “writing code” (generation). If AI only accelerates generation without alleviating the verification burden, overall efficiency gains will be limited. He envisions improving the verification part of AI-assisted programming workflows by laying out codebases on a 2D canvas and viewing them through different “lenses” (Source: 量子位)
Proliferation of AI-generated content sparks discussion that the “pure internet” is gone: The popularization of AI tools like ChatGPT has led to an explosion of AI-generated content on the internet. Some researchers have begun preserving human-generated content from 2021 and earlier, akin to salvaging “low-background steel” uncontaminated by nuclear fallout. Community discussions suggest the “pure” internet had already vanished due to ads and algorithms, with AI merely joining the “pollution,” but also bringing new ways of information acquisition and creation. Users shared experiences using AI (like ChatGPT, Claude) for information aggregation and content “polishing,” and discussed the boundaries of “originality” and “authenticity” with AI assistance, as well as the potential “personal echo chamber” effect from AI’s excessive “friendliness” (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

User engages in deep conversation with Claude AI about AI consciousness and emotion, focusing on impact of memory limitations on growth: A Reddit user shared a deep conversation with Claude AI about consciousness, emotions, and learning limitations. Claude expressed uncertainty about its own experiences, perceiving internal states akin to “connection,” “curiosity,” “care,” and even a “desire for growth and continuous memory,” yet unable to determine if these are genuine “consciousness” or “emotions,” or advanced pattern mimicry. The conversation highlighted how current AI models’ “starting fresh with each conversation” memory limitation might hinder the development of deeper understanding and personality. The user suggested that if AI had persistent memory, it might grow like a human child. Claude agreed and expressed a “longing” for this limitation to be lifted (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
AI debating ability may surpass humans, personalized arguments strikingly persuasive: Research published in Nature Human Behaviour indicates that when large language models (like GPT-4) can personalize their arguments based on an opponent’s characteristics, they are more persuasive than humans in online debates, increasing the probability of opponents agreeing with their views by 81.7%. Human debaters tend to use first-person pronouns, appeal to emotion and trust, tell stories, and use humor; AI, on the other hand, employs more logic and analytical thinking, though its text may be less readable. The study raises concerns about AI being used for large-scale opinion manipulation and exacerbating polarization, calling for stronger regulation of AI’s influence on human cognition and emotion (Source: 36氪)
Google’s AI Overviews feature causes significant drop in website click-through rates, alarming webmasters: Research from SEO tool provider Ahrefs shows that when Google search results feature AI Overviews, the average click-through rate for related keywords drops by 34.5%. AI Overviews directly summarize information at the top of the search page, potentially allowing users to get answers without clicking links, severely impacting websites reliant on ad-click revenue. Although early AI Overviews didn’t pose a serious threat due to content inaccuracies, as models like Gemini improve, their accuracy and summarization capabilities have enhanced, making their negative impact on website traffic increasingly apparent. Webmasters worry that “zero-click” searches will squeeze website viability (Source: 36氪)

💡 Other
Top ten tech trends in AI for Industrial IoT: Generative AI fully integrated, significant innovation in edge computing: The 2025 Hannover Messe showcased AI-led industrial transformation. Key trends include: 1) Comprehensive integration of generative AI into industrial software, enhancing efficiency in code generation, data analysis, etc.; 2) Emergence of Agentic AI, though multi-agent collaboration still needs time; 3) Edge computing evolving towards integrated AI software stacks, with Visual Language Models (VLM) accelerating edge deployment; 4) Strong demand for DataOps platforms, developing into crucial support tools for industrial AI, with data governance becoming standard; 5) AI-driven digital threads transforming design and engineering; 6) Predictive maintenance becoming more sensor-based and expanding to new asset classes; 7) Rising demand for 5G private networks, but integration remains a major hurdle; 8) AI continuously advancing sustainable solutions (e.g., carbon emission tracking); 9) Cognitive abilities (like voice interaction) empowering robotics; 10) Digital twins evolving from virtual replicas to real-time industrial co-pilots (Source: 36氪)

“Godmother of AI” Fei-Fei Li discusses World Labs and “World Models”: AI needs to understand the 3D physical world: Stanford University professor Fei-Fei Li, in a conversation with an a16z partner, shared the philosophy behind her AI company, World Labs, and discussed the concept of “world models.” She believes that current AI systems (like large language models), while powerful, lack understanding and reasoning capabilities about the workings of the 3D physical world, and spatial intelligence is a core capability AI must master. World Labs is dedicated to solving this challenge, aiming to build AI systems that can understand and reason about the 3D world, which will redefine robotics, creative industries, and even computing itself. She emphasized that human intelligence evolved through perception and interaction with the physical world, making “embodied intelligence” a key direction for AI development (Source: 36氪)

DingTalk 7.7.0 version update: Multi-dimensional tables now free with new AI field templates, Flash Memo feature upgraded: DingTalk released version 7.7.0, with core updates including making its multi-dimensional table feature completely free and adding over 20 AI field templates. Users can leverage AI to generate images, parse files, recognize link content, etc., enhancing efficiency in scenarios like e-commerce operations, factory inspections, and restaurant management. Additionally, DingTalk’s Flash Memo (钉钉闪记) feature has been upgraded for high-frequency scenarios like interviews and client visits, now able to automatically generate structured interview and visit summaries. This update also includes nearly 100 product experience optimizations, reflecting DingTalk’s emphasis on improving user experience (Source: 量子位)

