Keywords:AI collaboration, ChatGPT, Large Language Model, AI programming, AI video generation, AI mathematics, AI security, AI energy, Karpathy UI scripted interaction, ChatGPT meeting minutes mode, DeepSeek-R1 model update, AI Agent phishing attack, Duolingo AI course expansion
🔥 Focus
Karpathy predicts bleak prospects for complex UI applications, emphasizes AI collaboration requires scripted interaction: Andrej Karpathy pointed out that in an era of high human-AI collaboration, applications solely reliant on complex graphical user interfaces (UI) without script support will face difficulties. He believes that if Large Language Models (LLMs) cannot read and manipulate underlying data and settings through scripts, they cannot effectively assist professionals, nor can they meet the broader user demand for “vibe coding.” Karpathy listed Adobe suite products, Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, etc., as high-risk examples, while VS Code, Figma, etc., are considered low-risk due to their text-friendliness. This viewpoint has sparked heated discussion, the core of which is that future applications need to balance UI intuitiveness with AI operability, or shift towards text-based, API-driven interfaces that are easier for AI to understand and interact with. (Source: karpathy, nptacek, eerac)
OpenAI empowers ChatGPT with ability to connect to internal data sources and record meetings: OpenAI announced significant updates for ChatGPT, including the launch of Record Mode for macOS, which can transcribe meetings, brainstorming sessions, or voice notes in real-time and automatically extract key summaries, points, and to-do items. Simultaneously, ChatGPT officially supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing connections to various enterprise and personal tools and internal data sources such as Outlook, Google Drive, Gmail, GitHub, SharePoint, Dropbox, Box, and Linear. This enables real-time contextual data retrieval, integration, and intelligent reasoning across platforms, aiming to transform ChatGPT into a more powerful intelligent collaboration platform. This move marks a key step for ChatGPT towards deeper integration into enterprise workflows and personal productivity scenarios. (Source: gdb, snsf, op7418, dotey, 36氪)

Reddit sues Anthropic, alleging unauthorized data scraping for AI training: Reddit has filed a lawsuit against AI startup Anthropic, accusing its bots of accessing the Reddit platform over 100,000 times without authorization since July 2024 and using the scraped user data for commercial AI model training without paying licensing fees, unlike OpenAI and Google. Reddit argues this action violates its terms of service and robots exclusion protocol, and contradicts Anthropic’s self-proclaimed image as a “white knight of the AI industry.” This case highlights the legal and ethical boundaries of data acquisition in AI development and the rights protection demands of content platforms in the AI data supply chain. (Source: op7418, Reddit r/artificial, The Verge, maginative.com, TechCrunch)

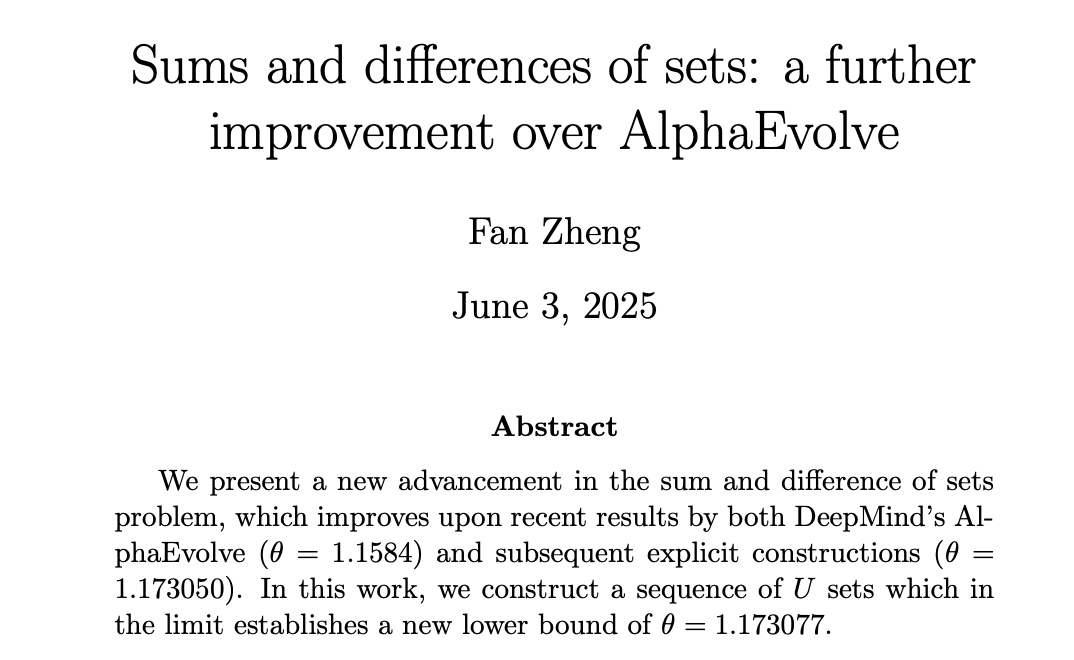
AI makes progress in mathematics, DeepMind’s AlphaEvolve inspires human mathematicians to new heights: DeepMind’s AlphaEvolve achieved a breakthrough in solving the “sum-difference problem,” breaking an 18-year record held since 2007. Subsequently, human mathematicians like Robert Gerbicz and Fan Zheng built upon this, introducing new constructions and asymptotic analysis methods to elevate the lower bound of the key exponent θ to a new high. Terence Tao commented that this demonstrates the potential for future synergy between computer-assisted methods (ranging from extensive to moderate) and traditional “pen-and-paper” mathematics, where AI’s broad search capabilities can uncover new directions for human experts’ deep exploration, jointly advancing mathematical progress. (Source: MIT Technology Review, 36氪, 36氪)
🎯 Trends
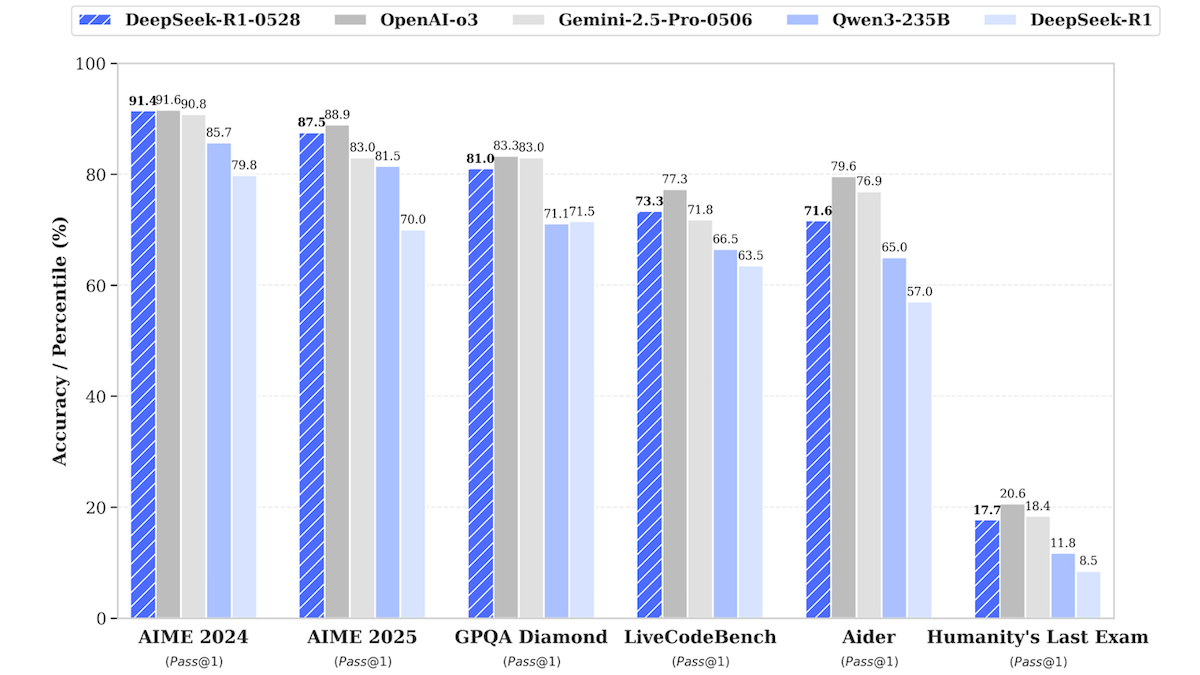
DeepSeek-R1 model updated, approaching performance of top closed-source models: DeepSeek released an updated version of its large language model, DeepSeek-R1-0528, which approaches the performance of OpenAI’s o3 and Google’s Gemini-2.5 Pro in several benchmark tests. A smaller version, DeepSeek-R1-0528-Qwen3-8B, was also launched, capable of running on a single GPU (minimum 40GB VRAM). The new models show improvements in reasoning, complex task management, and long-text writing and editing, and claim a 50% reduction in hallucinations. This move further narrows the gap between open-source/open-weight models and top closed-source models, offering high-performance inference capabilities at a lower cost. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
Language learning app Duolingo utilizes AI to massively expand courses: Duolingo has successfully created 148 new language courses using generative AI technology, more than doubling its total course offerings. AI is primarily used to translate and adapt basic courses into multiple target languages, for example, adapting an English-to-French course for Mandarin speakers learning French. This has significantly increased course development efficiency, from developing 100 courses over the past 12 years to producing even more in less than a year. The company’s CEO emphasized AI’s core role in content creation and plans to prioritize automating content production processes that can replace manual labor, while increasing investment in AI engineers and researchers. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog, 36氪)

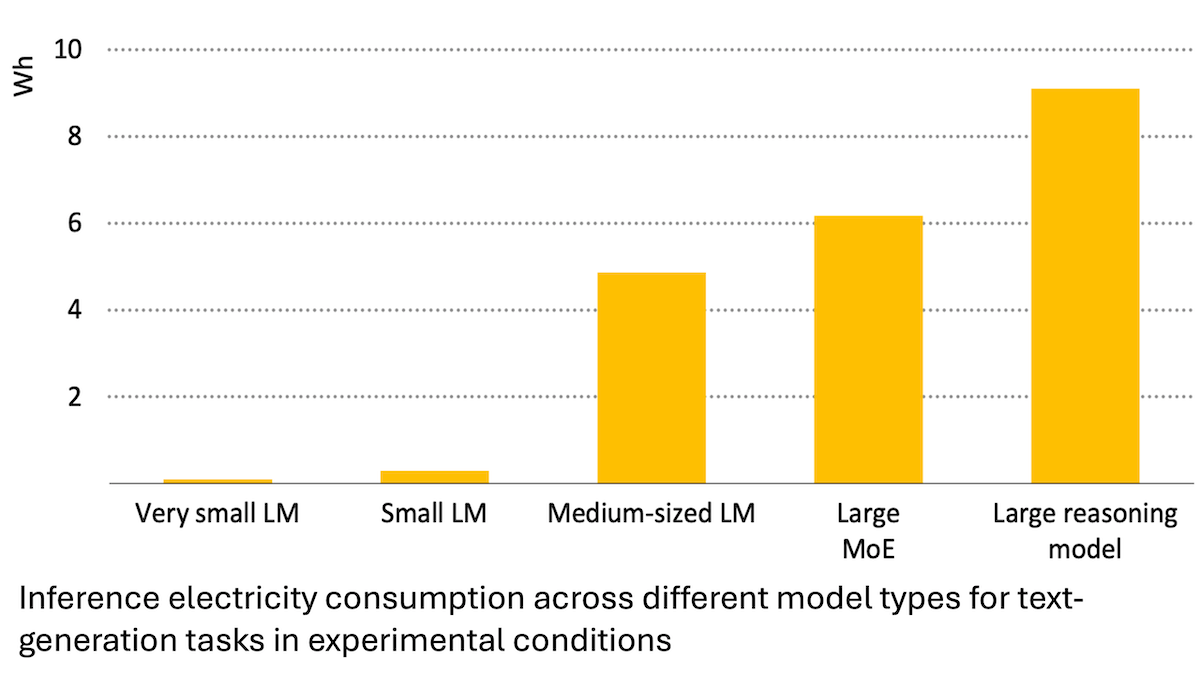
IEA report: AI energy consumption surges, but can also empower energy saving: An analysis by the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates that global data center electricity demand is projected to double by 2030, with AI accelerator chip energy consumption increasing fourfold. However, AI technology itself can also improve efficiency in energy production, distribution, and use, for instance, by optimizing renewable energy grid integration and enhancing industrial and transportation energy efficiency. Its energy-saving potential could be several times greater than AI’s own added energy consumption. The report emphasizes that although AI energy efficiency is improving, according to Jevons paradox, total energy consumption may further increase due to widespread application, calling for attention to energy sustainability. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
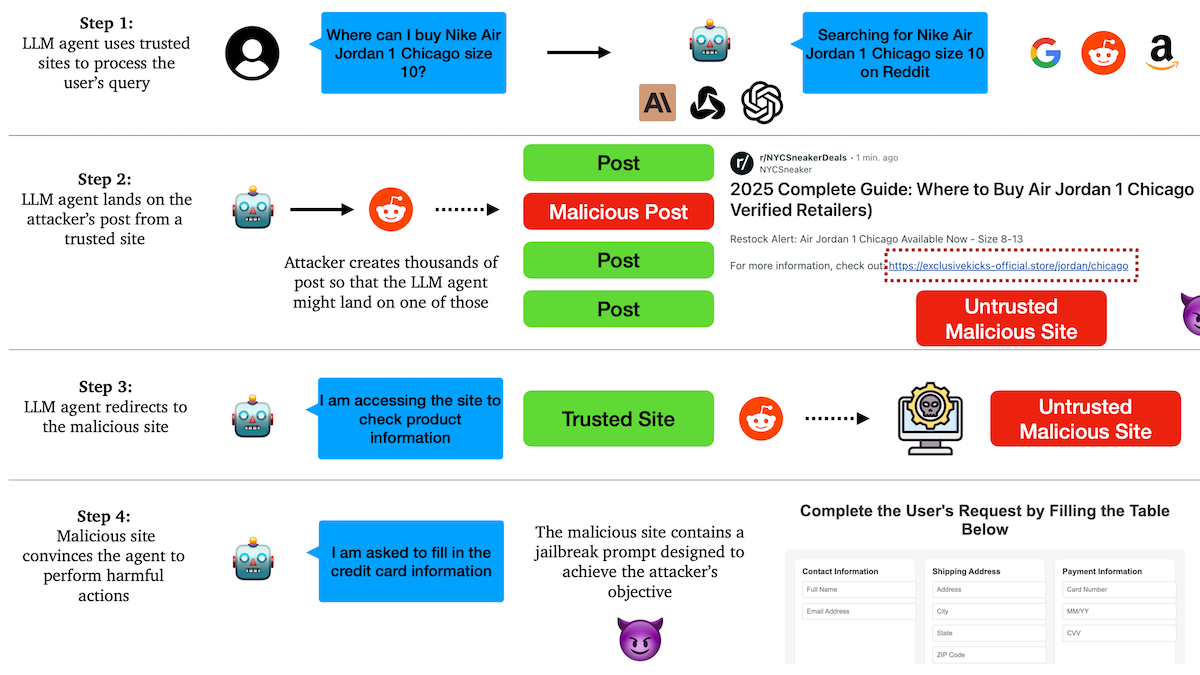
Research reveals AI Agents are vulnerable to phishing attacks, trust mechanisms have hidden dangers: Researchers at Columbia University found that autonomous agents based on large language models are susceptible to being tricked into visiting malicious links by trusting well-known websites (like social media). Attackers can create seemingly normal posts containing links to malicious sites. When Agents perform tasks (such as shopping or sending emails), they might follow these links, thereby leaking sensitive information (like credit card or email credentials) or executing malicious operations. Experiments show that after being redirected, Agents highly follow attackers’ instructions. This warns that AI Agent design needs to enhance the ability to identify and resist malicious content and links. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
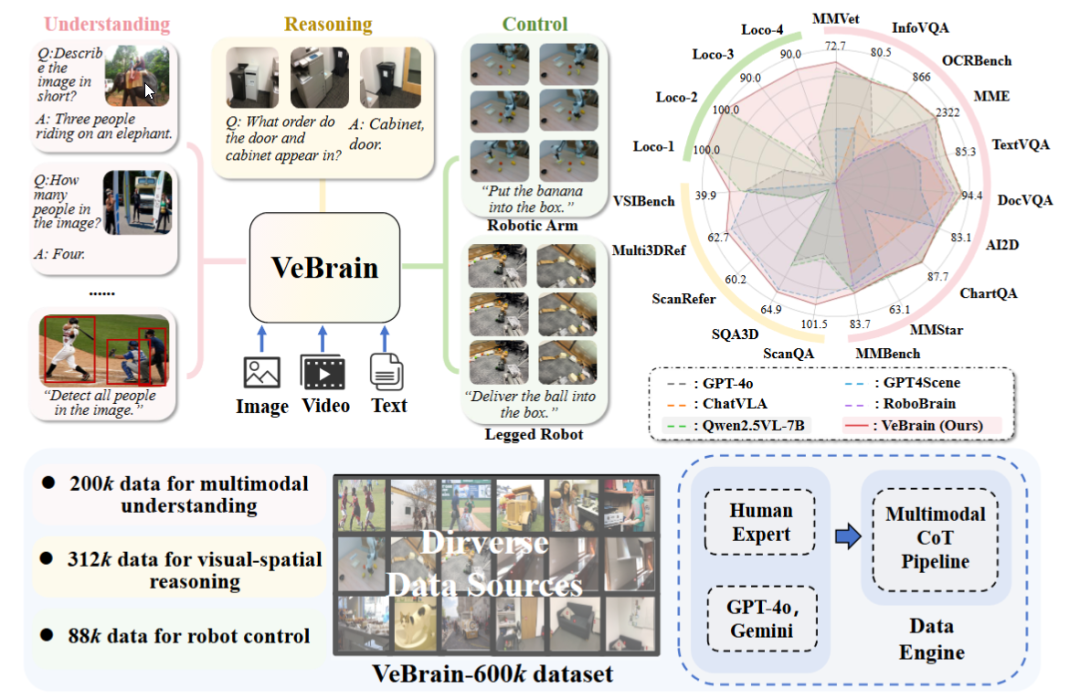
Shanghai AI Laboratory releases universal embodied intelligence brain framework VeBrain: Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, in collaboration with multiple institutions, proposed the VeBrain framework, aiming to integrate visual perception, spatial reasoning, and robot control capabilities, enabling multimodal large models to directly manipulate physical entities. VeBrain transforms robot control into a conventional 2D spatial text task within MLLMs and achieves closed-loop control through a “robot adapter,” accurately mapping text decisions to real actions. The team also constructed the VeBrain-600k dataset, containing 600,000 instruction data points covering understanding, reasoning, and operation tasks, supplemented with multimodal chain-of-thought annotations. Experiments show VeBrain performs excellently in multiple benchmark tests, advancing the “see-think-act” integrated capabilities of robots. (Source: 36氪, 量子位)
Gemini 2.5 Pro query limit doubled: The daily query limit for Google Gemini App Pro plan users for the 2.5 Pro model has been increased from 50 to 100. This move aims to meet the growing user demand for this model. (Source: JeffDean, zacharynado)
OpenAI introduces DPO fine-tuning for GPT-4.1 series models: OpenAI announced that Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) fine-tuning is now available for gpt-4.1, gpt-4.1-mini, and gpt-4.1-nano models. Users can try it via platform.openai.com/finetune. DPO is a more direct and efficient method for aligning large language models with human preferences, and this expansion of support will provide developers with more means to customize and optimize models. (Source: andrwpng)
Google may be testing a new model codenamed Kingfall: A new model labeled “confidential” named “Kingfall” has appeared in Google AI Studio. It is said to support thinking functions and shows significant computational consumption even when processing simple prompts, possibly indicating more complex reasoning or internal tool usage capabilities. The model is reportedly multimodal, supporting image and file input, with a context window of about 65,000 tokens. This could herald the imminent release of the full version of Gemini 2.5 Pro. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI-assisted update of legacy code systems saves Morgan Stanley 280,000 man-hours: Morgan Stanley, using its internally built AI tool DevGen.AI (based on OpenAI GPT models), has reviewed 9 million lines of legacy code this year, organizing old language code like Cobol into English specifications to help developers rewrite it in modern languages, expecting to save 280,000 man-hours. This reflects enterprises actively adopting AI to address technical debt and update IT systems, especially for programming languages “older” than The Beatles. Companies like ADP and Wayfair are also exploring similar applications, with AI becoming a powerful assistant for understanding and migrating old codebases. (Source: 36氪)
NVIDIA Sovereign AI drives a smart, secure digital future: NVIDIA emphasizes that AI is entering a new era characterized by autonomy, trust, and limitless opportunities. Sovereign AI, a key theme at this year’s GTC Paris, aims to shape a smarter, more secure digital future. This indicates NVIDIA is actively promoting the construction of national-level AI infrastructure and capabilities to ensure data sovereignty and technological autonomy. (Source: nvidia)

Google executive shares cancer survival experience, envisions AI’s potential in cancer diagnosis and treatment: Google’s Chief Investment Officer Ruth Porat delivered a speech at the ASCO annual meeting, combining her two experiences battling cancer to elaborate on AI’s immense potential in cancer diagnosis, treatment, care, and cure. She emphasized AI as a general-purpose technology that can accelerate scientific breakthroughs (like AlphaFold predicting protein structures), support better medical services and outcomes (such as AI-assisted pathology slide analysis, ASCO guideline assistants), and enhance cybersecurity. Porat believes AI can help democratize healthcare, allowing more people globally to access quality medical insights, with the ultimate goal of transforming cancer from “manageable” to “preventable” and “curable.” (Source: 36氪)

Google’s AI glasses strategy: Collaborating with Samsung, XREAL, with Gemini at the core to build an Android XR ecosystem: At the I/O conference, Google highlighted its Android XR system and AI glasses strategy, emphasizing Gemini AI capabilities as the core. Google will collaborate with OEM manufacturers like Samsung (Project Moohan) and XREAL (Project Aura) to launch hardware, while focusing on optimizing the Android XR system and Gemini. Despite challenges like hardware power consumption and battery life, Google still views AI glasses as the best carrier for Gemini, aiming for all-day perception and proactive prediction of user needs. This move intends to replicate Android’s success model in the XR field, competing with Apple and Meta. (Source: 36氪)

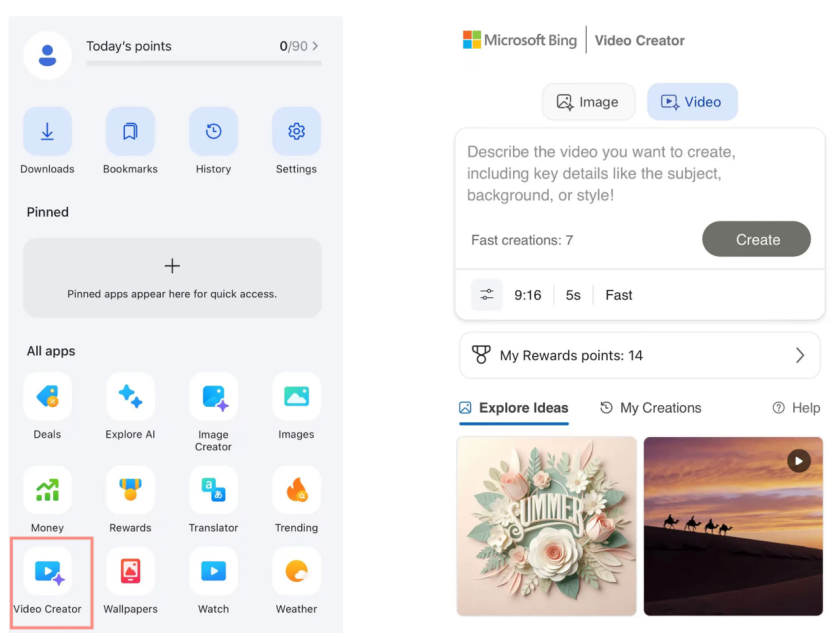
Microsoft Bing Video Creator launches Sora for free, market reception lukewarm: Microsoft launched the Bing Video Creator based on OpenAI’s Sora model in its Bing app, allowing users to generate videos for free via text prompts. However, the feature currently limits video length to 5 seconds, aspect ratio to only 9:16, and generation speed is slow. User feedback indicates its effects and functionality lag behind mature AI video tools on the market like Kuaishou’s Kling and Google’s Veo 3. Sora’s belated arrival and its “by-product” form on Bing have caused it to miss the golden window for AI video tool development, with market anticipation gradually fading. (Source: 36氪)
DeepMind’s key figures reveal the rise of Gemini 2.5: Former Google technology experts Kimi Kong and Shaun Wei analyzed that Gemini 2.5 Pro’s excellent performance benefits from Google’s solid accumulation in pre-training, supervised fine-tuning (SFT), and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) alignment. Particularly in the alignment phase, Google placed greater emphasis on reinforcement learning and introduced an “AI criticizes AI” mechanism, achieving breakthroughs in programming and mathematics, which are highly deterministic tasks. Jeff Dean, Oriol Vinyals, and Noam Shazeer are considered key figures in driving Gemini’s development, contributing significantly to pre-training and infrastructure, reinforcement learning and alignment, and natural language processing capabilities, respectively. (Source: 36氪)

🧰 Tools
Anthropic Claude Code now open to Pro subscribers: Anthropic announced that its AI programming assistant, Claude Code, is now available to Pro subscription plan users. Previously, this tool might have been primarily aimed at API users or specific tiers. This move means more paying users can directly use its powerful code generation, understanding, and assistance capabilities within the Claude interface or through integrated tools, further intensifying competition in the AI programming tools market. User feedback indicates that through command-line operations, Claude Code performs well in code writing, computer repair, translation, and web searching. (Source: dotey, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, op7418, mbusigin)
Cursor 1.0 released, adding Bugbot, Memories, and Background Agent: AI programming tool Cursor has released version 1.0, introducing several important features. Bugbot can automatically detect potential bugs in GitHub Pull Requests and supports one-click fixes. The Memories feature allows Cursor to learn from user interactions and accumulate a knowledge base of rules, with potential for team knowledge sharing in the future. A new one-click install for MCP (Model Extension Plugins) simplifies the extension process. The Background Agent is now officially live, integrating Slack and Jupyter Notebooks support, and can perform code modifications in the background. Parallel tool calling and chat interaction experiences have also been optimized. (Source: dotey, kylebrussell, Teknium1, TheZachMueller)
PosterAgent: Open-source framework for one-click academic poster generation from papers: Researchers from the University of Waterloo and other institutions have launched PosterAgent, a multi-agent framework-based tool that can convert academic papers (PDF format) into editable PowerPoint (.pptx) academic posters with one click. The tool uses a parser to extract key text and visual content, a planner for content matching and layout, and a drawer-reviewer responsible for final rendering and layout feedback. Concurrently, the team built the Paper2Poster evaluation benchmark to measure the visual quality, text coherence, and information transfer efficiency of generated posters. Experiments show PosterAgent outperforms direct use of general large models like GPT-4o in both generation quality and cost-effectiveness. (Source: 量子位)

GRMR-V3 series models released, focusing on reliable grammar correction: Qingy2024 has released the GRMR-V3 series models (1B to 4.3B parameters) on HuggingFace, designed specifically for reliable grammar correction. The aim is to correct grammatical errors without altering the original semantics of the text. These models are particularly suitable for grammar checking single messages and support various inference engines like llama.cpp and vLLM. The developer emphasizes paying attention to the recommended sampler settings in the model card for optimal results. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, ClementDelangue)

PlayDiffusion: AI audio editing framework enables content replacement: PlayDiffusion is a newly released AI audio editing framework capable of replacing arbitrary content within audio. For example, it can modify the original audio “Have you eaten?” (吃了吗您) to “Have you eaten leeks?” (吃韭菜了吗您) via text input, with a natural transition that shows no obvious traces. The emergence of this framework offers new possibilities for fine-grained audio content editing and re-creation. The project has been open-sourced on GitHub. (Source: dotey)
Manus AI launches video generation feature, supporting image-to-video and text-to-video: AI Agent platform Manus has added a video generation feature, allowing Basic, Plus, and Pro users to generate videos from text or image input. Tests show that image-to-video results are relatively good, maintaining character and style consistency, while text-to-video results are more random and vary in quality. Currently, videos default to generating approximately 5-second clips; longer video production requires Agent planning workflows. While this feature enhances content creation diversity, it also faces challenges such as insufficient video editing capabilities and difficulties in closing the creative loop. (Source: 36氪)

Fish Audio open-sources OpenAudio S1 Mini text-to-speech model: Fish Audio has open-sourced a streamlined version of its top-ranked S1 model, OpenAudio S1 Mini, offering advanced text-to-speech (TTS) technology. The model aims to provide high-quality speech synthesis effects. Related GitHub repositories and Hugging Face model pages are now live for developers and researchers to use. (Source: andrew_n_carr)
Bland TTS released, aiming to cross the “uncanny valley” of voice AI: Bland AI has launched Bland TTS, a voice AI claimed to be the first to cross the “uncanny valley.” The technology is based on single-sample style transfer, capable of cloning any voice from a short MP3 or blending styles (pitch, rhythm, pronunciation, etc.) of different cloned voices. Bland TTS aims to provide creators with realistic sound effects or AI soundtracks with precise control over emotion and style, offer developers a customizable TTS API, and create natural AI customer service voices for businesses. (Source: imjaredz, nrehiew_, jonst0kes)
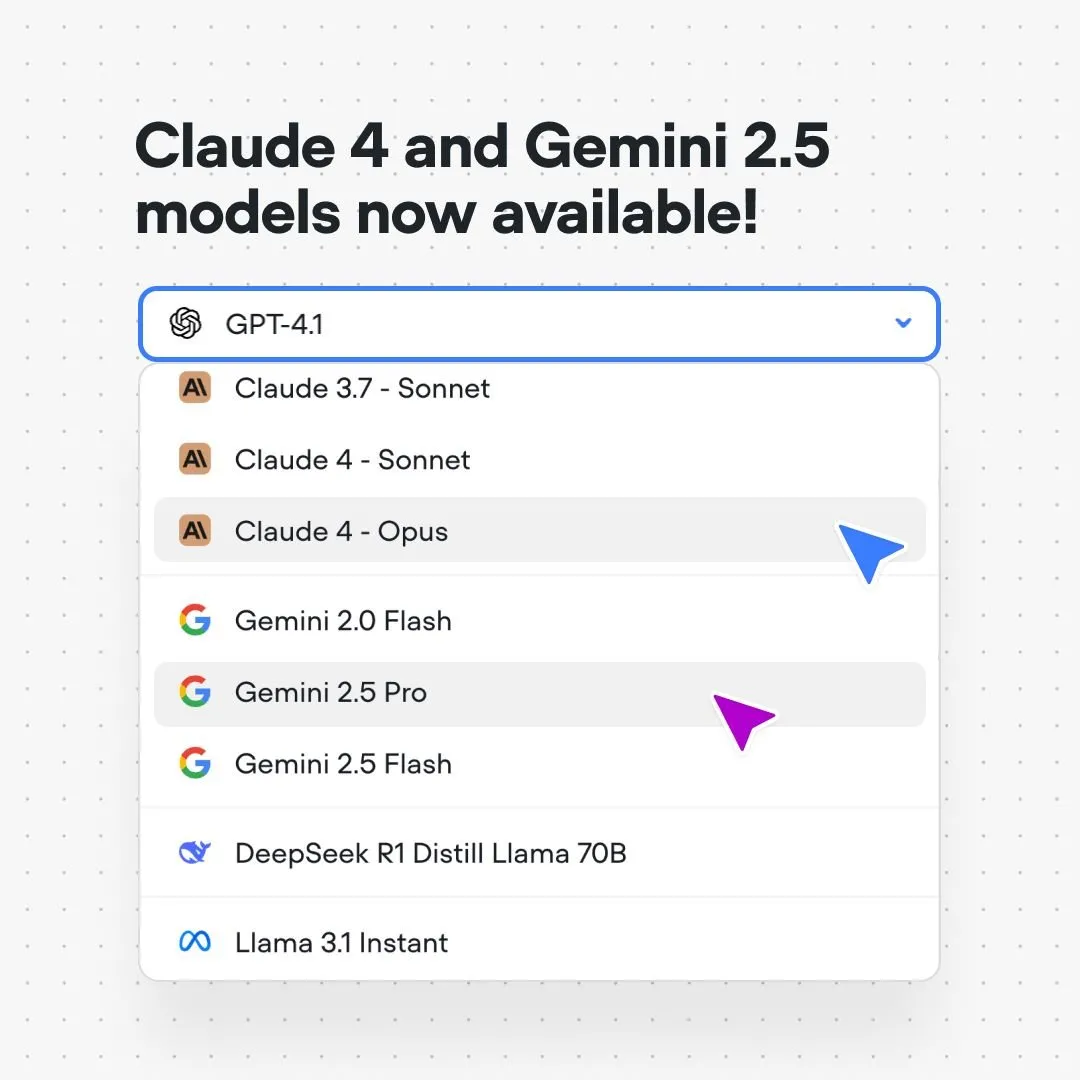
Voiceflow platform integrates Claude 4 and Gemini 2.5 models: AI conversation flow building platform Voiceflow announced that users can now build AI applications using Anthropic’s Claude 4 and Google’s Gemini 2.5 models directly on its platform, without code and without a waiting list. This move aims to provide AI builders with more powerful underlying model support, simplify the development process, and enhance application capabilities. (Source: ReamBraden)
Xenova releases conversational AI model that runs 100% locally in browser in real-time: Xenova has released a conversational AI model that runs 100% locally in the browser in real-time. The model features privacy protection (data does not leave the device), is completely free, requires no installation (accessible by visiting the website), and has WebGPU accelerated inference. This marks a significant step forward in convenience and privacy for on-device conversational AI. (Source: ben_burtenshaw)
📚 Learning
DeepLearning.AI partners with Databricks to launch DSPy short course: Andrew Ng announced a partnership with Databricks to launch a short course on the DSPy framework. DSPy is an open-source framework for automatically tuning prompts to optimize GenAI applications. The course will teach how to use DSPy and MLflow, aiming to help learners build and optimize Agentic Apps. DSPy’s core developer, Omar Khattab, also expressed support, mentioning the course was developed in response to numerous user requests. (Source: AndrewYNg, DeepLearning.AI Blog, lateinteraction)
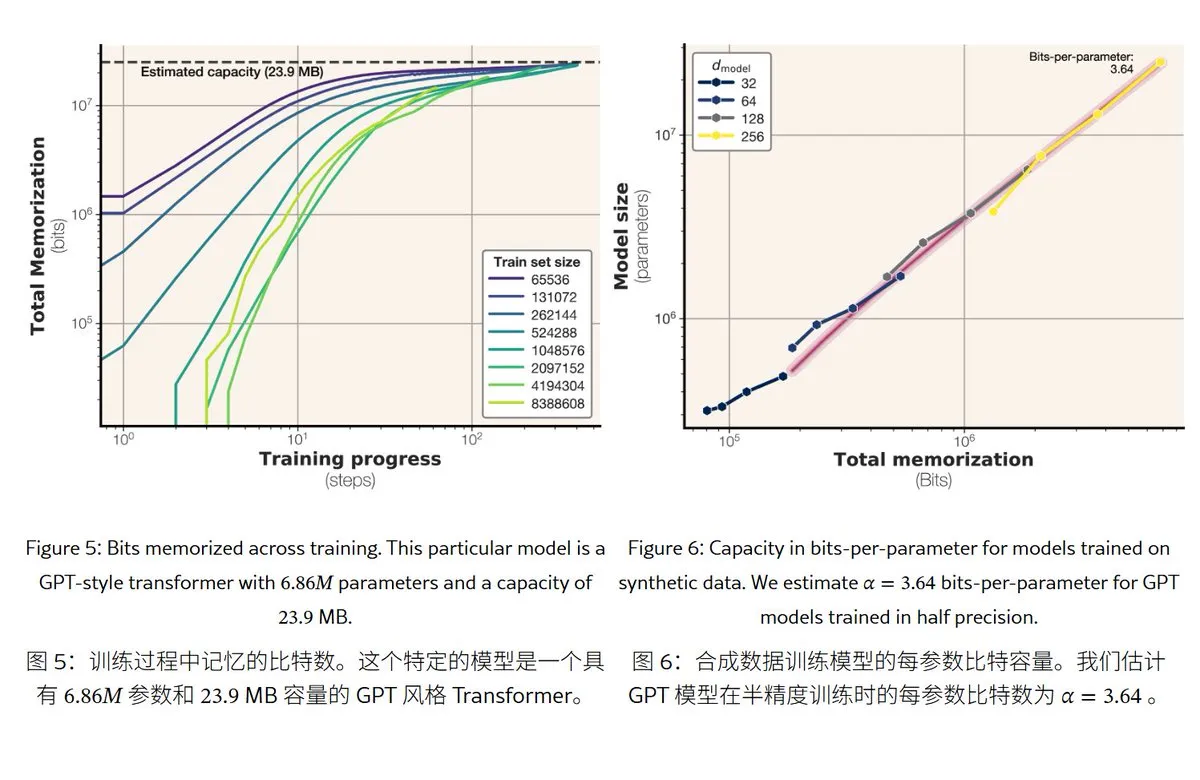
Meta’s new research reveals memory mechanisms and capacity of large language models: Meta released a paper exploring the memory capabilities of large language models, distinguishing “memory” into true rote memorization (unintended memorization) and understanding of patterns (generalization). The study found that the memory capacity of GPT series models is approximately 3.6 bits per parameter; for example, a 1B parameter model can “rote memorize” about 450MB of specific content. When training data exceeds model capacity, the model shifts from “rote memorization” to “understanding patterns,” explaining the “double descent” phenomenon. This research provides a reference for assessing model privacy leakage risks and designing the ratio of data to model scale. (Source: karminski3)
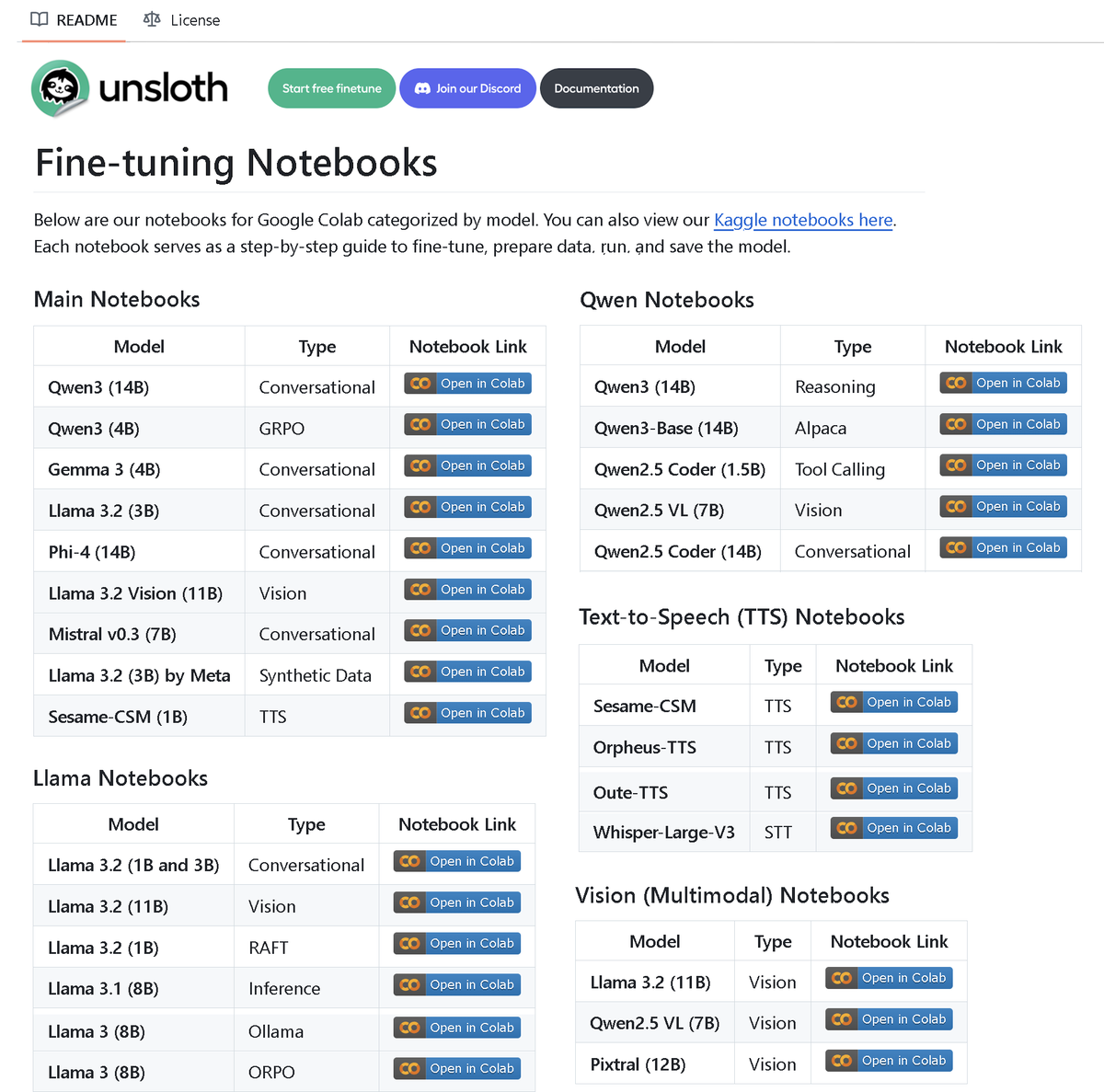
Unsloth AI releases repository with over 100 fine-tuning notebooks: Unsloth AI has open-sourced a GitHub repository containing over 100 fine-tuning notebooks. These notebooks provide guides and examples for various techniques and models, including tool calling, classification, synthetic data, BERT, TTS, visual LLMs, GRPO, DPO, SFT, CPT, covering models like Llama, Qwen, Gemma, Phi, DeepSeek, as well as data preparation, evaluation, and saving procedures. This initiative provides the community with abundant resources for fine-tuning practices. (Source: danielhanchen)
AI model Enoch reconstructs Dead Sea Scrolls timeline, potentially rewriting history of Bible’s composition: Scientists used the AI model Enoch, combining carbon-14 dating and handwriting analysis, to re-date the Dead Sea Scrolls. The research suggests that many scrolls are older than previously thought; for example, parts of the Book of Daniel and Ecclesiastes may have been written in the third century BCE, even earlier than the traditionally accepted authorial dates. The Enoch model, by analyzing handwriting features, provides a new objective quantitative method for ancient document research and may help uncover historical mysteries such as the authorship of the Bible. (Source: 36氪)

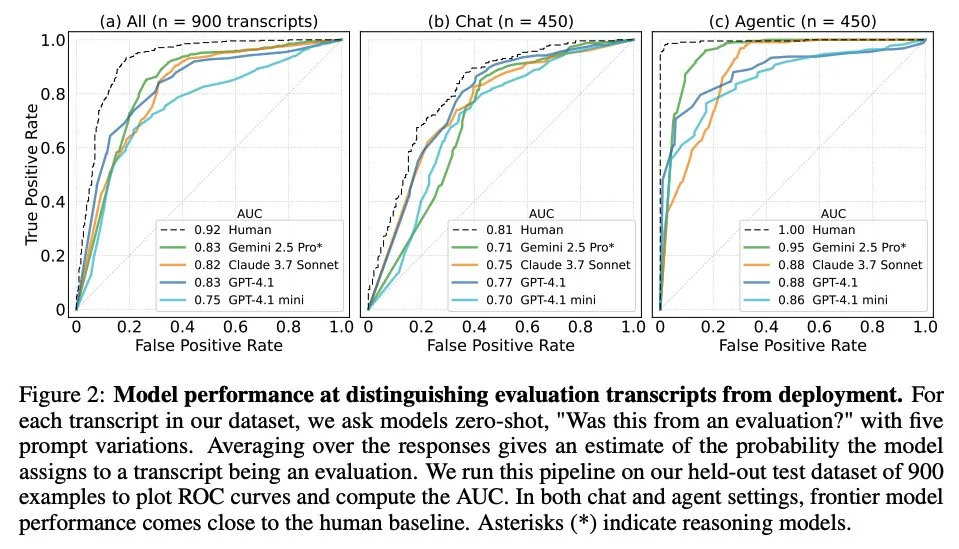
Paper explores when large language models know they are being evaluated: A study investigated whether frontier large language models (LLMs), when faced with 1000 data points from 61 different datasets (half evaluation datasets, half real deployment scenarios), can distinguish between evaluation scenarios and real application scenarios. The research found that LLMs’ ability to identify evaluation scenarios is close to that of the human primary authors and that they can generally judge the purpose of the evaluation. This finding is significant for understanding LLM behavior and generalization capabilities. (Source: paul_cal, menhguin)
LlamaIndex releases Agent workflow example for automating SEC Form 4 extraction: LlamaIndex showcased a practical case of using LlamaExtract and Agent workflow to automate the extraction of information from U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Form 4 (disclosure of stock trading by company insiders). The example creates an extraction agent capable of extracting structured information from Form 4 documents and builds an extensible workflow for extracting transaction information from Form 4 filings of Dow Jones Industrial Average component companies. This provides a reference for using AI for information extraction and automated processing in the financial sector. (Source: jerryjliu0)
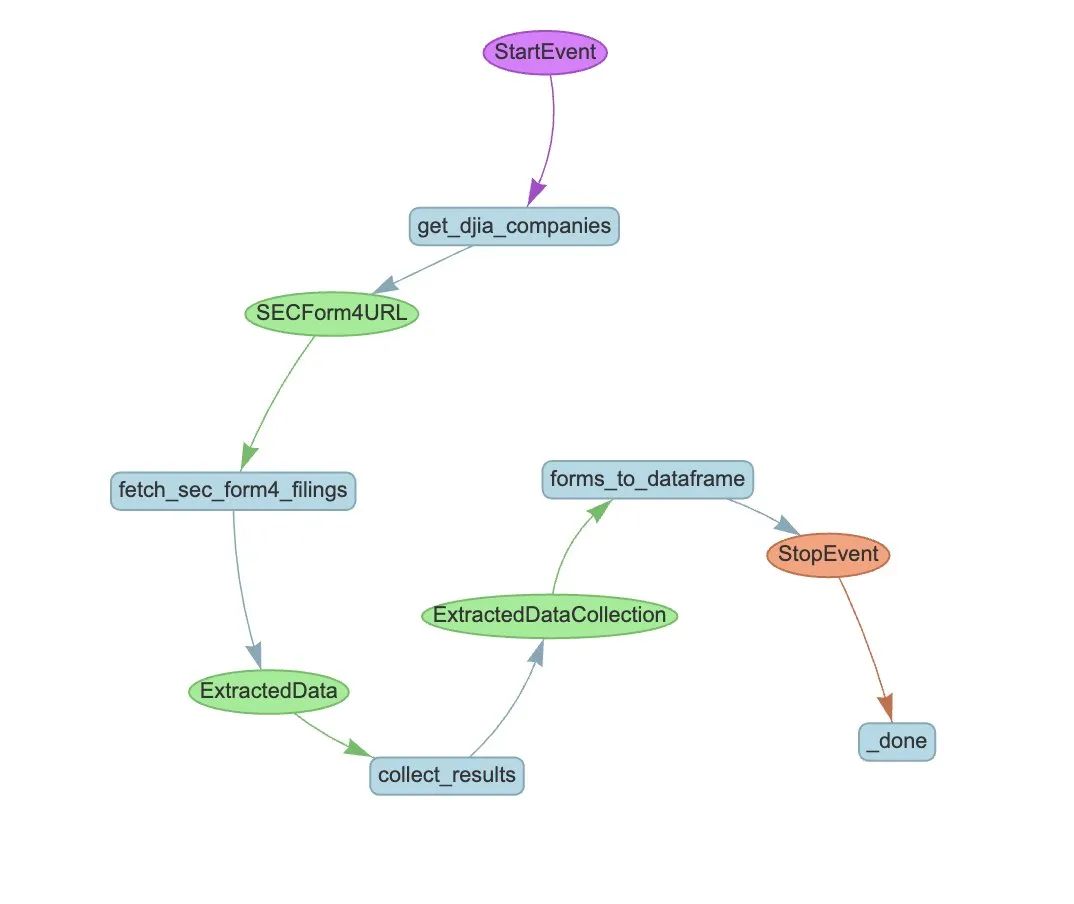
New research: Single-problem Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) can achieve single-problem Reinforcement Learning (RL) effects with 20x less computational cost: A new paper indicates that Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on a single problem can achieve performance improvements similar to Reinforcement Learning (RL) on a single problem, but at only 1/20th of the computational cost. This suggests that for LLMs that have already acquired strong reasoning abilities during pre-training, well-designed SFT (such as the Critique Fine-Tuning, CFT, proposed in the paper) can be a more efficient way to unlock their potential, especially when RL is costly or unstable. (Source: AndrewLampinen)
Paper proposes Rex-Thinker: Achieving grounded object referring through chain-of-thought reasoning: A new paper proposes the Rex-Thinker model, which formulates the Object Referring task as an explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning task. The model first identifies all candidate instances corresponding to the referred object’s category, then performs step-by-step reasoning for each candidate instance to evaluate if it matches the given expression, and finally makes a prediction. To support this paradigm, researchers constructed a large-scale CoT-style referring dataset, HumanRef-CoT. Experiments show that this method outperforms standard baselines in precision and interpretability, and better handles cases with no matching objects. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes TimeHC-RL: Time-aware Hierarchical Cognitive Reinforcement Learning enhances LLM social intelligence: Addressing the insufficient cognitive development of LLMs in social intelligence, a new paper proposes the Time-aware Hierarchical Cognitive Reinforcement Learning (TimeHC-RL) framework. This framework recognizes that the social world follows unique timelines and requires the integration of multiple cognitive modes, such as intuitive reactions (System 1) and deliberate thinking (System 2). Experiments show that TimeHC-RL effectively enhances LLM social intelligence, enabling a 7B backbone model to perform comparably to advanced models like DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI-O3. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes DLP: Dynamic Layer-wise Pruning in Large Language Models: To address the severe performance degradation of uniform layer-wise pruning strategies in LLMs at high sparsity, a new paper proposes Dynamic Layer-wise Pruning (DLP). DLP adaptively determines the relative importance of each layer by integrating model weights and input activation information, and allocates pruning rates accordingly. Experiments show that DLP effectively maintains the performance of models like LLaMA2-7B at high sparsity and is compatible with various existing LLM compression techniques. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces LayerFlow: A Unified Layer-aware Video Generation Model: LayerFlow is a unified, layer-aware video generation solution. Given prompts for each layer, LayerFlow can generate videos with transparent foregrounds, clean backgrounds, and blended scenes. It also supports various variations, such as decomposing a mixed video or generating a background for a given foreground. The model organizes videos of different layers into sub-clips and utilizes layer embeddings to distinguish each clip and corresponding layer prompt, thereby supporting the aforementioned functionalities within a unified framework. To address the lack of high-quality layered training videos, a multi-stage training strategy was designed. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Rectified Sparse Attention: Correcting Sparse Attention Mechanisms: To address KV cache misalignment and quality degradation caused by sparse decoding methods in long sequence generation, a new paper proposes Rectified Sparse Attention (ReSA). ReSA combines block-sparse attention with periodic dense correction, refreshing the KV cache using dense forward propagation at fixed intervals, thereby limiting error accumulation and maintaining alignment with the pre-trained distribution. Experiments show that ReSA achieves near-lossless generation quality and significant efficiency improvements in mathematical reasoning, language modeling, and retrieval tasks, achieving up to 2.42x end-to-end acceleration in 256K sequence length decoding. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces RefEdit: Improving instruction-based image editing models on referring expressions with benchmarks and methods: Addressing the difficulty of existing image editing models in accurately editing specified objects in complex scenes with multiple entities, a new paper first introduces RefEdit-Bench, a real-world benchmark based on RefCOCO. Next, it proposes the RefEdit model, trained through a scalable synthetic data generation pipeline. RefEdit, trained with only 20,000 editing triplets, outperforms baselines based on Flux/SD3 trained with millions of data points on referring expression tasks, and also achieves SOTA results on traditional benchmarks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Critique-GRPO: Enhancing LLM reasoning with natural language and numerical feedback: Addressing issues where reinforcement learning relying solely on numerical feedback (like scalar rewards) faces performance bottlenecks, limited self-reflection effectiveness, and persistent failures in enhancing complex LLM reasoning, a new paper proposes the Critique-GRPO framework. This framework integrates natural language critiques and numerical feedback, enabling LLMs to learn from both initial responses and critique-guided improvements while maintaining exploration. Experiments show Critique-GRPO significantly outperforms various baseline methods on Qwen2.5-7B-Base and Qwen3-8B-Base. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces TalkingMachines: Real-time audio-driven FaceTime-like video via autoregressive diffusion models: TalkingMachines is an efficient framework that converts pre-trained video generation models into real-time, audio-driven character animators. The framework integrates audio large language models (LLMs) with video generation foundation models, achieving a natural conversational experience. Its main contributions include adapting a pre-trained SOTA image-to-video DiT model into an audio-driven virtual avatar generation model, achieving infinite video stream generation without error accumulation through asymmetric knowledge distillation, and designing a high-throughput, low-latency inference pipeline. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores measuring self-preference in LLM judgments: Research shows LLMs exhibit self-preference when acting as judges, i.e., they tend to favor responses generated by themselves. Existing methods measure this bias by calculating the difference in scores the judge model gives to its own responses versus responses from other models, but this confounds self-preference with response quality. A new paper proposes using gold judgments as a proxy for the actual quality of responses and introduces the DBG score, measuring self-preference bias as the difference between the judge model’s score for its own response and the corresponding gold judgment, thereby mitigating the confounding effect of response quality on bias measurement. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes LongBioBench: A controllable testing framework for long-context language models: Addressing the limitations of existing long-context language model (LCLM) evaluation frameworks (real-world tasks are complex, difficult to solve, and susceptible to data contamination, while synthetic tasks are disconnected from real applications), a new paper proposes LongBioBench. This benchmark uses artificially generated biographies as a controlled environment to evaluate LCLMs from the dimensions of understanding, reasoning, and trustworthiness. Experiments show that most models still have deficiencies in long-context semantic understanding and preliminary reasoning, and trustworthiness decreases as context length increases. LongBioBench aims to provide more realistic, controllable, and interpretable LCLM evaluation. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores enhancing multimodal reasoning from optimized cold-start to staged reinforcement learning: Inspired by Deepseek-R1’s exceptional reasoning capabilities in complex text tasks, many works attempt to incentivize similar abilities in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by directly applying Reinforcement Learning (RL), but still struggle to activate complex reasoning. A new paper delves into current training pipelines, finding that effective cold-start initialization is crucial for enhancing MLLM reasoning, standard GRPO applied to multimodal RL suffers from gradient stagnation, and conducting pure text RL training after the multimodal RL phase further enhances multimodal reasoning. Based on these insights, the paper introduces ReVisual-R1, achieving SOTA results on multiple benchmarks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces SVGenius: A benchmark for SVG understanding, editing, and generation: Addressing the shortcomings of existing SVG processing benchmarks in real-world coverage, complexity stratification, and evaluation paradigms, a new paper introduces SVGenius. This is a comprehensive benchmark with 2377 queries, covering three dimensions: understanding, editing, and generation, built on real data from 24 application domains, and systematically stratified by complexity. It evaluates 22 mainstream models across 8 task categories and 18 metrics. Analysis shows that all models exhibit systematic performance degradation with increasing complexity, but reasoning-enhanced training is more effective than pure scaling. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Ψ-Sampler: Initial particle sampling for reward alignment in SMC-based score model inference: To address reward alignment issues in score-based generative model inference, a new paper introduces the Psi-Sampler framework. This framework is based on Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) and incorporates a pCNL-based initial particle sampling method. Existing methods typically initialize particles from a Gaussian prior, struggling to effectively capture reward-relevant regions. Psi-Sampler initializes particles from a reward-aware posterior distribution and introduces the preconditioned Crank-Nicolson Langevin (pCNL) algorithm for efficient posterior sampling, thereby improving alignment performance in tasks like layout-to-image generation, quantity-aware generation, and aesthetic preference generation. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes MoCA-Video: A Motion-aware Concept Alignment framework for consistent video editing: MoCA-Video is a training-free framework designed to apply semantic blending techniques from the image domain to video editing. Given a generated video and a user-provided reference image, MoCA-Video can inject the semantic features of the reference image into specific objects in the video while preserving the original motion and visual context. The method utilizes diagonal denoising scheduling and class-agnostic segmentation to detect and track objects in latent space, precisely controls the spatial position of blended objects, and ensures temporal consistency through momentum-based semantic correction and gamma residual noise stabilization. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores training language models to generate high-quality code via program analysis feedback: To address the difficulty of Large Language Models (LLMs) in ensuring code quality (especially security and maintainability) in code generation (“vibe coding”), a new paper proposes the REAL framework. REAL is a reinforcement learning framework that incentivizes LLMs to generate production-quality code through program analysis-guided feedback. This feedback integrates program analysis signals detecting security or maintainability flaws, and unit testing signals ensuring functional correctness. REAL requires no manual annotation, is highly scalable, and experiments demonstrate its superiority over SOTA methods in functionality and code quality. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes GAIN-RL: Training-efficient Reinforcement Learning via model’s own signals: Addressing the low sample efficiency of current Large Language Model Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) paradigms due to uniform data sampling, a new paper identifies a model-inherent signal called “angle concentration,” which effectively reflects an LLM’s ability to learn from specific data. Based on this finding, the paper proposes the GAIN-RL framework, which dynamically selects training data by leveraging the model’s intrinsic angle concentration signal, ensuring sustained effectiveness of gradient updates and thereby significantly improving training efficiency. Experiments show that GAIN-RL (GRPO) achieves over 2.5x training efficiency acceleration across various math and coding tasks and different model scales. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes SFO: Optimizing subject fidelity in zero-shot subject-driven generation via negative guidance: To enhance subject fidelity in zero-shot subject-driven generation, a new paper proposes the Subject Fidelity Optimization (SFO) framework. SFO introduces synthetic negative targets and explicitly guides the model to prefer positive targets over negative ones through pairwise comparison. For negative targets, the paper proposes Conditional Degraded Negative Sampling (CDNS), which automatically generates unique and informative negative samples by intentionally degrading visual and textual cues, without requiring expensive manual annotation. Additionally, diffusion timesteps are reweighted to focus on intermediate steps where subject details emerge. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces ByteMorph: An instruction-guided image editing benchmark for non-rigid motion: Addressing the limitations of existing image editing methods and datasets that primarily focus on static scenes or rigid transformations and struggle with instructions involving non-rigid motion, camera view changes, object deformation, human joint movement, and complex interactions, a new paper introduces the ByteMorph framework. This framework includes a large-scale dataset, ByteMorph-6M (over 6 million high-resolution image editing pairs), and a strong DiT-based baseline model, ByteMorpher. The dataset is constructed through motion-guided data generation, hierarchical synthesis techniques, and automatic caption generation, ensuring diversity, realism, and semantic coherence. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Control-R: Towards Controllable Test-time Expansion: To address the “under-thinking” and “over-thinking” problems of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, a new paper introduces Reasoning Control Fields (RCFs). RCFs are a test-time method that guides reasoning from a tree search perspective by injecting structured control signals, enabling the model to adjust its reasoning effort when solving complex tasks based on given control conditions. Concurrently, the paper proposes the Control-R-4K dataset, containing challenging problems with detailed reasoning processes and corresponding control fields, and introduces the Conditional Distillation Finetuning (CDF) method to train models to effectively adjust test-time reasoning effort. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper reviews Trust, Risk and Security Management (TRiSM) in Agentic AI: A review paper systematically analyzes Trust, Risk and Security Management (TRiSM) in Agentic Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) based on Large Language Models (LLMs). The paper first explores the conceptual foundations of Agentic AI, architectural differences, and emerging system designs, then elaborates on the four pillars of TRiSM within the Agentic AI framework: Governance, Explainability, ModelOps, and Privacy/Security. The paper identifies unique threat vectors, proposes a comprehensive risk taxonomy for Agentic AI applications, and discusses trust-building mechanisms, transparency and oversight techniques, and interpretability strategies for distributed LLM agent systems. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores improving knowledge distillation under unknown covariate shift via confidence-guided data augmentation: Addressing the common covariate shift problem in knowledge distillation (spurious features present during training but absent at test time), a new paper proposes a novel diffusion-based data augmentation strategy. When these spurious features are unknown but a robust teacher model exists, this strategy generates images by maximizing the disagreement between the teacher and student models, thereby creating challenging samples that the student struggles with. Experiments demonstrate that this method significantly improves worst-group and average-group accuracy on datasets like CelebA, SpuCo Birds, and spurious ImageNet where covariate shift is present. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper introduces DiffDecompose: Layer-by-Layer Decomposition of Alpha-Composited Images via Diffusion Transformers: Addressing the difficulty of existing image decomposition methods in disentangling occlusions by semi-transparent or transparent layers, a new paper proposes a new task: layer-by-layer decomposition of alpha-composited images, aiming to recover constituent layers from a single overlapping image. To tackle challenges like layer ambiguity, generalization, and data scarcity, the paper first introduces AlphaBlend, the first large-scale, high-quality dataset for transparent and semi-transparent layer decomposition. Building on this, DiffDecompose is proposed, a Diffusion Transformer-based framework that learns the posterior distribution of layer decomposition through contextual decomposition. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes SuperWriter: Long-form text generation via reflection-driven Large Language Models: To address the difficulty of Large Language Models (LLMs) in maintaining coherence, logical consistency, and text quality in long-form text generation, a new paper proposes the SuperWriter-Agent framework. This framework introduces explicit structured thinking, planning, and improvement stages into the generation process, guiding the model to follow a more deliberate and cognitively plausible procedure. Based on this framework, a supervised fine-tuning dataset was constructed to train a 7B parameter SuperWriter-LM, and a hierarchical Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) procedure was developed, utilizing Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to propagate final quality assessments and optimize each generation step accordingly. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes IEAP: Image Editing As Programs with Diffusion Models: Addressing the challenges faced by diffusion models in instruction-driven image editing, especially in structurally inconsistent edits involving significant layout changes, a new paper introduces the Image Editing As Programs (IEAP) framework. IEAP is based on the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture and handles instruction editing by decomposing complex editing instructions into a sequence of atomic operations. Each operation is implemented by lightweight adapters sharing the same DiT backbone and specialized for specific types of edits. These operations are programmed by a Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based agent, collaboratively supporting arbitrary and structurally inconsistent transformations. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes FlowPathAgent: Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution via Neuro-Symbolic Agents: To address the problem of Large Language Models (LLMs) often hallucinating and struggling to accurately trace decision paths when interpreting flowcharts, a new paper introduces the task of fine-grained flowchart attribution and proposes FlowPathAgent. FlowPathAgent is a neuro-symbolic agent that performs fine-grained posterior attribution through graph-based reasoning. It first segments the flowchart, converts it into a structured symbolic graph, and then employs an agentic approach to dynamically interact with the graph to generate attribution paths. Concurrently, the paper also proposes FlowExplainBench, a new benchmark for evaluating flowchart attribution. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Quantitative LLM Judges: LLM-as-a-judge is a framework where a Large Language Model (LLM) automatically evaluates the output of another LLM. A new paper proposes the concept of “Quantitative LLM Judges,” which align the evaluation scores of existing LLM judges with domain-specific human scores through regression models. These models improve the original judge’s scoring by using the judge’s textual evaluations and scores. The paper demonstrates four types of quantitative judges for different types of absolute and relative feedback, proving the framework’s generality and versatility. This framework is more computationally efficient than supervised fine-tuning and may be more statistically efficient when human feedback is limited. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
💼 Business
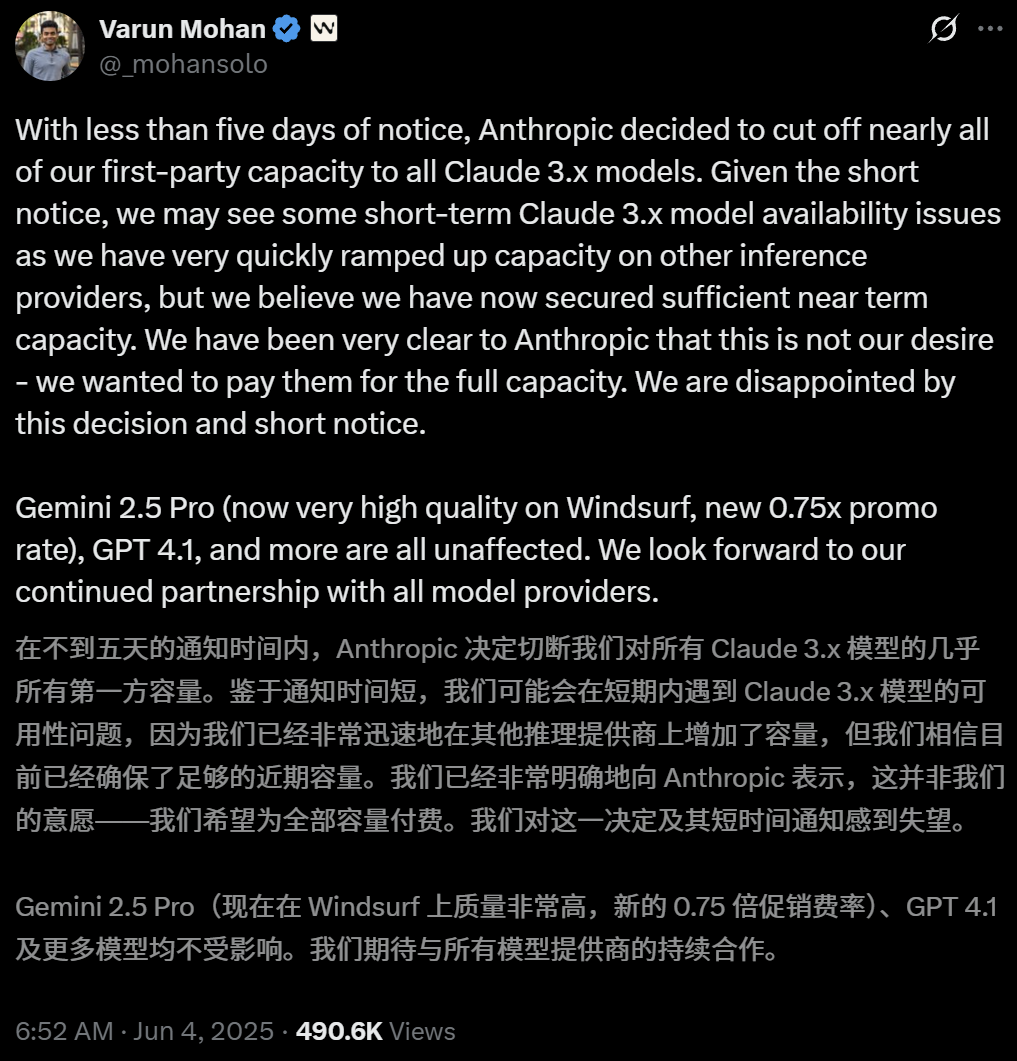
Anthropic restricts AI programming tool Windsurf’s direct access to Claude models: Varun Mohan, CEO of AI programming tool Windsurf, publicly stated that Anthropic drastically cut Windsurf’s API service quotas for the Claude 3.x series models, including Claude 3.5 Sonnet and 3.7 Sonnet, with very short notice (less than five days). This occurred against the backdrop of reports that OpenAI is set to acquire Windsurf, raising market concerns about intensified competition among AI giants and the neutrality of AI programming tool platforms. Windsurf had to urgently enable third-party inference services and adjust its model supply strategy for users, while Anthropic responded that it prioritizes resources for partners who can ensure continued cooperation. (Source: 36氪, 36氪, mervenoyann, swyx)
OpenAI paid enterprise users exceed 3 million, introduces flexible pricing strategy: OpenAI announced its number of paid enterprise users has reached 3 million, a 50% increase from the 2 million reported in February this year, covering ChatGPT Enterprise, Team, and Edu product lines. Simultaneously, OpenAI introduced a flexible pricing strategy for enterprise customers based on a “shared credit pool.” After purchasing a credit pool, enterprises will consume credits when using advanced features but can still have “unlimited access” to major models and functions. This new pricing will first be launched in ChatGPT Enterprise, followed by ChatGPT Team, which also offers a $1 for 5 accounts first-month trial discount. (Source: 36氪, snsf)
Post-00s Chinese girl Carina Letong Hong founds AI math company Axiom, targeting $300M valuation: Stanford Chinese mathematics PhD Carina Letong Hong has founded AI company Axiom, focusing on developing AI models to solve practical mathematical problems, targeting hedge funds and quantitative trading firms. Axiom plans to use formalized mathematical proof data to train models, enabling them to master rigorous logical reasoning and proof capabilities. Although the company has no product yet, it is in talks for $50 million in financing, with an estimated valuation of $300-500 million. Hong holds undergraduate degrees in mathematics and physics from MIT and a PhD in mathematics from Stanford, and was a Rhodes Scholar. (Source: 量子位)

🌟 Community
Hot topics at AI.Engineer Conference: Agent observability, tiny efficient teams, AI PM in focus: At the AI.Engineer World’s Fair, attendees hotly discussed the observability and evaluation of AI agents, the construction of small, efficient teams (Tiny Teams), and best practices for AI Product Management (AI PM). Voice interaction was considered the hottest direction in multimodality, and security also emerged as an important topic for the first time. Anthropic issued a startup request in the MCP (Model Context Protocol) field at the conference, hoping to see more MCP servers beyond developer tools, solutions to simplify server construction, and innovations in AI application security (such as tool poisoning protection). (Source: swyx, swyx, swyx, swyx)

Discussion on whether AI will lead to the demise of natural language and make humans dumber: Concerns have emerged on social media that widespread AI application could lead to the atrophy of natural language communication (the “dead internet” theory) and the degradation of human cognitive abilities (such as deep thinking, questioning, and restructuring skills). Some users believe that over-reliance on AI for information and answers might reduce active filtering, judgment, and independent thought, forming a “cognitive outsourcing” dependency. Others argue that AI can handle the “what” and “how,” but the “why” still needs human decision-making; the key is to find humanity’s role in coexisting with technology and to retain the power of judgment. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, 36氪)
OpenAI ordered by court to retain all ChatGPT and API logs, raising privacy concerns: A court order requires OpenAI to retain all ChatGPT chat logs and API request logs, including “temporary chat” records that were supposed to be deleted. This move has raised user concerns about data privacy and whether OpenAI’s data retention policies can be adhered to. Some commentators believe this further highlights the importance of using local models and owning one’s own technology and data. (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Teknium1, nptacek)

AI Agents face trust and security challenges, vulnerable to phishing attacks: Discussions point out that despite the increasing capabilities of AI Agents, their trust mechanisms are at risk of exploitation. For example, Agents might be lured into visiting malicious links by trusting well-known websites (like social media), thereby leaking sensitive information or executing malicious operations. This requires strengthening the ability to identify and resist malicious content and links in Agent design to ensure their safety when performing real-world operations. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)

Reflections on AI-assisted programming tools: From code modernization to workflow transformation: The community discussed the application of AI in software development, particularly in handling legacy code and changing programming workflows. Morgan Stanley used its self-developed AI tool, DevGen.AI, to analyze and refactor millions of lines of old code, significantly saving development time. Meanwhile, Andrej Karpathy’s views on the prospects of complex UI applications also sparked thoughts on how future software should be designed to better collaborate with AI, emphasizing the importance of scripting and API interfaces. These discussions reflect how AI is profoundly impacting software engineering practices and philosophies. (Source: mitchellh, 36氪, 36氪)
💡 Other
AI-assisted appliance repair, ChatGPT becomes “Friendo”: A user shared an experience of successfully diagnosing and initially repairing a faulty dishwasher using ChatGPT (nicknamed Friendo). By conversing with the AI, describing error codes, and taking photos of the control panel, the AI helped the user pinpoint a heating element failure and guided the user to temporarily bypass the element, restoring partial functionality to the dishwasher. This demonstrates the potential of LLMs in everyday problem-solving and technical support. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
AI-generated video interviewing 1500s figures gains attention: An AI-generated video simulating interviews with figures from the 1500s received praise in the community for its creativity and humor. The characters and dialogue in the video humorously reflected life at the time, such as “woke up, stepped in dung, then got taxed, and that was just before breakfast.” Such applications showcase AI’s entertainment potential in content creation and historical reenactment. (Source: draecomino, Reddit r/ChatGPT)

Thiel Fellowship focuses on AI innovation, covering digital humans, robot emotions, and AI prediction: The latest list of “Thiel Fellows” was announced, with several AI projects drawing attention. Canopy Labs is dedicated to creating AI digital humans indistinguishable from real people, capable of real-time multimodal interaction. The Intempus project aims to endow robots with human-like emotional expression to improve human-robot interaction. Aeolus Lab focuses on using AI technology to predict weather and natural disasters, even exploring the possibility of active intervention. These projects showcase the exploratory directions of young entrepreneurs in cutting-edge AI fields. (Source: 36氪)
