Keywords:Gemini 2.5 Pro, VeBrain, Segment Anything Model 2, Qwen3-Embedding, AI Agent, Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Think mode, VeBrain general embodied intelligence brain framework, SAM 2 image and video segmentation, Qwen3-Embedding 32k context, AI Agent multimodal understanding
🔥 Focus
Google Announces Multiple New AI Advancements, Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Think Mode Enhances Complex Reasoning Capabilities: At the Google I/O conference, Google announced the Deep Think mode for Gemini 2.5 Pro, aimed at significantly enhancing AI’s reasoning capabilities when tackling complex problems (such as USAMO-level math challenges). Concurrently, Google also launched AlphaEvolve, a Gemini-powered coding agent for algorithm discovery, which has achieved results in matrix multiplication algorithm design and solving open mathematical problems, and is applied to optimize Google’s internal data centers, chip design, and AI training efficiency. Additionally, the video model Veo 3, image model Imagen 4, and AI editing tool FLOW were also released, showcasing Google’s comprehensive layout and rapid progress in the multimodal AI field. (Source: OriolVinyalsML, demishassabis, demishassabis, op7418)
Shanghai AI Laboratory Jointly Releases General Embodied Intelligence Brain Framework VeBrain: Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, in collaboration with multiple institutions, launched VeBrain (Visual Embodied Brain), a general embodied intelligence brain framework aimed at unifying visual perception, spatial reasoning, and robot control capabilities. The framework transforms robot control tasks into 2D spatial text tasks within MLLMs (such as keypoint detection and embodied skill recognition) and introduces a “robot adapter” to achieve precise mapping and closed-loop control from text-based decisions to real-world actions. To support model training, the team constructed the VeBrain-600k dataset, containing 600,000 instruction data points, covering three categories of tasks: multimodal understanding, visual-spatial reasoning, and robot operation. Tests show that VeBrain has reached SOTA levels in multimodal understanding, spatial reasoning, and real-world robot control (robotic arms and robot dogs). (Source: QbitAI)

Anthropic Open-Sources LLM Visualization Tool “Circuit Tracing”, Enhancing Model Interpretability: Anthropic has launched “circuit tracing”, an open-source tool aimed at helping researchers understand the internal working mechanisms of Large Language Models (LLMs). The tool generates “attribution graphs” to visualize the internal super-nodes and their connections as the model processes information, similar to a neural network diagram. Researchers can verify the function of each node and decode the LLM’s decision-making logic by intervening in node activation values and observing changes in model behavior. The tool supports generating attribution graphs on mainstream open-source models and provides an interactive front-end interface, Neuronpedia, for visualization, annotation, and sharing. This initiative aims to promote AI interpretability research, enabling a broader community to explore and understand model behavior. (Source: QbitAI, swyx)
Meta Releases Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), Enhancing Image and Video Segmentation Capabilities: Meta AI Research (FAIR) has launched SAM 2, an upgraded version of its popular Segment Anything Model. SAM 2 is a foundational model focused on promptable visual segmentation tasks in images and videos, capable of accurately identifying and segmenting specific objects or regions in an image or video based on prompts (such as points, boxes, text). The model is now open-source, under the Apache License, available for researchers and developers to use and build applications freely, further advancing the field of computer vision. (Source: AIatMeta)
🎯 Trends
BAAI Open-Sources Video-XL-2, Achieving 10,000-Frame Video Understanding on a Single GPU: Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI), in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University and other institutions, has released the new-generation ultra-long video understanding model Video-XL-2. The model shows significant improvements in performance, processing length, and speed, capable of handling 10,000-frame video input on a single GPU and encoding 2048 frames of video in just 12 seconds. Video-XL-2 employs the SigLIP-SO400M visual encoder, a Dynamic Token Synthesis (DTS) module, and the Qwen2.5-Instruct large language model. It achieves high performance through a four-stage progressive training and efficiency optimization strategies (such as segmented prefilling and dual-granularity KV decoding). The model performs excellently on benchmarks such as MLVU and Video-MME, and its weights have been open-sourced. (Source: QbitAI)

Character.ai Launches AvatarFX Video Generation Feature, Allowing Image Characters to Move and Interact: Leading AI companion app Character.ai (c.ai) has launched the AvatarFX feature, allowing users to animate characters from static images (including non-human figures like pets), enabling them to speak, sing, and interact with users. The feature is based on the DiT architecture, emphasizing high fidelity and temporal consistency, maintaining stability even in complex scenarios like multi-character, long-sequence dialogues. AvatarFX is currently available to all users on the web version, with the app version launching soon. Concurrently, c.ai also announced new features such as Scenes (interactive story scenarios), Imagine Animated Chat (animated chat logs), and Stream (story generation between characters), further enriching the AI creation experience. (Source: QbitAI)

Nvidia Launches Llama-3.1 Nemotron-Nano-VL-8B-V1 Visual Language Model: Nvidia has released a new vision-to-text model, Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Nano-VL-8B-V1. This model can process image, video, and text inputs and generate text outputs, possessing a degree of image reasoning and recognition capabilities. The release of this model reflects Nvidia’s continued investment in the multimodal AI field. Meanwhile, community discussions suggest that Llama-4 abandoning models below 70B might create opportunities for models like Gemma3 and Qwen3 in the fine-tuning market. (Source: karminski3)
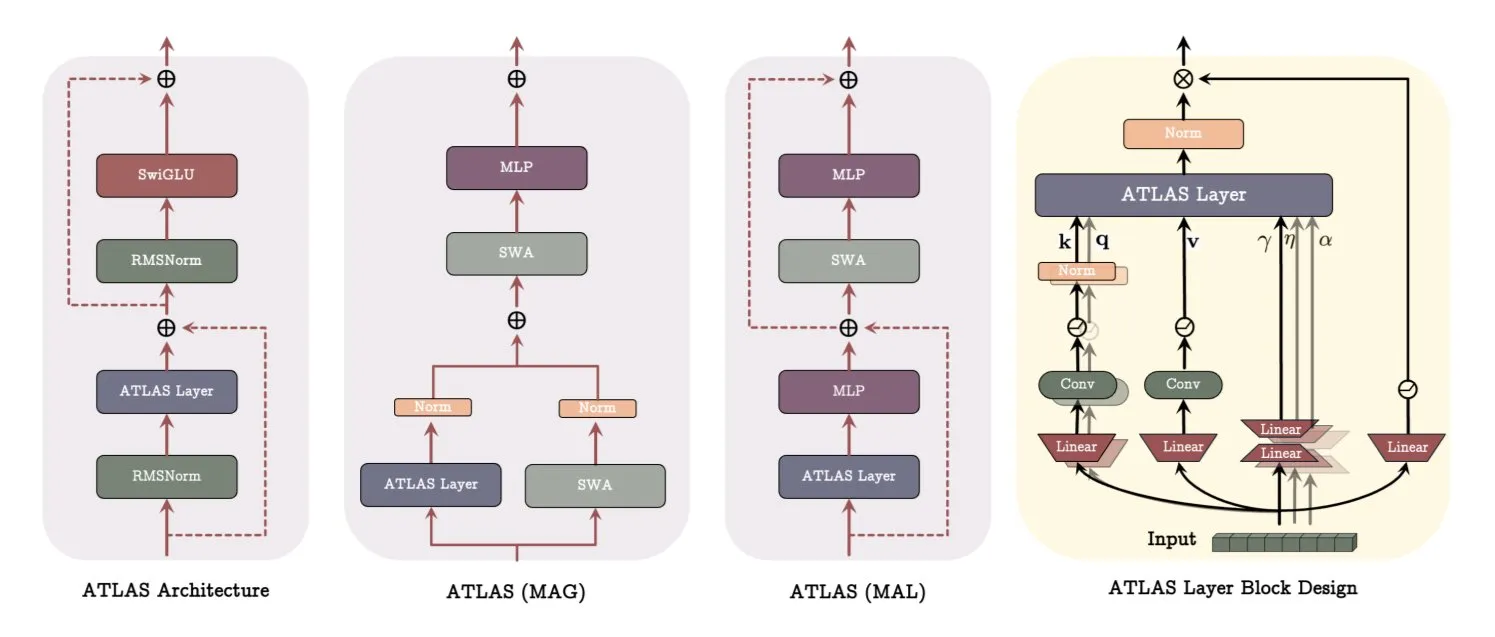
Google Releases ATLAS Architecture Paper, Revolutionizing Model Learning and Memory: Google’s latest paper introduces a new model architecture called ATLAS, designed to optimize model learning and memory capabilities through active memory (Omega rule processing the most recent c tokens) and smarter memory capacity management (polynomial and exponential feature mapping). ATLAS employs the Muon optimizer for more effective memory updates and introduces designs like DeepTransformers and Dot (Deep Omega Transformers), replacing traditional fixed attention with learnable, memory-driven mechanisms. This research marks a step towards more intelligent, context-aware AI systems, promising to enhance AI’s ability to process and utilize large-scale datasets. (Source: TheTuringPost)
Qwen Releases Qwen3-Embedding Model Series, Significantly Improving Embedding Performance: The Qwen team has released the new Qwen3-Embedding model series, including 0.6B, 4B, and 8B versions. These models support context lengths of up to 32k and 100 languages, achieving SOTA results on MTEB (Massive Text Embedding Benchmark), with some metrics leading the second place by 10 points. This advancement marks another significant breakthrough in text embedding technology, providing a more powerful foundation for applications such as semantic search and RAG. (Source: AymericRoucher, ClementDelangue)

Microsoft Bing Video Creator Launched, Based on OpenAI Sora Model and Free to Use: Microsoft has launched Bing Video Creator in its Bing application. The feature is based on OpenAI’s Sora model and allows users to generate videos for free using text prompts. This is the first time the Sora model has been made available to the public on a large scale for free. Despite being free, there are currently limitations, such as a video length of only 5 seconds, a 9:16 aspect ratio, and relatively slow generation speed. User feedback indicates that its performance lags behind current SOTA video models (like Kling, Veo3), sparking discussions about Sora’s technological iteration speed and Microsoft’s product strategy. (Source: 36Kr)
OpenAI Launches Multiple Enterprise-Grade Features, Enhancing Workplace Integration: OpenAI has released a series of new features for enterprise users, including dedicated connectors for applications like Google Drive, and meeting recording, transcription, and summarization functions within ChatGPT, along with support for SSO (Single Sign-On) and points-based enterprise pricing. These updates aim to integrate ChatGPT more deeply into enterprise workflows and improve office efficiency. (Source: TheRundownAI, EdwardSun0909)
Hugging Face Releases Efficient Robot Model SmolVLA, Capable of Running on a MacBook: Hugging Face has launched a robot model named SmolVLA, characterized by its extremely high efficiency, even capable of running on a MacBook. After fine-tuning on a small amount of demonstration data (e.g., 31 instances), the model can achieve or exceed the performance of single-task baselines on specific tasks (such as Koch Arm manipulation), demonstrating its potential for deploying robot AI in resource-constrained environments. (Source: mervenoyann, sytelus)
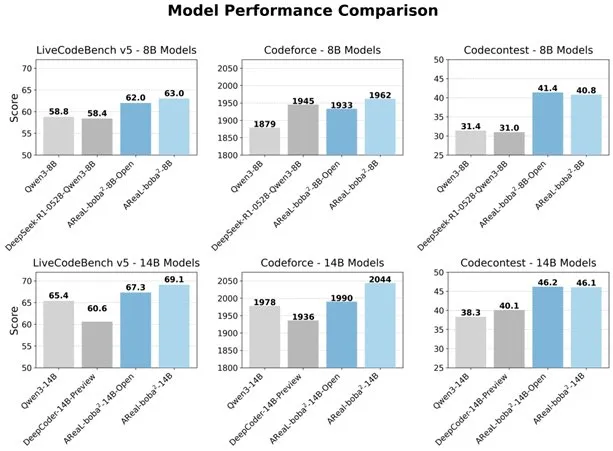
Alibaba Open-Sources Fully Asynchronous RL System AReaL-boba², Enhancing LLM Code Capabilities: Alibaba’s Qwen team has open-sourced the fully asynchronous reinforcement learning system AReaL-boba², specifically designed for Large Language Models (LLMs), and has achieved SOTA code reinforcement learning performance on Qwen3-14B. The system achieves a 2.77x training speedup through co-design of system and algorithm, scores 69.1 on LiveCodeBench, and supports multi-round reinforcement learning. (Source: _akhaliq)
DuckDB Launches DuckLake Extension, Integrating Data Lakes and Catalog Formats: DuckDB has released the DuckLake extension, an open lakehouse format based on SQL and Parquet. DuckLake stores metadata in a catalog database and data in Parquet files. With this extension, DuckDB can directly read and write data in DuckLake, supporting table creation, modification, querying, time travel, and schema evolution, aiming to simplify the construction and management of data lakes. (Source: GitHub Trending)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Ruby SDK Released: The Model Context Protocol (MCP) has released its official Ruby SDK, maintained in collaboration with Shopify, for implementing MCP servers. MCP aims to provide a standardized way for AI models (especially Agents) to discover and invoke tools, access resources, and execute predefined prompts. The SDK supports JSON-RPC 2.0 and provides core functionalities such as tool registration, prompt management, and resource access, making it easier for developers to build AI applications compliant with MCP specifications. (Source: GitHub Trending)
AI Technology Helps Zinc Batteries Achieve 99.8% Efficiency and 4300 Hours of Operation: Through artificial intelligence optimization, a new generation of zinc batteries has achieved 99.8% Coulombic efficiency and an operating time of up to 4300 hours. The application of AI in materials science, particularly in battery design and performance prediction, is driving breakthroughs in energy storage technology, promising more efficient and durable energy solutions for electric vehicles, portable electronic devices, and other fields. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

🧰 Tools
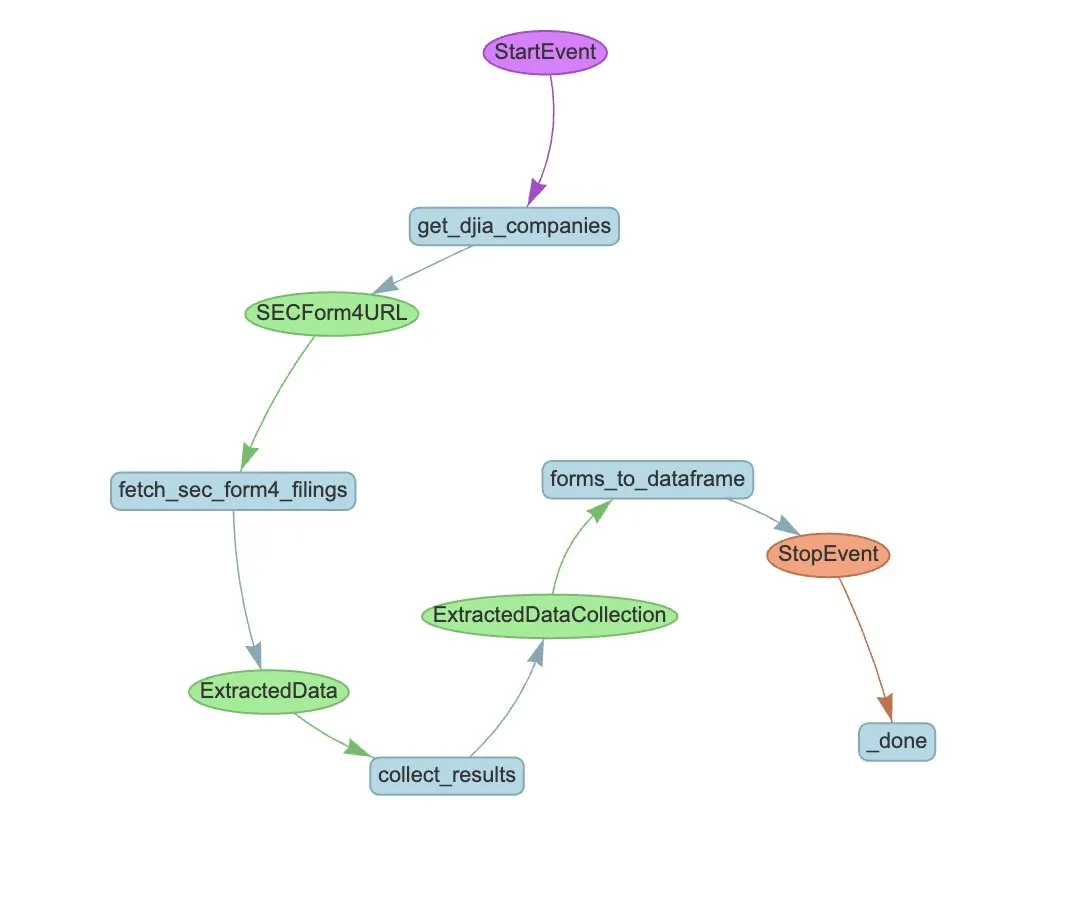
LlamaIndex Launches LlamaExtract and Agent Workflow to Automate SEC Form 4 Extraction: LlamaIndex demonstrated how to use LlamaExtract and Agent workflows to automatically extract structured information from SEC Form 4 filings. SEC Form 4 is an important document for executives, directors, and major shareholders of publicly traded companies to disclose stock transactions. By building extraction agents and scalable workflows, Form 4 filings for all companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average can be processed efficiently, enhancing market transparency and data analysis efficiency. (Source: jerryjliu0)
Cognee: An Open-Source Tool Providing Dynamic Memory for AI Agents: Cognee is an open-source project aimed at providing AI Agents with dynamic memory capabilities, claiming integration with just 5 lines of code. It helps Agents interconnect and retrieve past conversations, documents, images, and audio transcriptions by building scalable, modular ECL (Extract, Cognify, Load) pipelines, intended to replace traditional RAG systems, reduce development difficulty and costs, and support data processing and loading from over 30 data sources. (Source: GitHub Trending)

Claude Code Now Available to Pro Users, Community Version GitHub Action Launched: Anthropic’s AI programming assistant, Claude Code, is now available to Pro subscribers, who can use it via methods like the JetBrains IDE plugin. Community developers have also released a forked version of a Claude Code GitHub Action, allowing paying users to directly invoke Claude Code in GitHub Issues or PRs, utilizing their subscription quotas for tasks like code review and Q&A without incurring additional API fees. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
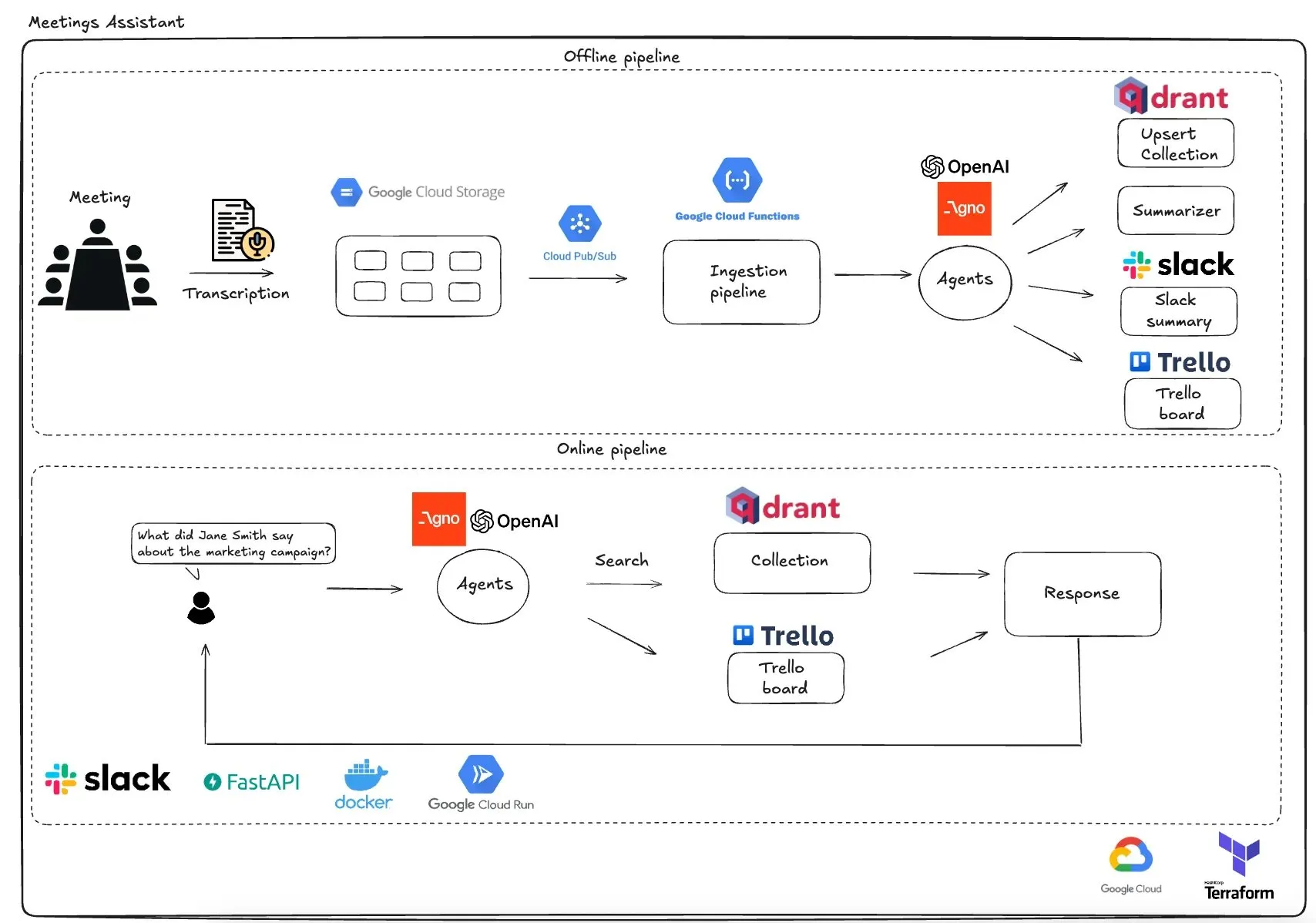
Qdrant Launches GCP-Based Multi-Agent Meeting Assistant: Qdrant showcased a fully serverless multi-agent meeting assistant system. The system can transcribe meeting content, use LLM agents for summarization, store contextual information in a Qdrant vector database, synchronize tasks to Trello, and deliver final results directly in Slack. The system utilizes AgnoAgi for agent orchestration, FastAPI running on Cloud Run, and OpenAI for embeddings and inference. (Source: qdrant_engine)
Microsoft Releases GUI-Actor for Coordinate-Free GUI Element Localization: Microsoft has released GUI-Actor on Hugging Face, a method for GUI (Graphical User Interface) element localization without coordinates. This method allows AI agents to directly point to native visual patches using a special <actor> token, rather than relying on text-based coordinate prediction, aiming to improve the accuracy and robustness of GUI agent operations. (Source: _akhaliq)

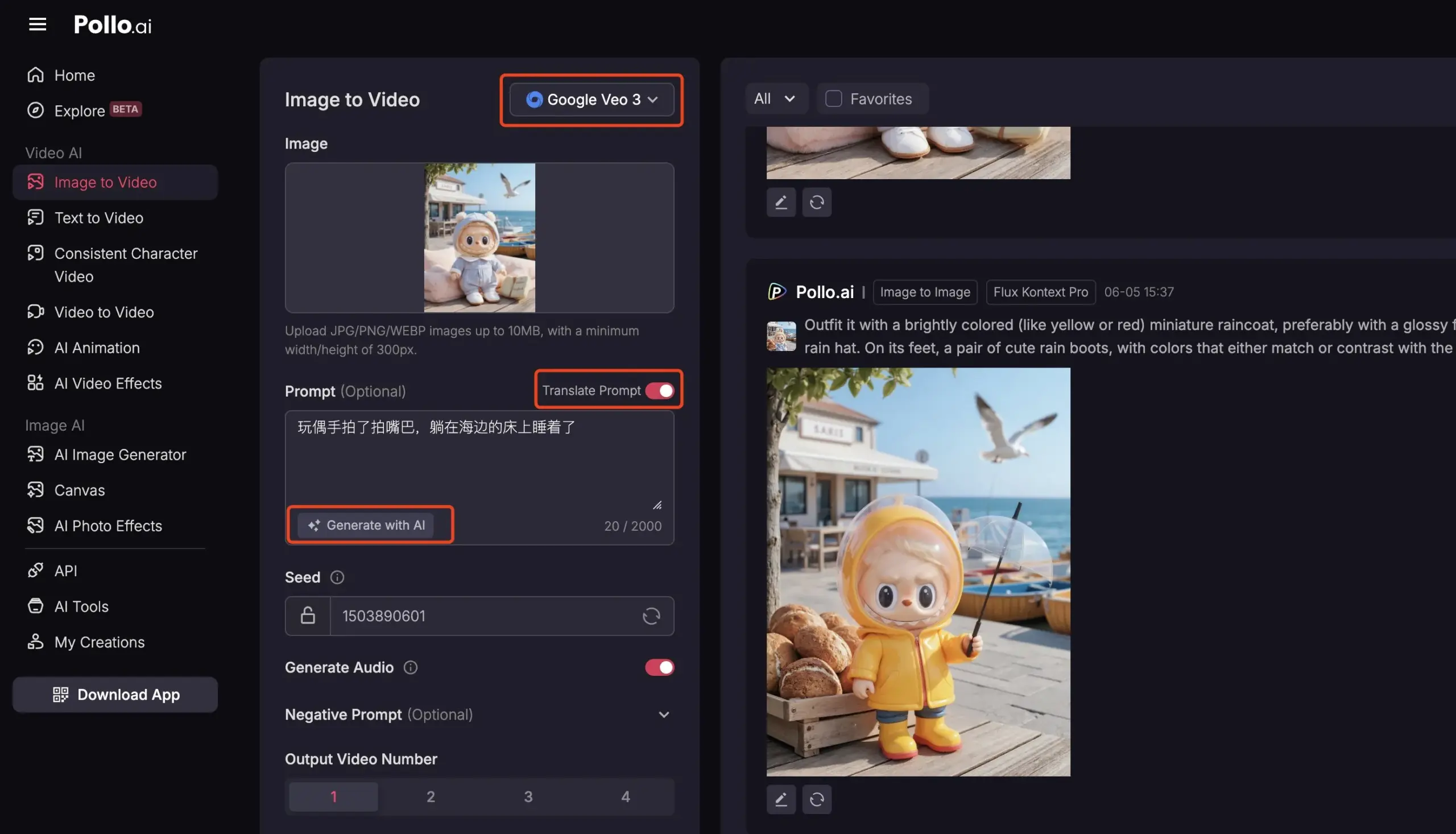
Pollo AI Integrates Veo3 and FLUX Kontext, Offering Comprehensive AI Video Services: AI tool platform Pollo AI has been frequently updated, integrating Google’s Veo3 video generation model and FLUX Kontext image editing features. Users can modify images on the platform using FLUX Kontext and then directly send them to Veo3 to generate videos. The platform also provides API interfaces, supporting one-stop access to various mainstream video large models on the market, and includes built-in auxiliary functions like AI prompt generation and multilingual translation, aiming to enhance the convenience and efficiency of AI video creation. (Source: op7418)
📚 Learning
In-depth Analysis of Meta-Learning: Enabling AI to Learn How to Learn: Meta-Learning, also known as “learning to learn,” has the core idea of training a model to quickly adapt to new tasks, even with only a few samples. This process typically involves two models: a base-learner that quickly adapts to specific tasks (e.g., few-shot image classification) in an inner learning loop, and a meta-learner that manages and updates the base-learner’s parameters or strategies in an outer learning loop to improve its ability to solve new tasks. After training, the base-learner is initialized using the knowledge learned by the meta-learner. (Source: TheTuringPost, TheTuringPost)

Paper Analysis: “A Controllable Examination for Long-Context Language Models”: This paper addresses the limitations of existing evaluation frameworks for Long-Context Language Models (LCLMs) (real-world tasks are complex and difficult to solve, susceptible to data contamination; synthetic tasks like NIAH lack contextual coherence). It proposes three characteristics that an ideal evaluation framework should possess: seamless context, controllable settings, and sound evaluation. It also introduces LongBioBench, a new benchmark that uses artificially generated biographies as a controlled environment to evaluate LCLMs from the dimensions of understanding, reasoning, and trustworthiness. Experiments show that most models still have shortcomings in semantic understanding, preliminary reasoning, and long-context trustworthiness. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Analysis: “Advancing Multimodal Reasoning: From Optimized Cold Start to Staged Reinforcement Learning”: Inspired by Deepseek-R1’s exceptional reasoning capabilities in complex text tasks, this study explores how to enhance the complex reasoning abilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) through optimized cold starts and staged Reinforcement Learning (RL). The research finds that effective cold start initialization is crucial for enhancing MLLM reasoning; initializing with carefully selected text data alone can surpass many existing models. Standard GRPO encounters gradient stagnation issues when applied to multimodal RL, while subsequent pure-text RL training can further enhance multimodal reasoning. Based on these findings, the researchers introduced ReVisual-R1, achieving SOTA results on multiple challenging benchmarks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Analysis: “Unleashing the Reasoning Potential of Pre-trained LLMs by Critique Fine-Tuning on One Problem”: This study proposes an efficient method to unleash the reasoning potential of pre-trained LLMs: Critique Fine-Tuning (CFT) on one problem. By collecting multiple solutions generated by the model for a single problem and using a teacher LLM to provide detailed critiques, critique data is constructed for fine-tuning. Experiments show that after performing single-problem CFT on Qwen and Llama series models, significant performance improvements were achieved on various reasoning tasks. For example, Qwen-Math-7B-CFT showed an average improvement of 15-16% on math and logic reasoning benchmarks, with computational costs far lower than reinforcement learning. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper Analysis: “SVGenius: Benchmarking LLMs in SVG Understanding, Editing and Generation”: To address the limited coverage, lack of complexity stratification, and fragmented evaluation paradigms of existing SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) processing benchmarks, SVGenius was created. It is a comprehensive benchmark containing 2377 queries, covering understanding, editing, and generation across three dimensions, built on real-world data from 24 application domains, and systematically stratified by complexity. It evaluated 22 mainstream models across 8 task categories and 18 metrics, revealing the limitations of current models in handling complex SVGs and pointing out that reasoning-enhanced training is more effective than purely scaling up. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Hugging Face Hub Changelog Released: Hugging Face Hub has released its latest changelog. Users can consult it to learn about new platform features, model library updates, dataset expansions, and toolchain improvements. This helps community users stay informed and leverage the latest resources and capabilities of the Hugging Face ecosystem. (Source: huggingface, _akhaliq)
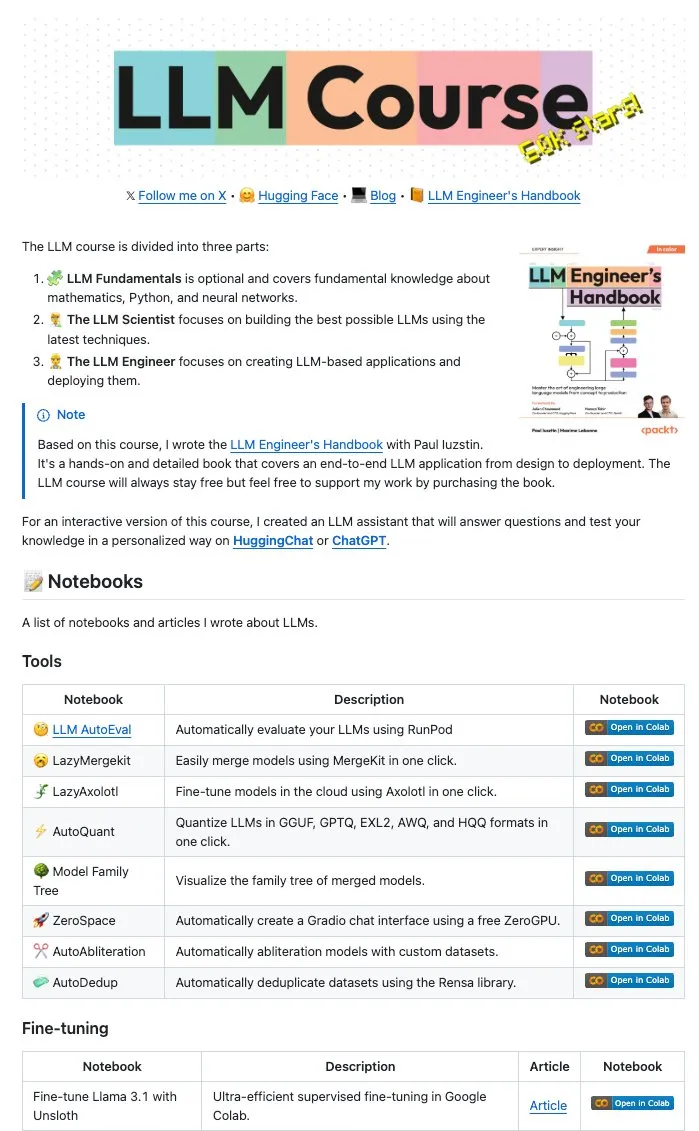
Maxime Labonne and Co-authors Open-Source Numerous LLM Notebooks: Maxime Labonne, author of the LLM Engineer Handbook, and Iustin Paul have open-sourced a series of LLM-related Jupyter Notebooks. These Notebooks are rich in content, covering not only basic fine-tuning techniques but also advanced topics such as automatic evaluation, lazy merges, building mixture-of-experts models (frankenMoEs), and decensoring techniques, providing valuable practical resources for LLM developers and researchers. (Source: maximelabonne)
DeepLearningAI Releases The Batch Weekly, Discusses How AI Fund Cultivates AI Builders: In his latest issue of The Batch weekly, Andrew Ng shares AI Fund’s experiences and strategies in cultivating AI talent and builders. This issue also covers hot topics such as DeepSeek’s new open-source model performing on par with top LLMs, Duolingo using AI to expand language courses, AI’s energy consumption trade-offs, and the potential misdirection of AI Agents by malicious links. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
💼 Business
Reddit Sues Anthropic, Alleging Unauthorized Use of User Data for AI Training: Reddit has filed a lawsuit against AI company Anthropic, accusing it of using automated bots to scrape Reddit content without permission for training its AI models (such as Claude), constituting breach of contract and unfair competition. This case highlights the current controversy surrounding the legality of data scraping and model training in AI development, and also reflects content platforms’ increasing emphasis on protecting the value of their data. (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, TheRundownAI)

Amazon Plans to Invest $10 Billion in North Carolina for AI Data Centers: Amazon has announced plans to invest $10 billion in North Carolina to build new data centers to support its growing AI business needs. This move reflects the continued investment by large tech companies in AI infrastructure, aimed at meeting the massive computing and storage resources required for AI model training and inference. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)

Anthropic Reduces Claude Model API Access for Windsurf.ai, Sparking Platform Risk Concerns: AI application development platform Windsurf.ai revealed that Anthropic significantly reduced its API access capacity for Claude 3.x and Claude 4 models with less than 5 days’ notice. This move forced Windsurf.ai to urgently seek third-party vendors to ensure service for paying users and offer a BYOK (Bring Your Own Key) option for free and Pro users. This incident has heightened developer concerns about platform risks from AI model providers, i.e., model providers may adjust service policies at any time, or even compete with downstream applications. (Source: swyx, scaling01, mervenoyann)
🌟 Community
AI Engineer Summit (@aiDotEngineer) Sparks Discussion, Focusing on Agent Design and AI Startups: The AI Engineer Summit (@aiDotEngineer) held in San Francisco became a hot topic in the community. LlamaIndex shared effective Agent design patterns for production environments; Anthropic issued a “request list” for startups at the conference, focusing on the application of MCP servers in new fields, simplifying server construction, and AI application security (such as tool poisoning); Graphite showcased an AI-driven code review tool. The conference also discussed fundamental research challenges in scaling next-generation GPT models and other topics. (Source: swyx, swyx, swyx, iScienceLuvr)

Researcher Rohan Anil Joining Anthropic Draws Attention: Researcher Rohan Anil announced he will be joining the Anthropic team, a piece of news that has garnered widespread attention and discussion in the AI community. Many industry insiders and followers congratulated him and look forward to his new contributions to Anthropic’s research work. This also reflects the potential impact of top AI talent mobility on the industry landscape. (Source: arohan, gallabytes, andersonbcdefg, scaling01, zacharynado)
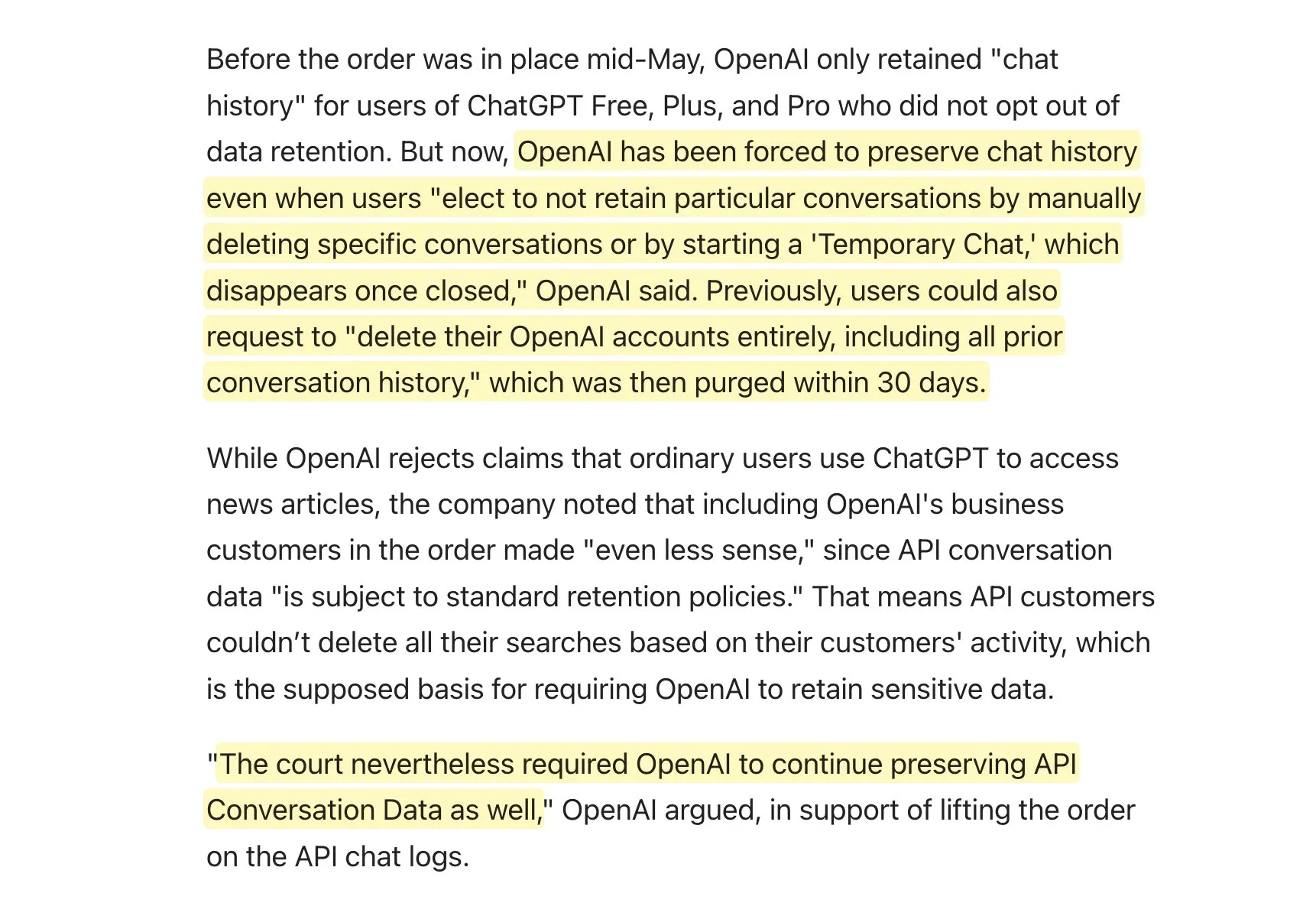
Court Orders OpenAI to Retain All ChatGPT Logs, Sparking Data Retention Policy Discussions: It is reported that OpenAI has been ordered by a court to retain all ChatGPT logs, including “temporary chats” and API requests that were supposed to be deleted. This news has sparked community discussions about data retention policies, especially for applications using the OpenAI API, as it could mean their own data retention policies cannot be fully adhered to, posing new challenges to user privacy and data management. Users are advised to prioritize using local models where possible to protect data. (Source: code_star, TomLikesRobots)
Proliferation of AI-Generated Content and “AI Slop” Phenomenon Raise Concerns: The increasing amount of low-quality, attention-grabbing AI-generated content (dubbed “AI Slop”) on social media, from AI-generated posts on Reddit to AI images like “Shrimp Jesus” on Facebook, is causing users to worry about information quality and the deterioration of the online environment. This content is often cheaply generated by bots or traffic-seekers, aiming to gain likes and shares through “engagement bait.” Research indicates that a large portion of internet traffic is already composed of “bad bots” that spread misinformation and steal data. This phenomenon not only affects user experience but also poses a threat to democracy and political communication, while potentially contaminating training data for future AI models. (Source: aihub.org)

LLM Cost Discussion: Gemini Offers High Cost-Performance, Claude 4 Coding Costs Draw Attention: Community discussions indicate significant cost differences in using current LLMs. For example, using Gemini to process an entire insurance document and ask numerous questions costs only about $0.01, demonstrating high cost-effectiveness. In contrast, while the Claude 4 model performs excellently in tasks like coding, its usage cost in “max mode” on platforms like Cursor.ai is high, prompting users to switch to more cost-effective options like Google Gemini 2.5 Pro. (Source: finbarrtimbers, Teknium1)
AI Agents Face Challenges Solving CAPTCHAs in Real-World Web Scenarios: The MetaAgentX team released the Open CaptchaWorld platform, focusing on evaluating the ability of multimodal interactive agents to solve CAPTCHAs. Tests show that even SOTA models like GPT-4o have a success rate of only 5%-40% when dealing with interactive CAPTCHAs in 20 real-world web environments, far below the human average success rate of 93.3%. This indicates that current AI Agents still have bottlenecks in visual understanding, multi-step planning, state tracking, and precise interaction, making CAPTCHAs a major obstacle to their practical deployment. (Source: QbitAI)

AI Agent Training Market is Booming, Course Quality and Job Prospects Draw Attention: With the rise of the AI Agent concept, related training courses have also emerged in large numbers. Some training institutions claim to offer comprehensive guidance from entry-level to employment, even promising “guaranteed employment,” with tuition fees ranging from a few hundred to tens of thousands of yuan. However, the quality of courses on the market is uneven, with some courses being criticized for shallow content, excessive marketing, and even resembling exploitative AI crash courses. Students and observers are cautious about the actual effectiveness of such training, instructor qualifications, and the authenticity of “guaranteed employment” promises, fearing it may become another “pseudo-demand” in the AI development transition period. (Source: 36Kr)

💡 Other
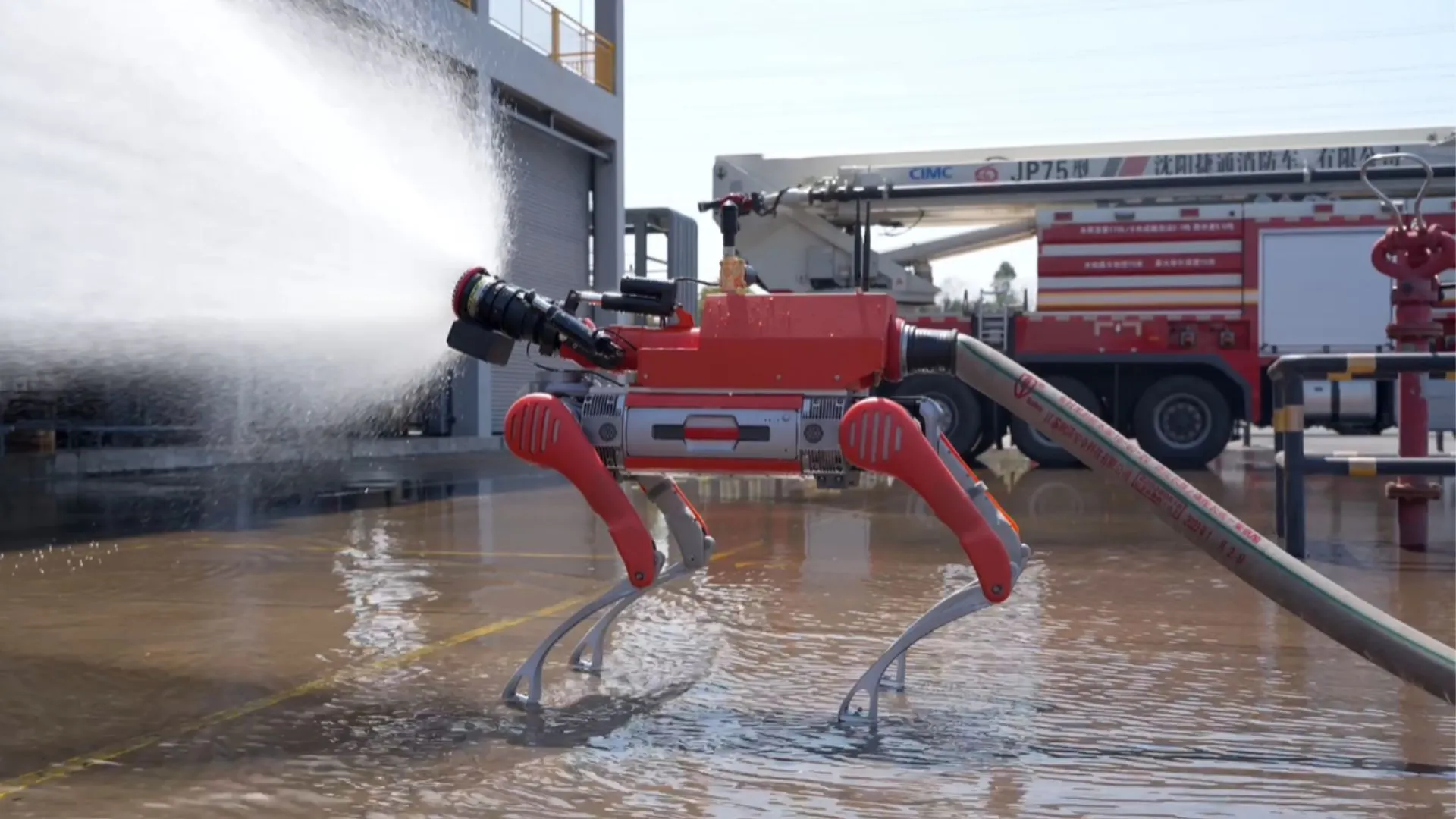
AI Application Progress in Robotics: Tactile Sensing Hands, Amphibious Robots, and Firefighting Robot Dogs: AI technology is pushing the boundaries of robot capabilities. Researchers have developed robotic hands with tactile perception, enabling them to better interact with the environment. Copperstone HELIX Neptune showcased an AI-driven amphibious robot capable of operating in different terrains. China has introduced a firefighting robot dog that can spray a 60-meter water jet, climb stairs, and conduct live rescue broadcasts. These advancements demonstrate AI’s potential in enhancing robot perception, decision-making, and execution of complex tasks. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)

Discussion Comparing AI Agents and Generative AI: Discussions have emerged in the community regarding the differences and connections between AI Agents (Intelligent AI) and Generative AI. Generative AI primarily focuses on content creation, while AI Agents are more centered on autonomous decision-making and task execution based on perception, planning, and action. Understanding the differences between the two helps to better grasp the development direction and application scenarios of AI technology. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)
Exploring Challenges of AI in Automating Complex Organizational Processes: While AI has made progress in automating or assisting specific tasks, replacing human labor or teams to achieve broader economic transformation faces immense complexity. Many organizations have undocumented but crucial processes that are high-risk but infrequent, and may have become routine to the point where their original reasons are forgotten. AI agents struggle to learn such tacit knowledge through trial and error due to high costs and limited learning opportunities. This requires new technological paradigms, not just simple machine learning. (Source: random_walker)
