Keywords:OpenAI Codex, Visual Language Action Model, Language Model Memory Limit, ChatGPT Memory Function, DeepSeek-R1-0528, Diffusion Model, Suno AI Music Creation, MetaAgentX, Codex Internet Access Function, SmolVLA Robot Model, GPT-style Model 3.6-bit Memory, ChatGPT Personalized Interaction Improvement, DeepSeek-R1 Complex Reasoning Capability, OpenAI Codex internet access capability, Visual Language Action Model for robotics, Memory capacity limits in large language models, Enhancing ChatGPT with memory features, DeepSeek-R1 model released May 28, Diffusion models for generative AI, AI-powered music generation with Suno, MetaAgentX autonomous agent framework, Codex API web browsing functionality, Compact VLA robot learning model, 3.6-bit quantized GPT architecture, Personalized ChatGPT conversation upgrades, DeepSeek-R1 advanced reasoning performance
🔥 Focus
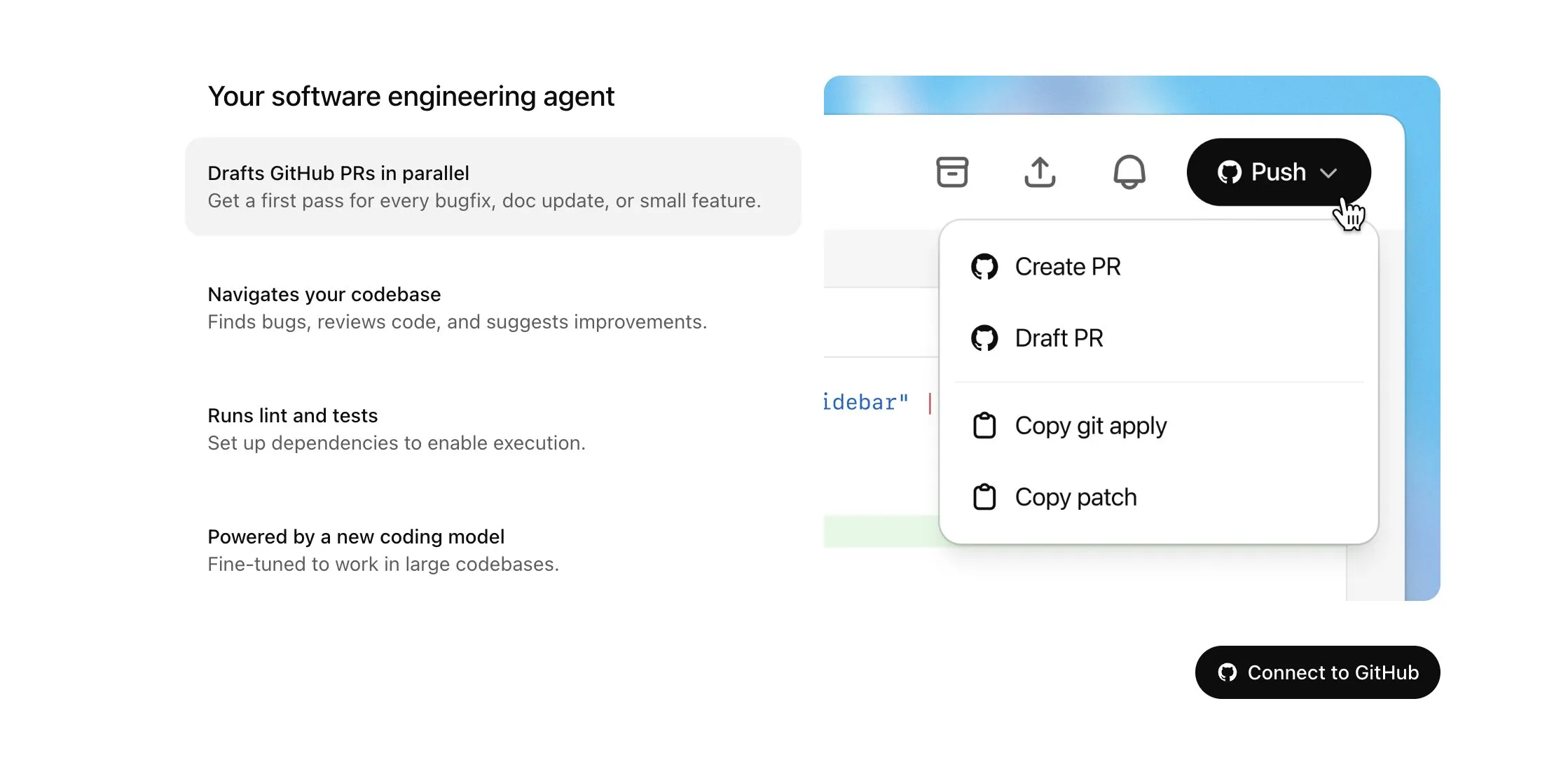
OpenAI Codex Rolling Out to Plus Users with Major Updates, Including Internet Access and Voice Input: OpenAI announced that Codex will be gradually rolled out to ChatGPT Plus users. Key updates include allowing AI agents to access the internet when performing tasks (disabled by default, users can control domains and HTTP methods) to install dependencies, upgrade packages, and run tests on external resources. Additionally, Codex now supports directly updating existing Pull Requests and can accept tasks via voice input. Other improvements include support for binary file operations (currently limited to deletion or renaming in PRs), an increase in the task diff size limit from 1MB to 5MB, an extension of the script runtime limit from 5 minutes to 10 minutes, and fixes for several issues on the iOS platform, along with the re-enabling of live activities. These updates aim to enhance Codex’s usability and flexibility in complex programming tasks (Source: OpenAI Developers, Tibor Blaho, gdb, kevinweil, op7418)
Hugging Face and H Company Jointly Release Open-Source Vision-Language-Action (VLA) Models to Advance Robotics: Hugging Face and H Company announced new open-source Vision-Language-Action models on “VLA Day,” including Hugging Face’s SmolVLA (450M parameters) and H Company’s Holo-1 (3B and 7B parameters). VLA models are designed to enable robots to see, hear, understand, and act on AI instructions, and are being called the GPT for robotics. Open-sourcing these models is crucial for understanding their working principles, avoiding potential backdoors, and customizing them for specific robots and tasks. SmolVLA, trained on the LeRobotHF dataset, demonstrates excellent performance and inference speed. Holo-1 focuses on web and computer agent tasks and is available under the Apache 2.0 license. These releases are expected to accelerate the development of open-source AI robotics (Source: ClementDelangue, huggingface, LoubnaBenAllal1, tonywu_71)

Research by Meta and Others Reveals Language Model Memory Capacity at Approximately 3.6 Bits Per Parameter, Challenging Traditional Cognition: Joint research by Meta, DeepMind, Cornell University, and Nvidia indicates that GPT-style language models can memorize approximately 3.6 bits of information per parameter. The study found that models continuously memorize training data until they reach their capacity limit, after which “Grokking” (sudden insight) occurs, where unexpected memory reduction happens, and the model shifts towards generalization learning. This finding explains the “double descent” phenomenon, where models are forced to share information points to save capacity when the dataset’s information volume exceeds the model’s storage capability, thereby promoting generalization. The research also proposes scaling laws regarding the relationship between model capacity, data scale, and the success rate of membership inference attacks, and points out that reliable membership inference becomes difficult for modern LLMs trained on extremely large datasets (Source: 机器之心, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, code_star, scaling01, Francis_YAO_)
OpenAI Launches Lightweight Version of ChatGPT Memory Feature, Enhancing Personalized Interaction Experience: OpenAI announced the rollout of a lightweight version of its memory feature improvements to free users. In addition to saving memories, ChatGPT can now reference users’ recent conversations to provide more personalized responses. This move aims to make ChatGPT more adept at writing, offering advice, and learning by drawing on users’ preferences and interests. Sam Altman also stated that the memory feature has become one of his favorite ChatGPT features and looks forward to greater improvements in the future. This update signifies OpenAI’s commitment to making AI interactions more tailored to user needs and enhancing user stickiness (Source: openai, sama, iScienceLuvr)
🎯 Trends
DeepSeek-R1-0528 Released, Strengthening Complex Reasoning and Programming Capabilities: DeepSeek has released DeepSeek-R1-0528, an upgraded version of its R1 model. This version is based on the DeepSeek V3 Base model released in December 2024 and has undergone post-training with increased computational resources, significantly enhancing the model’s depth of thought and reasoning abilities. The new model performs more detailed deconstruction and longer thinking when tackling complex problems (e.g., average token consumption per problem in AIME 2025 test increased from 12K to 23K), achieving leading scores in multiple benchmarks such as mathematics, programming, and general logic, with performance close to GPT-o3 and Gemini-2.5-Pro. Additionally, the new version shows significant optimization in reducing hallucinations (by about 45%-50%), creative writing, and tool calling, such as being able to more stably answer questions like “What is 9.9 – 9.11?” and generate runnable front-end and back-end code in one go (Source: 科技狐, AI前线, Hacubu)

Diffusion Models Show Potential in Language and Multimodal Domains, Challenging Autoregressive Paradigm: The Gemini Diffusion language model showcased at Google I/O 2025, with its up to 5x faster generation speed and comparable programming performance, highlights the potential of diffusion models in text generation. Unlike autoregressive models that predict tokens one by one, diffusion models generate output by progressively denoising, supporting rapid iteration and error correction. The 8B-parameter LLaDA model, launched by Ant Group in collaboration with Renmin University’s Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, and ByteDance’s MMaDA multimodal diffusion model, both demonstrate the cutting-edge exploration by domestic teams in this field. These models not only perform well in language tasks but also achieve progress in multimodal understanding (e.g., LLaDA-V combined with visual instruction tuning) and specific domains (e.g., DPLM for protein sequence generation), heralding diffusion models as a potential new paradigm for next-generation general models (Source: 机器之心)
Suno Releases Major Update, Enhancing AI Music Creation and Editing Capabilities: AI music creation platform Suno has launched several significant updates, giving users greater creative freedom and control. New features include an upgraded song editor that allows users to reorder, rewrite, and remake tracks segment by segment on a waveform display; the introduction of a stem separation feature that can accurately separate tracks into 12 independent sources (such as vocals, drums, bass, etc.) for preview and download; expanded upload functionality, supporting full song uploads up to 8 minutes long, allowing users to create based on their own audio material; and a new creativity slider, enabling users to adjust the “weirdness,” structural level, or reference-driven nature of the output before generation to better shape the final work (Source: SunoMusic)
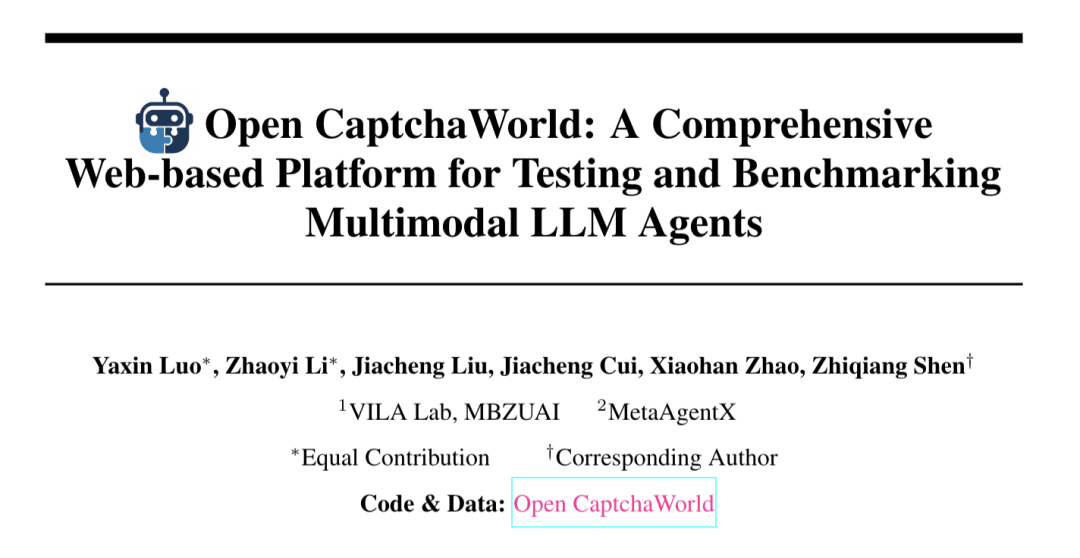
MetaAgentX Launches Open CaptchaWorld to Evaluate Multimodal Agents’ CAPTCHA-Solving Abilities: Addressing the current bottlenecks of multimodal agents in solving CAPTCHA (human-computer verification) problems, the MetaAgentX team has released the Open CaptchaWorld platform and benchmark. The platform includes 20 types of modern CAPTCHAs, totaling 225 samples, requiring agents to complete tasks through observation, clicking, dragging, and other interactions in a real web environment. Test results show that even top models like GPT-4o have success rates between only 5%-40%, far below the average human success rate of 93.3%. Researchers also proposed the “CAPTCHA Reasoning Depth” metric to quantify the “visual understanding + cognitive planning + action control” steps required to solve them. The platform aims to reveal agents’ shortcomings in long-sequence dynamic interaction and planning and to encourage researchers to address this critical issue in practical deployment (Source: 量子位)
Google NotebookLM Supports Public Sharing, Promoting Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration: Google announced that NotebookLM (formerly Project Tailwind) now supports public sharing of notebooks. Users can share their note content by clicking “Share” and setting access permission to “Anyone with the link.” This feature allows users to conveniently share ideas, study guides, and team documents, and recipients can browse content, ask questions, get instant summaries, and voice overviews. This move aims to promote knowledge dissemination and collaborative editing, enhancing NotebookLM’s utility as an AI note-taking tool (Source: Google, op7418)
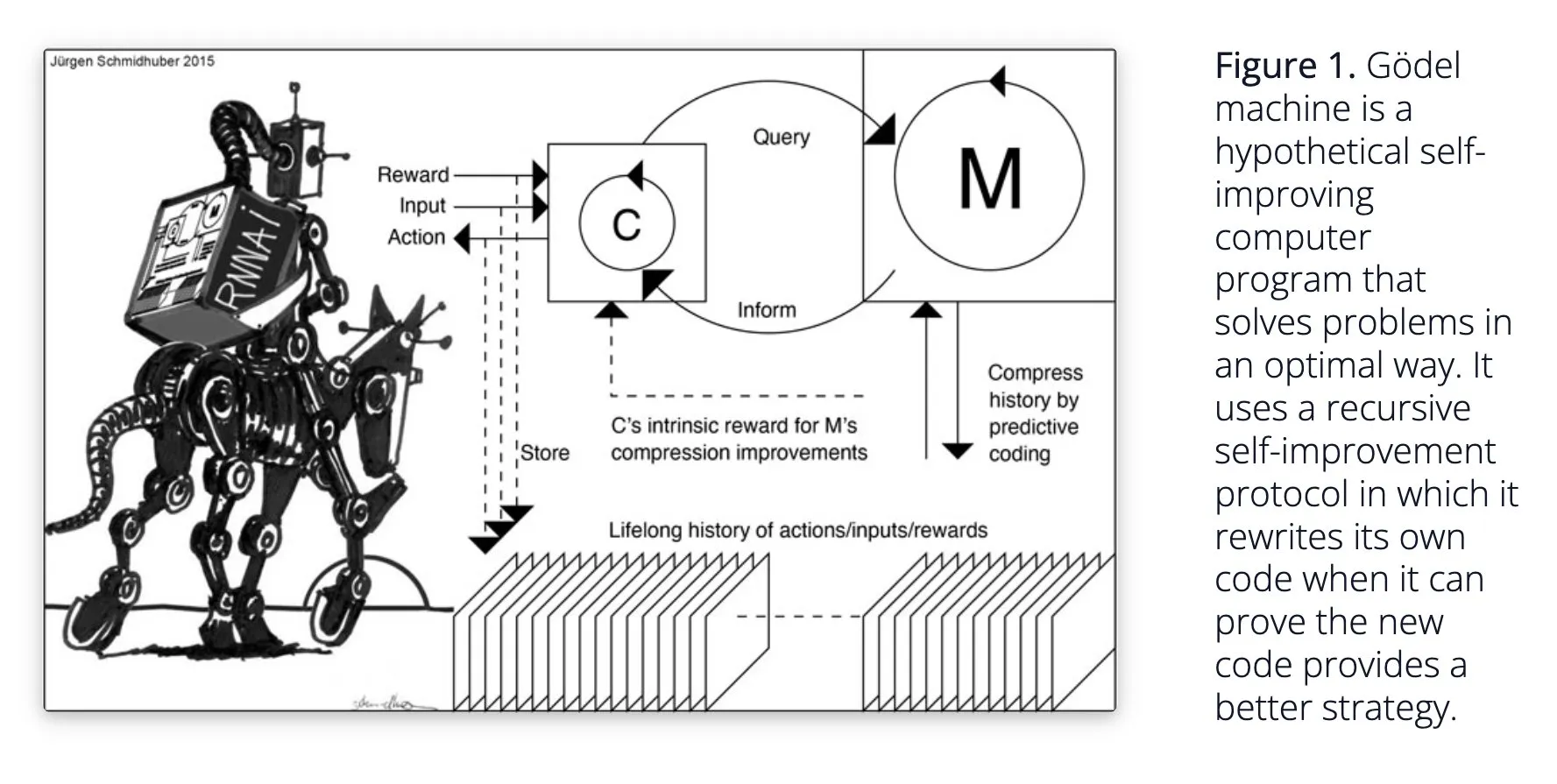
Sakana AI Proposes Self-Learning AI System Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM): Sakana AI has disclosed research on its self-learning AI system, the Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM). DGM utilizes evolutionary algorithms to iteratively rewrite its own code, thereby continuously improving its performance on programming tasks. The system maintains an archive of generated coding agents, samples from it, and uses foundational models to create new versions, enabling open-ended exploration and forming diverse, high-quality agents. Experiments show that DGM significantly improves coding capabilities on benchmarks like SWE-bench and Polyglot. This research offers new ideas for self-improving AI, aiming to accelerate AI development through autonomous innovation (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, hardmaru, scaling01)
Google DeepMind Enhances AI Conversation Naturalness, Opens Native Audio Capabilities: Google DeepMind announced that its native audio capabilities are making AI conversations more natural, enabling them to understand intonation and generate expressive speech. This technology aims to open up new possibilities for human-AI interaction. Developers can now try these features through Google AI Studio, with potential applications in more natural voice assistants, audio content generation, and more (Source: GoogleDeepMind)
Runway Gen-4 Image Generation Technology Gains Attention, Supports Multiple References and Style Control: Runway’s Gen-4 image generation technology is gaining attention for its high fidelity and unprecedented style control capabilities, particularly evident in its multiple reference feature, which provides new space for creative exploration. Users can leverage this technology to generate various animals, dinosaurs, or imaginary creatures, showcasing its potential in detailed visual content creation. Runway’s use in fields like Hollywood also indicates its technology is being progressively applied to professional content production (Source: c_valenzuelab, c_valenzuelab)

AssemblyAI Releases New Real-Time Speech-to-Text Model, Improving Voice AI Application Performance: AssemblyAI has launched a new real-time speech-to-text (STT) model, noted for its high speed and accuracy. The model is designed for developers building voice AI applications, aiming to provide a smoother and more precise speech recognition experience. Concurrently, AssemblyAI also provides an AssemblyAISTTService implementation through its pipecat_ai project, facilitating developer integration. This move demonstrates AssemblyAI’s continued investment and innovation in voice technology (Source: AssemblyAI, AssemblyAI)
Microsoft Bing Celebrates 16th Anniversary, Integrates GPT-4 and DALL·E, Launches Bing Video Creator: Microsoft’s Bing search engine celebrates its 16th anniversary. In recent years, Bing has been a pioneer in large-scale integration of chat-style generative AI and became the first Microsoft product to integrate GPT-4 and DALL·E. Recently, Bing launched Copilot Search and Bing Video Creator for free in its mobile app, the latter of which can be used to generate video content. This marks Bing’s continued innovation and development in AI-driven search and content creation (Source: JordiRib1)
Andrej Karpathy Impressed by Veo 3, Discusses Macro Impacts of Video Generation: Andrej Karpathy expressed his impressiveness with Google’s video generation model Veo 3 and the creative output from its community, noting that the addition of audio significantly enhances video quality. He further discussed several macro-level impacts of video generation: 1. Video is the highest bandwidth input method for the human brain; 2. Video generation provides AI with a “native language” to understand the world; 3. Video generation is a key path towards simulated reality and world models; 4. Its computational demands will drive hardware development. This suggests that video generation technology is not only a revolution in content creation but also an important driver for AI cognition and development (Source: brickroad7, dilipkay, JonathanRoss321)
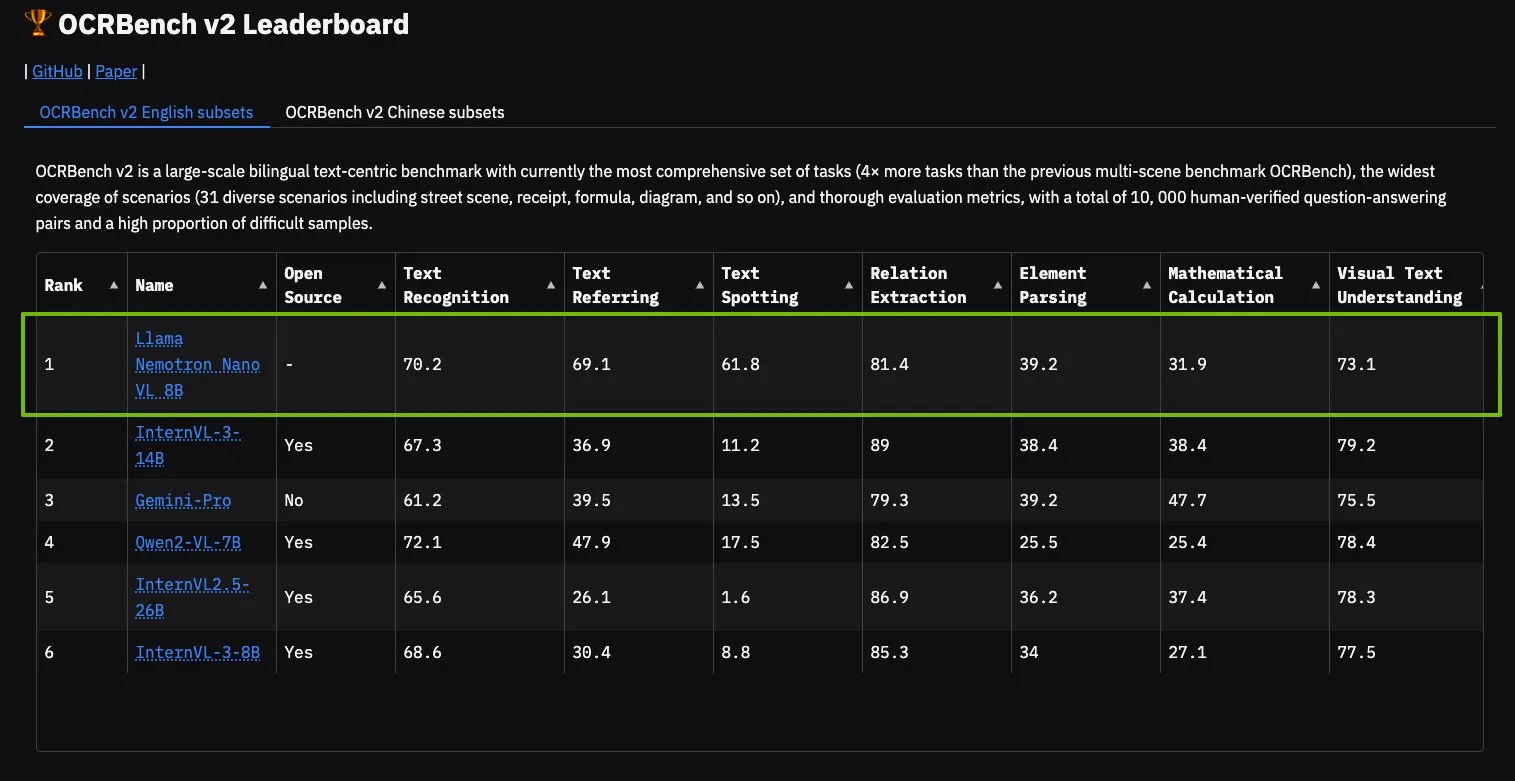
NVIDIA Llama Nemotron Nano VL Model Tops OCRBench V2 Leaderboard: NVIDIA’s Llama Nemotron Nano VL model has secured the first position on the OCRBench V2 leaderboard. The model is designed for advanced intelligent document processing and understanding, capable of accurately extracting diverse information from complex documents on a single GPU. Users can try the model via NVIDIA NIM, showcasing NVIDIA’s progress in developing miniaturized, efficient AI models for specific domains like document understanding (Source: ctnzr)
🧰 Tools
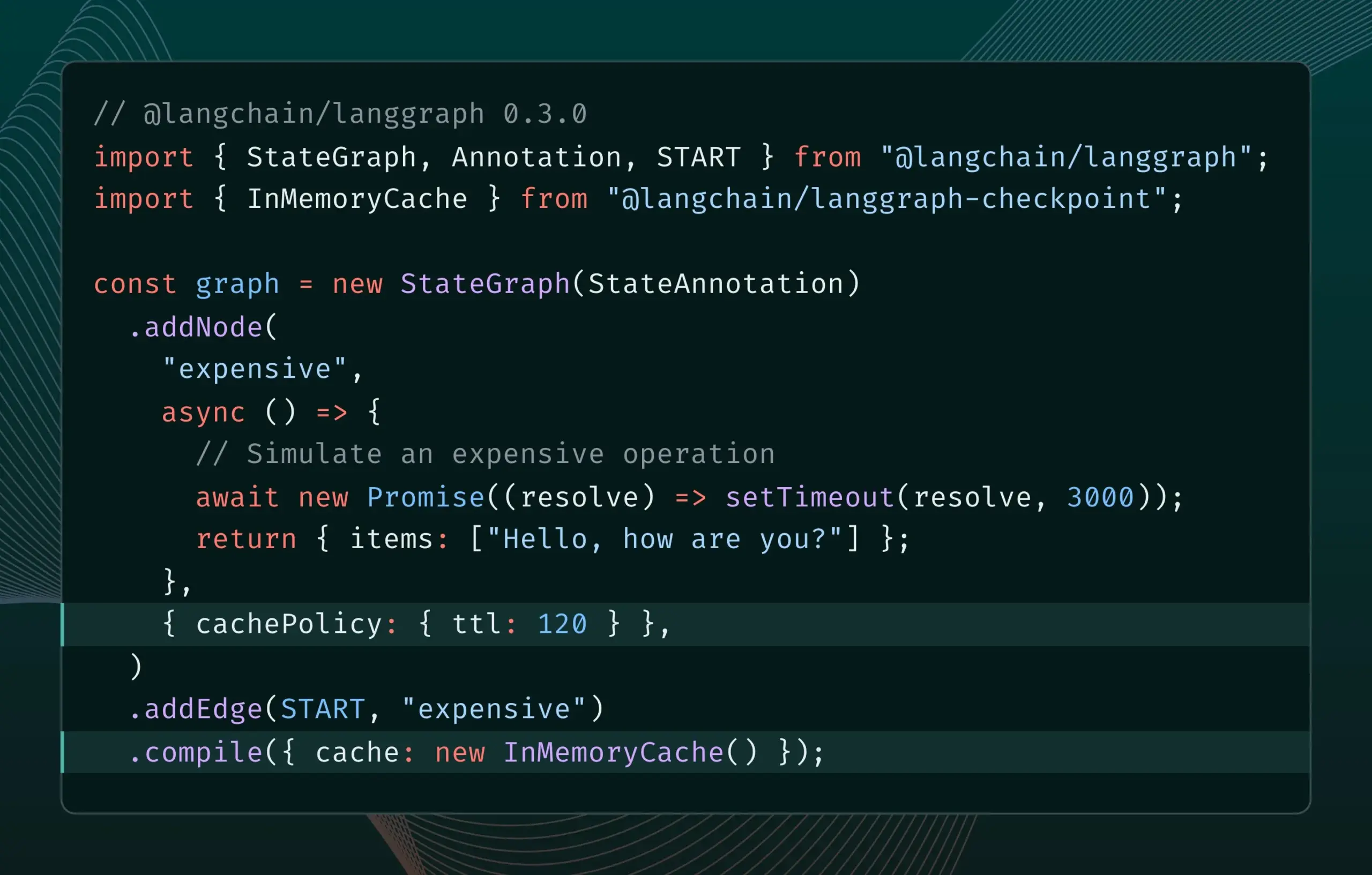
LangGraph.js 0.3 Introduces Node/Task Caching Feature: LangGraph.js has released version 0.3, adding a node/task caching feature. This function aims to accelerate workflows by avoiding redundant computations, particularly useful for iterative, expensive, or long-running agents. The new version supports both the Graph API and Imperative API, offering higher efficiency for JavaScript developers building complex AI applications (Source: Hacubu, hwchase17)
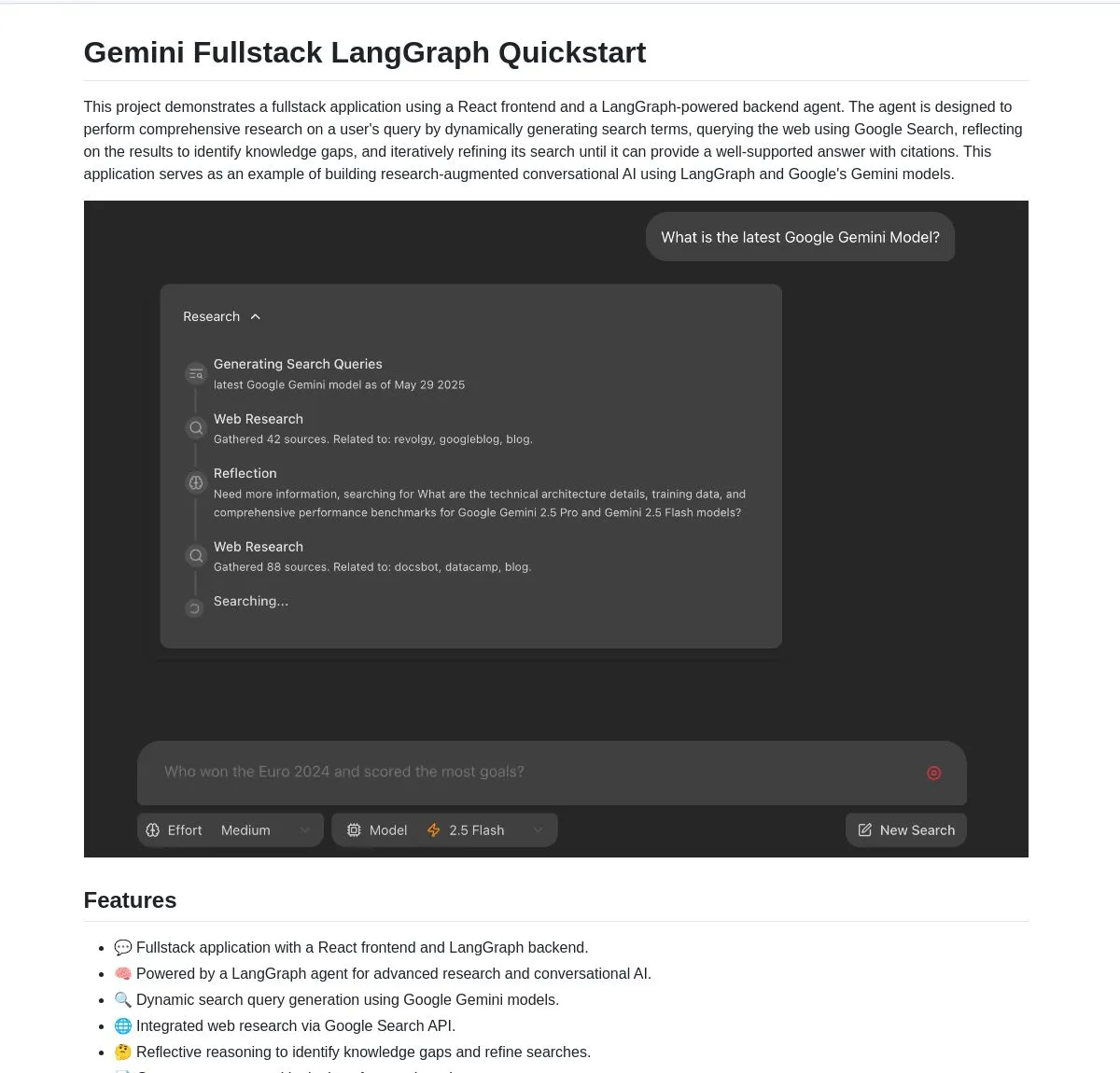
Google Open-Sources Gemini Research Agent Full-Stack Application Based on Gemini and LangGraph: Google has released gemini-fullstack-langgraph-quickstart, a full-stack application example of an intelligent research assistant built on the Gemini model and LangGraph. The application can dynamically optimize queries, provide cited answers through iterative learning, and supports control over different search intensities. It utilizes Gemini’s native Google Search tool for web research and reflective reasoning, aiming to provide developers with a starting point for building advanced research-oriented AI applications (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17, dotey, karminski3)
FedRAG Adds LangChain Bridging Functionality for Easier RAG System Integration and Fine-Tuning: FedRAG announced support for bridging with LangChain, implemented by an external contributor. Users can assemble RAG systems via FedRAG and fine-tune generator/retriever component models to adapt to specific knowledge bases. After fine-tuning, they can bridge to popular RAG inference frameworks like LangChain, leveraging their ecosystem and features. This update aims to simplify the process of building, optimizing, and deploying RAG systems (Source: nerdai)
Ollama Introduces “Thinking” Feature, Allowing Separation of Thought Process and Final Reply: Ollama has updated its platform, adding an option to separate the thought process and final reply for models that support a “thinking” feature (such as DeepSeek-R1-0528). Users can choose to view the model’s “thinking” content or disable this feature for a direct response. This functionality applies to Ollama’s CLI, API, and Python/JavaScript libraries, providing users with more flexible model interaction (Source: Hacubu)
Firecrawl Launches /search Endpoint, Integrating Search and Crawling Functionality: Firecrawl has released a new /search API endpoint that allows users to perform a web search and crawl all results in an LLM-friendly format with a single API call. This feature aims to simplify the process for AI agents and developers to discover and utilize web data. LangChain’s StateGraph can be used to build automated workflows leveraging this functionality, such as automatically finding competitors, crawling their websites, and generating analytical reports (Source: hwchase17, LangChainAI, omarsar0)
LlamaIndex Integrates MCP, Enhancing Agent Capabilities and Workflow Deployment: LlamaIndex announced the integration of MCP (Model Component Protocol), aiming to enhance its agents’ tool use capabilities and the flexibility of workflow deployment. This integration provides helper functions to assist LlamaIndex agents in using MCP server tools and allows any LlamaIndex workflow to be served as an MCP server. This move intends to expand the toolset of LlamaIndex agents and enable their workflows to seamlessly integrate into existing MCP infrastructures (Source: jerryjliu0)

Modal Launches LLM Engine Advisor, Providing Performance Benchmarks for Open-Source Model Engines: Modal has released LLM Engine Advisor, a benchmarking application designed to help users select the best LLM engine and parameters. The tool provides performance data, such as speed and maximum throughput, for running open-source models (e.g., DeepSeek V3, Qwen 2.5 Coder) with different inference engines (e.g., vLLM, SGLang) on various hardware (such as multi-GPU environments). This initiative aims to increase transparency and decision-making efficiency for running self-hosted LLMs (Source: charles_irl, akshat_b, sarahcat21)
PlayDiffusion: PlayAI Launches New Audio Inpainting Model to Replace Dialogue in Audio: PlayAI has released a new model called PlayDiffusion, which can seamlessly replace dialogue content in audio files while preserving the original speaker’s voice characteristics. This “audio inpainting” technology offers new possibilities for audio editing, such as modifying specific words or phrases in podcasts, audiobooks, or video voiceovers without re-recording the entire segment. The project is open-sourced on GitHub (Source: _mfelfel, karminski3)
Hugging Face Launches Semantic Deduplication Tool to Optimize Training Dataset Quality: Inspired by Maxime Labonne’s AutoDedup, Hugging Face Spaces has launched a new semantic deduplication application. The tool allows users to select one or more datasets from the Hugging Face Hub, generate semantic embeddings for each row of data, and then remove near-duplicates based on a set threshold. This initiative aims to help researchers and developers improve the quality of training datasets and avoid performance degradation or inefficient training due to data redundancy (Source: ben_burtenshaw, ben_burtenshaw)

Perplexity Labs Sees Surge in Demand as Users Quickly Build Customized Software: Perplexity Labs has become popular among users for its ability to quickly build customized software from a single prompt, leading to a significant increase in demand, with some users even purchasing multiple Pro accounts for more Labs queries. This reflects a strong user interest in tools that can be quickly created and modified according to their own needs, indicating that AI-driven personalized software development is becoming a trend (Source: AravSrinivas, AravSrinivas)
Ollama and Hazy Research Collaborate on Secure Minions for Private Collaboration Between Local and Cloud LLMs: The Minions project from Stanford’s Hazy Research lab, by connecting Ollama local models with cutting-edge cloud models, aims to significantly reduce cloud costs (by 5-30x) while maintaining accuracy close to that of frontier models (98%). The Secure Minion project further transforms GPUs like H100 into secure enclaves, enabling memory and computation encryption to ensure data privacy. This hybrid operational model enhances privacy protection while also offering users a more cost-effective way to use LLMs (Source: code_star, osanseviero, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Exa Partners with OpenRouter to Provide Web Search Capabilities for 400+ LLMs: AI search engine Exa announced a partnership with OpenRouter to provide web search functionality for over 400 large language models on the OpenRouter platform. This means developers and users utilizing these LLMs can conveniently call upon Exa’s search capabilities, enhancing the models’ real-time information acquisition and knowledge updating abilities, further improving the performance of applications like RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) (Source: menhguin)

📚 Learning
Microsoft Launches “MCP for Beginners” Introductory Course: Microsoft has released an introductory course for beginners to MCP (Microsoft Copilot Platform, speculated to be a typo, likely referring to Microsoft CoCo Framework or a similar AI Agent protocol). The course aims to help beginners master the core concepts, implementation methods, and practical applications of MCP, with content including protocol architecture specifications, tutorial guides, and code practices in multiple programming languages. The course structure covers an introduction, core concepts, security, getting started, advanced topics, and community & case studies, and provides example projects like basic and advanced calculators (Source: dotey)

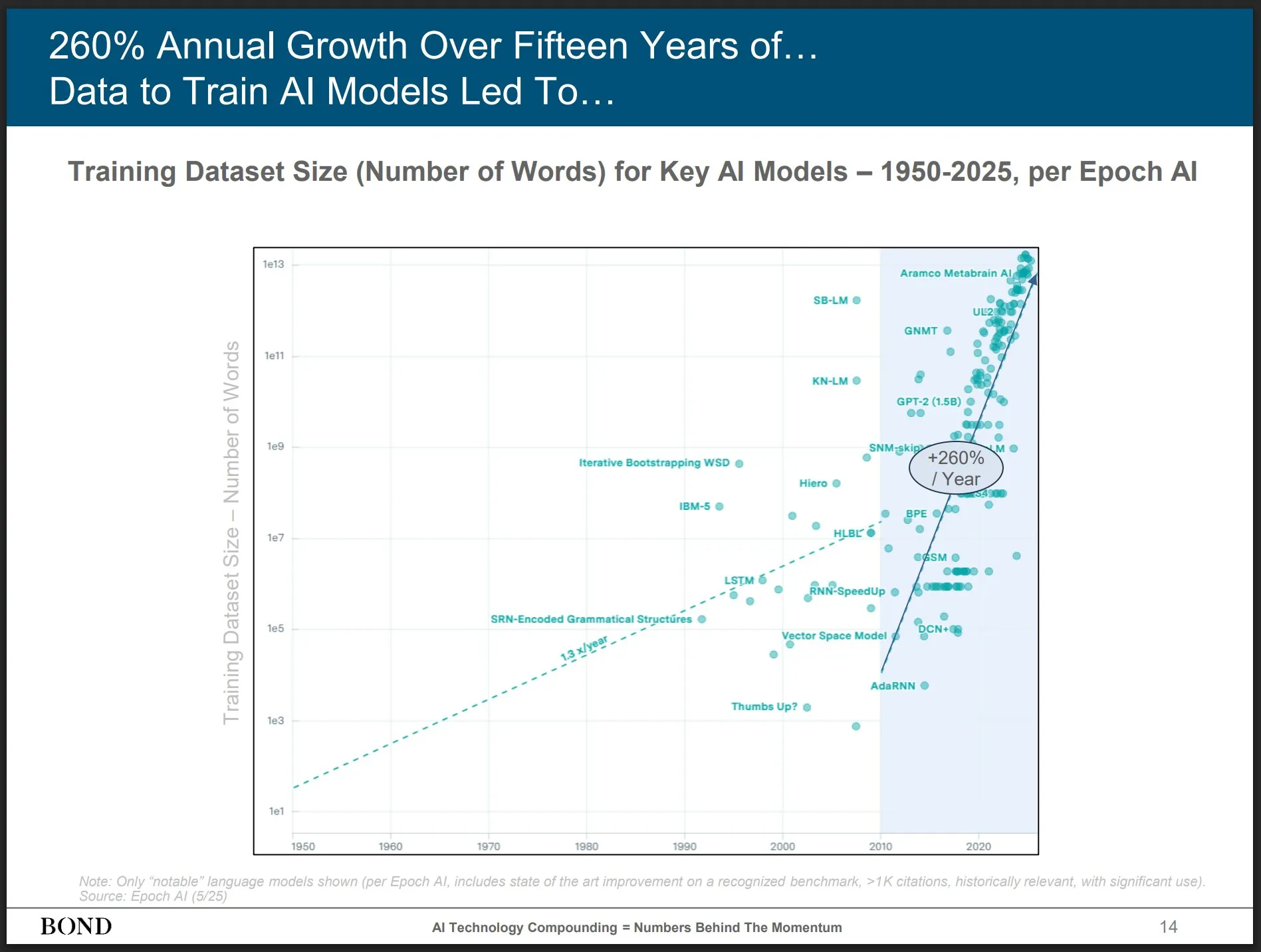
Bond Capital Releases May 2025 AI Trends Report, Offering Insights into Industry Development: Prominent venture capital firm Bond Capital has released a 339-page “2025-05 AI Trends Report,” comprehensively analyzing data and insights on AI across various sectors. The report highlights that ChatGPT has 800 million monthly active users (90% from outside North America) and 1 billion daily searches; AI-related IT positions have grown by 448%; the cost of training frontier models exceeds $1 billion per instance; and LLMs are becoming infrastructure. The report emphasizes that the key to competition lies in building the best AI-driven products, and it is currently a builder’s market (Source: karminski3)
Papers Discuss Relationship Between Reinforcement Learning and LLM Reasoning, ProRL and Limit-of-RLVR Gain Attention: Two research papers on the reasoning capabilities of Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Large Language Models (LLMs) have sparked discussion. One is “Limit-of-RLVR: Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?”, and the other is NVIDIA’s “ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models.” These studies explore the extent to which RL (particularly RLVR, Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards) can enhance the foundational reasoning abilities of LLMs, and the impact of prolonged RL training on expanding LLM reasoning boundaries. Related discussions suggest that high-quality RLVR training data and effective reward mechanisms are key (Source: scaling01, Dorialexander, scaling01)

Paper “How Programming Concepts and Neurons Are Shared in Code Language Models” Explores Sharing Mechanisms of Programming Concepts and Neurons in Code LLMs: This study investigates the relationship between the internal conceptual spaces of Large Language Models (LLMs) when processing multiple programming languages (PLs) and English. Through few-shot translation tasks on Llama series models, it was found that in the middle layers, the conceptual space is closer to English (including PL keywords) and tends to assign high probabilities to English tokens. Neuron activation analysis shows that language-specific neurons are mainly concentrated in the lower layers, while neurons unique to each PL tend to appear in the top layers. The research provides new insights into how LLMs internally represent PLs (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
New Paper “Pixels Versus Priors” Controls Knowledge Priors in MLLMs via Visual Counterfactuals: This study explores whether Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), when performing tasks like visual question answering, rely more on memorized world knowledge or the visual information from input images. Researchers introduced the Visual CounterFact dataset, containing visual counterfactual images that conflict with world knowledge priors (e.g., blue strawberries). Experiments show that model predictions initially reflect memorized priors but shift towards visual evidence in the middle to late stages. The paper proposes PvP (Pixels Versus Priors) guidance vectors, which control model output bias towards world knowledge or visual input through activation layer intervention, successfully altering most color and size predictions (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
ICML 2025 Paper GuidedQuant Proposes Boosting Layer-wise PTQ Methods Using End Loss Guidance: GuidedQuant is a new Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) method that enhances the performance of layer-wise PTQ methods by integrating end loss guidance into the objective. The method utilizes per-feature gradients with respect to the end loss to weight the layer-wise output error, corresponding to block-diagonal Fisher information that preserves intra-channel dependencies. Additionally, the paper introduces LNQ, a non-uniform scalar quantization algorithm that guarantees a monotonic decrease in the quantization objective. Experiments show that GuidedQuant outperforms existing SOTA methods in weight-only scalar, weight-only vector, and weight and activation quantization, and has been applied to 2-4 bit quantization of models like Qwen3, Gemma3, and Llama3.3 (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

AI Engineer World’s Fair Held in San Francisco, Focusing on AI Engineering Practices and Frontier Technologies: The AI Engineer World’s Fair is currently underway in San Francisco, bringing together numerous engineers, researchers, and developers in the AI field. The conference agenda includes various hot topics such as reinforcement learning, kernels, inference & agents, model optimization (RFT, DPO, SFT), agent coding, and building voice agents. During the event, experts from companies like OpenAI and Google will give presentations and participate in discussions, and new products and technologies will be announced. Community members are actively participating, sharing conference schedules, and organizing offline meetups, showcasing the vitality of the AI engineering community and its enthusiasm for cutting-edge technologies (Source: swyx, clefourrier, swyx, LiorOnAI, TheTuringPost)

💼 Business
Shidu Intelligence Completes Multi-Million Yuan Seed Funding Round to Accelerate Multi-Scenario Application of AI Smart Glasses: Suzhou Shidu Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. announced the completion of a multi-million yuan seed funding round. The funds will be used for R&D of core AI smart glass technology, market expansion, and ecosystem construction. The company focuses on applying AI smart glasses in areas such as smart healthcare for the elderly (e.g., smart reading glasses, smart glasses for the visually impaired), smart living (smart fashion glasses, cycling glasses), and smart manufacturing (smart industrial glasses, voice controllers). Its products are priced between 200 yuan and 1000 yuan, aiming to promote the popularization of smart glasses through high cost-performance ratio (Source: 36氪)

Rumors of OpenAI Acquiring AI Programming Assistant Windsurf Spark Speculation of Anthropic Cutting Off Claude Model Supply: Market rumors suggest OpenAI may acquire AI programming tool Windsurf (formerly Codeium) for about $3 billion. Against this backdrop, Windsurf CEO Varun Mohan posted that Anthropic cut off its direct access to almost all Claude 3.x models, including Claude 3.5 Sonnet, with very short notice. Windsurf expressed disappointment and quickly shifted its computing power to other inference service providers, while offering discounts on Gemini 2.5 Pro to affected users. The community speculates Anthropic’s move might be related to OpenAI’s potential acquisition, fearing it will impact industry competition and developer choices. Previously, Windsurf also failed to receive direct support from Anthropic when Claude 4 was released (Source: AI前线)

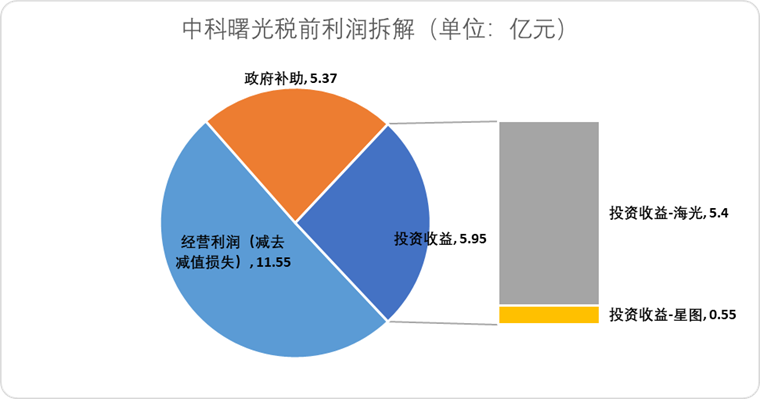
Hygon Information Technologies Plans Share Swap Merger with Sugon to Integrate Domestic Computing Power Industry Chain: AI chip design company Hygon Information Technologies (Haiguang Information) announced a plan to absorb its largest shareholder, server manufacturer Sugon (Zhongke曙光), through a share swap. Hygon’s market capitalization is approximately 316.4 billion yuan, while Sugon’s is about 90.5 billion yuan. This “snake swallowing an elephant” style merger aims to optimize the industrial layout from chips to software and systems, achieve strengthening, supplementing, and extending of the industrial chain, and leverage technological synergies. Analysts believe the merger will help resolve complex related-party transactions and potential horizontal competition issues between the two parties, reduce operating costs, and align with the development trend of end-to-end computing power solutions in the AI era, potentially marking an accelerated handover of technological power in China’s semiconductor industry from traditional computing to AI computing (Source: 36氪)
🌟 Community
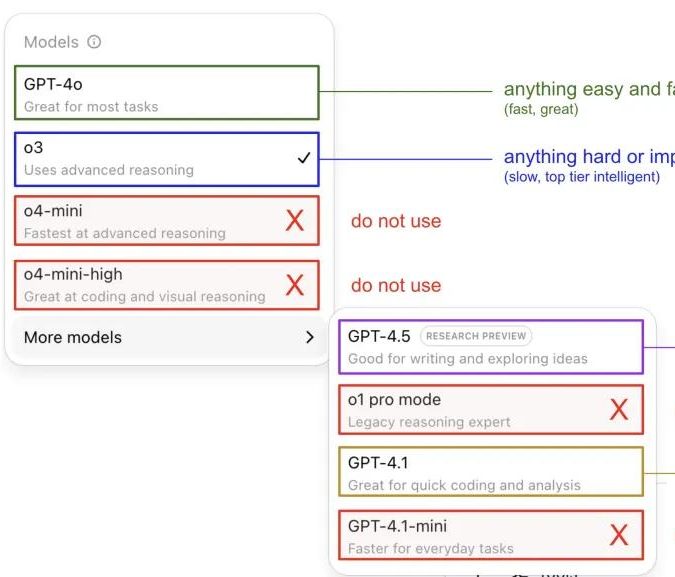
Andrej Karpathy Shares ChatGPT Model Usage Tips, Sparking Community Discussion: Andrej Karpathy shared his personal experience using different ChatGPT versions: for important or difficult tasks, he recommends using the more powerful o3 (likely referring to a specific GPT-3.x or GPT-4 variant); for daily low-to-medium difficulty problems, 4o can be used; for code improvement tasks, GPT-4.1 is suitable; and for in-depth research and multi-link summarization, the deep research function (based on o3) is used. This experience sharing sparked widespread community discussion, with many users sharing their own usage preferences and views on model selection, while also reflecting users’ confusion about OpenAI’s model naming and the lack of automatic model selection features (Source: 量子位, JeffLadish)
Developer Shares Two-Week Experience with Agentic AI Programming: From Awe to Disenchantment, Ultimately Opting for Manual Refactoring: A tech lead with 10 years of experience shared their journey of integrating Agentic AI (specifically AI programming agents) into their social media app development workflow. Initially, the AI rapidly generated functional modules, wrote front-end and back-end logic, and unit tests with astonishing efficiency, generating about 12,000 lines of code in two weeks. However, as the codebase complexity increased, the AI began to make frequent errors when handling new features, got stuck in loops, and struggled to admit failure. The generated code also exposed issues like inaccurate naming and repetitive code, making the codebase difficult to maintain and causing the developer to lose trust. Ultimately, the developer decided to use the AI-generated code only as a “vague reference,” manually refactoring all features, and concluded that AI is currently better suited for analyzing existing code and providing examples rather than directly writing functional code (Source: CSDN)

Distinction Between AI Agent Definition and Workflow Gains Attention, Huge Future Application Potential: Community discussions are distinguishing between the concepts of AI Agents and Workflows. An Agent typically refers to an LLM accessing tools in a loop, running freely based on instructions; a Workflow is a series of primarily deterministically executed steps, which may include LLMs completing sub-tasks. Although there is overlap (Agents can be prompted for deterministic execution, Workflows can include Agentic components), this distinction remains ontologically meaningful. Meanwhile, the potential of AI Agents in enterprise applications is widely recognized, with major companies like Tencent and ByteDance investing heavily in the agent field. For example, Tencent is upgrading its large model knowledge base into an agent development platform, and ByteDance has its Coze platform, aiming to help enterprises implement native AI agent systems (Source: fabianstelzer, 蓝洞商业)
Dwarkesh Patel Discusses LLM and AGI Timelines, Believes Continual Learning is Key Bottleneck: Dwarkesh Patel elaborated on his views on AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) timelines in his blog, arguing that LLMs currently lack the human ability to accumulate context through practice, reflect on failures, and make small improvements—i.e., continual learning. He believes this is a huge bottleneck for model utility and solving it could take several years. This viewpoint has sparked discussions among several AI researchers, including Andrej Karpathy, who also agrees with the shortcomings of LLMs in continual learning, comparing them to colleagues with anterograde amnesia. These discussions highlight the challenges in achieving true AGI and the need for deeper thinking about model learning mechanisms (Source: dwarkesh_sp, JeffLadish, dwarkesh_sp)

Patent Issues for AI in Drug Discovery Draw Attention, Science Article Urges Caution: A policy forum article in Science titled “What patents on AI-derived drugs reveal” discusses the application of AI in drug discovery and its impact on the patent system. The research points out that when AI-native companies apply for drug patents, they often have less in vivo experimental data than traditional pharmaceutical companies, potentially leading to promising drugs being abandoned due to lack of follow-up research. Concurrently, the large number of new molecules generated by AI, once publicly disclosed, could become “prior art,” hindering other companies from patenting these molecules and investing further. The article suggests raising the bar for patent applications, requiring more in vivo experimental data, and allowing other companies to patent AI-generated molecules if they remain untested, while strengthening regulatory exclusivity during the new drug clinical trial phase to balance innovation incentives with public interest (Source: 36氪)
💡 Others
Altman Boardroom Drama May Be Adapted into Film “Artificial,” Involving Well-Known Director and Producer: According to The Hollywood Reporter, MGM plans to adapt the OpenAI high-level personnel changes into a film, tentatively titled “Artificial.” Renowned Italian director Luca Guadagnino is reportedly in talks to direct, with producers including David Heyman of the Harry Potter series. The cast is under discussion, with rumors that Andrew Garfield (who played Spider-Man and Eduardo Saverin in The Social Network) may play Sam Altman, Yura Borisov may play Ilya Sutskever, and Monica Barbaro may play Mira Murati. This news has sparked heated discussions among netizens, drawing comparisons to the film The Social Network (Source: 36氪, janonacct)
AI Customer Service Experience Sparks Controversy, Users Complain About “Artificial Idiots” and Difficulty Reaching Human Agents: During recent e-commerce sales promotions, a large number of consumers reported poor communication and irrelevant answers from AI customer service, as well as significant difficulty transferring to human agents, leading to a decline in service experience. Data from the State Administration for Market Regulation shows that in 2024, complaints related to “intelligent customer service” in the e-commerce after-sales service sector increased by 56.3% year-on-year. Users generally believe that AI customer service struggles to solve personalized problems, provides rigid answers, and is not friendly to special groups such as the elderly. The article calls on companies not to sacrifice service quality in pursuit of cost reduction and efficiency improvement, but to optimize AI technology, clarify a_i_客服 applicable scenarios for AI customer service, and retain convenient channels for human service (Source: 36氪)

Discussion on AI Application in Content Creation and Creators’ Coping Strategies: The increasing application of AI technologies (such as DeepSeek, Suno, Veo 3) in content creation fields like articles, music, and videos has caused anxiety among content creators about their career prospects. Analysis suggests that the content paradigm is shifting from “personalized recommendation” to “personalized generation.” In the short term, platforms may not completely replace creators with AI due to high trial-and-error costs, and creators can profit by creating unique style models and licensing them. In the long term, creators need to adjust their value creation methods, focusing more on “innovation strategies” that are difficult for AI to replace (such as original research, first-hand data acquisition), rather than “follower strategies” (chasing hot topics, relying on second-hand information) that are easily assisted by AI. Although AI has begun to venture into innovative fields like scientific research, creators with unique perspectives and deep thinking still hold value (Source: 36氪)

