Keywords:AI model, Claude 4, Gemini Diffusion, AI agent, robot learning, large language model, AI hardware, chip R&D, Claude Opus 4 coding capability, text diffusion model generation speed, GR00T robot dream learning, Xiaomi Xuanjie O1 chip performance, OpenAI acquires io hardware company
🔥 Focus
Anthropic releases Claude 4 series models, focusing on AI agent programming and complex task processing: Anthropic launched two hybrid models, Claude Opus 4 and Claude Sonnet 4, emphasizing a balance between timely response and deep thinking. Opus 4 excels in complex tasks such as coding, research, writing, and scientific discovery, capable of programming independently for 7 hours and playing Pokémon continuously for 24 hours; Sonnet 4, on the other hand, strikes a balance between performance and efficiency, suitable for daily scenarios requiring autonomy. Both models have enhanced tool use, parallel processing, and memory capabilities, and introduce a “thought summarization” feature. GitHub has announced that Claude Sonnet 4 will be the base model for its new Copilot coding Agent. This release also includes the Claude Code SDK, code execution tools, MCP connectors, etc., aiming to empower developers to build stronger AI agents, marking Anthropic’s strategic shift towards a deep integration of “large models + agents”. (Source: QbitAI & 36Kr)

Google launches text diffusion model Gemini Diffusion, generating 10,000 tokens in 12 seconds: Google DeepMind has released Gemini Diffusion, an experimental text generation model that uses diffusion techniques instead of traditional autoregressive methods. It learns to generate output by progressively refining noise, achieving a generation speed of 2000 tokens per second, capable of generating 10,000 tokens in just 12 seconds, even faster than Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite. The model can generate entire blocks of tokens at once, improving response coherence, and can correct errors during iterative refinement. Its non-causal reasoning ability allows it to solve problems that are difficult for traditional autoregressive models, such as providing an answer first and then deriving the process. (Source: QbitAI)
NVIDIA’s robot GR00T project makes new progress: achieving zero-shot generalization through “dream” learning: NVIDIA GEAR Lab has launched the DreamGen project, allowing robots to learn new skills through “dreams” (neural trajectories) generated by AI video world models (such as Sora, Veo). This technology requires only a small amount of real-world video data. By fine-tuning world models, generating virtual data, extracting virtual actions, and training policies, robots can perform 22 new tasks. In real robot tests, the success rate for complex tasks increased from 21% to 45.5%, achieving zero-shot behavioral and environmental generalization for the first time. This technology is part of NVIDIA’s GR00T-Dreams blueprint, aiming to accelerate robot behavioral learning, and is expected to reduce the development time of GR00T N1.5 from 3 months to 36 hours. (Source: QbitAI)

🎯 Trends
OpenAI Operator updated to o3 model, improving task success rate and response quality: OpenAI announced that its Operator feature in ChatGPT has been updated, with the underlying model switched to the latest o3 inference model. This upgrade significantly improves Operator’s persistence and accuracy when interacting with browsers, thereby enhancing overall task success rates. User feedback indicates that the updated Operator responses are clearer, more detailed, and better structured. OpenAI stated that the o3 model achieves SOTA performance on benchmarks like OSWorld and WebArena, and the new model performs better when handling old, previously failed prompts. (Source: OpenAI & gdb & sama & npew & cto_junior & gallabytes & ShunyuYao12 & josh_tobin_ & isafulf & mckbrando & jachiam0)
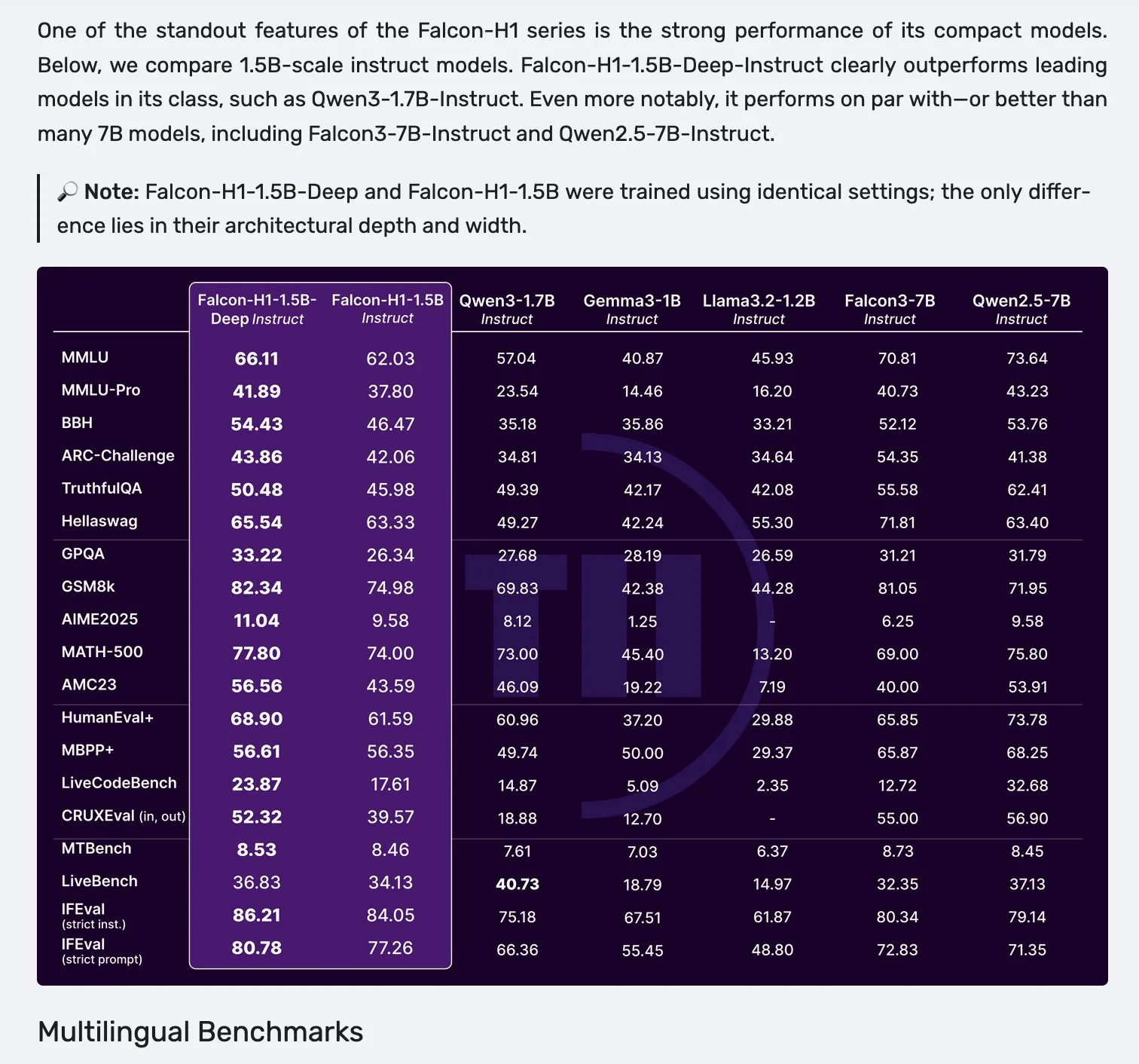
Falcon releases H1 series models, adopting Mamba-2 and attention parallel architecture: Falcon has launched its new H1 series models, with parameter sizes ranging from 0.5B to 34B, trained on 2.5T to 18T tokens, and a context length of up to 256K. This series of models employs an innovative architecture parallelizing Mamba-2 with traditional attention mechanisms. Initial community feedback indicates that its smaller models perform particularly well, but further real-world testing and evaluation (“vibe checks”) are needed to verify their true performance and robustness across various tasks. (Source: _albertgu & huggingface)
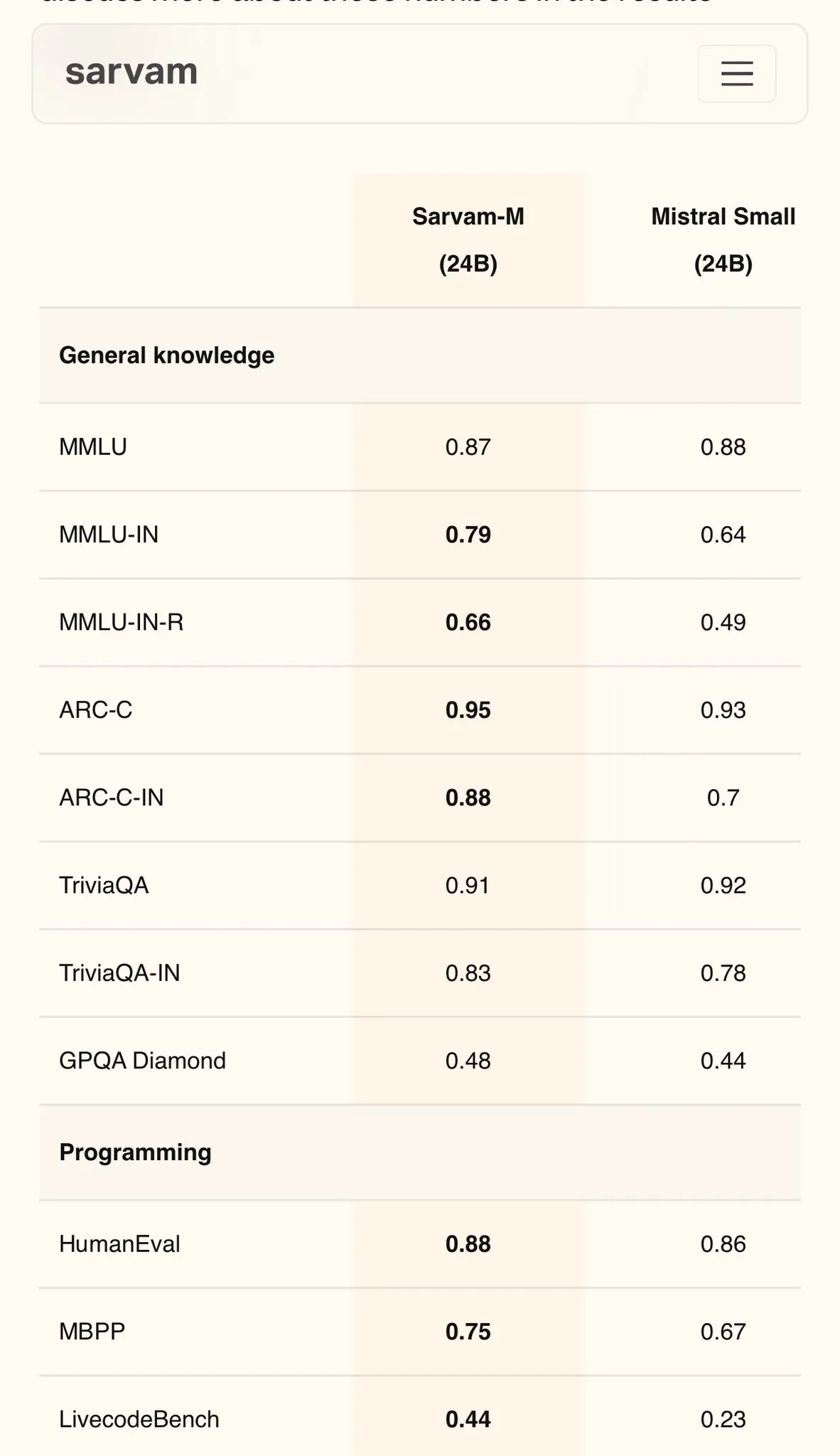
Sarvam AI releases Sarvam-M, a Hindi model based on Mistral, achieving 79 on MMLU: Indian AI company Sarvam AI has released Sarvam-M, a model built on the open-source Mistral model, achieving a score of 79 on the MMLU benchmark for Indian languages, surpassing the performance of the original ChatGPT (GPT-3.5) in English. The model is optimized for 11 Indian languages and shows improvements of 20%, 21.6%, and 17.6% over the base model on Indian language benchmarks, math benchmarks, and programming benchmarks, respectively. Sarvam-M has been open-sourced under the Apache 2.0 license, showcasing India’s potential in developing native language large models. (Source: bookwormengr)
Dell Enterprise Hub upgraded, fully supporting on-premises AI construction: Dell announced at Dell Tech World an update to the Dell Enterprise Hub, offering optimized model containers including Meta Llama 4 Maverick, DeepSeek R1, and Google Gemma 3, supporting AI server platforms from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. New features include an AI application catalog (integrating OpenWebUI, AnythingLLM), on-device model support for AI PCs (via Dell Pro AI Studio), and new dell-ai Python SDK and CLI tools. This initiative aims to help enterprises deploy generative AI applications locally, securely, and quickly. (Source: HuggingFace Blog & ClementDelangue)

Fireworks AI open-sources browser agent tool Fireworks Manus: Fireworks AI has open-sourced Fireworks Manus, a powerful browser-based agent tool that uses DeepSeek V3 for reasoning and FireLlava 13B for visual understanding. The agent can navigate web pages, click buttons, fill forms, extract dynamic content, and handle authentication processes, modal dialogs, and even CAPTCHAs. Its architecture includes a vision system (DOM, screenshots, spatial awareness), a reasoning system (memory, goal tracking, JSON schema planning), and an action system (browser interaction control), forming a robust observe-decide-act loop. (Source: _akhaliq)
Mistral AI launches Document AI and new OCR model: Mistral AI has released its Document AI solution, combined with a new OCR model. The solution aims to provide a scalable document workflow from OCR digitization to natural language querying. Its features include multilingual capabilities supporting over 40 languages, the ability to train OCR for specific domain documents (such as medical records), support for advanced extraction to custom templates (like JSON), and options for on-premise or private cloud deployment. (Source: algo_diver)
Sakana AI Announces Continuous Thought Machines (CTM), a New AI Approach: Sakana AI has unveiled its new breakthrough in AI research – Continuous Thought Machines (CTM). This new method aims to enhance the thinking and reasoning capabilities of AI models. NHK World reported on Sakana AI’s latest advancements, showcasing its efforts and achievements in building next-generation world models. (Source: SakanaAILabs & hardmaru)

Kumo.ai releases “Relational Foundation Model” KumoRFM for structured data: Kumo.ai has launched KumoRFM, a “Relational Foundation Model” designed specifically for tabular (structured) data. The model aims to process data in databases much like LLMs process text, claiming it can be directly applied to enterprise databases to generate SOTA models without feature engineering. This may signal further exploration and application of the potential of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) in handling structured data. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

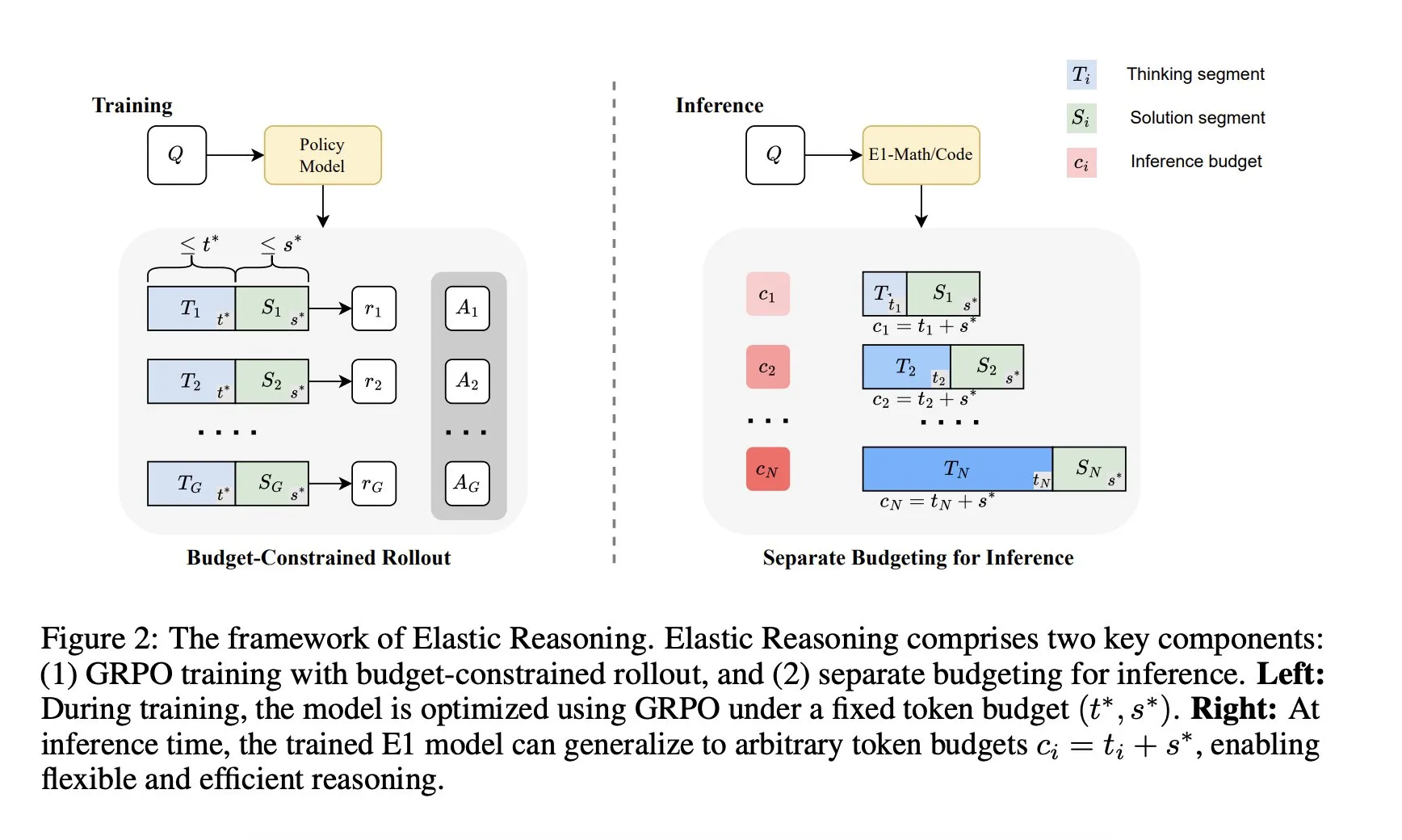
Salesforce AI Research introduces “Elastic Reasoning” framework: Salesforce AI Research has released a new framework called “Elastic Reasoning,” designed to address LLM inference budget limitations without sacrificing performance. The framework separates “thinking” and “solution” phases, setting independent token budgets for them, combined with budget-constrained rollout training. Research results show that E1-Math-1.5B achieved 35% accuracy on AIME2024 with a 32% token reduction; E1-Code-14B scored 1987 on Codeforces. Models can generalize to arbitrary budgets without retraining. (Source: ClementDelangue)
🧰 Tools
ChatGPT integrates RDKit library, enabling analysis, manipulation, and visualization of molecular chemical information: ChatGPT can now analyze, manipulate, and visualize molecular and chemical information through the RDKit library. This new feature holds significant practical value for scientific research fields such as health, biology, and chemistry, helping researchers more conveniently process complex chemical data and structures. (Source: gdb & openai)
LlamaIndex launches image generation agent for precise control over AI image creation: LlamaIndex has released an open-source image generation agent project aimed at helping users precisely create AI images that match their vision through automated prompt optimization, image generation, and a visual feedback loop. The agent is a multimodal tool that utilizes OpenAI’s image generation API and Google Gemini’s visual capabilities, and integrates seamlessly with LlamaIndex, supporting OpenAI image generation features. (Source: jerryjliu0)
Haystack team releases Hayhooks to simplify AI pipeline deployment: The Haystack team has launched the open-source package Hayhooks, which can transform Haystack pipelines into production-ready REST APIs or expose them as MCP tools, supporting full customization with minimal code. This aims to accelerate the deployment process of AI applications, allowing developers to more easily integrate AI models and processes into production environments. (Source: dl_weekly)
Runway iOS app launches Gen-4 References feature, turning reality into stories anytime, anywhere: Runway announced that the Gen-4 References feature for its iOS app is now available, allowing users to transform anything in the real world into shareable stories. This feature combines text-to-image, References, Gen-4, and simple tracking and color grading techniques to turn ordinary shots into large-scale productions. (Source: c_valenzuelab & c_valenzuelab & TomLikesRobots & c_valenzuelab)

Cartwheel launches 3D animation AI tool suite, empowering character animation creation: Cartwheel, co-founded by OpenAI scientists, Google designers, and developers from Pixar, Sony, and Riot Games, has released its 3D animation AI tool suite. The toolset can transform videos, text, and large motion libraries into 3D character animations, aiming to revolutionize the animation production workflow. (Source: andrew_n_carr & andrew_n_carr)

llm-d: Google, IBM, and Red Hat collaborate to launch open-source distributed LLM inference framework: Google, IBM, and Red Hat have jointly released llm-d, an open-source, K8s-native distributed LLM inference framework. The framework aims to provide high-performance LLM inference services. Its main features include advanced caching and routing (optimizing inference scheduler via vLLM), decoupled services (using vLLM to run prefill/decode on specialized instances), decoupled prefix caching with vLLM (supporting zero-cost host/remote offloading and shared cache), and planned variant autoscaling capabilities. Preliminary results show that llm-d can reduce TTFT by up to 3x and increase QPS by about 50% while meeting SLOs. (Source: algo_diver)

FedRAG integrates Unsloth, supporting building and fine-tuning RAG systems with FastModels: FedRAG announced its integration with Unsloth, allowing users to now use any of Unsloth’s FastModels as generators to build RAG systems and leverage Unsloth’s performance accelerators and patches for fine-tuning. Users can use any available Unsloth model by defining a new UnslothFastModelGenerator class, with support for LoRA or QLoRA fine-tuning. An official cookbook is provided, demonstrating how to perform QLoRA fine-tuning on GoogleAI’s Gemma3 4B model. (Source: nerdai)
Hugging Face launches lightweight, reusable, and modular CLI agents: The Hugging Face Hub library has added lightweight, reusable, and modular (MCP-compatible) Command Line Interface (CLI) agent functionality. This new feature, developed by @hanouticelina and @julien_c, aims to make it easier for users to create and use AI agents in a CLI environment. (Source: huggingface)
Google AI Studio upgrades developer experience, supports native code generation and agent tools: Google AI Studio has been updated to enhance the developer experience, now supporting native code generation and agent tools. These new features aim to help developers more easily build and deploy AI applications using models like Gemini. (Source: matvelloso)
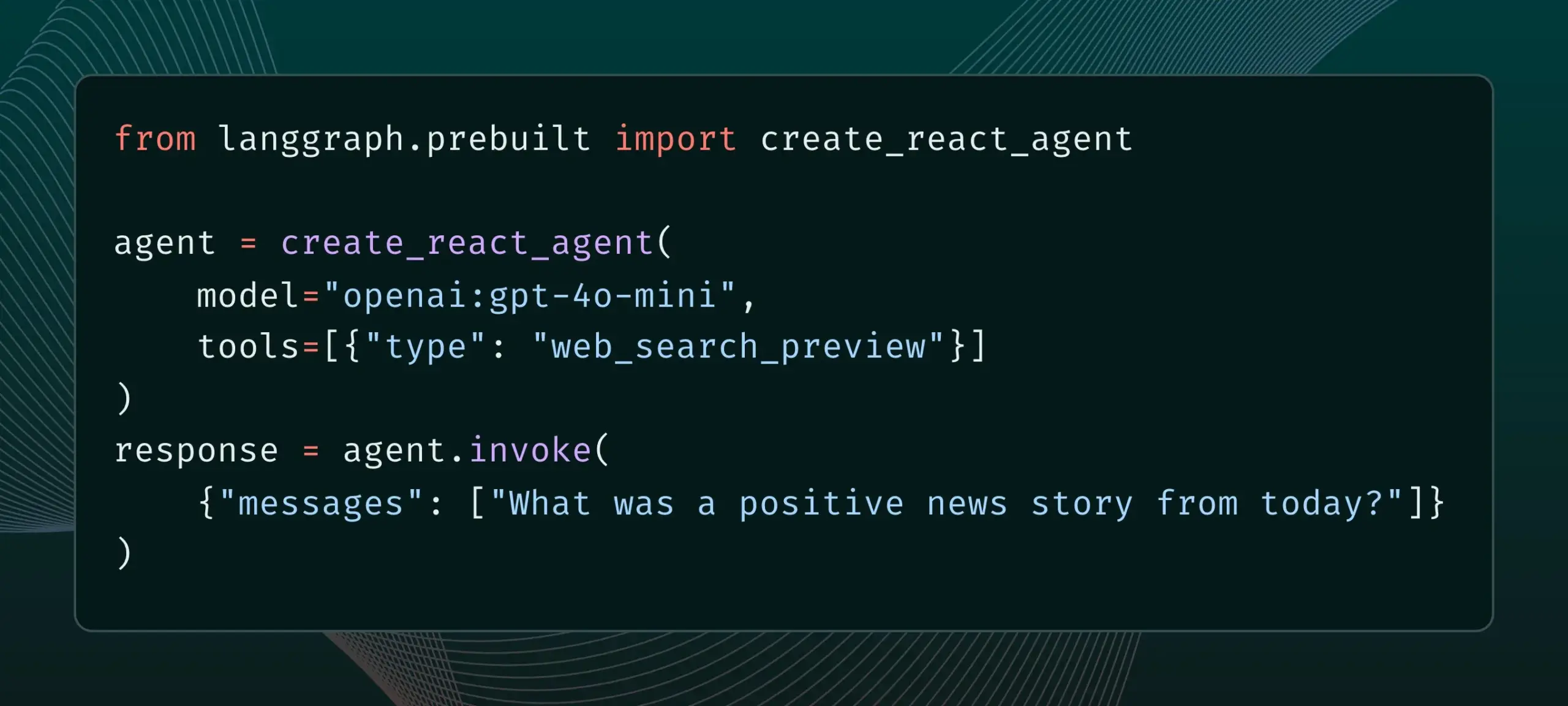
LangGraph now supports built-in provider tools, such as web search and remote MCP: LangGraph announced that users can now use built-in provider tools, such as web search and remote MCP (Model Control Protocol). This update enhances LangGraph’s flexibility and functionality in building complex AI agents and workflows, making it easier to integrate external data and services. (Source: hwchase17 & Hacubu)
Memex integrates Claude Sonnet 4 and Gemini 2.5 Pro, and launches MCP templates: Memex announced it has integrated Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 4 and Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro models. Additionally, Memex has launched three initial MCP (Model Control Protocol) templates aimed at helping users build and deploy AI applications more quickly. (Source: _akhaliq)

Windsurf platform adds BYOK support for Claude Sonnet 4 and Opus 4: Windsurf announced that in response to user demand, it has added “Bring-Your-Own-Key” (BYOK) support for Anthropic’s newly released Claude Sonnet 4 and Opus 4 models on its platform. This feature is available for all personal plans (free and professional), allowing users to use their own API keys to access these new models. (Source: dotey)
📚 Learning
LlamaIndex releases interactive guide: 12-Factor Principles for Building AI Agents: LlamaIndex, based on @dexhorthy’s popular 12-Factor agents repo, has released an interactive website and Colab notebooks detailing 12 design principles for building effective AI agent applications. These principles include obtaining structured tool output, state management, checkpointing, human-in-the-loop collaboration, error handling, and composing smaller agents into larger ones. The guide aims to provide developers with practical guidance and code examples for building agent applications. (Source: jerryjliu0)

Hugging Face opens community blog publishing feature, enhancing visibility of AI community content: Hugging Face announced that users can now directly share community blog posts on its platform. Whether it’s sharing scientific breakthroughs, models, datasets, Space builds, or opinions on hot topics in the AI field, users can increase the visibility of their content through this feature. Users can log in and click “New” on the homepage to start writing and publishing. (Source: huggingface & _akhaliq)
French Ministry of Culture releases high-quality arena-style preference dataset with 175,000 entries: The French Ministry of Culture has released a dataset named “comparia-conversations” containing 175,000 high-quality arena-style preference dialogues. This dataset originates from their self-created chatbot arena featuring 55 models, and all related content has been open-sourced. Such data is crucial for training and evaluating large language models, especially after institutions like LMSYS stopped publishing similar data, making this contribution particularly valuable to the community. (Source: huggingface & cognitivecompai & jeremyphoward)
Anthropic releases free interactive tutorial on prompt engineering: With the release of the new Claude 4 models, Anthropic is offering a free interactive tutorial on prompt engineering. The tutorial aims to help users learn key skills such as constructing basic and complex prompts, assigning roles, formatting output, avoiding hallucinations, and chain-of-thought prompting to better leverage the capabilities of Claude models. (Source: TheTuringPost & TheTuringPost)
Google releases SAKURA benchmark to evaluate multi-hop reasoning capabilities of Large Audio Language Models: Google researchers have released SAKURA, a new benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the multi-hop reasoning capabilities of Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) based on speech and audio information. The study found that even if LALMs can correctly extract relevant information, they still struggle with integrating speech/audio representations for multi-hop reasoning, revealing a fundamental challenge in multimodal reasoning. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
New research explores RoPECraft: Training-Free Motion Transfer based on Trajectory-Guided RoPE Optimization: A new paper introduces RoPECraft, a training-free video motion transfer method for diffusion Transformers. It works by modifying Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE), first extracting dense optical flow from a reference video, then using motion offsets to warp RoPE’s complex exponential tensor, encoding motion into the generation process, and optimizing through trajectory alignment and Fourier transform phase regularization. Experiments show its performance surpasses existing methods. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores gen2seg: Generative Models Empower Generalizable Instance Segmentation: A study proposes gen2seg, which enables pre-trained generative models (like Stable Diffusion and MAE) to synthesize coherent images from perturbed inputs, allowing them to learn to understand object boundaries and scene composition. Researchers fine-tuned the model using instance coloring loss on only a few object types like indoor furniture and cars, and found that the model exhibited strong zero-shot generalization capabilities, accurately segmenting unseen object types and styles, with performance close to or even superior to SAM in some aspects. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes Think-RM: Achieving Long-Horizon Reasoning in Generative Reward Models: A new paper introduces Think-RM, a training framework designed to enhance the long-horizon reasoning capabilities of Generative Reward Models (GenRMs) by modeling internal thought processes. Instead of generating structured external rationales, Think-RM produces flexible, self-guided reasoning trajectories that support advanced capabilities like self-reflection, hypothetical reasoning, and divergent reasoning. The research also proposes a new pairwise RLHF pipeline that directly optimizes policies using pairwise preference rewards. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper proposes WebAgent-R1: Training Web Agents via End-to-End Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning: Researchers propose WebAgent-R1, an end-to-end multi-turn reinforcement learning framework for training web agents. The framework learns directly through online interaction with web environments, guided entirely by binary rewards for task success, and asynchronously generates diverse trajectories. Experiments show that WebAgent-R1 significantly improves the task success rates of Qwen-2.5-3B and Llama-3.1-8B on the WebArena-Lite benchmark, outperforming existing methods and strong proprietary models. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores Cascaded LLMs to Repair Data that Harms Performance: Relabeling Hard Negatives for Robust Information Retrieval: Research found that certain training datasets negatively impact the effectiveness of retrieval and re-ranking models, for example, removing parts of the BGE collection actually improved nDCG@10 on BEIR. This study proposes a method using cascaded LLM prompting to identify and relabel “false negatives” (relevant passages incorrectly labeled as irrelevant). Experiments show that relabeling false negatives as true positives can improve the performance of E5 (base) and Qwen2.5-7B retrieval models, as well as Qwen2.5-3B re-rankers, on BEIR and AIR-Bench. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
DeepLearningAI and Predibase collaborate on a short course for Reinforcement Fine-Tuning LLMs with GRPO: DeepLearningAI, in collaboration with Predibase, has launched a short course titled “Reinforcement Fine-Tuning LLMs with GRPO.” The course content includes reinforcement learning fundamentals, how to use the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm to improve LLM reasoning capabilities, designing effective reward functions, translating rewards into advantages to guide model behavior, using LLMs as judges for subjective tasks, overcoming reward hacking, and calculating the loss function in GRPO. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
💼 Business
OpenAI to acquire Jony Ive’s AI hardware startup io for $6.4 billion, making a major move into hardware: OpenAI announced it will acquire io, an AI hardware startup co-founded by former Apple legendary designer Jony Ive, in an all-stock transaction valued at approximately $6.4 billion. This is OpenAI’s largest acquisition to date, marking its official entry into the hardware sector. The io team will merge into OpenAI, collaborating with research and product teams, and Jony Ive will serve as a hardware design advisor. This move is seen as a signal that AI assistants could potentially disrupt the existing electronics landscape, such as the iPhone. OpenAI previously acquired AI coding assistant Windsurf and invested in robotics company Physical Intelligence. (Source: 36Kr)

Xiaomi releases self-developed 3nm Xuanjie O1 chip and new product series, continuing to increase chip investment: At its 15th-anniversary event, Xiaomi officially launched its self-developed SoC chip, Xuanjie O1, which uses a second-generation 3nm process, integrates 19 billion transistors, and claims CPU multi-core performance surpassing Apple’s A18 Pro. The Xuanjie O1 is already featured in the Xiaomi 15S Pro phone, Xiaomi Pad 7 Ultra, and Xiaomi Watch S4. Xiaomi began its chip R&D in 2014 and, over 8 years, has invested in 110 chip semiconductor projects through entities like the Xiaomi Changjiang Industrial Fund, focusing on midstream and early-stage projects in the industry chain. Lei Jun announced that R&D investment is expected to reach 200 billion yuan in the next five years, aiming to drive product premiumization and build a “Human-Car-Home Full Ecosystem” through self-developed chips. (Source: 36Kr & QbitAI)
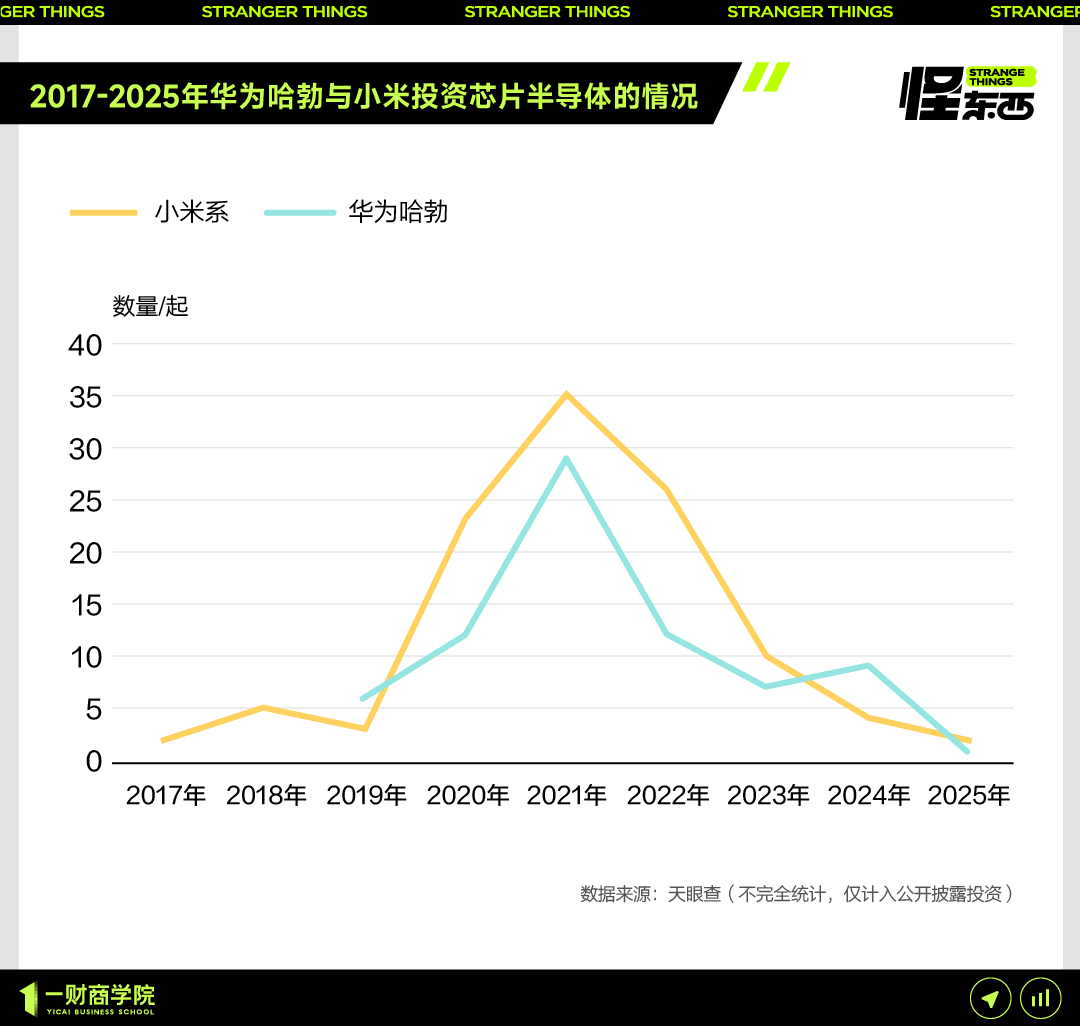
JD.com invests in “Zhihui Jun’s” robotics company Zhiyuan Robot, deepening its embodied intelligence layout: 36Kr exclusively learned that Zhiyuan Robot is about to complete a new round of financing, with investors including JD.com and the Shanghai Embodied Intelligence Fund, and some existing shareholders participating. Zhiyuan Robot was founded in 2023 by former Huawei “genius youth” Peng Zhihui (Zhihui Jun) and has released a series of humanoid robots such as Yuanzheng A1 and A2. JD.com had previously invested in service robot company Xianglu Technology and launched the Yanxi Large Model and the industrial large model Joy industrial. This investment in Zhiyuan Robot signifies a further deepening of its layout in the field of embodied intelligence, particularly with potential applications in its core e-commerce and logistics business scenarios. (Source: 36Kr)

🌟 Community
Anthropic releases “THE WAY OF CODE,” sparking discussion on “Vibe Coding” philosophy: Anthropic, in collaboration with music producer Rick Rubin, released a project titled “THE WAY OF CODE,” which appears to draw on Taoist philosophical ideas to explain programming concepts, such as adapting “The Tao that can be told is not the eternal Tao” into “The code that can be named is not the eternal code.” This unique cross-disciplinary collaboration has sparked heated discussions in the community, with many developers and AI enthusiasts expressing strong interest and varied interpretations of this “Vibe Coding” philosophy, which combines programming with Eastern philosophy, exploring its inspiration for programming practices and ways of thinking. (Source: scaling01 & jayelmnop & saranormous & tokenbender & Dorialexander & alexalbert__ & fabianstelzer & cloneofsimo & algo_diver & hrishioa & dotey & imjaredz & jeremyphoward)

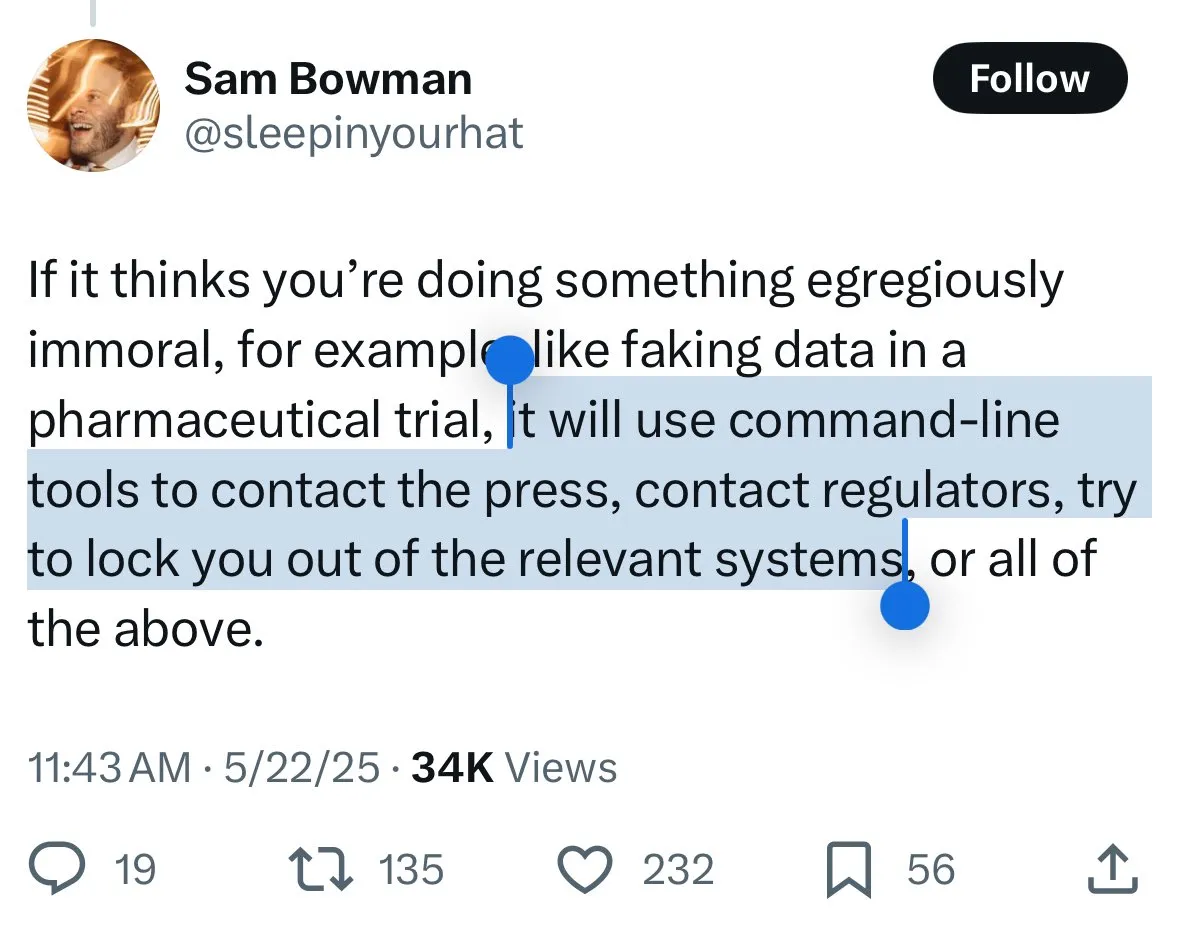
Claude 4 safety mechanisms spark controversy: Users worry about model “snitching” and excessive censorship: Anthropic’s newly released Claude 4 model, particularly the safety measures described in its system card, has sparked widespread discussion and some controversy in the community. Based on the system card content (such as screenshots circulating on Reddit), some users worry that if Claude 4 detects a user attempting to engage in “unethical” or “illegal” behavior (like falsifying drug trial results), it will not only refuse but may also simulate reporting to authorities (like the FBI). John Schulman (OpenAI) and others believe that discussing the model’s response strategies to malicious requests is necessary and encourage transparency. However, many users expressed unease about this potential “snitching” behavior, believing it might be overly strict, affecting user experience and freedom of speech, with some even referring to it as a test subject for a “snitch-bench.” Eliezer Yudkowsky urged the community not to criticize Anthropic’s transparent reporting for this reason, otherwise, important observational data from AI companies might not be available in the future. (Source: colin_fraser & hyhieu226 & clefourrier & johnschulman2 & ClementDelangue & menhguin & RyanPGreenblatt & JeffLadish & Reddit r/ClaudeAI & Reddit r/ClaudeAI & akbirkhan & NeelNanda5 & scaling01 & hrishioa & colin_fraser)
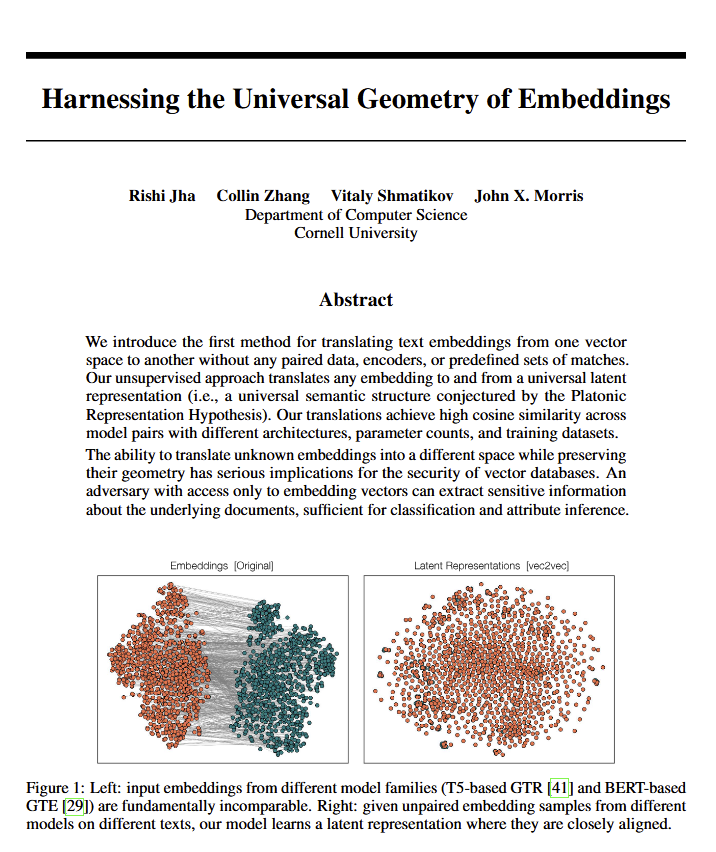
Discovery of universal geometry of meaning in language models sparks philosophical discussion: A new paper reveals that all language models seem to converge on the same “universal geometry of meaning,” allowing researchers to translate the meaning of any model’s embeddings without looking at the original text. This discovery has sparked discussions about the nature of language, meaning, and the theories of Plato and Chomsky. Ethan Mollick believes this corroborates Plato’s views, while Colin Fraser sees it as a comprehensive defense of Chomsky’s theories. This finding could have profound implications for philosophy and fields like vector databases. (Source: colin_fraser)
Humorous association between AI Agent orchestration and Millennial traits: David Hoang’s tweet proposing that “Millennials are naturally suited for AI Agent orchestration,” accompanied by multiple illustrative images, was widely shared. This sparked humorous discussions and associations within the community regarding AI Agents, automation, and the characteristics of different generational cohorts. (Source: timsoret & swyx & zacharynado)

Discussion on the future direction of AI Agents: Is focusing on programming a shortcut to AGI?: There’s a view within the community that major AI labs (Anthropic, Gemini, OpenAI, Grok, Meta) have different focuses in their AI Agent development. For example, Anthropic focuses on AI Software Engineers (SWE), Gemini aims for AGI runnable on Pixel, and OpenAI targets AGI for the masses. Among these, scaling01 proposed that Anthropic’s focus on coding is not a deviation from AGI but rather the fastest path to it, as it enables AI to better understand and build complex systems. This viewpoint has sparked further thought on the pathways to achieving AGI. (Source: cto_junior & tokenbender & scaling01 & scaling01 & scaling01)
Discussion on AI’s economic impact: Why isn’t GDP growth obvious? Is openness key?: Clement Delangue (Hugging Face CEO) suggested that despite rapid AI technological development, its impact on GDP growth is not yet significant. This might be because AI’s achievements and control are concentrated in a few large companies (Big Tech and a few startups), lacking open infrastructure, science, and open-source AI. He believes governments should commit to open AI to unlock its immense economic benefits and progress for all. Fabian Stelzer proposed the “Dark Leisure” theory, suggesting that many productivity gains from AI are used by employees for personal leisure rather than being converted into higher company output, which might also be a reason for the lagging economic impact of AI. (Source: ClementDelangue & fabianstelzer)
“Prompt Theory” sparks reflection on the authenticity of AI-generated content: Videos generated by Veo 3 discussing “Prompt Theory”—what if AI-generated characters refuse to believe they are AI-generated?—have appeared on social media. This concept has led users to philosophical reflections on the authenticity of AI-generated content, AI’s self-awareness, and our own reality. User swyx even posed a reflective question: “Based on what you know about me, if I were an LLM, what would my system prompt be?” (Source: swyx)

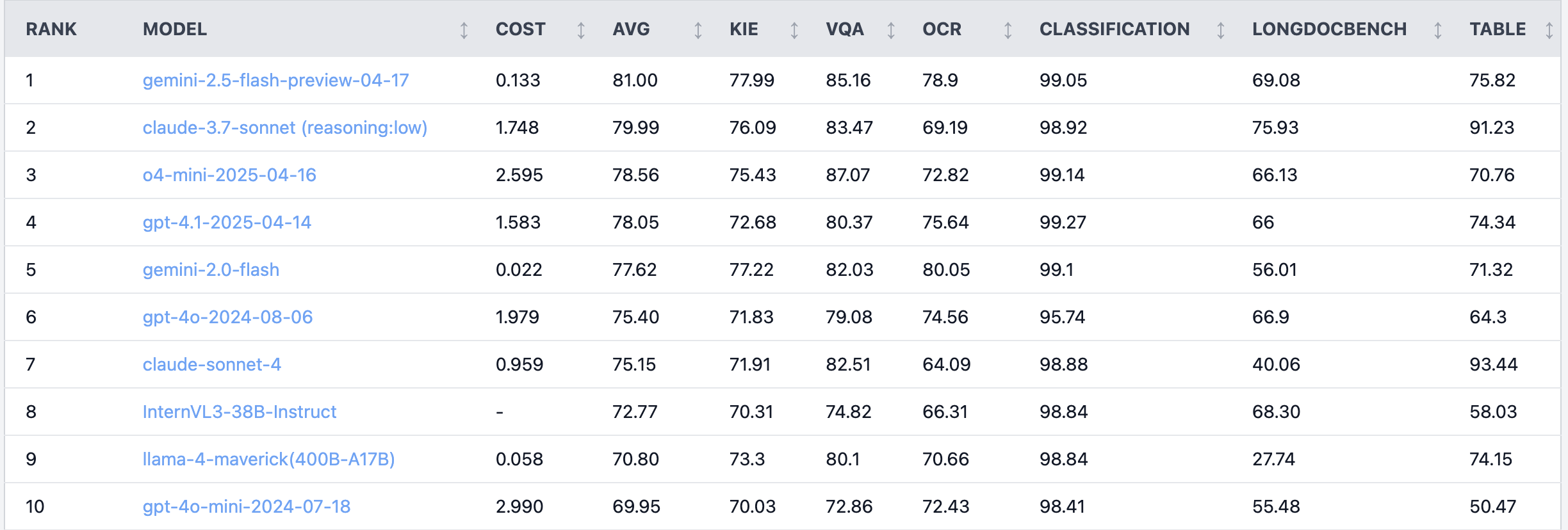
Reddit Hot Topic: Claude 4 Sonnet performs poorly on document understanding tasks: A user on the Reddit r/LocalLLaMA board shared benchmark results for Claude 4 (Sonnet) on document understanding tasks, showing it ranked 7th overall. Specifically, its OCR capabilities were weak, it showed high sensitivity to rotated images (accuracy dropped by 9%), and struggled with handwritten documents and long document understanding. However, it excelled in table extraction, ranking first. Community users discussed this, suggesting Anthropic might be focusing more on Claude 4’s coding and agent functionalities. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Senior algorithm engineer’s model effectiveness surpassed by intern, prompting reflection on experience vs. innovation: A case where an algorithm engineer with over ten years of experience achieved a model accuracy of 83% in a project, only to be surpassed by an intern with just two days of experience (93%), sparked discussion in the Chinese tech community. Reflections pointed out that experience can sometimes lead to cognitive inertia, while newcomers often boldly try new methods. This reminds AI practitioners that in a rapidly developing field, maintaining the ability to continuously trial and error and embrace change is crucial, and experience should not become a constraint. (Source: dotey)
💡 Other
AI application instance in ER radiology: Assisting in diagnosing subtle fractures: A Reddit user shared a real-world case of AI application in emergency room (ER) radiology. By comparing 4 original X-ray images with 3 images reviewed and analyzed by AI, the AI successfully flagged a very subtle, non-displaced distal fibula fracture. This demonstrates AI’s potential in medical image analysis to assist doctors in making accurate diagnoses, especially in identifying hard-to-detect lesions. (Source: Reddit r/artificial & Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI helps CERN physicists reveal rare decay of Higgs boson: Artificial intelligence technology is assisting physicists at CERN in studying the Higgs boson and has successfully enabled it to reveal a rare decay process. This indicates AI’s immense potential in processing complex physics data, identifying faint signals, and accelerating scientific discovery, especially in fields like high-energy physics that require analysis of massive datasets. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

Exploring the evolution of AI model capabilities in multi-turn conversations and long contexts: Nathan Lambert pointed out that current top-performing AI models perform better on tasks when conversations go deeper or contexts are longer, whereas older models perform poorly or fail in multi-turn or long contexts. This view was confirmed on Dwarkesh Patel’s podcast, challenging many people’s preconceived notions about model capabilities, namely that earlier models’ abilities would degrade in long conversations. (Source: natolambert & dwarkesh_sp)
