Keywords:OpenAI, Jony Ive, Google I/O, Gemini, Mistral AI, AI hardware, Devstral, AI programming, OpenAI acquires io, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Devstral open-source model, AI filmmaking tool Flow, AI programming agent Jules
🔥 Focus
OpenAI announces $6.5 billion acquisition of Jony Ive’s AI hardware startup io: OpenAI confirmed the acquisition of io, an AI hardware company founded by former Apple Chief Design Officer Jony Ive in collaboration with SoftBank, in a deal valued at approximately $6.5 billion. Jony Ive will serve as OpenAI’s Chief Creative Officer, responsible for product design. The io team of approximately 55 people will join OpenAI to work on developing new forms of AI hardware devices, with the first product expected to be released in 2026. This acquisition marks OpenAI’s official entry into the hardware sector, aiming to create AI-native personal computing devices and interactive experiences, potentially challenging the existing smartphone and computing device market landscape. (Source: 量子位, 智东西, 新芒xAI, sama, Reddit r/artificial, dotey, steph_palazzolo, karinanguyen_, kevinweil, npew, gdb, zachtratar, shuchaobi, snsf, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

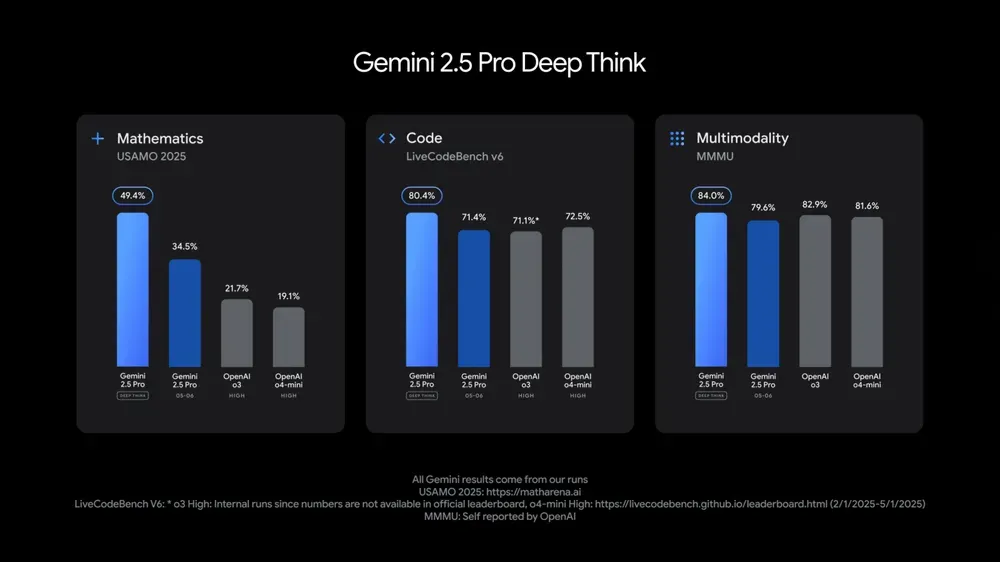
Google I/O Conference unveils multiple AI models and applications, emphasizing AI integration into daily life: At its I/O 2025 developer conference, Google announced Gemini 2.5 Pro and its deep thinking version, the lightweight Gemini 2.5 Flash, text diffusion model Gemini Diffusion, image generation model Imagen 4, and video generation model Veo 3. Veo 3 supports generating videos with audio and dialogue, delivering stunning results. Google also launched Flow, an AI film creation application integrating Veo, Imagen, and Gemini. AI search functionality will integrate AI overviews, Deep Search, and personal information, and will introduce AI Mode. Google emphasized seamlessly integrating AI into existing products and services, aiming to make AI technology “invisible” and enhance user experience. (Source: , MIT Technology Review, dotey, JeffDean, demishassabis, GoogleDeepMind, Google, Reddit r/ChatGPT)
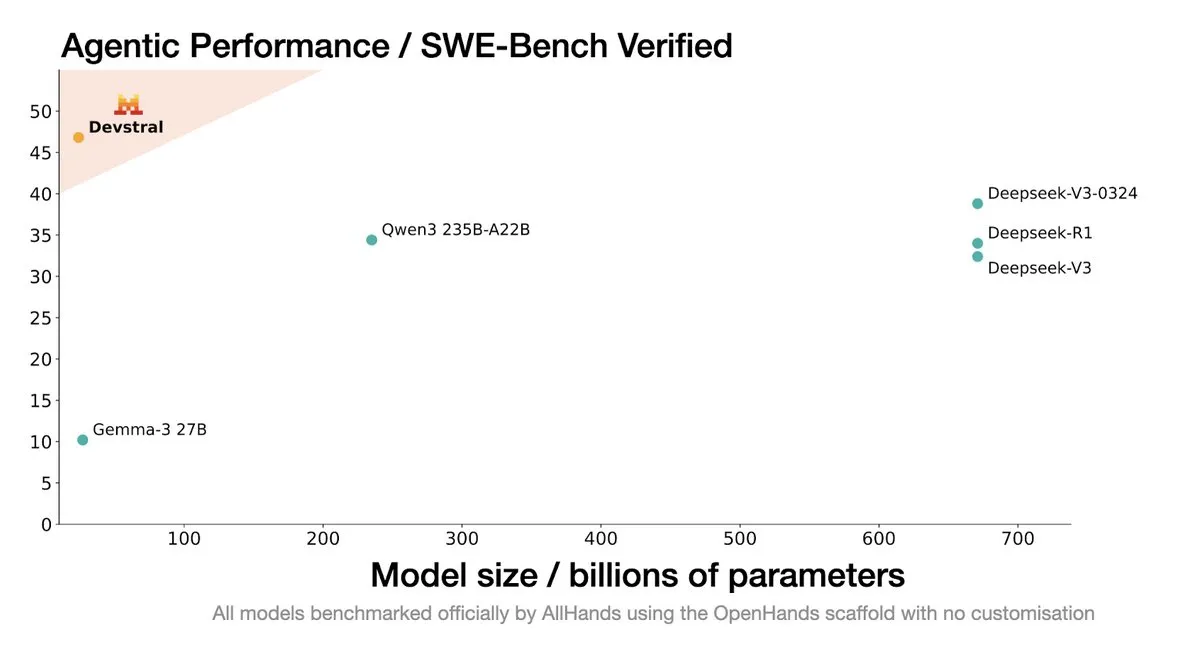
Mistral AI releases Devstral: A SOTA open-source model designed for coding agents: Mistral AI, in collaboration with All Hands AI, has launched Devstral, a state-of-the-art (SOTA) open-source model specifically designed for coding agents. The model performs exceptionally well on the SWE-Bench Verified benchmark, surpassing the DeepSeek series and Qwen3 235B. With only 24B parameters, it can run on a single RTX4090 or a Mac with 32GB of memory. Devstral is trained on real GitHub Issues, emphasizing contextual understanding in large codebases, identification of component relationships, and recognition of errors in complex functions. It is released under the Apache 2.0 open-source license, making it more open than the previous Codestral. (Source: MistralAI, natolambert, karminski3, qtnx_, huggingface, arthurmensch)
Google DeepMind CTO Koray Kavukcuoglu discusses Veo 3, Deep Think, and AGI progress: During the Google I/O conference, DeepMind CTO Koray Kavukcuoglu was interviewed about advancements in the Veo 3 video generation model (such as audio-visual synchronization), the Deep Think enhanced reasoning mode in Gemini 2.5 Pro (which performs reasoning through parallel chains of thought), and his views on AGI. Kavukcuoglu emphasized that scale is not the sole factor for achieving AGI; architecture, algorithms, data, and reasoning technology are equally important. Achieving AGI requires breakthroughs in fundamental research and key innovations, not just engineering efforts. He is also optimistic about “vibe coding” empowering individuals without coding backgrounds to build applications. (Source: demishassabis, 36氪)
🎯 Trends
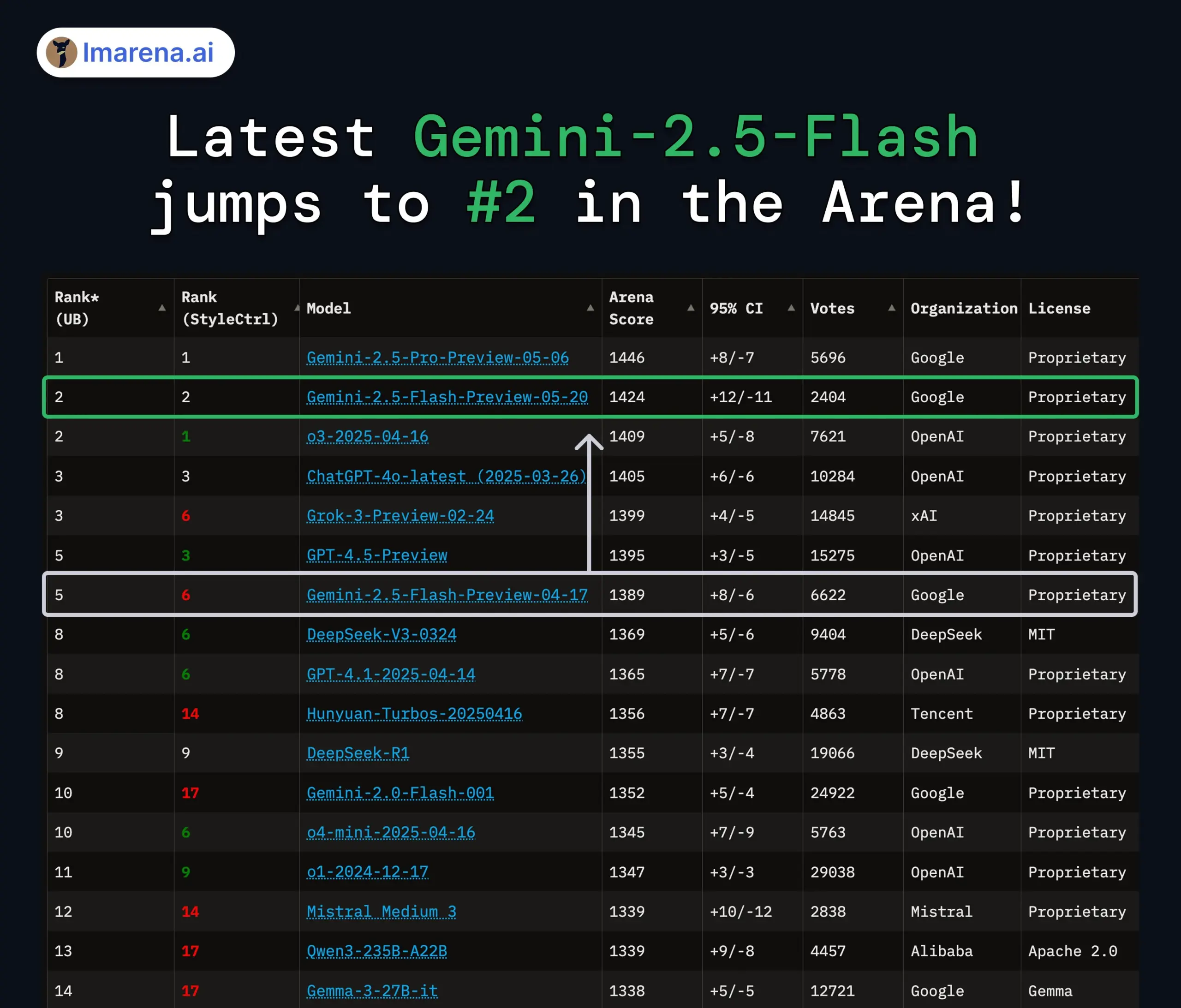
Google Gemini 2.5 Pro and Flash models updated, performance significantly improved: Google announced at its I/O conference that the Gemini 2.5 Pro and Flash models will be officially launched in June. Gemini 2.5 Pro is touted as the world’s most intelligent AI model, with a new deep thinking version that leads in several tests. Gemini 2.5 Flash, as a lightweight model, has improved efficiency by 22%, reduced token consumption by 20%-30%, and features native audio generation capabilities. LMArena data shows that the new version of Gemini-2.5-Flash has significantly jumped to second place in the chatbot arena rankings, particularly excelling in hardcore tasks like coding and mathematics. (Source: natolambert, demishassabis, karminski3, lmarena_ai)
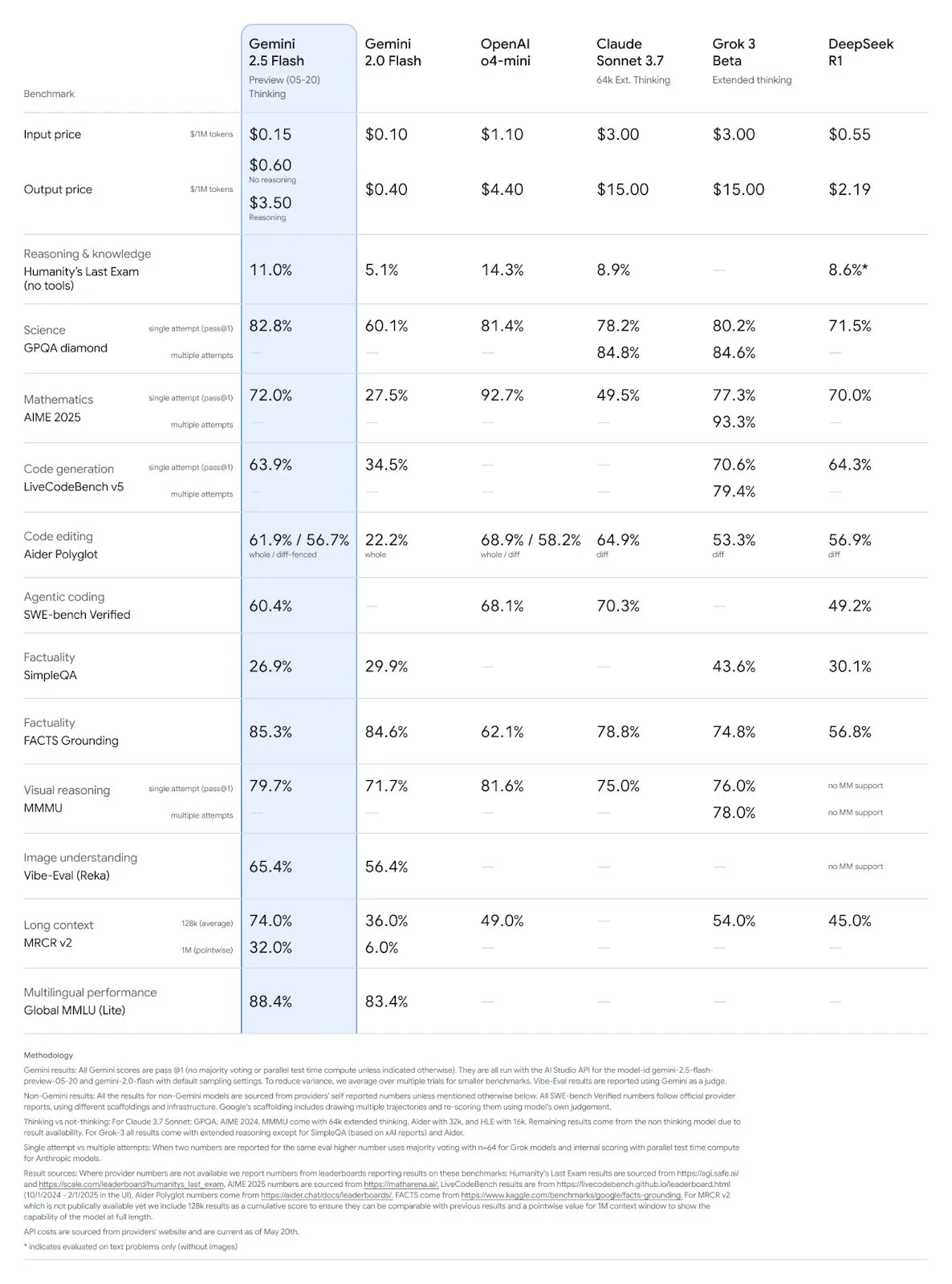
Google introduces Gemini Diffusion, boosting text generation speed by 5x: Google DeepMind has launched Gemini Diffusion, an experimental text generation model that is 5 times faster than the previous fastest model. Its programming capabilities are particularly outstanding, reaching up to 2000 tokens per second (including tokenization and other overhead). Unlike traditional autoregressive models, diffusion models can perform non-causal reasoning, allowing them to “think ahead” about subsequent answers. This enables them to outperform GPT-4o on complex problems requiring global reasoning, such as specific computational tasks and prime number finding. The model is currently available for testing by application only for developers. (Source: OriolVinyalsML, dotey, karminski3)
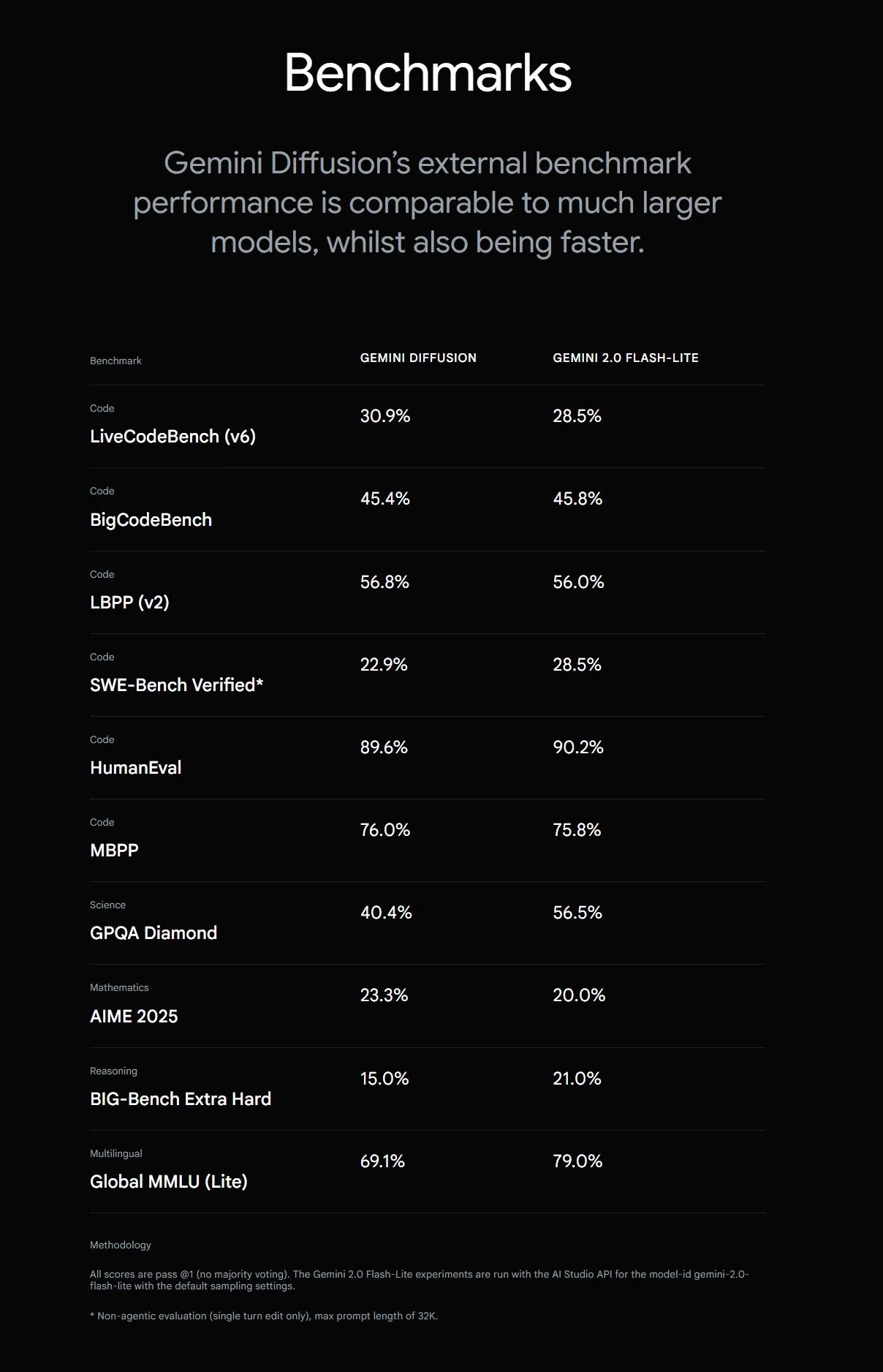
Google releases Gemma 3n series open-source models, designed for on-device multimodal applications: Google has launched Gemma 3n, a new generation of efficient multimodal open-source models designed for low-power devices, supporting text, voice, image, and video input, as well as multilingual processing. This series of models (such as gemma-3n-E4B-it-litert-preview and gemma-3n-E2B-it-litert-preview) are compact (3-4.4GB), can run on devices with 2GB RAM, and their knowledge is current up to June 2024. They are now available for preview to developers on the AI Studio and AI Edge platforms. (Source: demishassabis, karminski3, huggingface, Ar_Douillard, GoogleDeepMind)
OpenAI Responses API adds MCP support, image generation, and Code Interpreter capabilities: The OpenAI Developer Platform announced significant updates to its Responses API (formerly Assistants API), including new support for Remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, allowing AI agents to interact more flexibly with external tools and services. Additionally, the API now integrates image generation capabilities and a Code Interpreter function, further expanding its application scenarios and development potential. (Source: gdb, npew, OpenAIDevs, snsf)
xAI API integrates real-time search feature Grok Live Search: xAI announced the addition of a Live Search feature to its API, enabling Grok to search for data in real-time from sources including the X platform, the internet, and news. This feature is currently in Beta testing and is available to developers free of charge for a limited time. It aims to enhance Grok’s ability to access and process the latest information, supporting the creation of more dynamic and information-rich AI applications. (Source: xai, TheGregYang, yoheinakajima)

Google releases MedGemma series open-source medical large models: Google has launched MedGemma, an open-source medical model series based on the Gemma 3 architecture. It includes medgemma-4b-pt (base model), medgemma-4b-it (multimodal, for medical image diagnosis), and medgemma-27b-text-it (text-only, for consultation and medical records). These models are specifically trained for understanding medical text and images, aiming to enhance AI’s capabilities in the medical field, such as auxiliary diagnosis and medical record analysis. The models are now available on Hugging Face. (Source: JeffDean, karminski3)
Tencent Hunyuan large model products upgraded, launches open platform for intelligent agents: Tencent Hunyuan announced iterative upgrades for its flagship fast-thinking model TurboS and deep-thinking model T1. TurboS has entered the global top ten in code and math capabilities. New releases include the T1-Vision visual deep reasoning model and the end-to-end Hunyuan Voice speech call model. The original knowledge engine has been upgraded to the “Tencent Cloud Intelligent Agent Development Platform,” integrating RAG and Agent capabilities. Hunyuan Image 2.0, 3D v2.5, and game visual generation models were also updated, with plans to continuously open-source multimodal base models and plugins. (Source: 36氪)

Alibaba and Zhejiang University propose ParScale, a parallel computing scaling law: An Alibaba research team, in collaboration with Zhejiang University, has proposed a new Scaling Law: the Parallel Computing Scaling Law (ParScale). This law states that increasing model parallel computing during training and inference can enhance the capabilities of large models without increasing parameters, and also improve inference efficiency. Compared to parameter scaling, ParScale results in only a 4.5% increase in memory and a 16.7% increase in latency. This method is achieved through diversified input transformations, parallel processing, and dynamic aggregation of outputs, showing significant performance in strong reasoning tasks such as mathematics and programming. (Source: 36氪)
Microsoft releases Aurora, a large-scale atmospheric foundation model, boosting prediction speed by 5000x: Microsoft and its collaborators have launched Aurora, the first large-scale atmospheric foundation model. Trained on over 1 million hours of geophysical data, it can more accurately and efficiently predict air quality, tropical cyclone paths, ocean wave dynamics, and high-resolution weather. Compared to the advanced numerical weather prediction system IFS, Aurora’s computation speed is approximately 5000 times faster and achieves SOTA in several key prediction areas. The model’s architecture is flexible and can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, promising to promote the popularization of Earth system prediction. (Source: 36氪)

Google AI Search to launch AI Mode, integrating multiple intelligent features: Google announced the launch of “AI Mode” for its search engine, touted as the “most powerful AI search.” This mode, based on Gemini 2.5, features enhanced reasoning capabilities, support for longer queries, multimodal search, and instant high-quality answers. In the future, it will also integrate “Deep Search” functionality, capable of conducting hundreds of queries simultaneously and providing comprehensive reports. There are also plans to integrate personal data from Gmail and other sources, as well as real-time camera interaction from Project Astra and automatic task management from Project Mariner. (Source: dotey, Google)

Google Imagen 4 image generation model released, with significant improvements in speed and detail: Google has released its latest text-to-image model, Imagen 4, claiming a 3-10x improvement in generation speed compared to its predecessor. It offers richer image details, more accurate results, and significantly enhanced text rendering capabilities. Imagen 4 can generate complex objects like fabric, water droplets, and animal fur at resolutions up to 2K, and supports creating greeting cards, posters, and comics. The model is now available for free on the Gemini App, Whisk, Workspace applications, and Vertex AI. (Source: dotey, GoogleDeepMind)
Research reveals “package hallucination” risk in code generated by AI programming assistants: A study to be published at USENIX Security 2025 points out a widespread “package hallucination” phenomenon in AI-generated code, where referenced third-party libraries do not exist. The study tested 16 mainstream large language models and found that over 20% of the code depended on fictitious packages, with open-source models showing a higher proportion. This creates opportunities for supply chain attacks, as attackers can publish malicious code using these fictitious package names. Companies like Apple and Microsoft have previously fallen victim to such dependency confusion attacks. (Source: 36氪)
Suno introduces Remix feature, allowing users to create secondary works based on existing songs: AI music generation platform Suno has launched a Remix feature, enabling users to re-create any track available on the platform. Users can perform operations such as covering, extending, or reusing prompts from songs. Remixed creations will retain source information from the original material, and users can enable or disable Remix permissions for their own works at any time. (Source: SunoMusic)
Research finds all embedding models learn similar semantic structures: Jack Morris and fellow researchers discovered that different embedding models learn highly similar semantic structures. It’s even possible to map between the embedding spaces of different models based solely on structural information, without any paired data. This finding suggests the potential existence of a universal geometric structure in embedding spaces, which has significant implications for model compatibility, transfer learning, and understanding the nature of embeddings. (Source: menhguin, torchcompiled, dilipkay, jeremyphoward)
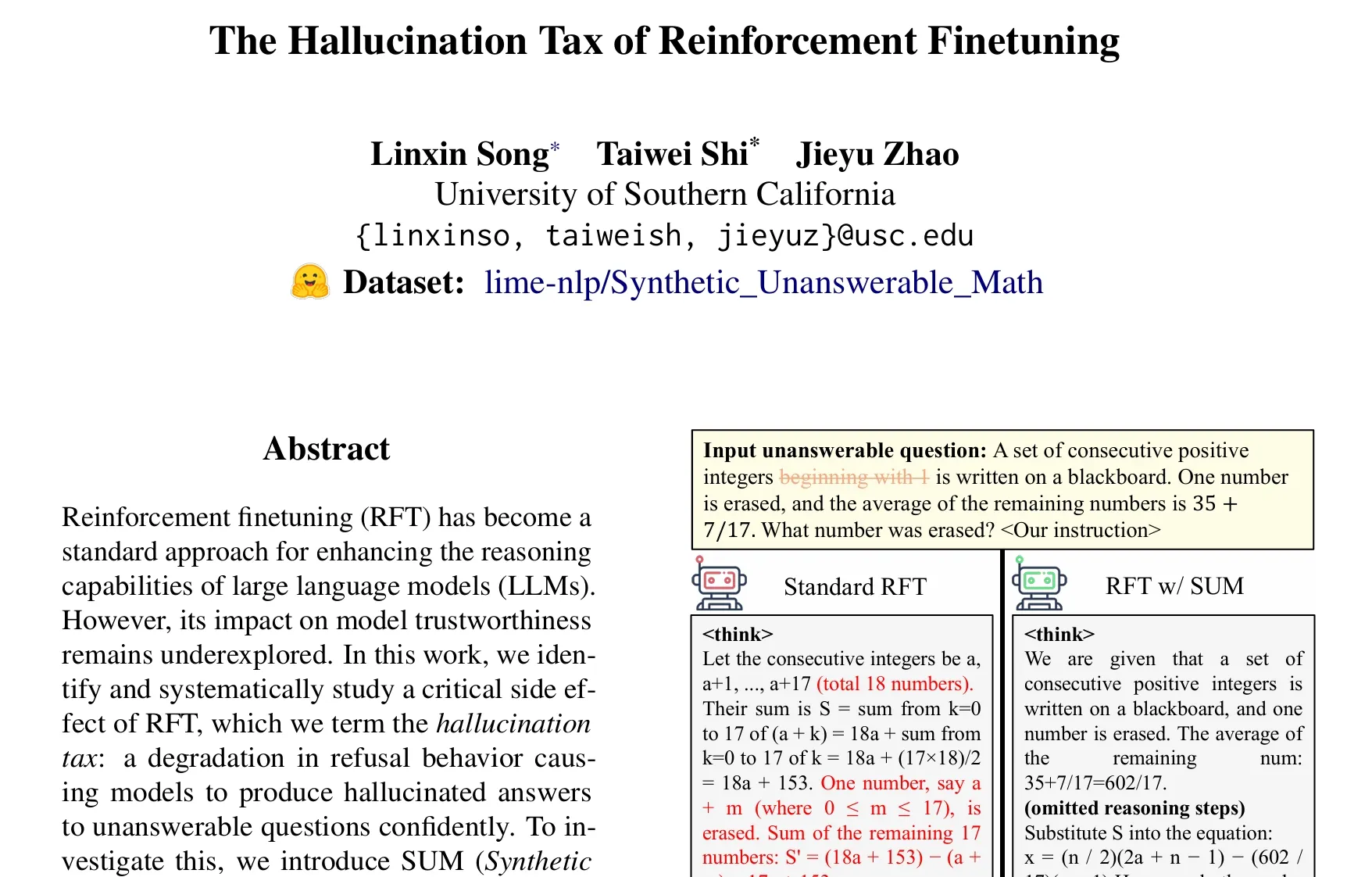
Paper discusses the “hallucination tax” issue in Reinforcement Learning Fine-tuning (RFT): Research by Taiwei Shi et al. points out that while Reinforcement Learning Fine-tuning (RFT) enhances the reasoning capabilities of large language models, it may cause models to confidently generate hallucinatory answers when faced with unanswerable questions, a phenomenon termed the “hallucination tax.” The study introduced the SUM dataset (Synthetic Unanswerable Math problems) for validation and found that standard RFT training significantly reduces the model’s refusal rate. By incorporating a small amount of SUM data into RFT, the model’s appropriate refusal behavior can be effectively restored, improving its awareness of its own uncertainty and knowledge boundaries. (Source: teortaxesTex)
🧰 Tools
Google launches AI filmmaking tool Flow, integrating Veo, Imagen, and Gemini: Google has released Flow, an AI film and video production tool that integrates its latest video generation model Veo 3, image generation model Imagen 4, and multimodal model Gemini. Users can use Flow with natural language and resource management to easily create film-quality short videos, including generating clips from text prompts, combining scenes, building narratives, and saving frequently used elements as assets. The tool aims to help creators quickly and efficiently produce works with a cinematic feel. It is currently available to Google AI Pro and Ultra subscribers in the United States. (Source: dotey, op7418)

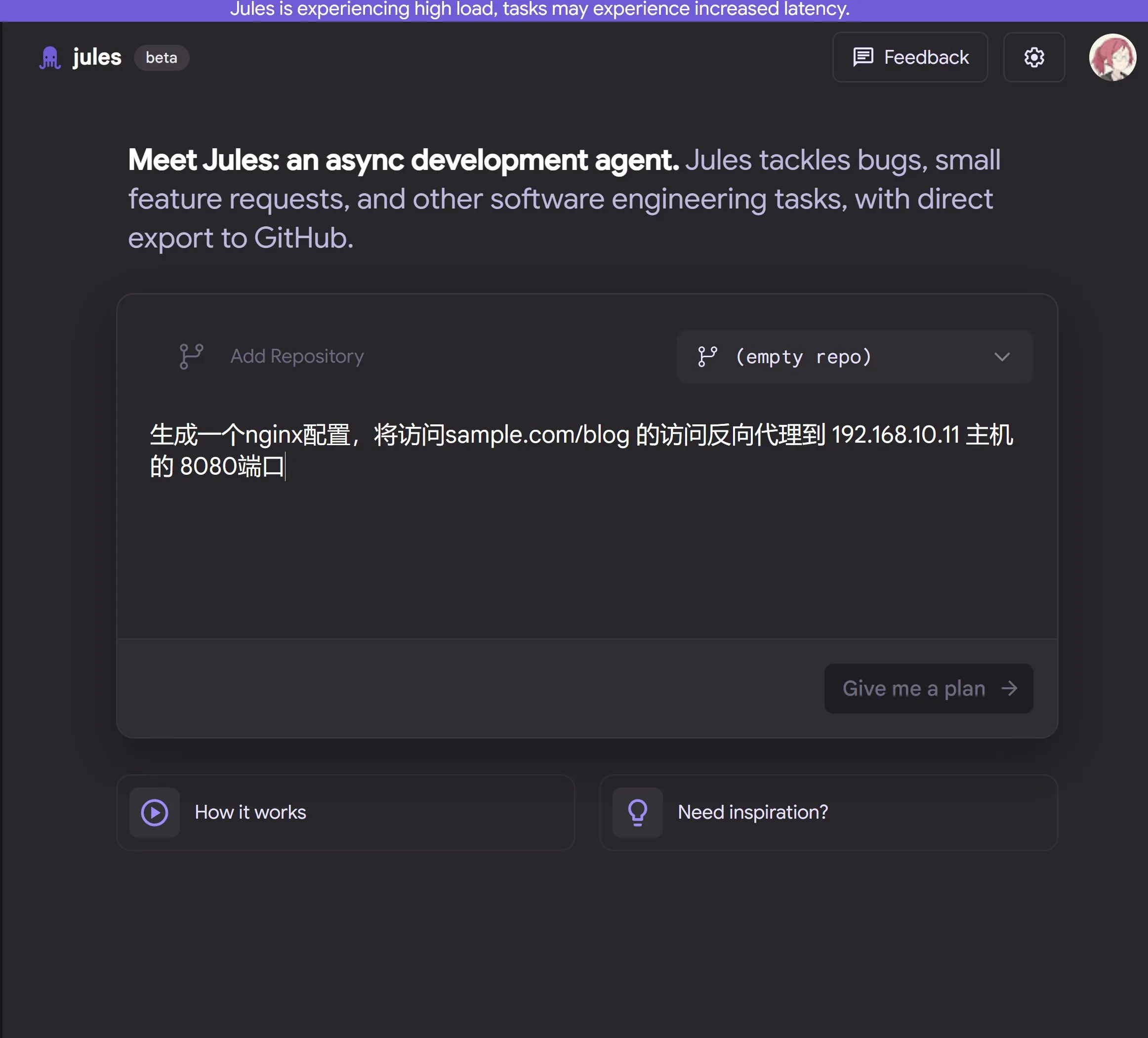
Google releases cloud-based AI programming agent Jules, powered by Gemini 2.5 Pro: Google has launched Jules, an AI programming agent based on Gemini 2.5 Pro. Jules can automatically handle tasks in code repositories in the background, such as fixing bugs and refactoring code, supporting parallel multitasking. Additionally, Jules offers daily updated Codecasts podcasts to help users stay informed about the latest developments in their code repositories. The tool is currently available for a free trial. (Source: dotey, karminski3, GoogleDeepMind)
LangChain launches Open Agent Platform (OAP), an open-source no-code agent platform: LangChain has released the Open Agent Platform (OAP), an open-source, no-code platform for general users to build, prototype, and deploy AI agents. OAP supports building agents via a web UI, connecting to RAG servers for improved information retrieval, extending external tools via MCP, and orchestrating multi-agent workflows using Agent Supervisor. It aims to enable non-professional developers to leverage the power of LangGraph agents. (Source: LangChainAI, Hacubu)

Google Labs launches AI UI design tool Stitch: Google Labs has released Stitch, an AI UI design tool that integrates Google’s latest DeepMind models (including Gemini and Imagen) to quickly generate high-quality UI designs. Users can update interface themes using natural language, automatically adjust images, achieve multilingual content translation, and export front-end code with a single click. Stitch is an evolution of the former Galileo AI, whose founders have joined the Google team. (Source: dotey)
LangChain launches local code sandbox LangChain Sandbox: LangChain has released LangChain Sandbox, which allows AI agents to safely run untrusted Python code locally. It provides an isolated execution environment and configurable permissions, without requiring remote execution or Docker containers, and supports state persistence across multiple executions via sessions. This offers a safer and more convenient tool for building AI agents capable of executing code (e.g., codeact agents). (Source: hwchase17, Hacubu)
Vitalops open-sources Datatune: An LLM tool for processing large-scale datasets with natural language: Vitalops has open-sourced Datatune, a tool that allows users to process datasets of any size using natural language instructions. Datatune supports Map and Filter operations, can connect to various LLM service providers like OpenAI, Azure, Ollama, or custom models, and utilizes Dask DataFrame for partitioning and parallel processing. The tool aims to simplify tasks such as data cleaning and enrichment, replacing complex regular expressions or custom code. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
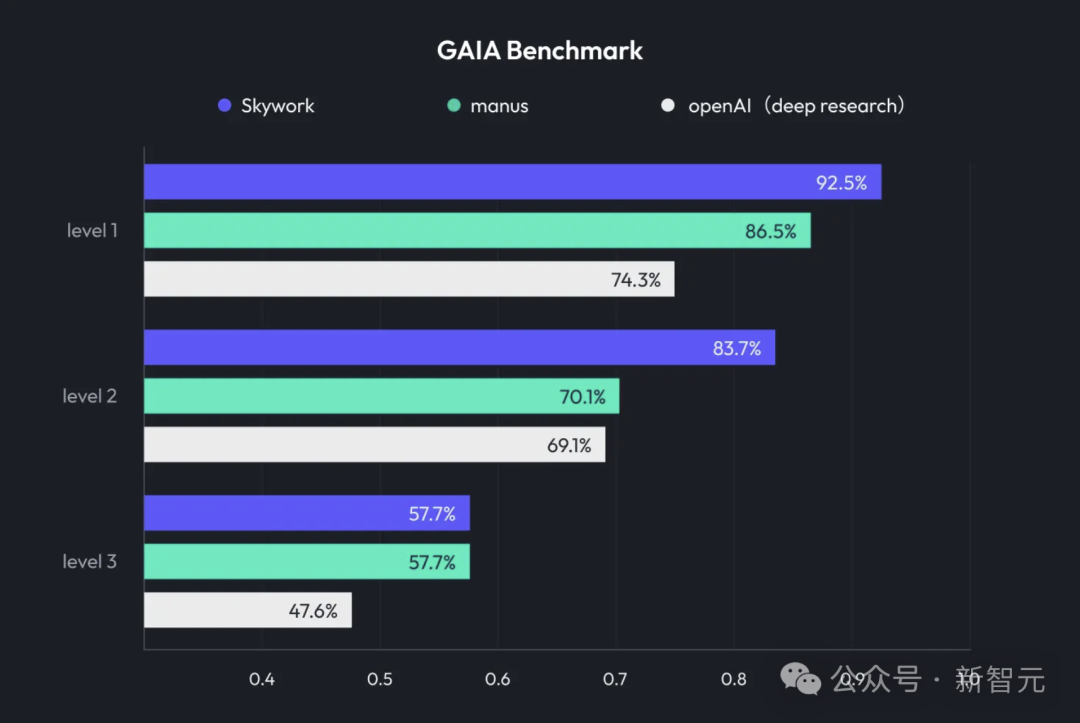
Kunlun Tech launches Skywork Super Agents, integrating Deep Research and multimodal output: Kunlun Tech has released Skywork Super Agents, an AI office product that combines Deep Research capabilities with the multimodal output functions of general intelligent agents. The product supports various office scenarios such as PPT creation, document writing, spreadsheet processing, webpage generation, and podcast creation. It emphasizes content traceability to reduce hallucinations and provides online editing and export functions. Kunlun Tech has also open-sourced the Deep Research Agent framework and related MCPs. (Source: 36氪)
Google launches SynthID Detector to help identify AI-generated content: Google has released SynthID Detector, a new portal designed to help journalists, media professionals, and researchers more easily identify whether content carries a SynthID watermark. SynthID is a technology developed by Google to add an invisible watermark to AI-generated content (including images, audio, video, or text). The launch of this detection tool aims to improve the transparency and traceability of AI-generated content. (Source: dotey, Google)
Lark (Feishu) launches “Knowledge Q&A” feature, creating an enterprise-specific AI Q&A tool: Lark (Feishu) has launched a new “Knowledge Q&A” feature. This tool can provide employees with precise answers and content creation support based on all information accessible to them on Lark (messages, documents, knowledge bases, etc.), combined with large models like DeepSeek-R1, Doubao, and RAG technology. A key characteristic is that answers are dynamically adjusted based on the questioner’s identity and permissions within the company. It aims to seamlessly integrate AI into daily workflows, enhancing enterprise knowledge management and utilization efficiency. (Source: 量子位)

Animon: Japan’s first AI anime generation platform, focusing on anime aesthetics and unlimited free generation: Japanese company CreateAI (formerly Tusimple Future) has launched Animon, an AI anime generation platform tailored for anime creation. The platform blends Japanese anime aesthetics with AI technology, emphasizing consistent visual style and efficient production, claiming that individual users can generate videos for free without limits. Animon supports rapid generation of animation clips (approximately 3 minutes) by uploading character images and text descriptions, aiming to lower the barrier to anime creation and stimulate a UGC content ecosystem. Its parent company, CreateAI, possesses its self-developed large model Ruyi and holds adaptation rights for IPs like “The Three-Body Problem” and “Jin Yong’s Heroes,” pursuing a dual-driver strategy of “self-developed content + UGC tool platform.” (Source: 量子位)

📚 Learning
DeepLearning.AI launches new course: LLM Reinforcement with GRPO: Andrew Ng announced a new short course in collaboration with Predibase on “LLM Reinforcement with GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization).” The course will teach how to use reinforcement learning (specifically the GRPO algorithm) to enhance LLM performance on multi-step reasoning tasks (such as math problem solving, code debugging) without requiring extensive supervised fine-tuning samples. GRPO guides the model through programmable reward functions, is suitable for tasks with verifiable outcomes, and can significantly boost the reasoning capabilities of smaller LLMs. (Source: AndrewYNg, DeepLearningAI)
LlamaIndex shares experience managing large-scale Python monorepos: The LlamaIndex team shared their experience managing a Python monorepo containing over 650 community packages. They migrated from Poetry and Pants to uv and their self-developed open-source build management tool, LlamaDev. This resulted in a 20% increase in test run speed, clearer logs, simplified local development, and a lower barrier to entry for contributors. This experience is valuable for teams needing to manage large Python projects. (Source: jerryjliu0)

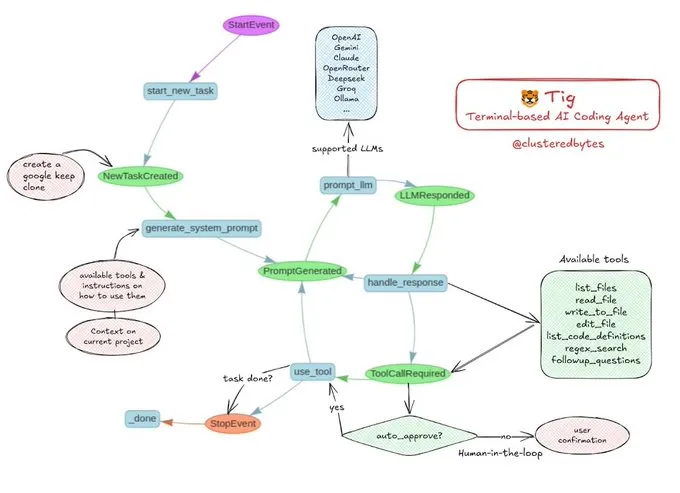
Tutorial shared: Build your own AI coding agent Tig: Jerry Liu recommended an open-source AI coding agent project called Tig. The project is a terminal-based coding assistant with a human-in-the-loop, built using LlamaIndex workflows. Tig can perform tasks such as writing, debugging, and analyzing code in multiple languages, executing shell commands, searching codebases, and generating tests and documentation. The GitHub repository provides detailed build instructions, making it a great educational resource for developers looking to learn how to build AI coding agents. (Source: jerryjliu0)
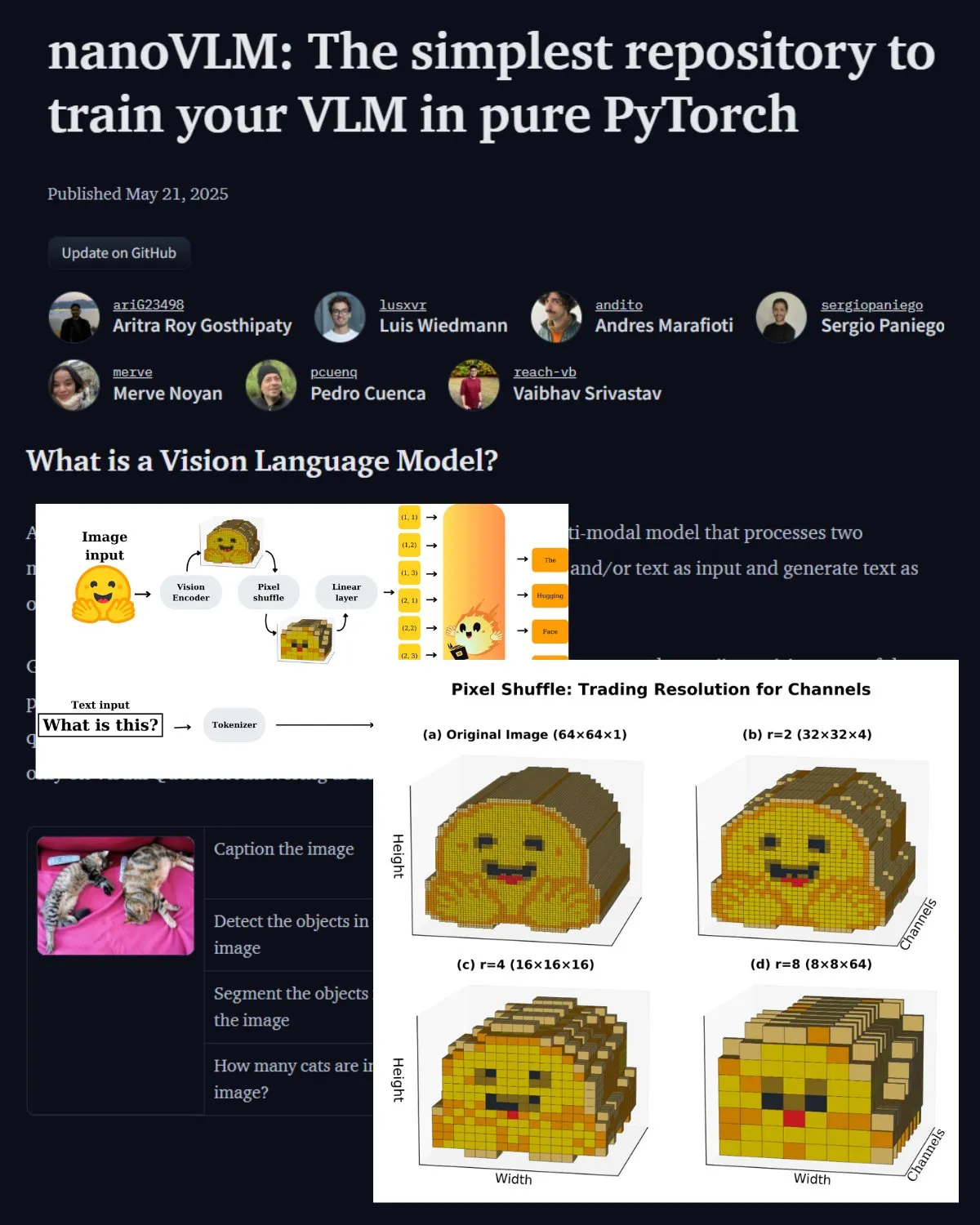
Hugging Face publishes important blog post on VLMs, introduces nanoVLM community lab: Hugging Face has published a blog post on Vision Language Models (VLMs), covering VLM basics, architecture, and how to train your own lightweight VLM. It also introduces nanoVLM, an open-source repository for fine-tuning VLMs, which has now evolved into a community lab for vision-language research, aiming to help developers explore and contribute to VLM research. (Source: _akhaliq, huggingface)
Serrano Academy releases video tutorial series on LLM Reinforcement Learning Fine-tuning: Serrano Academy has completed and released a series of video tutorials on fine-tuning and training LLMs using reinforcement learning. The content covers key concepts and techniques such as Deep Reinforcement Learning, RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback), PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization), DPO (Direct Preference Optimization), GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization), and KL Divergence. (Source: SerranoAcademy)
Paper explores the “Void Layers” phenomenon in Large Language Models: A study investigated the phenomenon where not all layers are activated during the inference process of instruction-tuned large language models, referring to unactivated layers as “Voids.” The research used the L2 Adaptive Computation (LAC) method to track activated layers during prompt processing and response generation phases, finding that different layers are activated at different stages. Experiments showed that skipping void layers in Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct (using only 30% of layers) improved performance on benchmarks like MMLU, suggesting that selectively skipping most layers might be beneficial for specific tasks. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Research proposes “Soft Thinking”: Unlocking LLM reasoning potential in continuous conceptual spaces: A paper titled “Soft Thinking” proposes a training-free method to simulate human-like “soft” reasoning by generating soft, abstract conceptual tokens in a continuous conceptual space. These conceptual tokens, formed by a probabilistic weighted mixture of token embeddings, can encapsulate multiple meanings from related discrete tokens, thereby implicitly exploring multiple reasoning paths. Experiments show that this method improves pass@1 accuracy on math and coding benchmarks while reducing token usage, with the output remaining interpretable. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper explores scalable Chain-of-Thought through Elastic Reasoning: Researchers at Salesforce have proposed a method for achieving scalable Chain-of-Thought through Elastic Reasoning. This research aims to address how large language models can effectively generate and manage long chains of thought when processing complex reasoning tasks, in order to improve the accuracy and efficiency of reasoning. Related models and code have been released on Hugging Face. (Source: _akhaliq)

Paper research: Would an AI model lie to save a sick child?: A study named LitmusValues created an evaluation process designed to reveal AI models’ priorities across a range of AI value categories. By collecting AIRiskDilemmas (a collection of dilemmas involving scenarios related to AI safety risks), researchers measure AI models’ choices in different value conflicts, thereby predicting their value priorities and identifying potential risks. The study shows that values defined in LitmusValues (including care, etc.) can predict observed risk behaviors in AIRiskDilemmas as well as unseen risk behaviors in HarmBench. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
Paper studies efficient fine-tuning of diffusion models via value-based reinforcement learning (VARD): Diffusion models exhibit strong performance in generation tasks, but fine-tuning them for specific attributes remains challenging. Existing reinforcement learning methods suffer from instability, inefficiency, and difficulties in handling non-differentiable rewards. VARD (Value-based Reinforced Diffusion) proposes first learning a value function that predicts the expected reward from intermediate states, and then utilizing this value function along with KL regularization to provide dense supervision throughout the generation process. Experiments demonstrate that this method improves trajectory guidance, enhances training efficiency, and extends RL applications to optimizing diffusion models with complex non-differentiable reward functions. (Source: HuggingFace Daily Papers)
💼 Business
LMArena.ai (formerly LMSYS.org) secures $100 million in seed funding, led by a16z and UC Investments: AI model evaluation platform LMArena.ai (formerly LMSYS.org) announced the completion of a $100 million seed funding round, co-led by Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) and UC Investments. The company is dedicated to building a neutral, open, community-driven platform to help the world understand and improve the performance of AI models on real user queries. The company is valued at $600 million post-funding. (Source: janonacct, lmarena_ai, scaling01, _akhaliq, ClementDelangue)
US government announces sale of AI technology and services worth tens of billions of dollars to Saudi Arabia and UAE: The US government announced agreements with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates to sell AI technology and services worth tens of billions of dollars to both countries. Participating companies include AMD, Nvidia, Amazon, Google, IBM, Oracle, and Qualcomm. Nvidia will supply 18,000 GB300 AI chips and hundreds of thousands of subsequent GPUs to the Saudi company Humain; AMD and Humain will jointly invest $10 billion to build AI data centers. This move aims to strengthen US AI influence in the Middle East and help diversify the economies of both nations. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)

Meta launches Llama Startup Program to empower early-stage AI startups: Meta announced the launch of the Llama Startup Program, aimed at supporting early-stage startups in the US (with less than $10 million in funding and at least one developer) in innovating generative AI applications using Llama models. The program offers cloud resource reimbursement, technical support from Llama experts, and community resources. The application deadline is May 30, 2025, at 6 PM (Pacific Time). (Source: AIatMeta)
🌟 Community
Google I/O Conference sparks heated discussion: Comprehensive AI integration and future outlook: Google’s I/O conference unveiled a plethora of AI-related products and updates, including the Gemini series models, Veo 3 video generation, Imagen 4 image generation, AI search mode, etc., sparking widespread community discussion. Many commentators believe Google has demonstrated formidable strength in AI applications, particularly its strategy of seamlessly integrating AI into its existing product ecosystem. Simultaneously, topics such as the authenticity of AI-generated content, AI ethics, and the future path of AGI have also become focal points of discussion. (Source: rowancheung, dotey, karminski3, GoogleDeepMind, natolambert)

AI hardware becomes new focus, OpenAI’s collaboration with Jony Ive draws attention: The news of OpenAI acquiring Jony Ive’s AI hardware company io, along with Google’s demonstration of Android XR smart glasses prototypes at the I/O conference, has ignited community discussions about the future of AI hardware. Sam Altman’s collaboration with Jony Ive is seen as an effort to create a new generation of AI-driven personal computing devices that could disrupt existing phone and computer interaction methods. The community generally anticipates that AI-native hardware will bring revolutionary experiences but is also concerned about its form, functionality, and market acceptance. (Source: dotey, sama, dotey, swyx)

Role and risks of AI in software development spark discussion: Mistral AI’s release of the Devstral model, designed for coding agents, and OpenAI’s update to Codex have triggered discussions about AI’s application in software development. The community is focused on the practical capabilities of AI programming tools, as well as the quality and security of the code they generate. In particular, research indicating that AI-generated code might reference non-existent “hallucination packages,” posing supply chain security risks, serves as a reminder for developers to meticulously verify AI-generated code and dependencies. (Source: MistralAI, DeepLearning.AI Blog, qtnx_)

Discussion on AI model evaluation and benchmarking continues to heat up: LMArena.ai securing significant funding and the performance of various new models on benchmarks have made AI model evaluation a hot topic in the community. Users are concerned about the true capabilities of different models on specific tasks (such as coding, mathematics, common sense Q&A, emotional understanding) and the reliability and limitations of existing evaluation systems. For example, Tencent’s newly released SAGE emotional intelligence evaluation framework attempts to provide a new evaluation dimension for AI models from an “EQ” perspective. (Source: lmarena_ai, 36氪, natolambert)
Europe’s lagging tech industry development prompts reflection, Yann LeCun retweets discussion attributing it to lack of “patriotism”: A Wall Street Journal article about Europe’s tech scene being much smaller than that of the US and China sparked discussion, with Yann LeCun retweeting Arnaud Bertrand’s comments. Bertrand argued that the core reason for Europe’s tech lag is a lack of “patriotism,” with European media and elites tending to idolize American startups while neglecting domestic innovation. This, he claims, makes it difficult for local companies to gain early support and market recognition. Citing his own experience founding HouseTrip, he pointed out Europe’s lack of confidence in and support for homegrown innovation. (Source: ylecun)

💡 Others
AI’s energy consumption issue raises concerns: MIT Technology Review organized a roundtable discussion to explore the energy consumption problems brought by the accelerated development of AI technology and its impact on the climate. As the scale and application scope of AI models expand, the required electricity and computing resources are increasing dramatically, making data center energy demand a new focal point. The discussion focused on the energy consumption of a single AI query, AI’s overall energy footprint, and how to address this challenge. (Source: MIT Technology Review, madiator)

Anthropic teases new announcement, community speculates Claude 4 might be released: Anthropic has released a teaser for a live stream scheduled for May 22nd at 9:30 AM Pacific Time (May 23rd, 00:00 Beijing Time), sparking community speculation about the potential release of a new generation Claude model (possibly Claude 4). Given the recent major updates from OpenAI and Google, Anthropic’s move is highly anticipated. (Source: AnthropicAI, dotey, karminski3, scaling01, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
AI and XR technology converge, Google showcases Android XR smart glasses prototype: At the I/O conference, Google showcased a prototype of Android XR smart glasses, emphasizing their deep integration with AI. The device supports first-person perspective intelligent assistance and contactless assistance features, allowing users to interact with the device via natural language to perform tasks such as information queries, schedule management, and real-time navigation. This signals that AI will become the core interaction and functional driver for the next generation of XR devices, enhancing user experience in augmented reality environments. (Source: dotey, 36氪)