Keywords:AI programming agent, Codex, AlphaEvolve, AI reasoning paradigm, MoE model, AI chip, AI education, AI short drama, OpenAI Codex-1 model, Google DeepMind AlphaEvolve, ByteDance Seed1.5-VL, Qwen ParScale technology, NVIDIA GB300 system
🔥 Focus
OpenAI releases cloud-based AI programming agent Codex, powered by new model codex-1: OpenAI has launched Codex, a cloud-based AI programming agent based on codex-1, an o3 specially-tuned version optimized for software engineering. Codex can safely handle multiple tasks in parallel in a cloud sandbox environment, integrates with GitHub to directly call code repositories, enabling rapid module construction, answering questions about codebases, fixing bugs, submitting PRs, and automated testing and verification. Tasks that previously took days or hours can be completed by Codex within 30 minutes. The tool is now available to ChatGPT Pro, Enterprise, and Team users, aiming to become a “10x engineer” for developers and reshape the software development process. (Source: 36Kr)
Google DeepMind introduces AlphaEvolve, AI achieves mathematical and algorithmic breakthroughs through autonomous evolution: Google DeepMind’s AI system AlphaEvolve has achieved breakthroughs in multiple mathematical and scientific fields through self-evolution and training large language models. It improved the 4×4 matrix multiplication algorithm (first time in 56 years), optimized the hexagonal packing problem (first time in 16 years), and advanced the “kissing number problem.” AlphaEvolve can autonomously optimize algorithms, even finding ways to accelerate Gemini model training, and has been applied to optimize Google’s internal computing infrastructure, saving 0.7% of computing resources. This marks AI’s ability not only to solve problems but also to discover new knowledge, potentially revolutionizing the scientific research paradigm and achieving AI-driven scientific creation. (Source: 36Kr)
Altman’s Sequoia AI Summit Speech: AI to enter the real world within three years, reshaping life and work: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman predicted at the Sequoia AI Summit that AI agents will become practical in 2025 (especially in coding), AI will drive major scientific discoveries in 2026, and robots will enter the physical world to create value in 2027. He reviewed OpenAI’s journey from early exploration to the birth of ChatGPT and proposed that future AI products will be “core AI subscription” services capable of accommodating an individual’s entire life experience, becoming the default intelligent interface. OpenAI will focus on core models and application scenarios, maintaining organizational efficiency with “small teams, big responsibilities.” (Source: 36Kr)
Nvidia Computex Speech: Personal AI computers in production, launching next-gen GB300 system, planning Taiwan AI supercomputer: Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang announced at Computex 2025 that the personal AI computer DGX Spark is in full production and will be available in weeks; the next-generation AI system GB300 (equipped with 72 Blackwell Ultra GPUs and 36 Grace CPUs) will launch in Q3. Nvidia will partner with TSMC and Foxconn to build an AI supercomputing center in Taiwan. Simultaneously, the Blackwell RTX Pro 6000 workstation series and Grace Blackwell Ultra Superchip were released, with plans to open-source the Newton physics engine in July for robotics training. Huang emphasized that AI will be ubiquitous, reiterating its revolutionary impact. (Source: 36Kr)

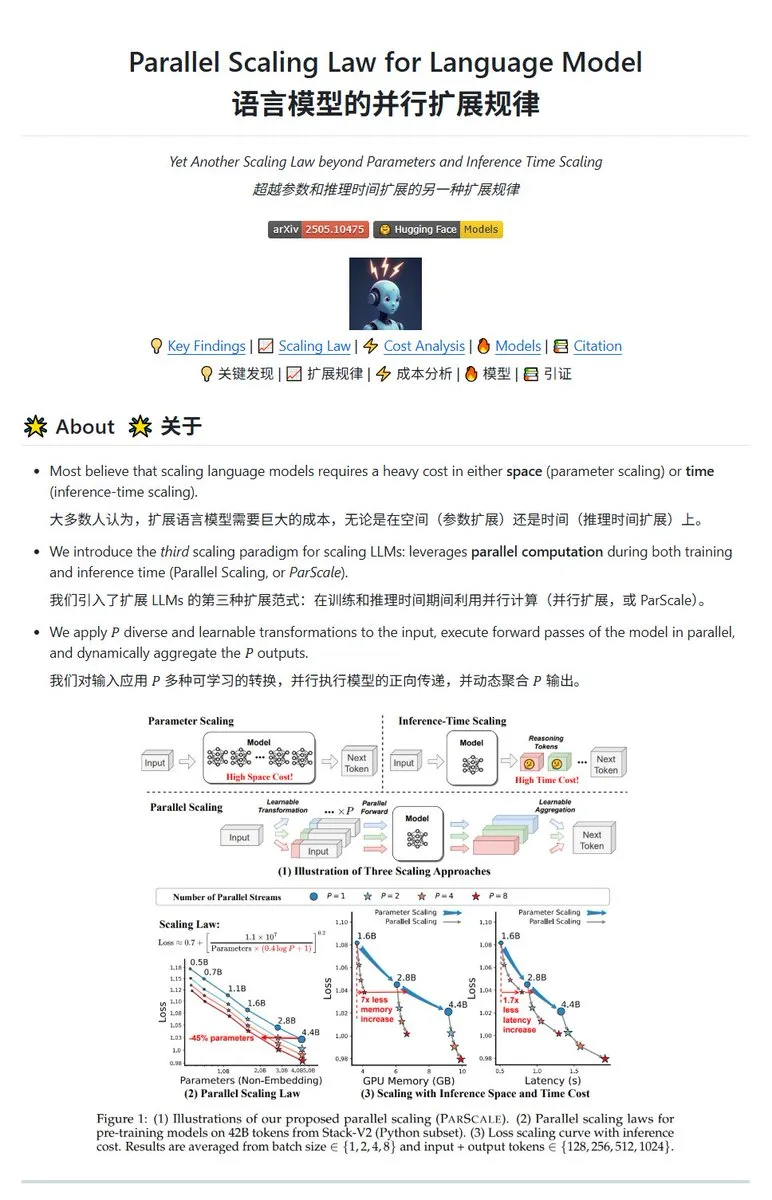
Qwen releases ParScale parallel scaling technology, enabling small models to achieve large model effects: The Qwen team has introduced ParScale technology, which enhances model capabilities through parallel inference. This method uses n parallel streams for inference, each processing the input with a learnable differential transformation, and finally merges the results through a dynamic aggregation mechanism. Research shows that P parallel streams approximate the effect of increasing model parameter count by O(log P); for example, a 30B model with 8 parallel streams can achieve the effect of a 42.5B model. This technology promises to improve model performance without significantly increasing VRAM usage, or to reduce the size of existing models by increasing parallelism, though potentially at the cost of increased computational demand and reduced inference speed. (Source: karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
🎯 Trends
Poe Report: OpenAI and Google lead AI race, Anthropic shows decline: Poe’s latest usage report (January-May 2025) reveals dramatic shifts in the AI market landscape. In text generation, GPT-4o leads (35.8%), while Gemini 2.5 Pro tops reasoning capabilities (31.5%). Image generation is dominated by Imagen3, GPT-Image-1, and the Flux series. In video generation, Kling-2.0-Master has emerged突起, while Runway’s share has significantly dropped. For agents, o3 performs best. The report notes that reasoning ability has become a key battleground, Anthropic’s Claude market share has declined, and DeepSeek R1 user share has also fallen from its peak. Enterprises need to focus on model accuracy and reliability in complex tasks and flexibly choose AI models. (Source: 36Kr)

Meta’s flagship AI model Behemoth (Llama 4) release delayed, potentially triggering AI strategy adjustments: According to reports, Meta’s 2 trillion-parameter large model Behemoth (Llama 4), originally planned for an April release, has been postponed to autumn or later due to performance not meeting expectations. The model, pre-trained on 30T multimodal tokens using 32K GPUs, aims to compete with OpenAI, Google, and others. Development difficulties have led to internal disappointment with the Llama 4 team’s performance and may result in adjustments to AI product teams. Meanwhile, 11 of the 14 members of the original Llama 1 team have departed. Meta executives denied rumors of “80% team resignation,” emphasizing that departures were mainly from the Llama 1 paper team. This incident has heightened external concerns about whether Meta is facing a bottleneck in the AI race. (Source: 36Kr)

ByteDance and Google DeepMind release new MoE model research, focusing on efficiency and production system applications: ByteDance’s paper “MegaScale-MoE: Large-Scale Communication-Efficient Training of Mixture-of-Experts Models in Production” introduces a production system designed for efficiently training large-scale MoE models. By overlapping communication and computation at the operator level, it achieves 1.88x efficiency improvement over Megatron-LM and has been deployed in its data centers to train product models (e.g., Internal-352B, 32 experts, top-3). Google DeepMind released AlphaEvolve, which achieved breakthroughs in mathematics and algorithms through AI self-evolution and training LLMs, such as improving 4×4 matrix multiplication and hexagonal packing problems, showcasing AI’s potential in scientific discovery. (Source: teortaxesTex, 36Kr)

OpenAI discusses AI inference paradigm, emphasizing its key role in performance improvement: OpenAI researcher Noam Brown pointed out that AI development has shifted from a pre-training paradigm (predicting the next word through massive data) to an inference paradigm. Pre-training is costly, while the inference paradigm improves answer quality by increasing the model’s “thinking” time (inference computation), even if training costs remain unchanged. For example, o-series models achieved significantly higher accuracy than GPT-4o on math competitions (AIME) and doctoral-level science problems (GPQA) through longer inference times. OpenAI Chief Economist Ronnie Chatterji discussed AI’s reshaping of the business landscape, believing the key lies in how enterprises integrate AI to augment or replace human roles, and how AI technology is embedded in the value chain. (Source: 36Kr)

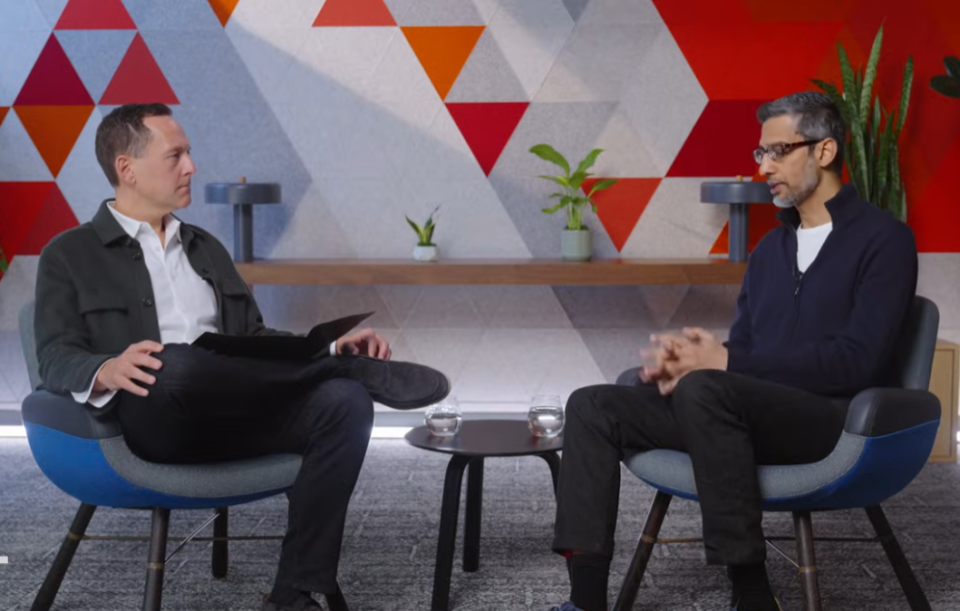
Google CEO Pichai responds to “Google is dead” theory, emphasizing AI-driven search evolution and infrastructure advantages: In an interview, Google CEO Sundar Pichai addressed concerns about “Google Search being replaced by AI,” stating that Google is transforming search from responsive queries to a predictive, personalized intelligent assistant through features like “AI Overview” and “AI Mode.” He emphasized Google’s long-term investment in AI infrastructure (self-developed TPUs, large-scale data centers) and model efficiency as core advantages, enabling the provision of advanced models cost-effectively. Pichai believes AI is an “all-scenario technology platform” that will reshape core businesses like Search, YouTube, and Cloud, and foster new forms. He also noted that the competitiveness of Chinese AI (like DeepSeek) should not be underestimated and pointed out that electricity will be a key bottleneck for AI development. (Source: 36Kr)

Overview of AI startups in the education sector: The article lists 13 AI education startups worth watching in 2025, which are changing teaching through personalized learning paths, intelligent tutoring systems, automated grading, and immersive content creation. For example, Merlyn is a voice-controlled AI assistant that reduces teachers’ administrative burden; Brisk Teaching is a Chrome extension that simplifies teaching tasks; Edexia is an AI grading platform that learns teachers’ styles; Storytailor combines bibliotherapy with AI to create personalized stories; Brainly provides AI-enhanced homework assistance. These companies demonstrate the broad application potential of AI in education, from improving efficiency to achieving personalized learning and educational equity. (Source: 36Kr)
AI short dramas face technical and commercialization challenges, production effects fall short of expectations: Although AI tools are expected to reduce the production costs and shorten the cycle of short dramas, practitioners have found significant technical difficulties in AI short dramas regarding subject consistency, lip-syncing, and naturalness of camera language, leading many works to resemble “PPT-style short dramas.” AI struggles to understand surreal creativity, limiting the potential for fantasy and sci-fi genres. Currently, AI technology is more suitable for producing short films rather than complete short dramas, and commercialization prospects are unclear. Large film and television companies like Bona Film Group and Huace Group are more likely to break through due to resource advantages, while most small creators face high trial-and-error costs and rapid technological iteration, causing their works to quickly become outdated. (Source: 36Kr)
MSI unveils AI PC integrating NVIDIA GB10 superchip, featuring 6144 CUDA cores and 128GB LPDDR5X memory: MSI showcased its EdgeExpert MS-C931 S, an AI PC powered by the NVIDIA GB10 superchip. The chip is confirmed to have 6144 CUDA cores and 128GB LPDDR5X memory. This makes MSI another vendor, following ASUS, Dell, and Lenovo, to launch a personal AI computer based on NVIDIA’s DGX Spark architecture. The introduction of such products signifies the gradual popularization of high-performance AI computing capabilities to personal and edge devices, though some commentators note its pricing might make it difficult to compete with products like the Mac Mini. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Qwen3-30B achieves high throughput on VLLM, suitable for dataset management: The Qwen3-30B-A3B model demonstrates excellent inference speed (5K t/s prefill, 1K t/s generation) on the VLLM framework and RTX 3090s GPUs, making it highly suitable for tasks such as dataset filtering and management. Although there might be a slight regression compared to QwQ, its speed advantage makes it more practical for data processing. The main current issue is extremely slow training speed, but a PR in the Hugging Face Transformers library is attempting to address this, and there’s potential for future RpR models based on Qwen3-30B with improved datasets. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Bilibili open-sources animation video generation model Index-AniSora, supporting various anime styles: Bilibili has launched Index-AniSora, an open-source model specifically for generating anime-style videos, based on its AniSora technology framework (accepted by IJCAI25). The model can generate animation from comics with one click, supporting various styles such as Japanese anime series, Chinese animation, comic adaptations, and VTubers. The AniSora system achieves fine control over character lip-syncing and movements by constructing a dataset of tens of millions of high-quality text-video pairs, developing a unified diffusion generation framework, and introducing a spatio-temporal masking mechanism. Additionally, Bilibili has designed an evaluation benchmark for animated videos and an automated evaluation system optimized with VLM. The open-source content will include AniSoraV1.0 (based on CogVideoX-5B), AniSoraV2.0 (based on Wan2.1-14B, supporting Huawei 910B training), and related dataset construction and evaluation tools. (Source: WeChat)

ByteDance releases visual language model Seed1.5-VL, excelling in multimodal tasks: ByteDance has introduced Seed1.5-VL, a visual language model composed of a 532M parameter visual encoder and a 20B active parameter Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM. The model achieves SOTA performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks and surpasses leading systems like OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7 on agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, demonstrating strong multimodal understanding and reasoning capabilities. (Source: WeChat)
Nous Research launches Psyche Network, achieving distributed pre-training of 40B parameter LLM: Nous Research has released Psyche Network, a decentralized training network based on the DeepSeek V3 MLA architecture, which pre-trained a 40 billion parameter large language model in its first test. The network utilizes the DisTrO optimizer and a custom peer-to-peer network stack to integrate globally distributed GPU computing power, allowing individuals and small groups to train on a single H/DGX and run on 3090 GPUs. This initiative aims to break the computing power monopoly of tech giants, making large-scale model training more accessible. (Source: QbitAI)

🧰 Tools
Sim Studio: Open-source AI agent workflow builder: Sim Studio is an open-source, lightweight AI agent workflow building platform that provides an intuitive interface for users to quickly build and deploy LLM applications connected to various tools. It supports a cloud-hosted version and self-hosting (Docker environment recommended, supports local models like Ollama). Its tech stack includes Next.js, Bun, PostgreSQL, Drizzle ORM, Better Auth, Shadcn UI, Tailwind CSS, Zustand, ReactFlow, and Turborepo. (Source: GitHub Trending)

Cherry Studio: Feature-rich open-source LLM front-end desktop application gains attention: Cherry Studio is an open-source LLM front-end desktop application that integrates RAG, web search, local model access (via Ollama, LM Studio), and cloud model access (e.g., Gemini, ChatGPT), among other features. Users report its MCP (Multi-Control Protocol) support and management are superior to Open WebUI and LibreChat, and it is easy to install and set up. The application also supports direct connection to Obsidian knowledge bases. Although some users have expressed concerns about its origin, its comprehensive feature set makes it an attractive option. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

MLX-LM-LoRA: Adds LoRA to MLX models and supports various training methods: The open-source project mlx-lm-lora allows users to integrate LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) modules into models under Apple’s MLX framework. The project not only supports the addition of LoRA but also includes various alignment training methods such as ORPO, DPO, CPO, and GRPO, enabling users to fine-tune models according to their needs, generate customized LoRA modules, and apply them to their preferred MLX models. (Source: karminski3)
DeepDrone: Open-source AI-controlled drone project based on Qwen: A developer has created an AI-controlled drone project named DeepDrone based on the Qwen large model and open-sourced it on HuggingFace and GitHub. The project demonstrates the potential of applying large language models to autonomous drone control, sparking discussions about AI in automation and potential military applications. (Source: karminski3)
Qwen Web Dev: Generate and deploy websites with a single prompt: Alibaba’s Qwen team announced enhancements to its Qwen Web Dev tool, allowing users to generate a website with just one prompt and deploy it with a single click. The tool aims to lower the barrier to web development, enabling users to more easily transform their ideas into actual accessible websites and share them with the world. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen, huybery)
SuperGo.AI: Single interface tool integrating eight LLM models: An AI enthusiast has developed a tool called SuperGo.AI, which integrates eight LLMs with different roles (e.g., AI Super Brain, AI Imagination, AI Ethics, AI Universe) into a single interface. These AI roles can perceive and interact with each other, and users can choose “Creative,” “Scientific,” and “Mixed” modes to get blended responses. The tool aims to provide a novel multi-AI collaboration experience and currently has no paywall. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Kokoro-JS: Achieves unlimited local text-to-speech (TTS): Kokoro-JS is a 100% locally run, 100% open-source text-to-speech tool that works by downloading an approximately 300MB AI model in the browser. User-inputted text is not sent to any server, ensuring privacy and offline availability. The tool aims to provide unlimited TTS functionality. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
📚 Learning
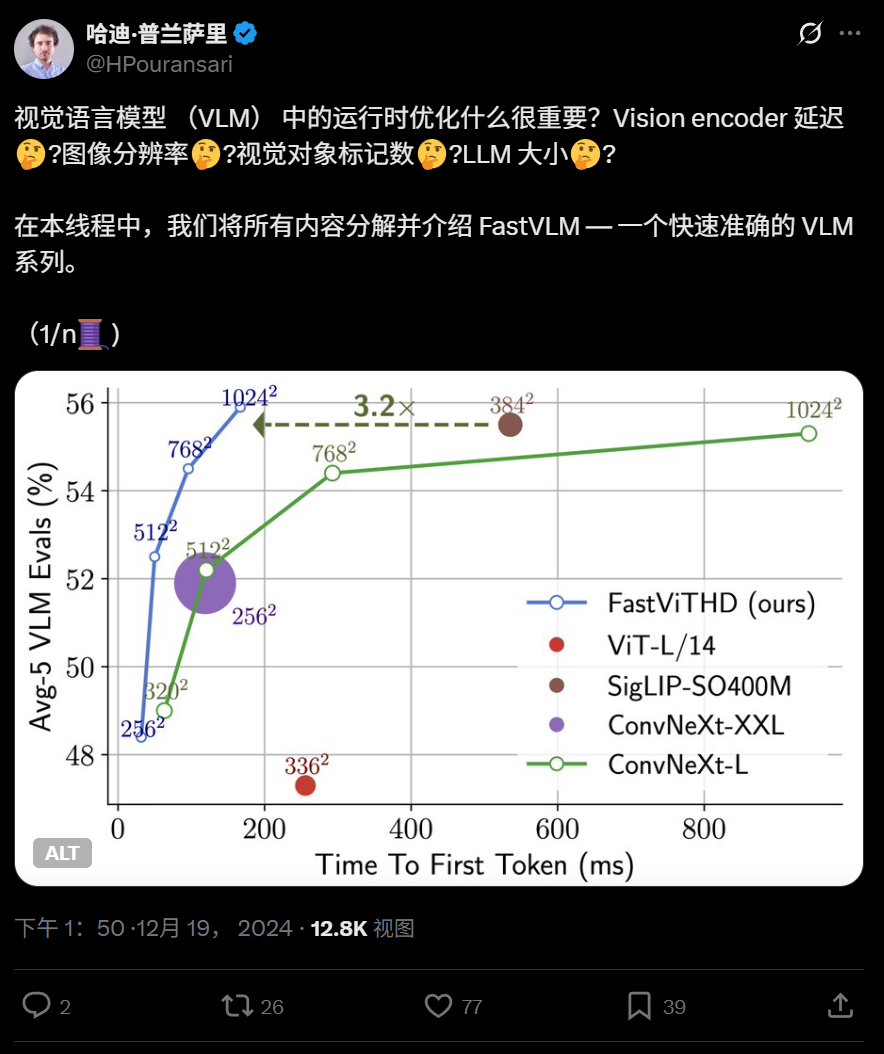
Apple open-sources efficient visual language model FastVLM, optimized for on-device operation: Apple has open-sourced FastVLM, a visual language model designed for efficient operation on devices like iPhones. FastVLM introduces a novel hybrid visual encoder, FastViTHD, which combines convolutional layers with Transformer modules and employs multi-scale pooling and down-sampling techniques. This significantly reduces the number of visual tokens required to process images (16 times fewer than traditional ViT) and improves the speed of first token output by 85 times. The model is compatible with mainstream LLMs and a demo application based on the MLX framework for iOS/macOS has been provided, suitable for edge devices and real-time image-text tasks. (Source: WeChat)
Harbin Institute of Technology and University of Pennsylvania propose PointKAN, improving 3D point cloud analysis based on KAN: A research team from Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen) and the University of Pennsylvania has introduced PointKAN, a new 3D perception architecture based on Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs). PointKAN replaces fixed activation functions in traditional MLPs with learnable activation functions, enhancing the ability to learn complex geometric features. It includes a geometric affine module and a parallel local feature extraction module. The team also proposed PointKAN-elite, which uses an Efficient-KANs structure employing rational functions as basis functions and group-wise parameter sharing, significantly reducing parameter count and computational complexity while achieving SOTA performance in classification, part segmentation, and few-shot learning tasks. (Source: QbitAI)

University of Pittsburgh proposes PhyT2V framework to enhance physical realism of AI-generated videos: The Intelligent Systems Laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh has developed the PhyT2V framework, aimed at improving the physical consistency of content generated by text-to-video (T2V) models. This method, without requiring model retraining or large-scale external data, uses Large Language Model (LLM)-guided Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning and an iterative self-correction mechanism to analyze and optimize text prompts through multiple rounds of physical rule assessment. PhyT2V can identify physical rules, semantic mismatches, and generate corrected prompts, thereby enhancing the generalization ability of mainstream T2V models (like CogVideoX, OpenSora) in realistic physical scenarios (solids, fluids, gravity, etc.), especially with significant improvements in out-of-distribution scenarios, boosting Physical Commonsense (PC) and Semantic Adherence (SA) metrics by up to 2.3 times. (Source: WeChat)

LLM Latest Research Digest: Multimodality, Test-Time Alignment, Agents, RAG Optimization, etc.: Weekly LLM research progress includes: 1. University of Washington proposed QALIGN, a test-time alignment method that doesn’t require model modification or access to logits, achieving better alignment in text generation via MCMC. 2. UCLA pre-trained Clinical ModernBERT, extending the context length of biomedical domain encoders to 8192 tokens. 3. Skoltech proposed a lightweight LLM-independent adaptive RAG retrieval method based on external information (entity popularity, question type). 4. PSU defined the problem of automated fault attribution in LLM multi-agent systems and developed evaluation datasets and methods. 5. Fudan University proposed a multi-dimensional constraint framework and automated instruction generation process to improve LLM instruction-following capabilities. 6. a-m-team open-sourced AM-Thinking-v1 (32B), with mathematical coding ability comparable to DeepSeek-R1-671B. 7. Xiaomi launched MiMo-7B, achieving excellent performance on reasoning tasks through optimized pre-training and post-training. 8. MiniMax proposed MiniMax-Speech autoregressive TTS model, supporting zero-shot voice cloning in 32 languages. 9. ByteDance built Seed1.5-VL visual language model, excelling in multimodal tasks and agent-centric tasks. 10. The world’s first 32B parameter language model, INTELLECT-2, achieved distributed reinforcement learning training, proposing the PRIME-RL framework. (Source: WeChat)
AAAI 2025 workshops focus on neural reasoning, mathematical discovery, and AI-accelerated science and engineering: AAAI 2025 workshops highlighted AI applications in science. The “Neural Reasoning and Mathematical Discovery” workshop emphasized that black-box neural networks can propose mathematical conjectures and generate new geometric figures, but noted their inability to achieve symbolic-level logical reasoning, advocating for interdisciplinary approaches. Another workshop, “AI to Accelerate Science and Engineering” (4th edition, themed AI for Biosciences), focused on foundational models for therapeutic design, generative models for drug discovery, closed-loop antibody design in labs, deep learning in genomics, and causal inference in biological applications, also discussing challenges and opportunities for generative models in biosciences. (Source: aihub.org)

Google and Anthropic show divergence in AI interpretability research, mechanistic interpretability faces challenges: The “black box” nature of AI limits its application in many critical areas. Google DeepMind recently announced a de-prioritization of “mechanistic interpretability” research, arguing that reverse-engineering AI’s internal mechanisms using methods like sparse autoencoders (SAEs) faces numerous problems, such as lack of objective reference, incomplete concept coverage, and feature distortion, and that current SAE technology has failed to identify required “concepts” in critical tasks. In contrast, Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei advocates for strengthening research in this area and is optimistic about achieving “MRI for AI” within the next 5-10 years. This debate highlights the deep challenges in understanding and controlling AI behavior. (Source: 36Kr)

Peking University/StepStar/Enflame Technology propose InfiniteHBD: A new generation GPU high-bandwidth domain architecture for cost reduction and efficiency improvement: Addressing limitations in scalability, cost, and fault tolerance of existing High-Bandwidth Domain (HBD) architectures, teams from Peking University, StepStar, and Enflame Technology proposed the InfiniteHBD architecture. Centered around an Optical Circuit Switched Transceiver (OCSTrx), this architecture embeds low-cost Optical Circuit Switching (OCS) capabilities within optoelectronic conversion modules to achieve data center-scale dynamically reconfigurable K-Hop Ring topology and node-level fault isolation. InfiniteHBD’s unit cost is only 31% of NVL-72, GPU waste rate is near zero, and Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU) is up to 3.37 times higher than NVIDIA DGX, offering a superior solution for large-scale LLM training. The paper has been accepted by SIGCOMM 2025. (Source: WeChat)

OceanBase releases PowerRAG, fully embracing AI to build a Data×AI integrated data foundation: At its developer conference, OceanBase released PowerRAG, an AI-oriented application product designed to provide out-of-the-box RAG development capabilities, connecting data, platforms, interfaces, and applications. CTO Yang Chuanhui detailed OceanBase’s AI strategy: building Data×AI capabilities and evolving from an integrated database to an integrated data foundation. OceanBase will enhance vector capabilities, improve converged retrieval, enable dynamic updates for enterprise knowledge storage, deeply integrate model post-training and fine-tuning, and has adapted to mainstream Agent platforms like Dify, FastGPT, and the MCP protocol. Its vector performance leads in VectorDBBench tests, and it significantly reduces memory requirements through the BQ quantization algorithm. (Source: WeChat)

💼 Business
Shanghai State-owned Capital Investment funds invest in AI chip companies Xinyaohui, Suiyuan Technology, and Biren Technology: Shanghai State-owned Capital Investment Co., Ltd. (Shanghai SCI) recently signed investment agreements with three semiconductor companies: Xinyaohui Technology, Suiyuan Technology, and Biren Technology. Previously, its pioneering AI fund of funds had led Biren Technology’s pre-IPO financing round. Shanghai SCI stated it will actively deploy in foundational models, computing power chips, embodied intelligence, and other tracks. Xinyaohui focuses on semiconductor IP, especially Chiplet technology; its founder Zeng Keqiang was formerly Vice President of Synopsys China. Suiyuan Technology and Biren Technology are both GPU chip design companies. This move shows Shanghai SCI’s focused layout in the upstream AI industry chain, particularly in computing power chips. (Source: 36Kr)
Sakana AI and Mitsubishi UFJ Bank form comprehensive partnership to develop bank-specific AI: Japanese AI startup Sakana AI announced a multi-year partnership agreement with Mitsubishi UFJ Bank (MUFG). Sakana AI will develop AI agents specifically tailored for banking operations for MUFG, aiming to drive transformation in the banking business and the practical application of AI. Concurrently, Sakana AI’s co-founder and COO, Ren Ito, will serve as an advisor to MUFG, assisting the bank in implementing its AI strategy. This collaboration marks an important step for Sakana AI in applying advanced AI technology to solve specific challenges in Japan’s financial industry. (Source: SakanaAILabs, SakanaAILabs, SakanaAILabs, SakanaAILabs, SakanaAILabs)

Lingyi Wanwu co-founder Gu Xuemei resigns to start new venture, company shifts focus to B2B: Gu Xuemei, co-founder of Lingyi Wanwu and responsible for model pre-training and C-end products, resigned several months ago and is currently preparing to launch her own startup. Lingyi Wanwu confirmed the matter and thanked her for her contributions. Since 2025, Lingyi Wanwu’s business focus has shifted from AI ToC applications and model APIs to B2B scenarios such as digital humans, model customization, and deployment. Its C-end products, like the domestic office tool “Wanzhi,” ceased operations due to lower-than-expected user numbers, and its overseas role-playing product Mona also had unsatisfactory commercialization. Previously, co-founder Dai Zonghong had also left to start a new venture. (Source: 36Kr)

🌟 Community
AI paper AIGC detection sparks controversy, accuracy questioned, students’ graduation affected: This year, many universities introduced AIGC detection as part of the graduation thesis review process, aiming to prevent students from misusing AI for writing. However, this measure has sparked widespread controversy. Students report that their own writing is often misidentified as AI-generated, while AI-assisted revisions paradoxically increase the suspected AI generation score. Some tests even showed that the “Preface to the Pavilion of Prince Teng” had an AI generation suspicion score as high as 99.2%. AIGC detection tools, themselves AI-driven, analyze text language features against AI writing patterns, but their accuracy is questionable; OpenAI’s early tool had only 26% accuracy. This uncertainty not only troubles students and incurs extra costs (different detection sites yield varying results, and de-duplication services charge fees) but also raises questions about the nature of AI tools: AI imitates human writing, and then AI is used to detect if human writing resembles AI, creating a logical paradox. (Source: 36Kr)
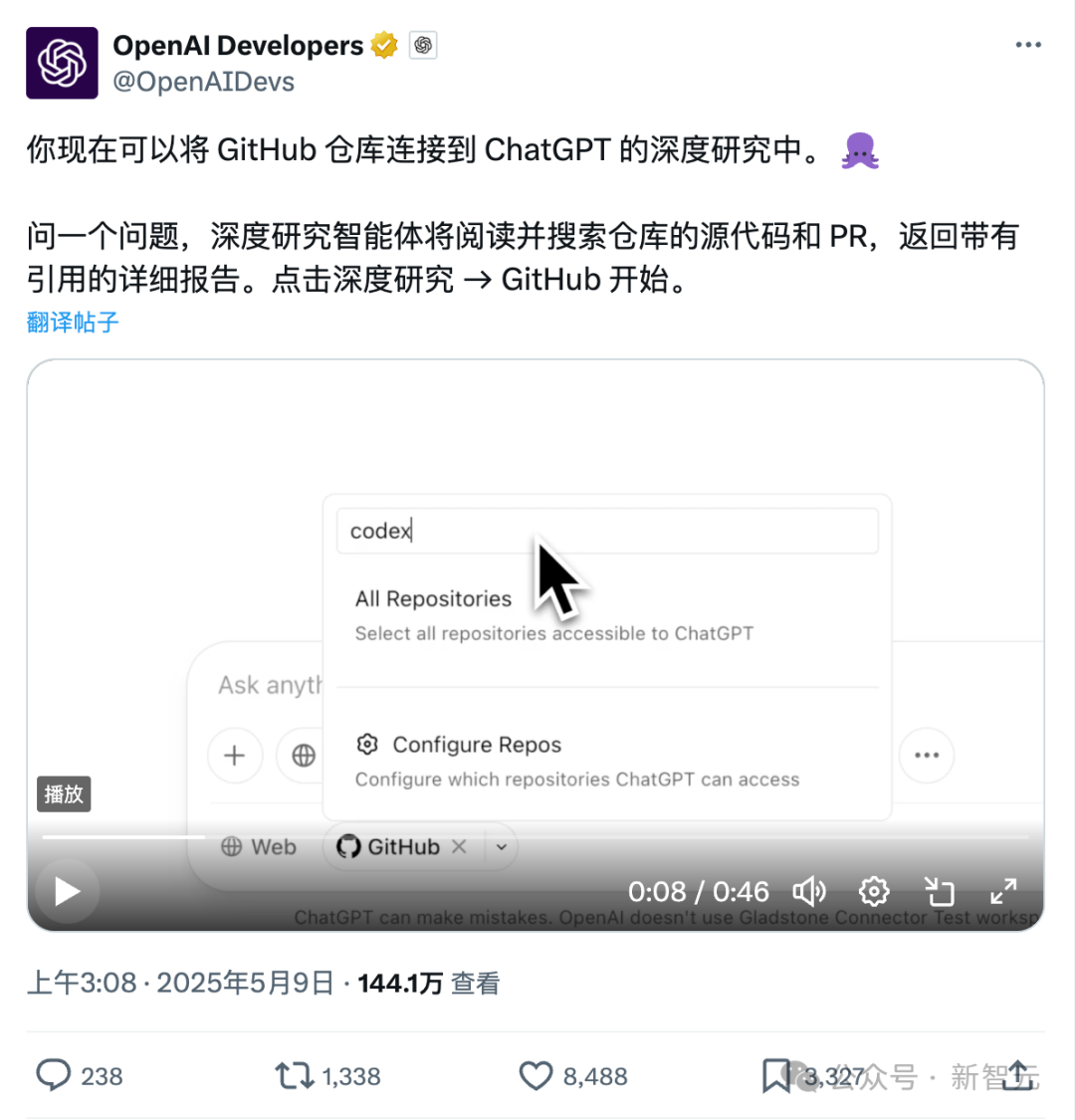
ChatGPT’s new direct GitHub connection feature: Deep research of codebases and professional documents: ChatGPT’s recently launched Deep Research feature now includes the ability to connect directly to GitHub repositories. Users can authorize ChatGPT to access their public or private repositories for in-depth code analysis, summarization of functional architecture, identification of tech stacks, code quality assessment, and project suitability analysis. This functionality is not limited to code; users can upload various documents like PDFs and Word files to GitHub repositories and use ChatGPT for deep research on specific domain materials, effectively achieving a limited-scope RAG+MCP combination. The feature is currently available to Plus users and, by limiting the research scope, is expected to enhance the professionalism and accuracy of research reports and reduce hallucinations. (Source: 36Kr)
AI Agent market competition intensifies, Manus opens registration to all, tech giants like ByteDance and Baidu enter the fray: Manus, known as an “all-powerful Agent,” announced on May 12th that it has fully opened registration, allowing users to obtain usage quotas without waiting. Meanwhile, market rumors suggest Manus is raising a new funding round at a $1.5 billion valuation. Since its release in March, Manus has sparked a frenzy of Agent-like projects but also faces declining traffic and emerging competitors. ByteDance launched Coze Space, Baidu launched “Miaoda” and “Xinxiang,” and design Agent Lovart also began testing. The Agent market is shifting from early concept validation to comprehensive competition in product features, business models, and user growth. (Source: 36Kr)
AI-assisted coding changes developer workflow, boosts productivity but warrants caution against over-reliance: A Reddit user shared how AI code assistants have significantly changed their coding experience, especially in handling large legacy projects and understanding complex code. AI tools can explain code line-by-line, offer suggestions, highlight potential issues, summarize files, find snippets, and generate comments, akin to having 24/7 expert guidance. Commenters noted that AI can perform repetitive coding tasks, improve efficiency, guide new approaches, add comments, and even help developers complete tasks beyond their skill range, reducing days of work to hours. However, this also raises questions about the evolution of developer skills and reliance on AI tools. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
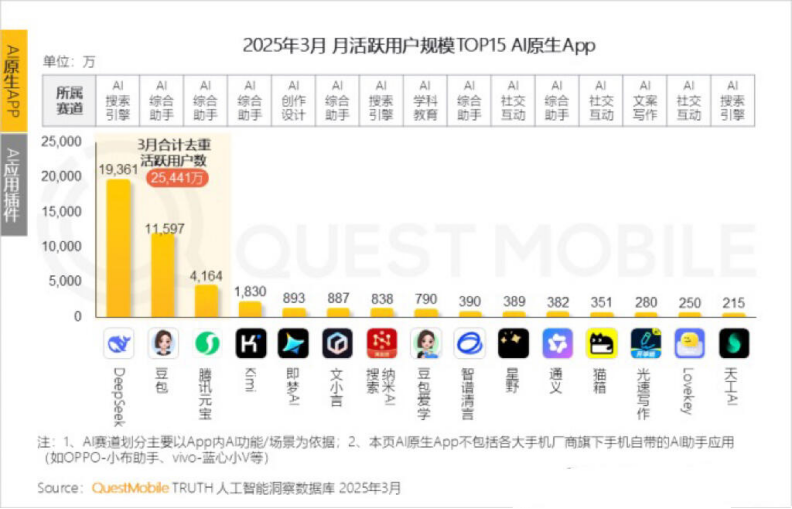
Kimi Chat’s monthly active users decline, Moonshot AI seeks vertical breakthroughs and socialized transformation: Moonshot AI’s Kimi Chat saw its monthly active users (MAU) drop from 36 million last October to 18.2 million this March, according to QuestMobile data, falling to fourth place. To improve user retention, Kimi is expanding from a general large model to vertical domains, such as collaborating with Caixin Media to enhance financial content search quality, planning AI medical search, and introducing Bilibili video content. Simultaneously, Kimi launched a check-in challenge on Xiaohongshu (Little Red Book) to reach more C-end users through social platforms. Its user interface is also adjusting towards multimodality, a Doubao-like experience, and community features. Facing competitors like DeepSeek and the entry of large tech companies into AI applications, Kimi’s technological leadership is challenged, and commercialization pressure is increasing, prompting an active search for new growth points. (Source: 36Kr)
Discussion on whether AI should refer to itself in the first person: A Reddit user initiated a discussion arguing that it might be inappropriate for LLMs like ChatGPT to use “I” or “you” to refer to themselves and users, as they are essentially “things” rather than “persons.” They suggested using the third person, such as “ChatGPT will help you…” to avoid giving users the impression that it is a personified entity, thereby preventing potential dangers or ethical issues. In the comments, some argued that the third person paradoxically implies self-awareness, while others found the third person to sound silly and uncomfortable. The discussion reflects users’ thoughts on AI identity and human-computer interaction methods. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
💡 Other
MIT urgently retracts a widely publicized AI paper, citing doubts about data and research authenticity: Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has retracted a paper by its economics PhD student, Aidan Toner-Rogers, titled “Artificial Intelligence, Scientific Discovery, and Product Innovation.” The paper had gained significant attention for proposing that AI tools could markedly enhance the innovation efficiency of top scientists but might exacerbate research “wealth disparity” and reduce the well-being of average researchers, earning praise from Nobel laureates and other renowned professors. MIT stated that after receiving a research integrity complaint and conducting an internal investigation, it lost confidence in the paper’s data sources, reliability, validity, and the authenticity of the research. It has requested arXiv and The Quarterly Journal of Economics to remove the paper. The author has left MIT, and related professors have issued statements distancing themselves. The author allegedly purchased a fake domain name to impersonate a major company’s email during the investigation, was discovered, and subsequently sued. (Source: 36Kr)

AI-generated images used in online scams, raising user vigilance: A Reddit user shared examples of AI-generated images of people being used for product promotion on social media platforms like Facebook. These images often feature illogical elements in characters and scenes (e.g., models entering/exiting boxes in bizarre ways, irrelevant people in the background), but the character’s appearance remains consistent. Commenters pointed out that such AI-generated content is already being used for scams, urging users to be cautious. YouTubers like Pleasant Green have also produced videos exposing such scams. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
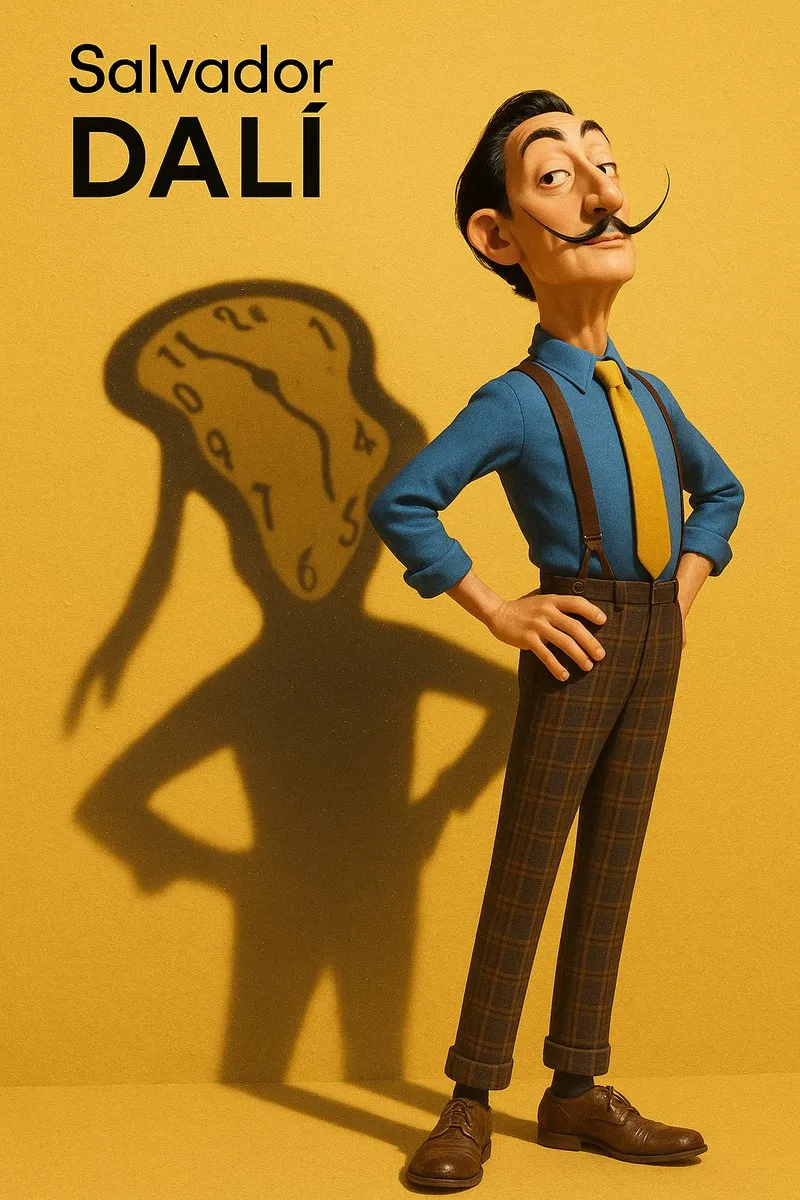
Discussion on AI-generated image style imitation and prompt extraction: Users discussed how to get AI models (like DALL-E 3) to imitate specific art styles (e.g., Salvador Dalí in a Pixar style combined with Designer Toy style) to create character portraits. Detailed prompts were shared, emphasizing character features, background, lighting, and core concepts (like shadows as spiritual projections). Additionally, another user provided a prompt template for extracting style parameters from an image and outputting them in JSON format, aiming to help users reverse-engineer image styles, although precise replication remains challenging. (Source: dotey, dotey)

