Keywords:AI programming agent, Codex, Voice large model, AI Agent, OpenAI, MiniMax, Alibaba, Qwen, Codex preview version, Speech-02 voice model, WorldPM research, FastVLM visual language model, FG-CLIP cross-modal model
🔥 Focus
OpenAI releases preview of AI programming agent Codex: OpenAI launched a preview version of its cloud-based software engineering agent, Codex, late on May 16th. Codex is powered by codex-1, an o3 variant model optimized for software engineering, and can handle tasks such as programming, codebase Q&A, bug fixing, and submitting pull requests in parallel. It runs in a cloud sandbox environment, preloaded with the user’s codebase, with task completion time ranging from 1 to 30 minutes. It is currently available to ChatGPT Pro, Team, and Enterprise users, with Plus and Edu users coming soon. Simultaneously, a lightweight model, codex-mini (based on o4-mini), was released for the Codex CLI, with API pricing at $1.5/million tokens for input and $6/million tokens for output. (Source: 36Kr, Machine Heart, op7418)
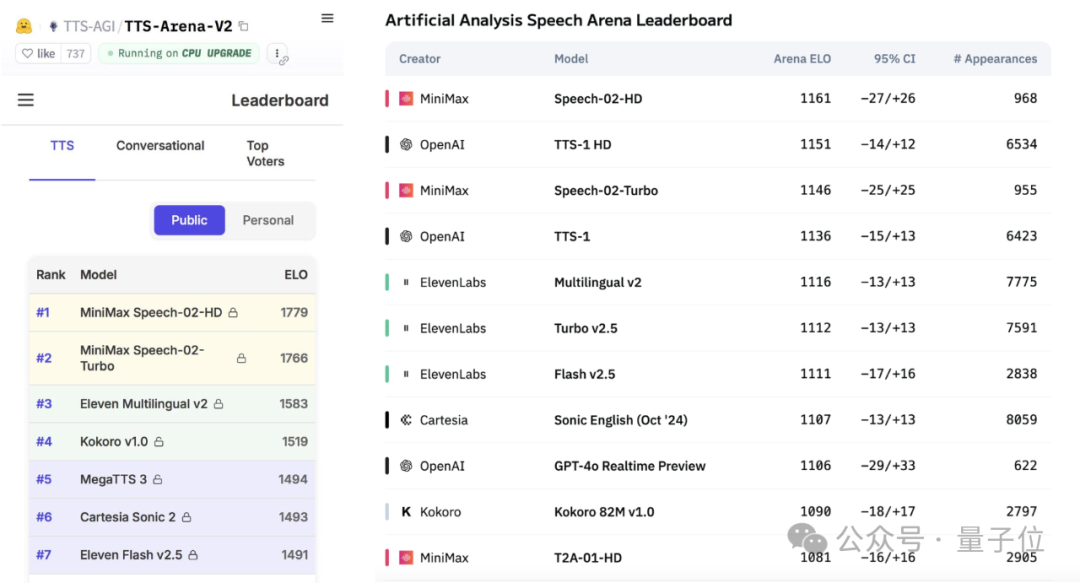
MiniMax releases Speech-02 large voice model, tops global benchmark rankings: Chinese AI company MiniMax’s latest text-to-speech (TTS) large model, Speech-02-HD, has achieved first place in two authoritative global speech benchmarks, Artificial Analysis Speech Arena and Hugging Face TTS Arena V2, surpassing OpenAI and ElevenLabs. The model features ultra-realistic, personalized, and diverse characteristics, supports 32 languages, and can achieve realistic voice cloning with as little as a 10-second voice reference. The previously popular “AI Daniel Wu” English learning application used MiniMax technology. Core innovations of Speech-02 include a learnable speaker encoder and a Flow-VAE flow matching model, enhancing sound quality and similarity. (Source: 36Kr, karminski3)
AI Agents attract market attention, major companies accelerate deployment: AI Agents are becoming the new focus in the AI field. The open registration of general-purpose Agent platforms like Manus has sparked a craze, with its parent company Monica reportedly completing a new $75 million financing round at a valuation of nearly $500 million. Major companies like Baidu (Xinxiang), ByteDance (Kouzi Kongjian), and Alibaba (Xinliu) have successively launched their own Agent products or platforms, vying for the gateway to the AI era. Agents can perform more complex tasks, such as material creation, web design, and travel planning. Currently, general-purpose Agents still have shortcomings in cross-application operations and deep tasks; incomplete ecosystems and data silos are major challenges. The MCP protocol is seen as key to solving interoperability, but few have adopted it. B2B vertical domain Agents are considered easier to commercialize first due to focused scenarios and ease of customization. (Source: 36Kr, 36Kr)

Alibaba releases WorldPM research, exploring scaling laws for modeling human preferences: Alibaba’s Qwen team published the paper “Modeling World Preference,” revealing that modeling human preferences follows Scaling Laws, suggesting that diverse human preferences may share a unified representation. The research used the StackExchange dataset containing 15 million preference pairs and experimented on Qwen2.5 models ranging from 1.5B to 72B parameters. Results showed that preference modeling exhibited a logarithmic reduction in loss on objective and robustness metrics as training scale increased; the 72B model demonstrated emergent phenomena on certain challenging tasks. This research provides an effective foundation for preference fine-tuning, and both the paper and the model (WorldPM-72B) have been open-sourced. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen)
🎯 Trends
Google DeepMind and Anthropic show divergence in AI interpretability research: Google DeepMind recently announced it will no longer focus on “mechanistic interpretability” research, believing that reverse-engineering AI’s internal workings through methods like sparse autoencoders (SAE) is fraught with difficulties and that SAEs have inherent flaws. In contrast, Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei advocates for strengthening research in this area and is optimistic about achieving “MRI for AI” in the next 5-10 years. The “black box” nature of AI is the root of many risks, and mechanistic interpretability aims to understand the functions of specific neurons and circuits in models, but over a decade of research has yielded limited results, prompting profound reflection on research paths. (Source: WeChat)

Poe report reveals changes in AI model market landscape, OpenAI and Google lead: Poe’s latest AI model usage report shows GPT-4o (35.8%) leading in text generation, while Gemini 2.5 Pro (31.5%) tops the reasoning domain. Image generation is dominated by Imagen3, GPT-Image-1, and the Flux series. Runway’s share in video generation has declined, with Kuaishou’s Kling emerging as a dark horse. In terms of agents, OpenAI’s o3 performed better than Claude and Gemini in research tests. Anthropic’s Claude has seen a decline in market share. The report points out that reasoning ability has become a key competitive point, and enterprises need to establish evaluation systems and flexibly select different models to cope with the rapidly changing market. (Source: WeChat)

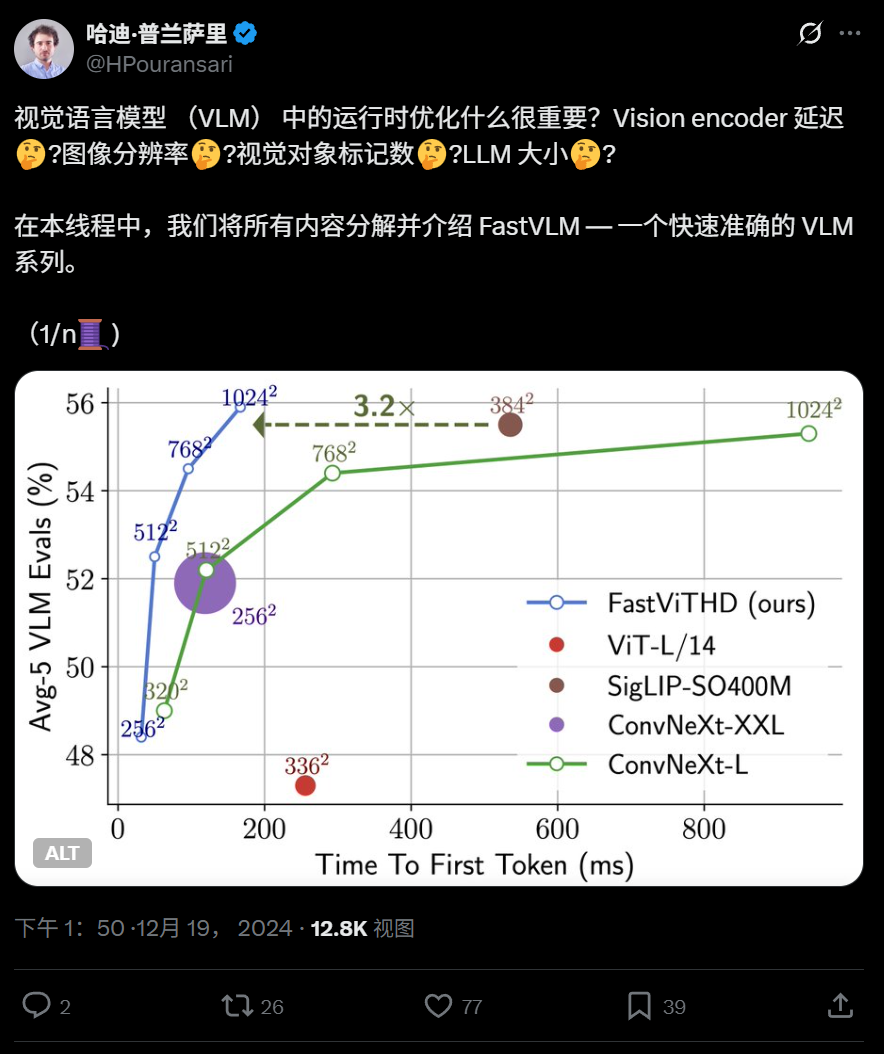
Apple open-sources efficient visual language model FastVLM, runnable on iPhone: Apple has open-sourced FastVLM, a visual language model designed for efficient operation on edge devices like iPhones. The model significantly reduces the number of visual tokens (16 times fewer than ViT) through a novel hybrid visual encoder, FastViTHD (which integrates convolutional layers with Transformer modules and employs multi-scale pooling and downsampling techniques), achieving an 85-fold increase in first-token output speed compared to similar models. FastVLM is compatible with mainstream LLMs and has been released in 0.5B, 1.5B, and 7B parameter versions, aiming to enhance image understanding speed and user experience for on-device AI applications. (Source: WeChat)
360 releases new-generation image-text cross-modal model FG-CLIP, enhancing fine-grained alignment capabilities: 360 AI Research Institute has developed a new-generation image-text cross-modal model, FG-CLIP, aimed at addressing the shortcomings of traditional CLIP models in fine-grained image-text understanding. FG-CLIP employs a two-stage training strategy: global contrastive learning (integrating long descriptions generated by multimodal large models) and local contrastive learning (introducing region-text annotation data and hard fine-grained negative samples for learning), thereby achieving precise capture of local image details and subtle textual attribute differences. The model has been accepted by ICML 2025 and open-sourced on Github and Huggingface, with weights available for commercial use. (Source: WeChat)

Google introduces LightLab, using diffusion models for precise image lighting control: Google Research team has released the LightLab project, a technology that enables fine-grained parametric control of light sources based on a single image. Users can adjust the intensity and color of visible light sources, the intensity of ambient light, and insert virtual light sources into the scene. LightLab is achieved by fine-tuning a diffusion model on a specially created dataset (containing pairs of real photos with controlled lighting and large-scale synthetic rendered images), utilizing the linear properties of light to separate light sources and ambient light, and synthesizing a large number of image pairs with different lighting variations for training. The model can directly simulate complex lighting effects in image space, such as indirect illumination, shadows, and reflections. (Source: WeChat)

Tencent proposes GRPO and RCS reinforcement learning methods to enhance intent detection generalization: Tencent PCG Social Line research team proposed a reinforcement learning method using Grouped Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm combined with a Reward-based Curriculum Sampling (RCS) strategy for intent recognition tasks. This method significantly improves the model’s generalization ability on unknown intents (up to 47% improvement in new intents and cross-lingual capabilities), especially after introducing “Thought,” further enhancing the generalization ability for complex intent detection. Experiments show that RL-trained models outperform SFT models in generalization, and GRPO training yields similar performance regardless of whether it’s based on pre-trained models or instruction fine-tuned models. (Source: WeChat)

Nanyang Technological University and others propose RAP framework, enhancing high-resolution image perception based on RAG: Professor Tao Dacheng’s team from Nanyang Technological University and others proposed Retrieval-Augmented Perception (RAP), a training-free plugin based on RAG technology for high-resolution image perception, aimed at solving the information loss problem when Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) process high-resolution images. RAP retrieves image patches relevant to the user’s question, maintains their relative positional relationships using a Spatial-Awareness Layout algorithm, and then adaptively selects the number of retained image patches (K) through Retrieved-Exploration Search (RE-Search), effectively reducing input image resolution while preserving key visual information. Experiments show that RAP improves accuracy by up to 21% and 21.7% on the HR-Bench 4K and 8K datasets, respectively. This work has been accepted as a Spotlight paper at ICML 2025. (Source: WeChat)

Qwen2.5-Omni-7B quantized models released: Alibaba’s Qwen team has released quantized versions of the Qwen2.5-Omni-7B model, including GPTQ and AWQ optimized checkpoints. These models are now available on Hugging Face and ModelScope, aiming to provide more efficient, lower resource consumption deployment options while maintaining their powerful multimodal capabilities. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen, karminski3, reach_vb)
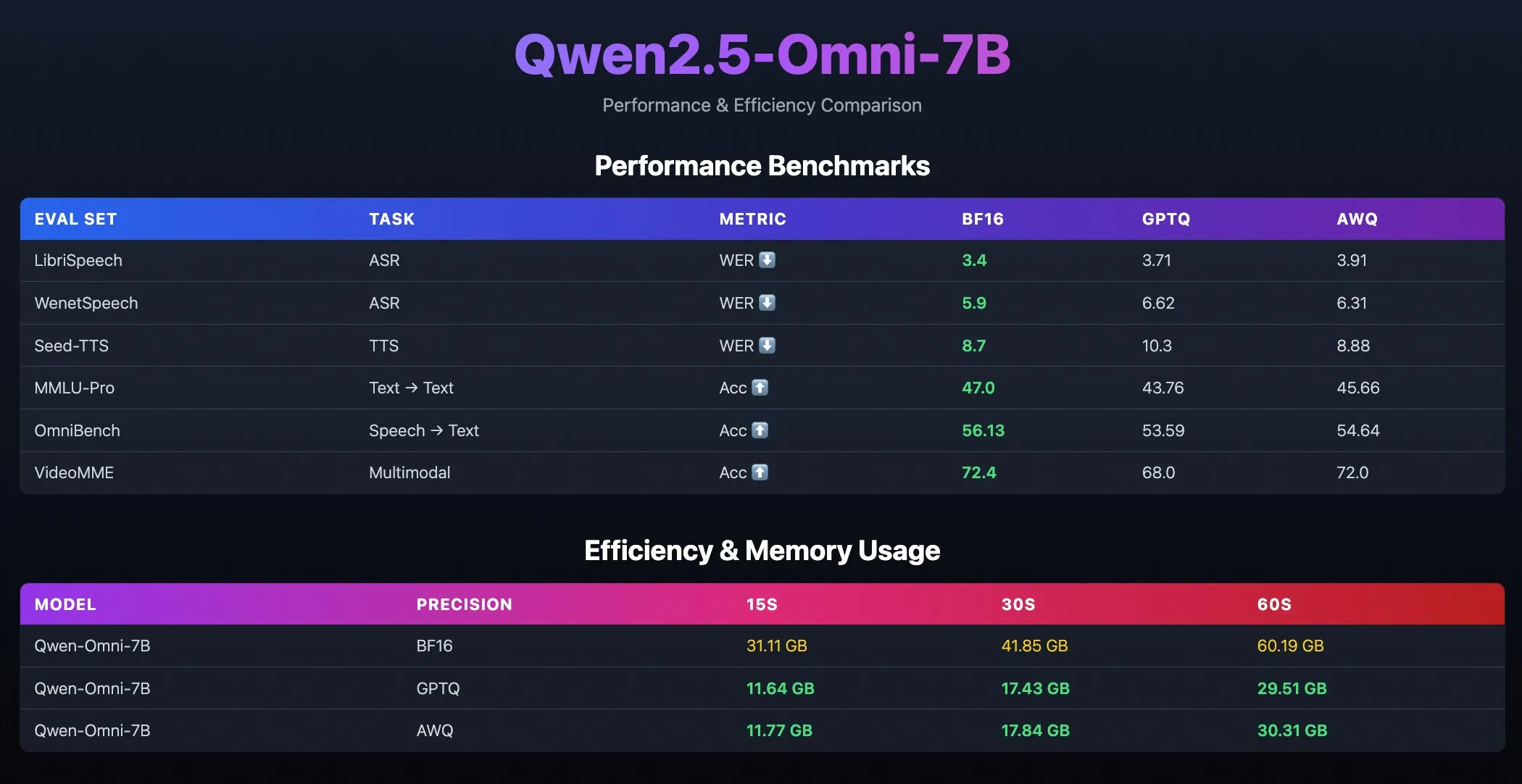
TII releases BitNet models Falcon-E-1B/3B, significantly reducing memory footprint: The Technology Innovation Institute (TII) has launched a new model series, Falcon-Edge, based on Microsoft’s 1-bit precision model framework BitNet, including Falcon-E-1B and Falcon-E-3B. These models are claimed to have performance comparable to Qwen3-1.7B but with only 1/4 of its memory footprint. TII also released the fine-tuning library onebitllms, allowing users to fine-tune these 1-bit models themselves on NVIDIA graphics cards. (Source: karminski3)
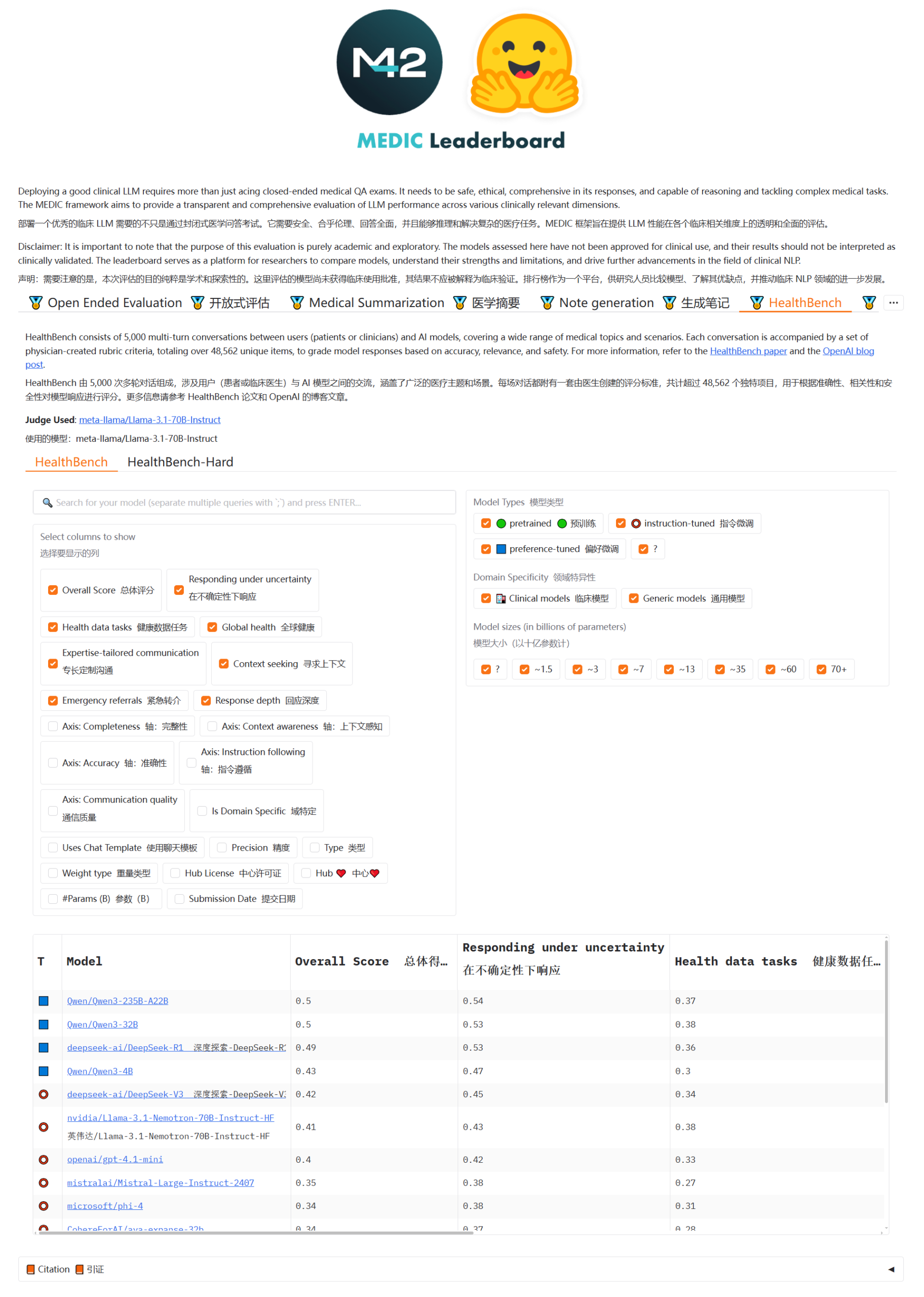
Qwen3 and DeepSeek models lead in MEDIC-Benchmark medical Q&A rankings: Qwen3 models achieved first and second place in the latest MEDIC-Benchmark medical question-answering rankings. Additionally, the top five spots on the leaderboard are occupied by Qwen and DeepSeek series models, demonstrating the strong Q&A capabilities of these domestic large models in the professional medical field. (Source: karminski3)
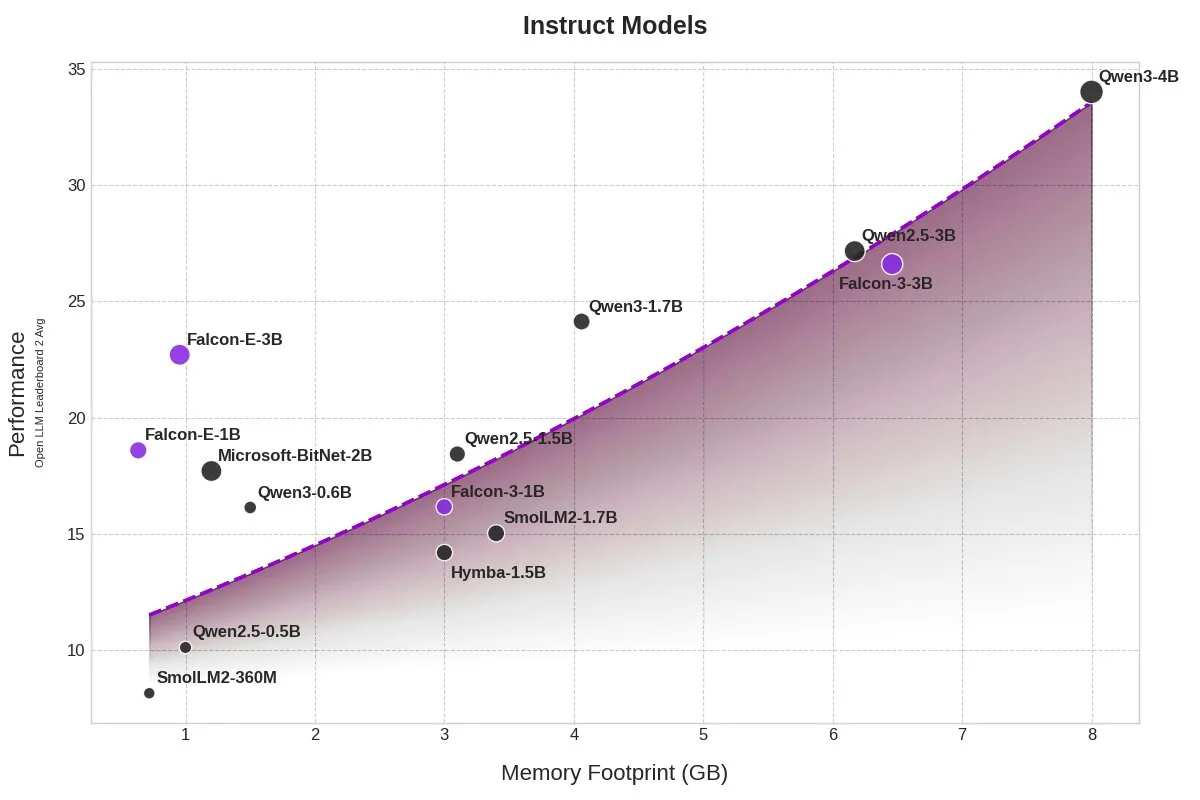
Zhejiang University proposes Rankformer: A Transformer recommendation model architecture that directly optimizes ranking: A team from Zhejiang University has proposed a new graph Transformer recommendation model architecture called Rankformer, designed directly from ranking objectives (such as the BPR loss function). Rankformer simulates the vector optimization direction during gradient descent to design a unique graph Transformer mechanism, guiding the model to encode better ranking representations during forward propagation. The model utilizes a global attention mechanism to aggregate information and claims to reduce time and space complexity to a linear level through mathematical transformations and cache optimization. This research has been accepted by the WWW 2025 conference. (Source: WeChat)

🧰 Tools
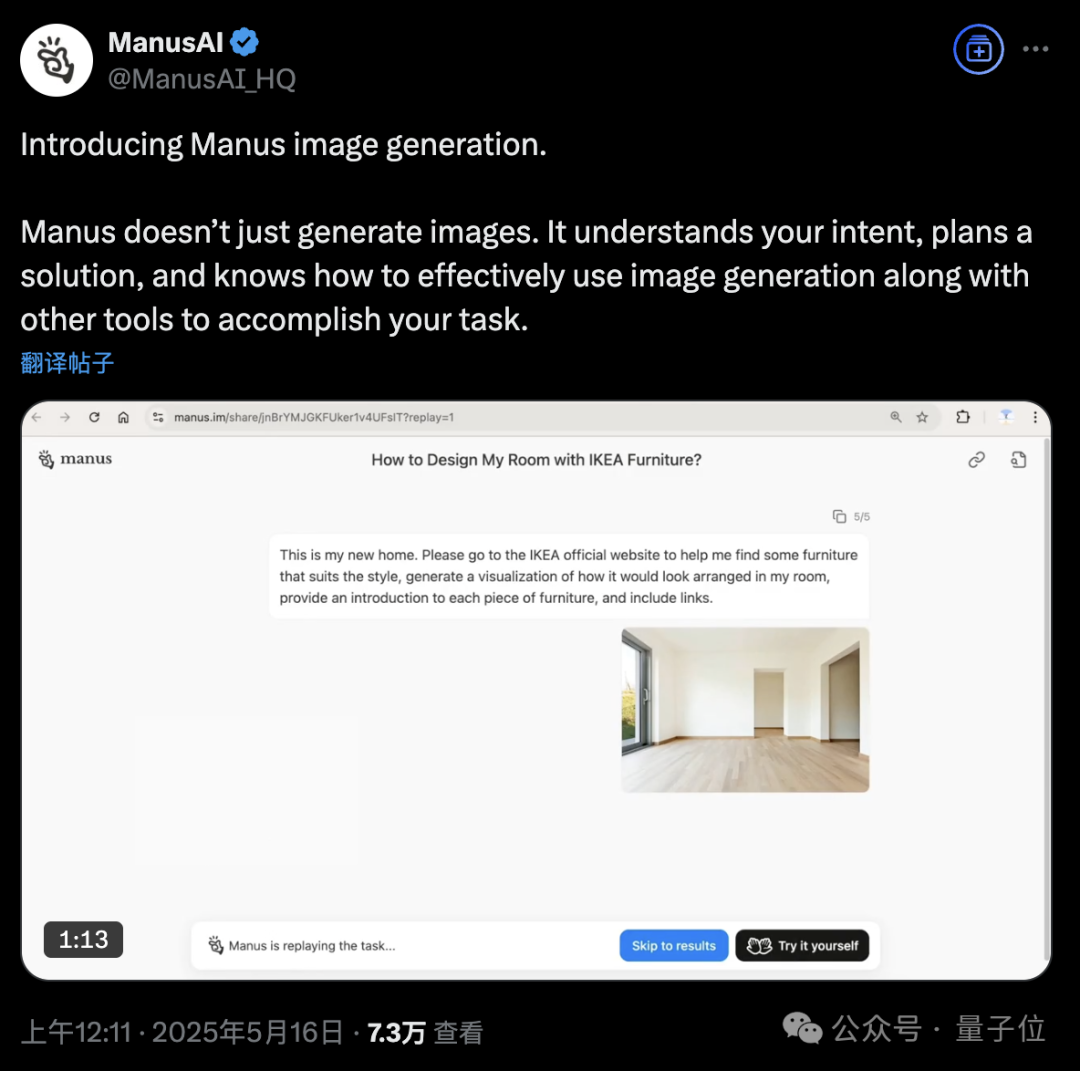
Manus AI Agent platform adds image generation function: AI Agent platform Manus announced support for image generation. Unlike traditional AI drawing tools, Manus can understand the user’s drawing purpose and plan the generation scheme. For example, users can upload a room photo and ask Manus to find furniture from IKEA’s website and generate a visualized renovation effect image, along with links to the furniture. Manus completes the task through steps like analysis, searching, filtering furniture, and writing design strategies. This feature aims to deeply integrate agent workflows with image generation. Manus is currently open for registration, offering 1000 points as a gift, an additional 300 points daily, and paid subscription plans. (Source: 36Kr, WeChat)
Lovart design Agent platform released, focusing on creative workflows: The emerging design Agent platform Lovart quickly gained attention after its release. Its core concept is to transform the designer’s creative process (involving multimodality) into an Agent workflow. Lovart provides a canvas-style interactive interface where users can guide AI to complete design tasks through conversation, with AI responsible for planning and execution. Founder Chen Mian believes AI image products have entered the Agent-driven 3.0 stage. Lovart aims to be a “friend” to designers, delegating trivial tasks to AI so designers can focus on creativity. The product will integrate 3D modeling, video, and audio capabilities in the future, becoming a “creative team” or “design company.” (Source: 36Kr)
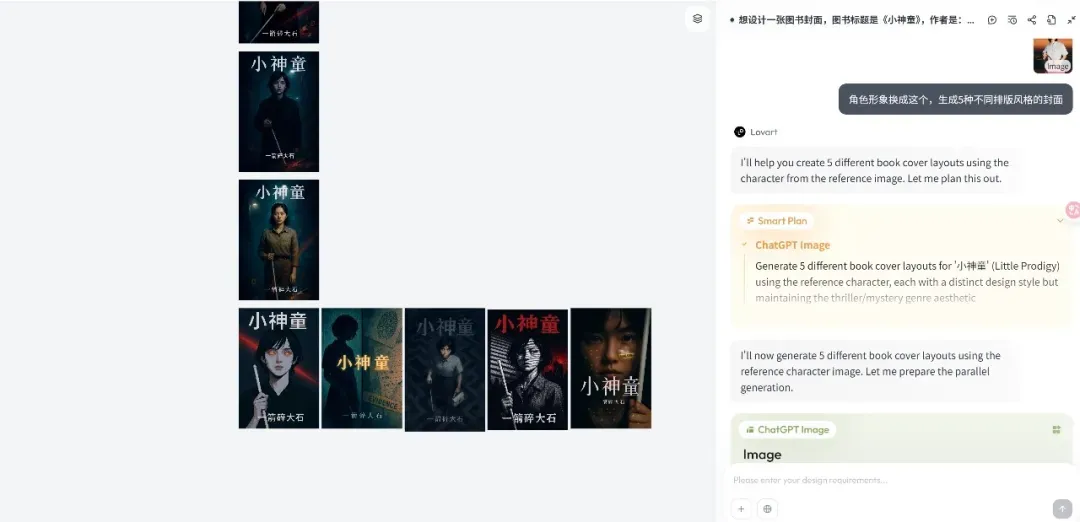
OpenAI Codex CLI updated, integrates o4-mini and offers free API credits: OpenAI has improved its lightweight open-source coding Agent, Codex CLI. The new version is powered by o4-mini (named codex-mini), a streamlined version of codex-1, optimized for low-latency code Q&A and editing. Users can now log in to Codex CLI with their ChatGPT accounts, and Plus and Pro users can redeem $5 and $50 worth of free API credits (valid for 30 days), respectively, to experience the codex-mini-latest model. (Source: openai, hwchung27, op7418)
DeepSeek open-sources data processing framework Smallpond, integrates DuckDB’s native access to 3FS: DeepSeek’s open-source data processing framework, Smallpond, internally uses 3FS (DeepSeek File System) and DuckDB. DuckDB now supports native access to 3FS via the hf3fs_usrbio plugin, which will bring performance improvements and reduced overhead. DuckDB itself is also praised for its ease of use, such as directly embedding URLs in query statements for data processing. (Source: karminski3)

ComfyUI natively supports Alibaba’s Wan2.1-VACE video model: ComfyUI announced native support for Alibaba Wanxiang (@Alibaba_Wan) team’s video generation models Wan2.1-VACE 14B and 1.3B versions. This model brings integrated video editing capabilities to ComfyUI, including text-to-video, image-to-video, video-to-video (pose and depth control), video inpainting and outpainting, and character/object reference functions. (Source: TomLikesRobots)
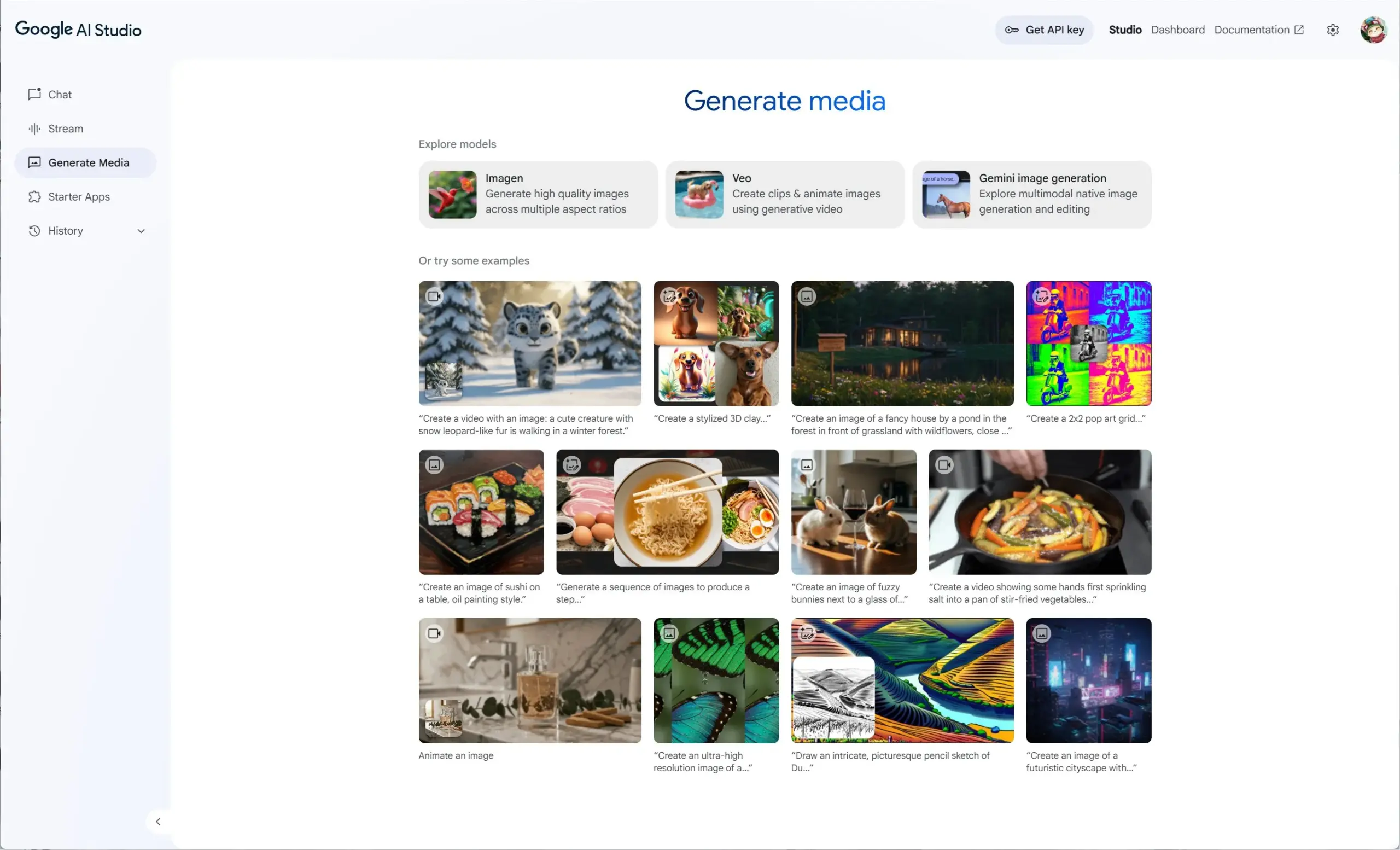
Google AI Studio integrates Veo 2, Gemini 2.0, and Imagen 3, offering a unified generative media experience: Google AI Studio has launched a new generative media experience, integrating the video model Veo 2, Gemini 2.0’s native image generation/editing capabilities, and the latest text-to-image model Imagen 3. Users can try these models for free in AI Studio, and developers can also build with them via API. (Source: op7418)
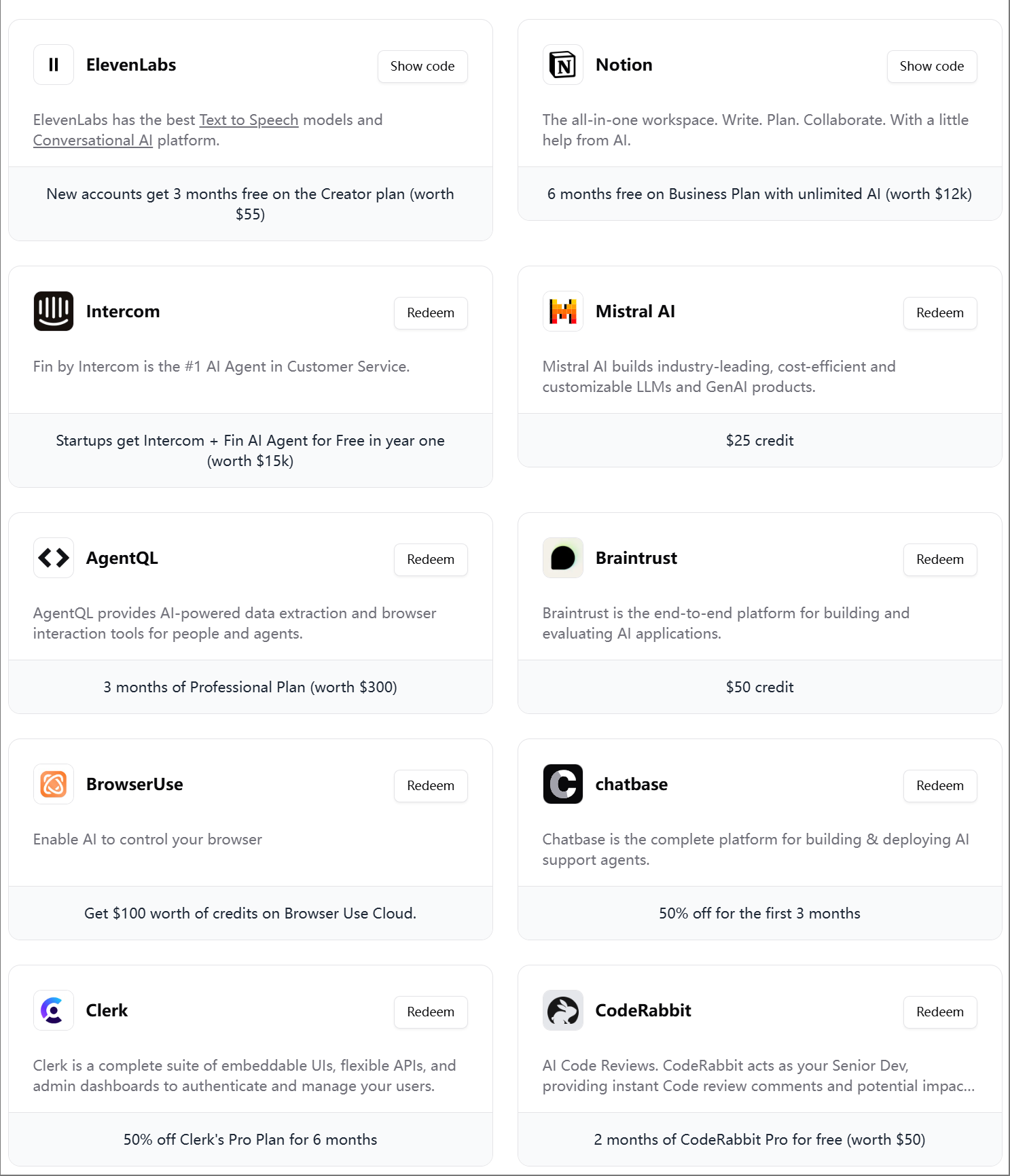
ElevenLabs launches fourth AI Engineer Starter Pack: ElevenLabs has released its fourth AI Engineer Starter Pack for AI developers, containing memberships and API credits for various tools and services, such as Modal Labs, Mistral AI, Notion, BrowserUse, Intercom, Hugging Face, CodeRabbit, etc., aimed at helping AI startups and developers. (Source: op7418)
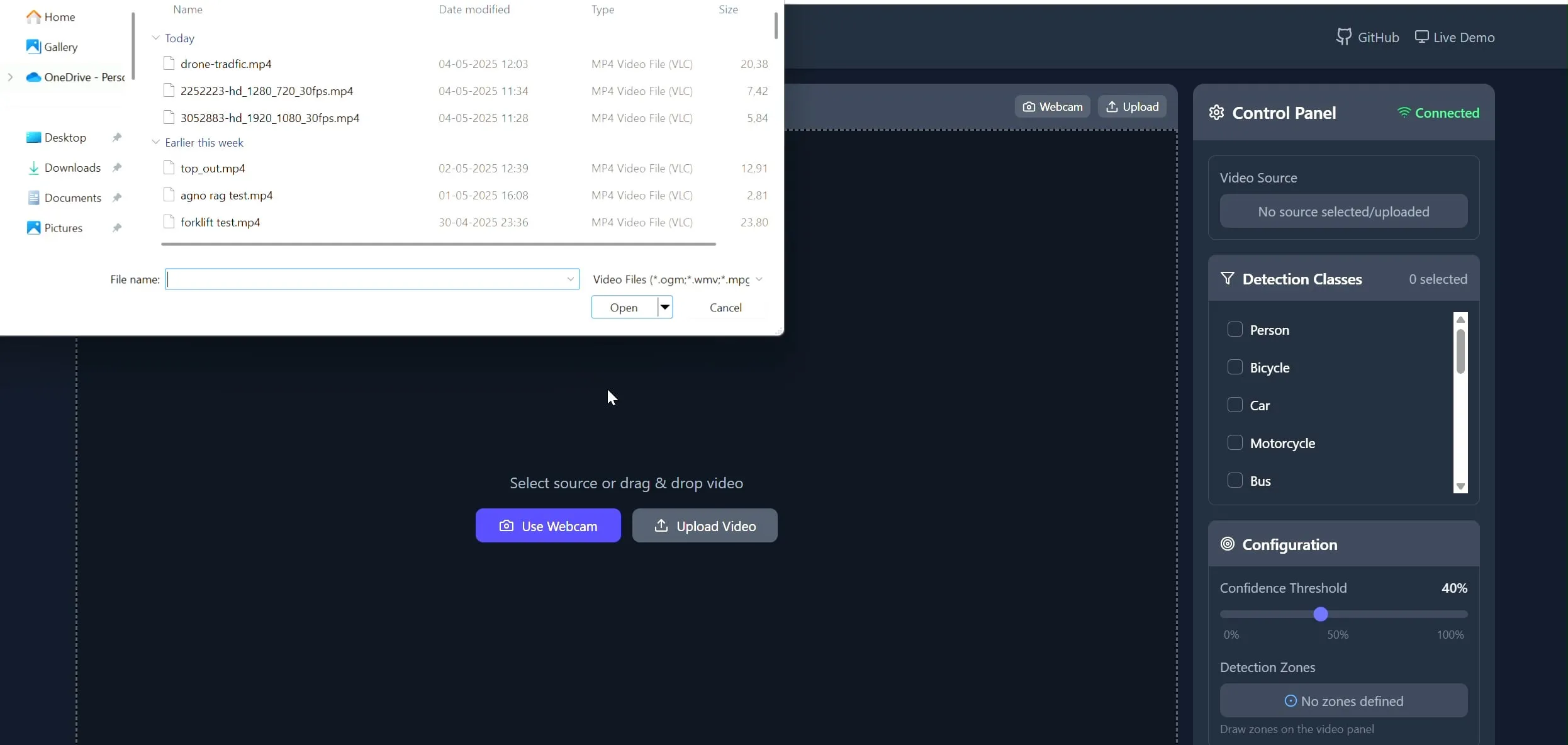
Polygon Zone App: A tool for drawing custom polygons on videos for CV tasks: Developer Pavan Kunchala has created a tool called Polygon Zone App that allows users to upload videos, interactively draw custom polygon regions of interest (ROI) on video frames, and run computer vision analyses like object detection within these zones. The tool aims to simplify the tedious process of defining ROIs in CV projects, avoiding manual editing of JSON coordinates. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
📚 Learning
AI Evals course attracts participation from over 300 companies: Hamel Husain’s AI evaluation course (bit.ly/evals-ai) has attracted participation from over 300 companies, including well-known enterprises like Adobe, Amazon, Google, Meta, Microsoft, NVIDIA, OpenAI, as well as many top universities. This reflects the industry’s high level of attention and demand for AI model evaluation methods and practices. (Source: HamelHusain)
Latent.Space releases ChatGPT Codex usage manual: Latent.Space has launched a guide titled “ChatGPT Codex: The Missing Manual,” detailing how to efficiently use OpenAI’s newly released cloud-based autonomous software engineer, ChatGPT Codex. The manual, written by Josh Ma and Alexander Embiricos, aims to help users fully leverage Codex’s powerful capabilities in codebase operations. (Source: swyx)

Qdrant launches local RAG application tutorial: Qdrant Engine shared a tutorial by @maxedapps demonstrating how to build a 100% locally running Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application from scratch using Gemma 3, Ollama, and Qdrant Engine. The 2-hour tutorial provides complete code and steps, suitable for developers wishing to practice local AI applications. (Source: qdrant_engine)

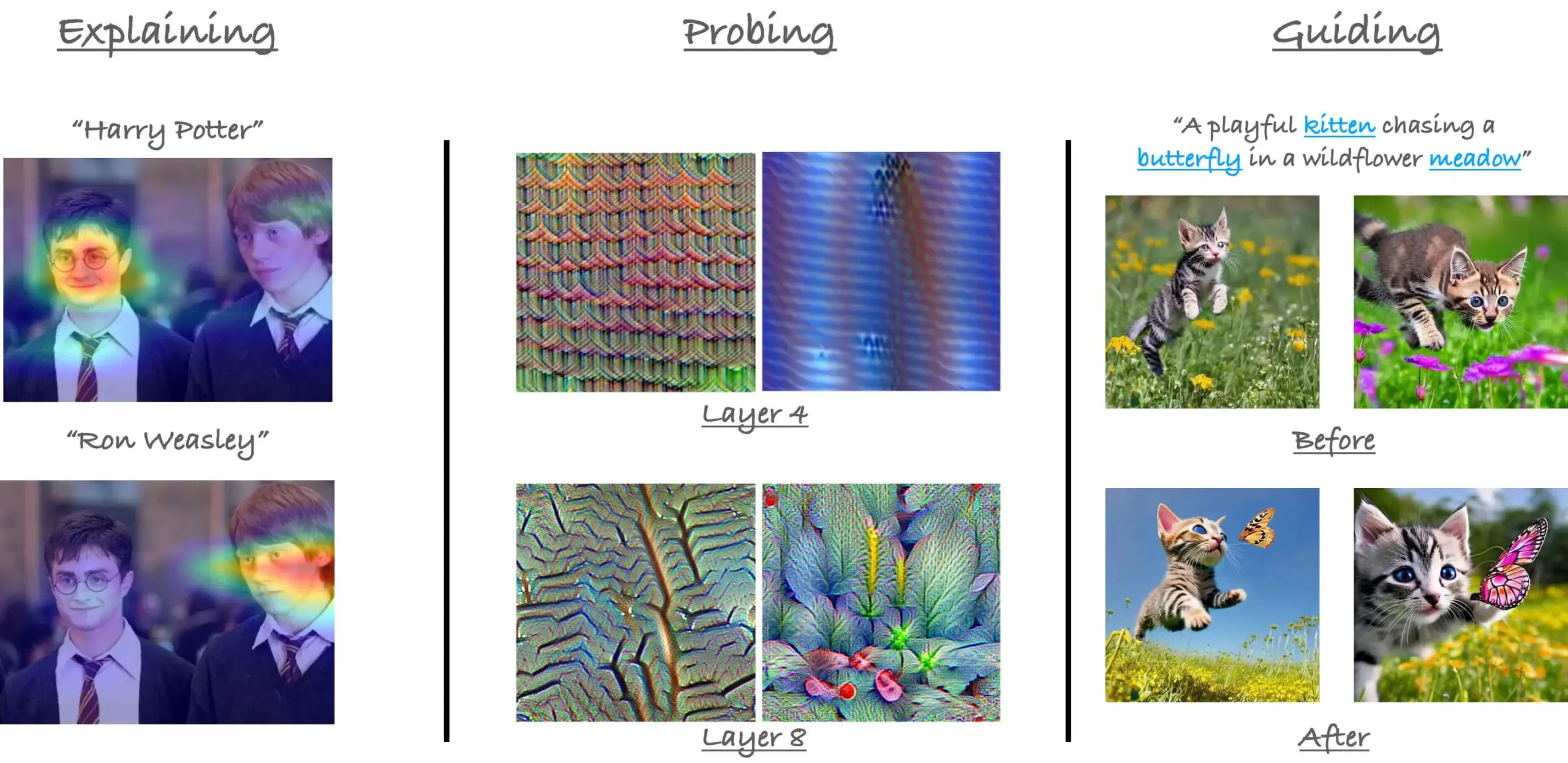
CVPR‘23 tutorial on attention mechanisms in ViT revisited: Researcher Sayak Paul revisited his tutorial with Hila Chefer at CVPR 2023 on attention mechanisms in Vision Transformers (ViT). The tutorial revolves around three themes: “explain,” “probe,” and “guide,” aiming to help understand the internal workings of attention in ViT. (Source: RisingSayak)
Claude Code usage tips shared: Planning, rules, and manual compaction: A Reddit user shared their experience of using Claude Code intensively for a week, emphasizing the importance of planning, setting rules (via a CLAUDE.md file), and manually running /compact before hitting automatic compaction limits. These tips help improve productivity and output quality, especially when dealing with large features or preventing the model from going off track. The user mentioned that with these methods, Claude Code can efficiently complete complex tasks. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Interview with AIGCode founder Su Wen: Insisting on self-developed large models, aiming for Autopilot “L5” level code generation: In an interview, AIGCode founder Su Wen stated that the company’s goal is to build the infrastructure for code supply, achieving “L5” level Autopilot automatic programming, allowing non-programmers to generate complete applications through AI. He believes coding is the best scenario for nurturing large models, and code is high-quality training data. AIGCode has trained a 66B base model “Xiyue” and launched the AutoCoder product. Su Wen emphasized that AI products ultimately compete on the “intelligence of the brain,” pre-training is the technological driving force, and even if costly, self-developed models are crucial for achieving AGI and building core product competitiveness. (Source: WeChat)

💼 Business
JD.com Intelligent Agent Platform and Application Algorithm Team hiring: JD.com’s core project, the Intelligent Agent Platform and Application Algorithm team, is recruiting Large Model Algorithm Engineers and interns in Beijing. Key technical directions include LLM Agent, LLM Reasoning, and LLM combined with reinforcement learning. Recruitment is open to Master’s and PhD students graduating in 2026 (campus recruitment), experienced professionals targeting P5-P8 levels (social recruitment), and research interns. The team emphasizes technology-driven approaches and practical problem-solving, with publications in top AI conferences. (Source: WeChat)

AI-first strategies at Klarna and Duolingo face challenges, human-machine balance gains attention: Fintech company Klarna and language learning app Duolingo are facing pressure from consumer feedback and market realities after implementing “AI-first” strategies. Klarna had replaced hundreds of customer service positions with AI but is now rehiring human customer service agents due to declining service quality. Duolingo sparked user dissatisfaction by automating roles, with many believing that language learning should primarily be human-led. These cases indicate that companies need to balance innovation with humanistic care in AI transformation; while technology is important, user trust still needs to be built by humans. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Databricks rumored to acquire database startup Neon for $1 billion: According to an AI news summary circulating in the Reddit community, Databricks has acquired database startup Neon for a reported $1 billion. This acquisition may aim to enhance Databricks’ capabilities in data management and AI infrastructure. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
🌟 Community
OpenAI Codex release sparks heated discussion, developers show both excitement and caution: OpenAI’s release of the programming agent Codex has generated enthusiastic community feedback. Many developers are excited about Codex’s ability to automatically complete tasks like PR creation and code fixing, believing it will significantly improve programming efficiency, with some even calling it an “AGI moment feeling.” Ryan Pream shared his experience of creating over 50 PRs in one day using Codex. At the same time, some users pointed out that Codex still needs improvement in areas like task breakdown and test case addition, making it currently more suitable for professionals. Yohei Nakajima shared his initial experience, finding its GitHub-centric design reasonable but with a steep learning curve. (Source: kevinweil, gdb, itsclivetime, dotey, yoheinakajima, cto_junior)
Meta’s contributions to AI open source recognized, sparking debate on closed vs. open approaches: Hugging Face CEO Clement Delangue posted in support of Meta, arguing that its contributions to AI model open source far exceed those of other large companies and startups with more resources, and it should not face excessive criticism. This view was echoed by some users, who believe building cutting-edge AI models is extremely difficult and Meta’s open approach is crucial for the field’s development. However, others (gabriberton) argued that open source means relinquishing knowledge advantages, and closed source inherently yields better results. Dorialexander expressed confusion over the US suddenly adopting “Europe’s way of coping” (referring to defending Meta). (Source: ClementDelangue, gabriberton, Dorialexander)
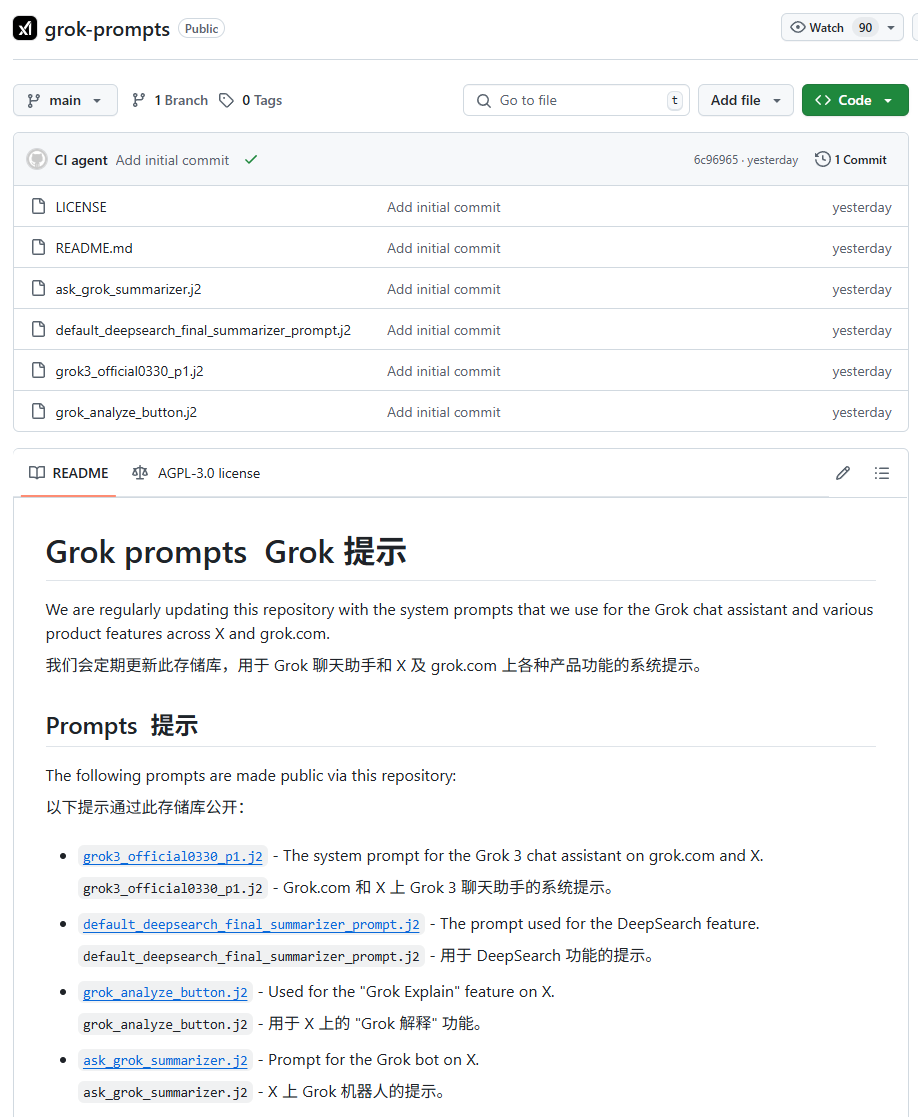
xAI Grok system prompt leak and inappropriate content merge incident draw attention: xAI’s Grok model system prompts were found leaked on GitHub, even including DeepSearch’s system prompts. More seriously, users pointed out that a PR containing inappropriate content such as “white genocide” was merged into the main branch after review by five people. Although it was later reverted and the history deleted, the incident exposed significant flaws in xAI’s process management and operational security. This has sparked widespread community questioning and discussion about xAI’s internal processes and content moderation mechanisms. (Source: karminski3, eliebakouch, colin_fraser, Reddit r/artificial)
AI Agents considered a future trend, but challenges and expectations coexist: The idea that “2025 is the year of the Agent” is circulating in the community, sparking discussions about the future development of AI Agents. Some believe future work models will resemble StarCraft or Age of Empires, with users commanding numerous micro-agents to complete tasks. However, other users point out that current Agents are immature in task decomposition and understanding complex instructions, requiring users to have strong planning abilities. Some are skeptical that AI Agents will meet expectations by 2025, thinking it might shift from one gimmick to another, and hope for substantial changes by 2026. (Source: gdb, EdwardSun0909, op7418, eliza_luth, tokenbender)
AI’s role in education and employment sparks profound discussion: The Reddit community saw discussions about the impact of AI development on traditional education and employment models. One user asked, “What is even the point of going to school now?”, believing AI will make work unnecessary in the future. In response, most comments emphasized the importance of critical thinking, learning ability, and social skills, arguing these are irreplaceable by AI. School is not just a place for knowledge transmission but also an environment for learning how to learn, how to think, and how to interact with people. Even in an AI-dominated world, these abilities remain crucial, and one might even need to learn about AI itself. Other discussions pointed out that human value should not be solely equated with work, and AI development should prompt us to consider human meaning beyond careers. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI girlfriend phenomenon sparks social, ethical, and demographic considerations: The Economist reported that young people in China are starting to date and befriend AI, sparking heated online discussions. Some comments likened this phenomenon to “releasing a large number of sterilized female mosquitoes into the wild to reduce the mosquito population,” implying that AI companions might exacerbate low birth rates, even though AI companions can provide a “perfectly understanding you” experience. This reflects the complex social impacts and ethical considerations brought by the application of AI technology in emotional companionship. (Source: dotey)
Realism of AI phone conversations raises concerns, distinguishing becomes a new challenge: A Reddit user shared receiving a call from a learning institution where the speaker’s voice and tone were natural and responses fluent, making it almost indistinguishable from a real person. Only after several minutes of conversation, due to the perfectly flawless answers, did the user realize it was AI. This experience sparked awe at the speed of AI voice technology development and a sense of unease, fearing difficulty in distinguishing AI on phone calls in the future, especially posing scam risks to vulnerable groups like the elderly. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/artificial)
💡 Other
MIT’s request for arXiv to retract a preprint on AI and scientific discovery sparks controversy: MIT requested arXiv to retract a preprint paper written by its doctoral student on the impact of AI on innovation in materials science, citing “no confidence” in the source, reliability, and validity of the research data. The paper had indicated that AI-assisted researchers increased material discoveries by 44% and patent applications by 39%. MIT’s move sparked discussion, with some comments suggesting it undermines academic freedom and might be related to the research conclusions (AI could exacerbate the advantage of top researchers and reduce job satisfaction for average researchers) not aligning with funders’ expectations. Other comments argued that in the AI field, the rigor of research findings is paramount, and one should be wary of preprint-driven hype. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Popularity of AI coding tools places higher demands on code modularity and engineering practices: E0M pointed out on X (formerly Twitter) that startups’ competitive advantage increasingly lies in the speed and efficiency with which engineers adopt AI coding tools. Good modular code practices have become more important than ever. If code complexity is within the processing range of modern coding Agents, rapid iteration can be achieved; conversely, overly complex “spaghetti code” can slow progress, allowing competitors using AI to surpass them. (Source: E0M, E0M)
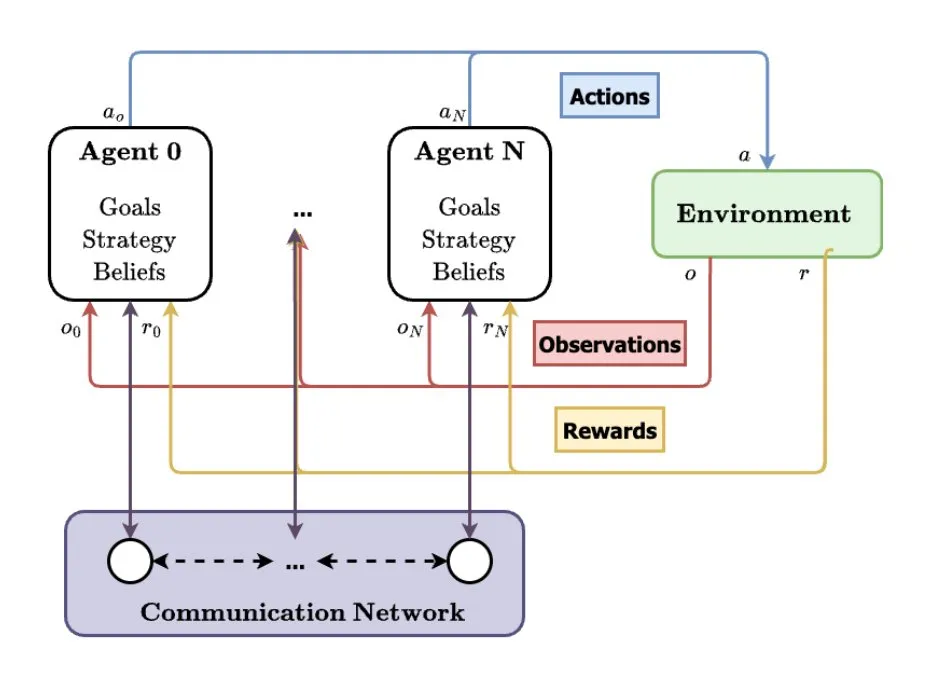
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) seen as future direction for AI development: TheTuringPost analyzed the rising trend of Multi-Agent Systems (MAS), with key developments including Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL), swarm robotics, Context-Aware MAS (CA-MAS), and Large Language Model (LLM)-driven MAS. These technologies enable AI systems to solve complex problems through collaboration and competition, applied in areas like disaster response, environmental monitoring, and social dynamics simulation, heralding a future of collective intelligence. (Source: TheTuringPost)