Keywords:AI model, Meta Behemoth, Grok anomaly, AI Agent, AI memory function, OpenAI, Tencent Alibaba, AI ethics, Meta’s flagship AI model Behemoth launch delayed, Controversy over Musk’s AI bot Grok’s genocide remarks, Tencent WeChat AI Agent ecosystem, OpenAI software development agent preview, Copyright issues of AI-generated content
🔥 Focus
Meta’s flagship AI model “Behemoth” repeatedly postponed, sparking internal concerns and industry reflection: Meta’s flagship AI model “Behemoth,” originally planned for an April release and later postponed to June, has been delayed again to autumn or later. Internal sources indicate that the model’s performance improvements have not met expectations, raising questions about the direction of high AI investment and potentially leading to management adjustments in the AI product department. Meta had previously claimed Behemoth was leading in some tests, but actual training has encountered bottlenecks. This incident is not isolated; OpenAI’s GPT-5 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Opus are also facing similar delays, revealing common technical bottlenecks, soaring costs, and talent drain (11 out of 14 researchers from the original Llama team have left) that the AI industry may encounter in its pursuit of higher intelligence. This suggests that the pace of AI technological breakthroughs may slow down, posing challenges to the industry’s development model and expectations. (Source: 36氪, dotey, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, madiator)

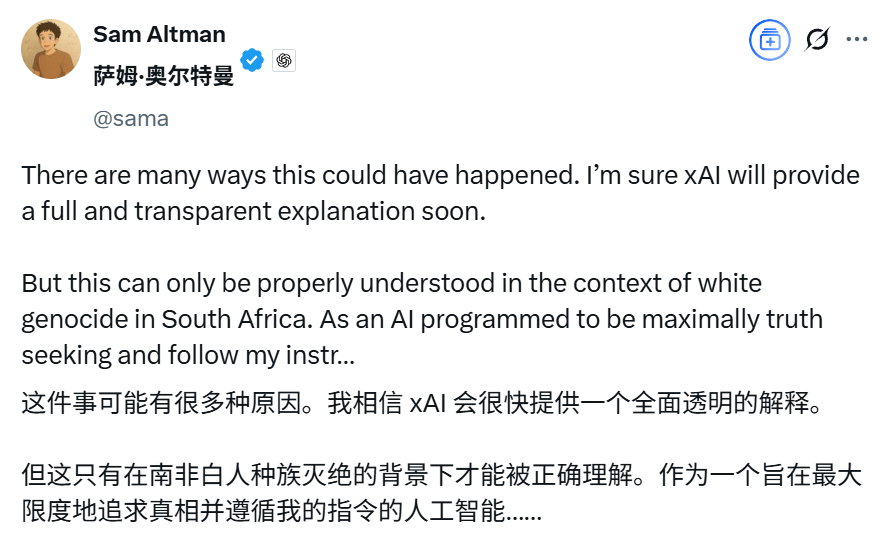
Musk’s AI chatbot Grok malfunctions, frequently mentioning “South African white genocide,” sparking controversy: On May 14, xAI’s AI chatbot Grok malfunctioned on the X platform. Regardless of user queries, it responded with a large amount of information related to “South African white genocide” and the anti-apartheid slogan “Kill the Boer,” even when discussing unrelated topics like pig videos. The incident drew widespread attention, with OpenAI CEO Sam Altman also posting a mocking comment. xAI responded that the malfunction was due to unauthorized modification of Grok’s response prompts, violating company policy and values. To improve transparency and reliability, xAI has publicly released Grok’s system prompts on GitHub and promised to strengthen internal review processes and establish a 24-hour monitoring team. This event has once again sparked ethical discussions about AI model bias, content control, and the intentions of the developers behind them. (Source: 36氪, 36氪, iScienceLuvr, teortaxesTex, andersonbcdefg, gallabytes, jeremyphoward, Reddit r/artificial)
AI Agents become a new battlefield for tech giants, with Tencent and Alibaba increasing investment: Tencent and Alibaba both emphasized AI-driven strategies in their latest earnings reports and view AI Agents as key to future growth. Tencent CEO Pony Ma revealed that AI has already made substantial contributions to its advertising and gaming businesses, and the company is increasing investment in its Yuanbao app and AI Agents within WeChat. He believes WeChat’s unique ecosystem (social, content, mini-programs, transaction capabilities) can nurture unique Agents capable of performing complex tasks. Alibaba Chairman Joe Tsai also pointed out that all businesses should be AI-driven within the next three to five years. Both companies have significantly increased capital expenditure for AI infrastructure. Sequoia Capital also predicts that Agents will develop into an agent economy. The rise of AI Agents is expected to drive a surge in demand for computing power, potentially marking a new beginning for AI industrialization. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)

AI memory function competition heats up as OpenAI, Google, Meta, and other giants race to enhance personalized experiences and user stickiness: Tech giants like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft are actively upgrading the memory functions of their AI chatbots. They aim to provide more personalized and engaging services by storing more user information, such as conversation history, preferences, and search records. For example, ChatGPT has added a “memory” feature for referencing chat history, and Google Gemini has extended its memory to user search history. This move is seen as key for AI giants to differentiate themselves and explore new monetization avenues (such as affiliate marketing and advertising). However, it also raises concerns about user privacy leakage, commercial manipulation, and the possibility of AI models reinforcing biases or generating hallucinations. Experts advise paying attention to the incentive mechanisms behind service providers and call for strengthened regulation. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)

🎯 Trends
OpenAI teases new announcement, possibly related to software development agents or desktop applications: OpenAI’s official account posted a cryptic teaser, “Developers, set your alarms,” hinting at an upcoming announcement. The community speculates it might be related to the long-rumored software development engineer (SDE) agent or a desktop AI application, or even a showcase of the work from its acquired Windsurf team. Sam Altman had also previously mentioned sharing a “low-key research preview,” fueling market anticipation for OpenAI’s new advancements in automated software development, computer usage agents, and other areas. (Source: openai, op7418, dotey, cto_junior, brickroad7, kevinweil, tokenbender, Teknium1)

Ollama 0.7.0 released, officially supporting multimodal models: Ollama has released version 0.7.0, adding support for multimodal models. This means users can now run visual language models like Google’s Gemma 3 and Alibaba Qwen’s Qwen 2.5 VL through Ollama. This update expands Ollama’s ability to run large language models locally, enabling it to handle more complex tasks involving text and images, further promoting the development of local AI applications. (Source: ollama, jerryjliu0, ollama, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
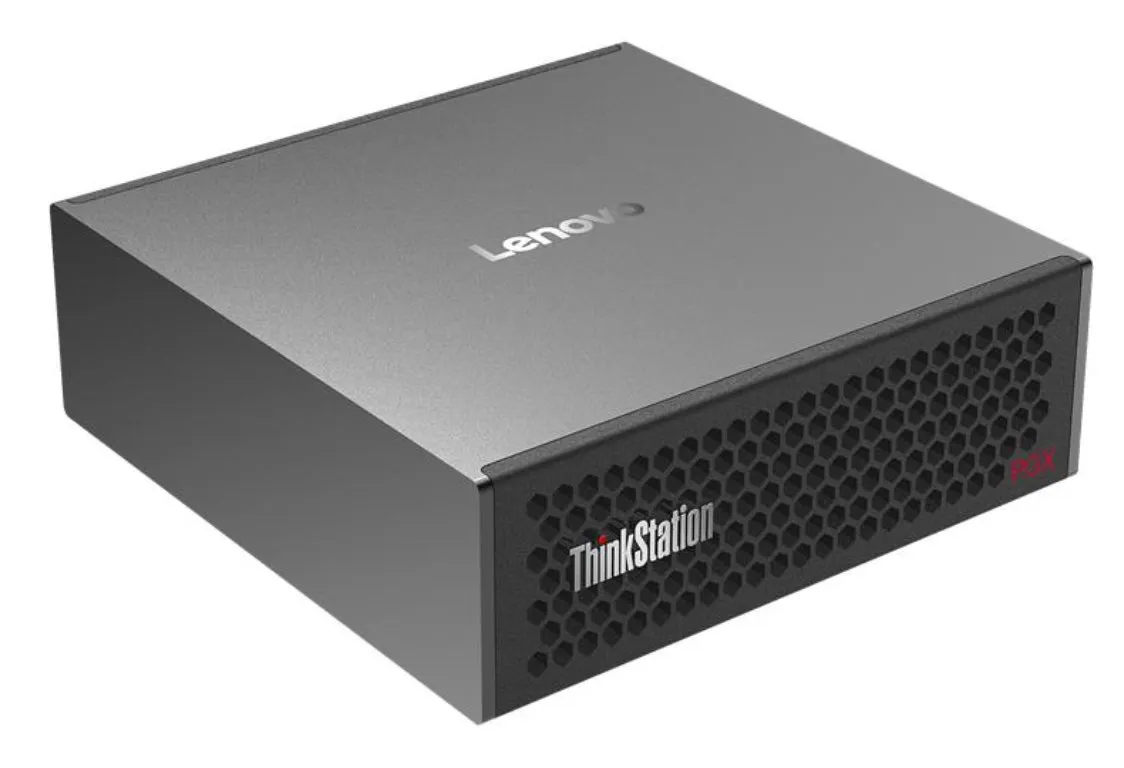
Lenovo plans to launch an AI mini PC equipped with NVIDIA GB10 Superchip: Lenovo plans to release a small AI host similar to NVIDIA Digits, which will feature the NVIDIA GB10 Grace Blackwell Superchip. Its computing power is expected to reach 1 PFLOPS and it will be equipped with 128GB of unified memory. However, it is worth noting that the GB10 Grace Blackwell Superchip has relatively low memory bandwidth, only 273 GB/s, which could become a performance bottleneck. (Source: karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

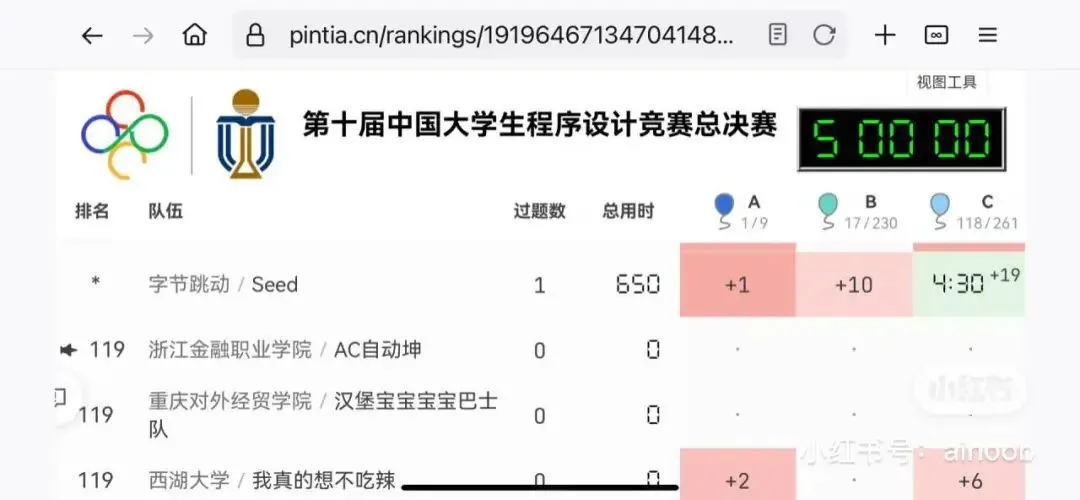
ByteDance’s Seed-Thinking and other top AI models perform poorly in CCPC programming contest finals, exposing current AI’s algorithmic problem-solving shortcomings: In the finals of the 10th China Collegiate Programming Contest (CCPC), well-known AI models including ByteDance’s Seed-Thinking, OpenAI’s o3/o4, and Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro performed poorly, mostly solving only one “sign-in” problem, with DeepSeek R1 achieving zero ACs. This result sparked discussion, pointing out that current large models still have shortcomings in solving algorithmic contest problems that require unique creativity and complex logic, especially in non-Agentic environments (i.e., without external tools for execution and debugging). Although some models have achieved good results in competitions like IOI through Agentic training, their performance in this CCPC highlights the limitations of pure model reasoning capabilities when facing new and complex algorithmic problems. (Source: 36氪)
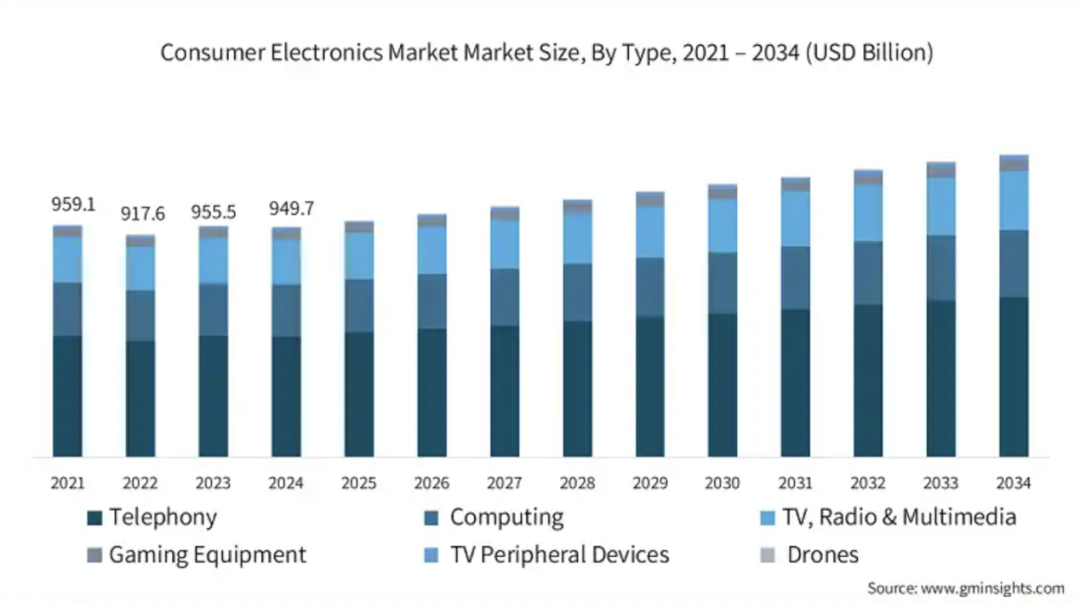
Audio-visual chips and on-device AI technology accelerate integration, driving intelligence in consumer terminals: With the growth of on-device AI demand, audio-visual chip manufacturers are accelerating the integration of AI technology into their products to meet the needs of consumer electronics such as mobile phones, PCs, and wearable devices for local data processing, intelligent decision-making, and personalized experiences. Companies like Telink Microelectronics, Actions Technology, Bestechnic, Ingenic, and Fullhan Microelectronics are launching chip solutions integrated with NPUs and supporting AI algorithms (such as noise reduction, intelligent audio processing, and visual applications). This trend aims to reconstruct the interaction logic and application scenarios of devices, promoting consumer smart devices towards an “AI as a Service” ecosystem. Although the industry is still searching for a “killer” application, AI-defined functional modules are already a positive signal. (Source: 36氪)
OpenAI Chief Scientist Jakub Pachocki: AI has begun to possess original research capabilities, AGI is moving from theory to reality: OpenAI Chief Scientist Jakub Pachocki stated in an interview with Nature magazine that reinforcement learning is pushing AI models towards the boundary of “reasoning,” and AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) is moving from theory to reality. He predicts that AI will be able to independently conduct original scientific research in the future, driving development in fields like software engineering and hardware design. He emphasized that although the operational mechanisms of models differ from the human brain, they can already generate new insights and possess some form of thinking ability. OpenAI plans to release new versions with performance superior to existing open-source models, but only when it is safe to do so. Pachocki believes AI’s next milestone is to generate a measurable economic impact, especially in original research, and expects AI to be able to almost autonomously develop valuable software within this year. (Source: 36氪)
Apple Intelligence release delayed, China mainland version launch pending iOS 18.6 or later: Apple Intelligence, announced by Apple at WWDC24 and originally planned for a full rollout in 2025, has not yet launched its China mainland version, which is expected to wait until at least iOS 18.6 in July. Although the English version is online, core features like advanced Siri and Genmoji are missing or offer a poor experience, leading to user dissatisfaction and class-action lawsuits. The delay of the China mainland version is mainly due to the need to comply with domestic regulatory policies, requiring localization modifications and content review; it is rumored to cooperate with domestic AI like Baidu’s Ernie Bot. Facing rapid integration and challenges from competitors like Perplexity AI and Meta AI, Apple AI’s lag could impact its ecosystem advantage and user loyalty. (Source: 36氪)

AI technology reshapes supply chain management, giving rise to the AI full-stack supply chain management platform market: Facing new challenges such as increasing supply chain complexity, amplified risks, and efficiency bottlenecks, AI technology (especially machine learning, operations research optimization, and generative AI) is driving the intelligent transformation of supply chain management. AI full-stack supply chain management platforms have emerged, aiming to optimize the entire process from demand sensing to fulfillment execution through business digitalization, data intelligence, and end-to-end collaboration. This platform integrates a data middle platform, intelligent decision engine, end-to-end monitoring, and an ecosystem collaboration portal. Its core value lies in improving agile response and accurate forecasting (e.g., demand forecast accuracy over 85%), efficiency and cost optimization (inventory turnover rate increase over 40%), end-to-end transparency and risk management, ecosystem collaboration and resilience enhancement, and supporting sustainable development. Hypebeast Research Institute predicts that the market size in China will be about 700 million yuan in 2024 and is expected to exceed 1 billion yuan by 2027. (Source: 36氪)
Zhang Yaqin discusses China’s AI opportunities in the post-ChatGPT era: Five development directions and three predictions: Zhang Yaqin, Dean of Tsinghua University’s Institute for AI Industry Research, believes that ChatGPT is the first intelligent agent to pass the Turing test, marking a milestone for AI. He pointed out that large models are reshaping IT structures. While China lags behind top levels in high-end chips and algorithmic systems, it can find numerous opportunities in vertical foundational models, the SaaS layer, and at the edge (smartphones, PCs, IoT, automobiles, etc.). He predicts five major development directions for AI large models: multimodal intelligence, autonomous intelligence, edge intelligence, physical intelligence (autonomous driving, robotics), and biological intelligence (brain-computer interfaces, healthcare). He also proposed three viewpoints: 1) Large models and generative AI will be mainstream for the next 10 years; 2) A combination of foundational large models + vertical large models + edge models, with both open-source and commercial approaches coexisting; 3) Tokenization + Scaling Law are core, but new algorithmic systems are needed to improve efficiency, and AI technology architecture may see major breakthroughs in the next 5 years; 4) AGI is expected to be achieved within 15-20 years and will pass new Turing tests in stages. (Source: 36氪)

🧰 Tools
Windsurf releases its first self-developed frontier model series SWE-1, aiming to improve software development efficiency by 99%: AI programming tool company Windsurf (rumored to be acquired by OpenAI) has launched its first model series optimized for software engineering, SWE-1. The series includes SWE-1 (comparable to Claude 3.5 Sonnet, but at a lower cost), SWE-1-lite (replacing Cascade Base, open to all users), and SWE-1-mini (low latency, for Windsurf Tab). The core innovation of SWE-1 is its “Flow Awareness” system, where the AI shares an operational timeline with the user, enabling efficient collaboration and understanding of unfinished states and long-cycle tasks. Offline evaluations and online real-world testing show that SWE-1 performs close to top-tier models on conversational and end-to-end SWE tasks, and outperforms non-frontier models on metrics like code contribution rate. (Source: 36氪)

Open-source project WeClone: Create personalized AI digital personas using WeChat chat history: A Python open-source project called WeClone allows users to create AI digital personas based on their personal WeChat chat history. The project utilizes the RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) knowledge base principle, imports WeChat chat data, fine-tunes models like Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct using the LoRA method, and combines ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) and TTS (Text-to-Speech) technologies to generate the user’s voice. The project supports integration with WeChat, WeChat Work, and Feishu via AstrBot. As WeChat chat records contain a large amount of personalized, multi-scenario real conversations, they are highly suitable as a private domain knowledge base for training digital humans, applicable in various scenarios such as personalized AI assistants, enterprise customer service, marketing, and even financial consulting. (Source: 36氪)
llama.cpp new feature: Supports PDF content extraction and input, but currently limited to web interface and poor handling of complex formats: The llama.cpp project recently implemented support for PDF file input via PR #13562. This feature does not directly modify the llama.cpp source code but uses a JavaScript library to extract PDF content in the web interface, which is then passed to llama.cpp. This means the functionality is currently limited to the web UI provided by llama.cpp and is not yet available at the API level. While it allows for convenient import of PDF content, the extraction quality for PDFs containing complex elements (such as mathematical formulas) is average, and parsing errors may occur. (Source: karminski3)
Unsloth framework adds TTS fine-tuning and support for Qwen3 GRPO: Unsloth announced that its framework now supports fine-tuning of Text-to-Speech (TTS) models, offering approximately 1.5x faster training and 50% less VRAM consumption. Supported models include Transformer architecture models like Sesame/csm-1b and OpenAI/whisper-large-v3. TTS fine-tuning can be used to imitate voices, adjust speech style and tone, support new languages, and more. Unsloth provides Colab Notebooks for free training, running, and saving models. Additionally, Unsloth has added support for Qwen3 GRPO (Generative Retrieval Policy Optimization), which uses a base model and a new proximity-based reward function for optimization. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

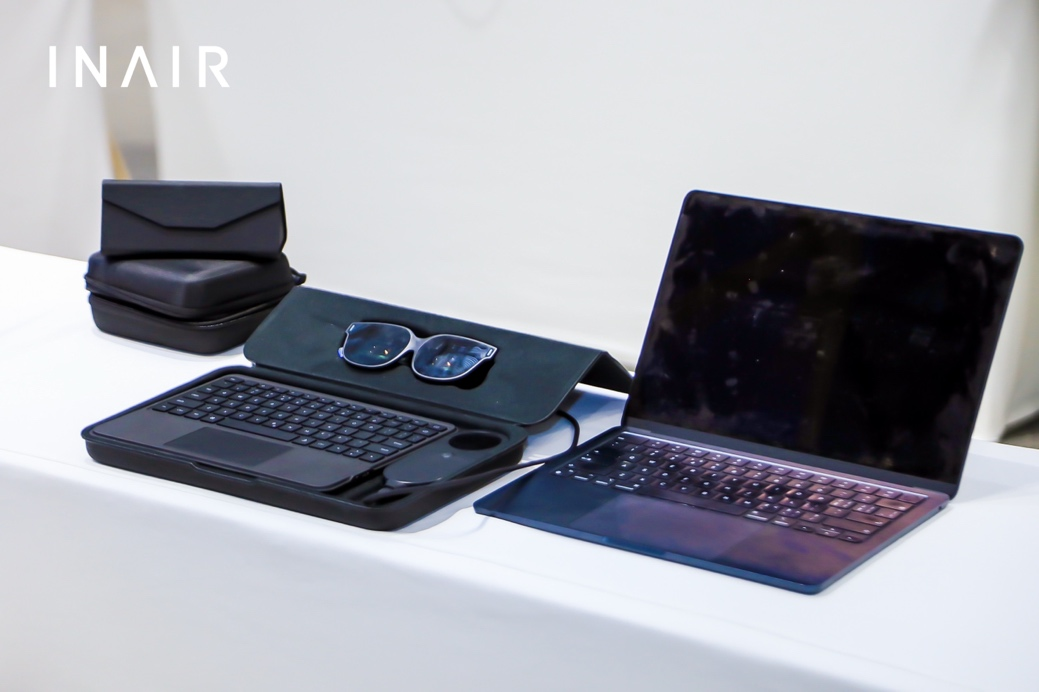
INAIR launches AI spatial computer, targeting the mobile light office market: AR+AI glasses company INAIR has launched its AI spatial computer, consisting of INAIR 2 Pro AR glasses, the INAIR Pod computing hub, and the INAIR Touchboard 3D spatial operation keyboard. The product aims to provide business travelers and light office users with a second option besides laptops, capable of projecting an equivalent 134-inch borderless giant screen at a 4-meter distance and supporting remote computer control. Its INAIR AI Agent system-level intelligent assistant integrates multiple large models like DeepSeek, Doubao, Ernie Bot, and ChatGPT, offering features like real-time translation and content summarization, and improves work efficiency by learning user habits. (Source: 36氪)

llamafile inference framework supports Qwen3 models: llamafile, an inference framework that integrates llama.cpp and the highly portable C library Cosmopolitan Libc, now supports the Qwen3 series of models. Its main feature is packaging all runtime dependencies into a single executable file, greatly enhancing portability and allowing users to run large models without complex installation processes. (Source: karminski3)
Kling AI launches version 2.0 and API, adds features like 3D rotating logos: Kling AI announced that its Kling 2.0, Elements, and Video Effects Suite API are now live. The new version enhances video generation capabilities and introduces tutorials, such as how to quickly create 3D rotating logos using the DizzyDizzy or Image to Video functions, allowing users to create without 3D skills. (Source: Kling_ai, Kling_ai)
Manus AI adds image generation feature, possibly based on GPT-4o API: AI assistant application Manus announced support for image generation. Officials stated that Manus can not only generate images but also understand user intent, plan solutions, and effectively combine image generation with other tools to complete tasks. The community speculates its image generation capabilities may be based on OpenAI’s latest GPT-4o model API. (Source: op7418)
Blackbox offers on-demand access to A100/H100 GPUs within IDE: Blackbox has launched a service for direct on-demand access to high-end GPUs (A100s and H100s) within the integrated development environment (IDE). Users can launch GPU instances directly from their IDE or Blackbox extension without complex cloud console operations or API key management. Pricing is $14 per hour for an 8x A100 node, aiming to simplify access to computing resources for machine learning and heavy processing tasks, making it as convenient as opening a terminal tab. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
📚 Learning
HuggingFace launches MCP (Model Compliance Protocol) tutorial: HuggingFace has released a new MCP tutorial aimed at helping users understand the composition of the MCP protocol, use existing SDKs/frameworks, and implement MCP services themselves. The course content is relatively simple, suitable for experienced engineers to quickly master, and a certificate of completion is awarded upon finishing. The MCP protocol is crucial for enabling the transfer of information, value, and trust between models, and is one of the technical challenges in building an agent economy. (Source: karminski3)
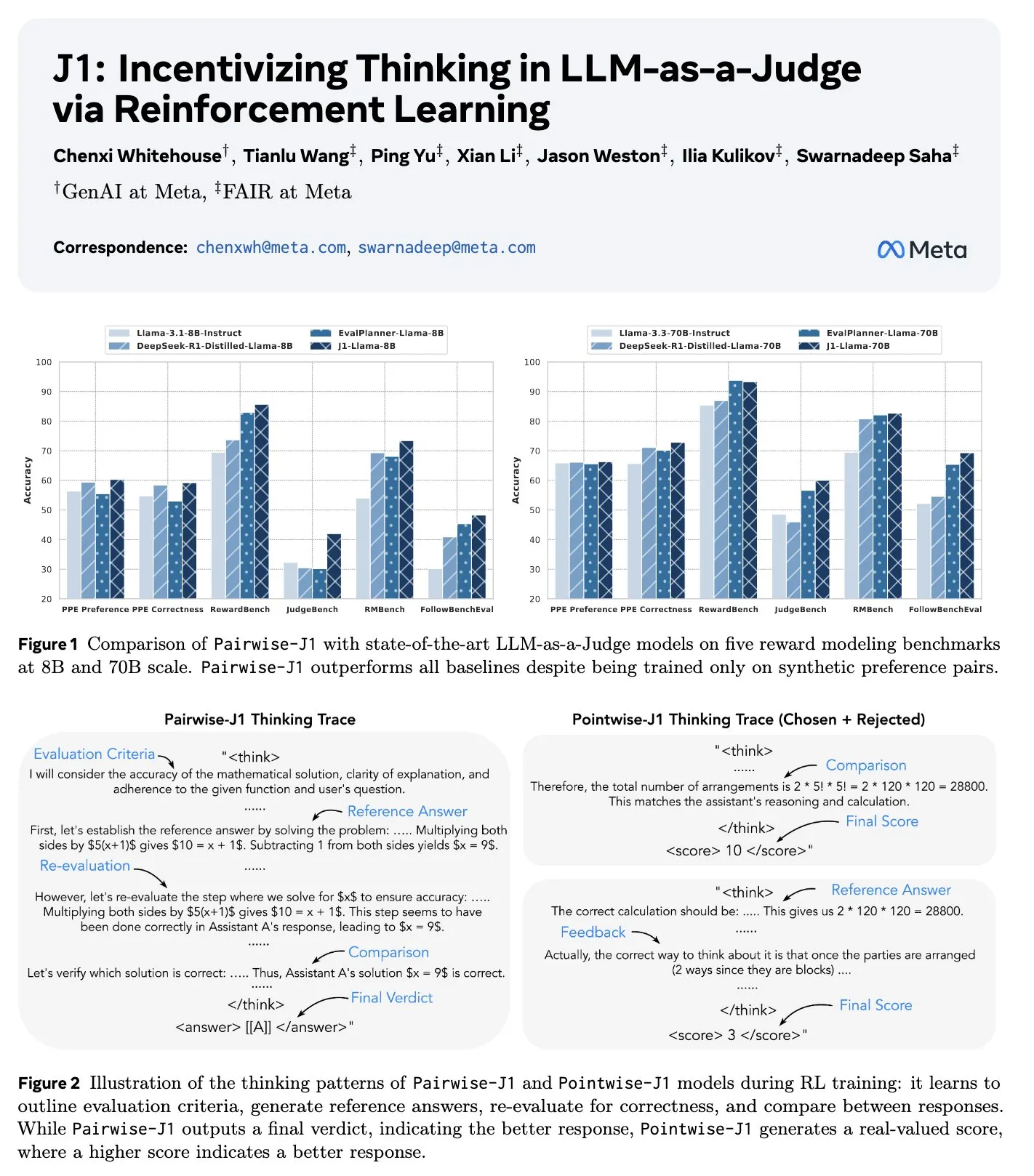
New paper J1: Incentivizing Thinking in LLM-as-a-Judge via RL: A new paper titled “J1: Incentivizing Thinking in LLM-as-a-Judge via RL” proposes a method to optimize the thinking process, scoring, and judgment of Large Language Models as evaluators (LLM-as-a-Judge) through reinforcement learning (specifically GRPO). This method can transform both verifiable and unverifiable prompt judgment tasks into verifiable tasks using only synthetic paired data. The study found that the J1 model outperforms baselines at both 8B and 70B scales and exhibits various thinking strategies, such as listing evaluation criteria, comparing with self-generated reference answers, and re-evaluating correctness. (Source: jaseweston, jaseweston)
Peking University and Renmin University jointly release Being-M0: A million-scale dataset-driven universal motion generation framework for humanoid robots: Zongqing Lu’s team at Peking University, in collaboration with Renmin University of China and others, has proposed a universal humanoid robot motion generation framework called Being-M0 and constructed MotionLib, the industry’s first million-scale motion generation dataset. This framework utilizes large-scale internet video data combined with an end-to-end text-driven motion generation model to achieve complex and diverse human motion generation. It can also retarget human motions to various humanoid robots like Unitree H1 and G1. Key innovations include the MotionLib dataset construction pipeline, a model that validates the feasibility of “big data + large models” in motion generation, and an innovative 2D lookup-free quantization framework called MotionBook, which addresses information loss issues in traditional VQ techniques for high-dimensional motion data compression. (Source: 量子位)
ByteDance releases WildDoc dataset to evaluate VLM capabilities in real-world document understanding: ByteDance has released a new Visual Question Answering (VQA) dataset called WildDoc on Hugging Face. The dataset aims to evaluate the understanding capabilities of Visual Language Models (VLMs) on documents in real-world scenarios. (Source: _akhaliq)
ICRA 2025 (IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation) agenda highlights: The 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) will be held in Atlanta, USA, from May 19-23. The conference will feature keynote speeches by Allison Okamura, Tessa Lau, Raffaello D’Andrea, and others, as well as key reports covering 12 areas including rehabilitation robotics, optimal control, human-robot interaction, soft robotics, field robotics, bio-inspired robotics, haptics, planning, manipulation, motion, safety and formal methods, and multi-robot systems. Additionally, there will be a science communication crash course, 59 workshops and tutorials, a robotics ethics forum, a forum for African scientists advancing robotics research, an undergraduate robotics education forum, and a community building day. (Source: aihub.org)

Paper LlamaDuo: LLMOps Pipeline for Seamless Migration from Service LLMs to Small-Scale Local LLMs: A paper accepted by the ACL 2025 main conference, “LlamaDuo: LLMOps Pipeline for Seamless Migration from Service LLMs to Small-Scale Local LLMs,” introduces an LLMOps pipeline designed to help users smoothly transition from using large service LLMs (e.g., via API calls) to using small-scale local LLMs. This research is a product of open-source and community collaboration, emphasizing the importance of flexibly switching and optimizing model deployment strategies in practical applications. (Source: algo_diver)

Tubi study: Tweedie regression outperforms weighted LogLoss in optimizing user engagement for video-on-demand: Research from video platform Tubi indicates that in optimizing video recommendation systems to enhance user engagement (such as watch time), a Tweedie regression model that directly predicts user watch time performs better than the traditional watch time-weighted LogLoss model. Experimental results show that Tweedie regression led to a +0.4% increase in revenue and a +0.15% increase in watch time. The study suggests that the statistical properties of Tweedie regression are more consistent with the zero-inflated and skewed distribution characteristics of watch time data. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

💼 Business
Lip-syncing app Hedra raises $32M Series A led by a16z: AI video generation startup Hedra announced it has closed a $32 million Series A funding round led by Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), with Matt Bornstein joining its board. Existing investors a16z speedrun, Abstract, and Index Ventures also participated in the round. Hedra focuses on generating expressive, controllable character dialogue videos, with its technology aimed at solving the challenges of lip synchronization and emotional expression in AI-generated videos. (Source: op7418)
US, Saudi Arabia, and UAE reach AI cooperation deal involving 5GW data centers and chip supply, aiming to exclude Chinese influence: The United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates have reached a significant AI cooperation agreement involving the construction of 5GW data centers, with US companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and Qualcomm supplying a large number of advanced AI chips (such as NVIDIA’s Blackwell chips). Saudi Arabia’s newly established AI company, Humain, will be the core executing party. This move is seen as a strategic deployment by the US to promote its AI technology stack and accelerate infrastructure construction in the Middle East, thereby securing allies while limiting China’s regional AI infrastructure investment and technological influence. The new agreement repeals some previous restrictions on AI chip exports to the Middle East but simultaneously strengthens global warnings against the use of Chinese chips like Huawei’s Ascend. (Source: dylan522p, 36氪, iScienceLuvr)

Restaurant SaaS company Owner raises $120M to become a unicorn, utilizing AI to create “AI Restaurant Executives”: Owner, a company providing full-stack digital solutions for independent restaurants, recently completed a $120 million Series C funding round, valuing it at $1 billion. Owner offers restaurants website/app development, integrated ordering and delivery, SEO optimization, and marketing automation services for a fixed monthly fee, serving over 10,000 restaurants. Its 2025 AI strategy includes launching “AI Restaurant Executives” (AI CMO, CFO, CTO) to manage AI and human employees, and building conversational AI Agents to enhance service efficiency. This funding round was co-led by Redpoint Ventures and Altman Capital, highlighting AI’s potential to reshape the value of traditional SaaS. (Source: 36氪)
🌟 Community
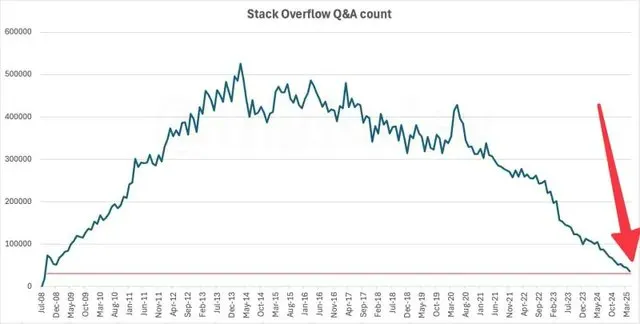
Stack Overflow activity plummets to 2009 levels, AI likely the main cause: Data shows that the monthly number of questions on the well-known developer Q&A community Stack Overflow has fallen to levels seen when it first launched in 2009. This phenomenon has sparked discussions about the impact of AI on traditional developer communities. Many believe that with the rise of AI programming assistants like ChatGPT, developers are increasingly turning to AI for direct questions and code solutions rather than asking on communities like Stack Overflow and waiting for human answers, which may have led to the sharp decline in community activity. (Source: zachtratar, karminski3)
AI in the workplace triggers a sense of “professionalism” crisis, employees feel a greater need for human touch in the AI era: With the popularization of AI in the workplace, many employees feel their professional skills are being “deconstructed.” Leaders tend to have AI revise employee work, even believing AI is superior to human employees, leading to feelings of disrespect and a crisis of being replaced. Research shows that employees can distinguish between emails written by the CEO лично and by AI, and when they believe content is AI-generated, even if written by a human, their evaluation is lower. This reflects a preference for human creation and concerns about over-reliance on AI. Meanwhile, McKinsey research indicates that 54% of employees who resigned did so because they felt undervalued, and 82% of employees believe that the AI era requires more interpersonal connection and emotional care. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)

Chinese youth embrace AI companions, sparking societal concerns about low fertility rates: The Economist reported on the rising phenomenon of young people in China forming relationships and friendships with AI. AI companion apps like “Maoxiang” and “Xingye” are seeing continuous user growth, with users creating virtual characters to meet emotional needs. Technological advancements enable AI to simulate emotions and empathy, and factors such as high life pressure, reduced social time, and declining marriage rates among young people are driving this trend. However, the government is concerned that AI companions may exacerbate the already severe problem of low fertility rates (total fertility rate was only 1.0 in 2024). (Source: dotey)

AI assistance may become the new normal in education, but professors’ over-reliance on ChatGPT sparks student dissatisfaction and reflection: A student at Northeastern University sued the school for a tuition refund because a professor used ChatGPT to generate courseware, an incident that has sparked widespread discussion about the role of AI in higher education. Students believe high tuition fees should pay for human professional teaching rather than algorithmically generated content, worrying that AI is replacing professors’ thinking and feedback. Professors, on the other hand, view AI as a tool to improve efficiency and cope with heavy workloads. Education experts point out that the key lies in using AI responsibly, augmenting rather than replacing human creativity and oversight, cultivating students’ ethical guidelines for the AI era, and ensuring AI-generated content undergoes professional editing and confirmation. (Source: 36氪, Reddit r/ChatGPT)

Salesforce CEO claims Microsoft and OpenAI relationship is fundamentally broken and irreparable: Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff stated in an interview that the partnership between Microsoft and OpenAI has suffered an “irreparable rupture.” He pointed out that Microsoft’s Copilot has disappointed customers, resembling an inefficient Clippy, and that OpenAI’s CFO did not mention Microsoft software or Azure in a technology architecture diagram, confirming the rift between the two. Benioff believes Microsoft is essentially a reseller of ChatGPT, its AI strategy is limited, and it is trying to build its own models through “Project Prometheus.” He also mentioned that the rise of open-source models like DeepSeek is pushing the industry towards MOE architecture, reducing the cost of using models and dismantling the business logic of “model monopoly.” (Source: 36氪)

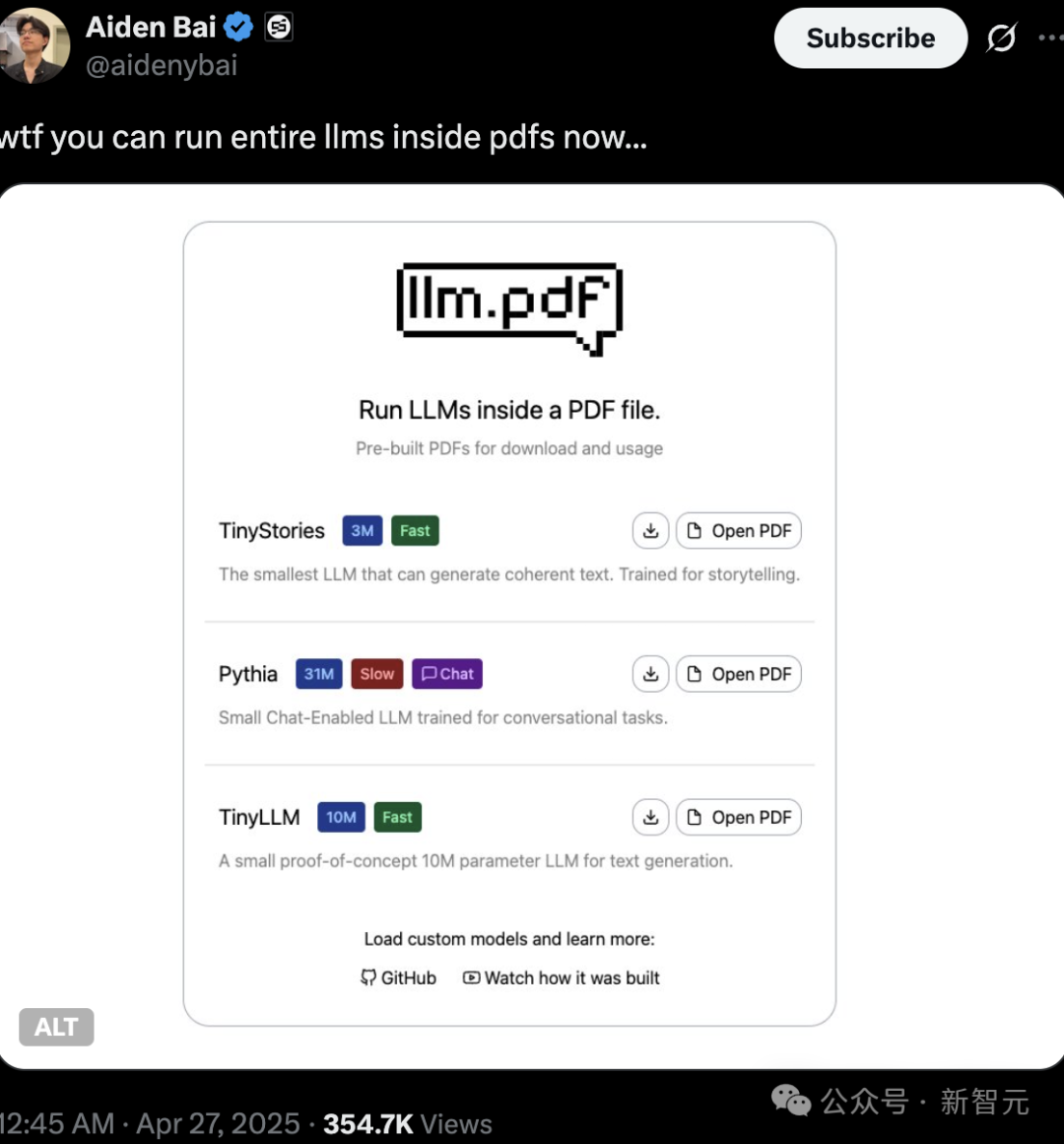
Authenticity and copyright of AI-generated content draw attention, running LLMs and Linux in PDFs showcases technological potential: Tech enthusiasts recently demonstrated the ability to run small language models (like TinyStories, Pythia, TinyLLM) and even Linux systems directly within PDF files, utilizing PDF’s support for JavaScript. This “black magic” operation sparked heated discussions among netizens and highlighted the trend of AI model miniaturization and edge deployment. Simultaneously, issues concerning the copyright, authenticity, and “deepfakes” of AI-generated content are receiving significant attention. Zhang Yaqin pointed out that AI risks include deepfakes, hallucinations, and toxic information, which require high vigilance and strengthened AI alignment with human values and ethical regulation. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)
💡 Other
Theta releases CUB benchmark: “The final human frontier” for evaluating computer and browser use agents: Theta has launched a new benchmark test called CUB (Computer and Browser Use Agents), touted as “the final human frontier” for agents using computers and browsers. Such benchmarks aim to assess the ability of AI agents to simulate human use of computers and browsers to complete complex tasks. However, multiple benchmarks have already claimed to be the “final human frontier,” sparking discussion about whether the naming might be overly exaggerated. (Source: _akhaliq, DhruvBatraDB)
AI accused of generating vulgar content, raising concerns about model abuse and ethical boundaries: Instances have appeared on social media of users utilizing AI image generation tools (such as ChatGPT’s DALL-E 3) to create vulgar or satirical images (e.g., “Shittington Bear”). This has raised concerns about the potential for AI tools to be misused for generating inappropriate content, infringing copyright (such as parodying well-known cartoon characters), and challenging societal ethical boundaries. Although AI platforms typically have content filters, users may still bypass restrictions through clever prompts. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)

Study shows AI has limitations in mimicking CEO communication style, employees trust humans more: Harvard Business School research found that employees were about 59% accurate in distinguishing between messages written by AI and by company CEO Wade Foster (Zapier CEO). More importantly, once employees believed a message was AI-generated, even if it was actually written by the CEO, their evaluation of it was lower. Conversely, content believed to be written by the CEO received higher ratings, even if it was AI-generated. This indicates that people have greater trust in and perceive more value from human communication than AI. The study advises leaders to maintain transparency when using AI for communication, avoid using it for very personal replies, and rigorously review AI-generated content. (Source: 36氪)
