Keywords:AlphaEvolve, DeepSeek V3, GPT-4.1, Speech-02, Claude Model, Falcon-Edge, BLIP3-o, AM-Thinking-v1, Gemini-powered Evolutionary Coding Agent, Hardware-software co-design to reduce large model costs, Zero-shot voice cloning technology, Extreme reasoning capability, 1.58-bit BitNet architecture
🔥 Highlights
DeepMind introduces AlphaEvolve: A Gemini-powered evolutionary coding agent, advancing algorithm discovery: AlphaEvolve combines the creativity of Gemini models with an automated evaluator, utilizing an evolutionary framework to optimize algorithms. It has achieved breakthroughs in multiple fields, such as completing 4×4 complex matrix multiplication with 48 scalar multiplications, improving upon Strassen’s algorithm; and discovering 593 outer sphere configurations in 11-dimensional space, advancing the 300-year-old “kissing number problem.” Additionally, AlphaEvolve has optimized Google data center scheduling (saving 0.7% of computing resources), next-generation TPU design (removing redundant bits), and AI model training (accelerating key kernels by 23%), among others. Fields Medalist Terence Tao also participated in exploring its mathematical applications. (Source: DeepMind)

DeepSeek V3 Paper Explained: Co-design of Software and Hardware Reduces Cost and Power Consumption of Large Models: The DeepSeek team released a paper detailing how DeepSeek-V3 achieves cost-effectiveness in large-scale training and inference through software-hardware co-design. Core technologies include: 1) Memory Optimization: Adopting Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) to compress key-value caches, and FP8 mixed-precision training to reduce memory consumption. 2) Computation Optimization: Applying Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models, activating only a portion of parameters, combined with FP8 training, significantly reducing computational costs. 3) Communication Optimization: Utilizing a multi-plane fat-tree network topology and Dual Micro-batch Pipelining (DualPipe) technology to reduce latency and improve GPU utilization. 4) Inference Acceleration: Introducing a Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) framework to predict and validate multiple candidate tokens in parallel, enhancing generation speed. The paper also presents five outlooks for future AI hardware design, including low-precision computation support, expansion and fusion, network topology optimization, memory system optimization, and robustness & fault tolerance. (Source: arXiv)

OpenAI GPT-4.1 Model Officially Launched on ChatGPT, Directly Selectable by Users: OpenAI announced that the GPT-4.1 model is now available in ChatGPT. Plus, Pro, and Team users can access it via the model selector, while Enterprise and Education users will gain access later. GPT-4.1 mini will also replace GPT-4o mini for all users. GPT-4.1 has garnered attention for its excellent performance in coding tasks and instruction following. The previous API version supported a context window of up to 1 million tokens. However, some users’ tests revealed that the context length of the GPT-4.1 version in ChatGPT still seems to be 128k, not reaching the API version’s 1M, leading to some disappointment. (Source: OpenAI Developers)

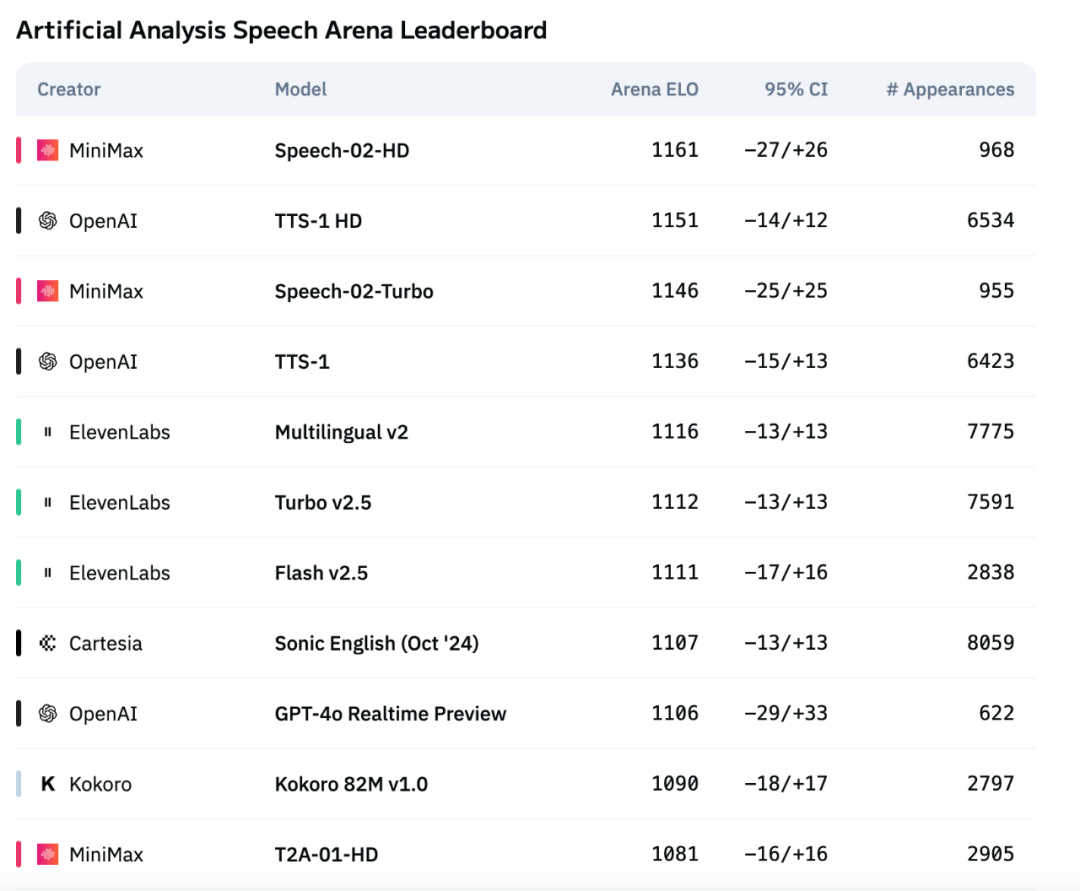
MiniMax’s New-Generation Speech Model Speech-02 Tops Artificial Analysis Speech Benchmark: MiniMax’s latest text-to-speech (TTS) model, Speech-02, achieved the highest ELO rating on the internationally authoritative Artificial Analysis Speech Arena benchmark, surpassing similar products from OpenAI and ElevenLabs. The model performs excellently on key metrics such as Word Error Rate (WER) and Speaker Similarity (SIM), especially demonstrating local advantages in Chinese and Cantonese processing. The core innovations of Speech-02 lie in achieving true zero-shot voice cloning (requiring only a few seconds of reference audio, without text) and adopting a new Flow-VAE architecture, enhancing the naturalness and emotional expressiveness of speech generation, supporting 32 languages. Its cost is also highly competitive, at about 1/4 of ElevenLabs’ competing product. (Source: 机器之心)
🎯 Trends
New Version of Anthropic’s Claude Model May Feature “Extreme Reasoning” Capability: According to The Information and community observations, Anthropic may release new versions of its Claude Sonnet and Claude Opus models in the coming weeks, with the main highlight being “Extreme reasoning” capability. This feature allows the model to pause, re-evaluate, and adjust its strategy when encountering difficult problems, rather than directly providing an answer. In tasks like code generation, the model can automatically test and correct errors. This dynamic loop of reasoning and tool use aims to enable the model to handle complex problems more intelligently, reduce reliance on human supervision, and more closely resemble the thinking process of a human collaborator. Some users have discovered that Anthropic is testing a model named Claude Neptune (possibly Claude 3.8), which supports a 128k token context. (Source: 量子位)
TII Releases Falcon-Edge Series of Efficient Bitnet Models and onebitllms Fine-tuning Toolkit: The Technology Innovation Institute (TII) has released Falcon-Edge, a series of highly compressed language models based on the BitNet architecture, characterized by being powerful, versatile, and fine-tunable. Concurrently, they have open-sourced onebitllms, a lightweight Python toolkit (installable via pip) specifically designed for fine-tuning or continuing pre-training of these 1.58-bit models. This initiative aims to lower the barrier to using large models and promote the development and application of 1-bit LLM technology. (Source: younes)

Hugging Face Transformers Library Undergoes Major Upgrade, Becoming Central Standard for Model Definition: Hugging Face announced that its Transformers library is undergoing significant adjustments, aiming to become the central standard for model definition across different backends and runtimes. Through collaborative efforts with numerous ecosystem partners such as vLLM, LlamaCPP, SGLang, MLX, DeepSpeed, Microsoft, and NVIDIA, they are promoting the standardization of model code to bring greater consistency and reliability to the entire AI ecosystem. This move has been widely praised by the community as an important step in advancing open-source AI development. (Source: Arthur Zucker)

Salesforce Releases BLIP3-o on Hugging Face: A Fully Open-Source Unified Multimodal Model Series: Salesforce has launched the BLIP3-o model series, a family of fully open-source unified multimodal models. This series covers model architecture, training methods, and datasets, aiming to advance the development and application of multimodal AI technology. The release of BLIP3-o provides researchers and developers with powerful multimodal processing tools and resources. (Source: AK)

NVIDIA Showcases Use of Synthetic Data to Advance Full Self-Driving Technology: NVIDIA released a new video demonstrating how it utilizes synthetic data to accelerate the research and development of Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology. By generating large-scale, diverse virtual driving scenarios and data, NVIDIA can more efficiently train and validate its autonomous driving algorithms, overcoming the limitations of real-world data collection and pushing autonomous driving technology towards greater safety and reliability. (Source: SawyerMerritt)
A-M-team Releases 32B Inference Model AM-Thinking-v1, Surpassing DeepSeek-R1 in Some Performance Metrics: Chinese research team A-M-team has open-sourced its 32B parameter inference model, AM-Thinking-v1, on Hugging Face. The model demonstrates outstanding performance in tasks such as mathematical reasoning (AIME series score of 85.3) and code generation (LiveCodeBench score of 70.3). It is claimed to surpass DeepSeek-R1 (671B MoE) in these specific benchmarks and approach larger models like Qwen3-235B-A22B. The team focuses on optimizing the inference capabilities of 32B dense models through post-training schemes (including cold-start SFT, pass-rate guided data filtering, and dual-stage RL), aiming to explore pathways to strong inference under limited computational resources and open-source data conditions. (Source: AI科技评论)

Marigold Update: Stable Diffusion Model Transformed into Depth Estimator, Supports Single-Step Inference and High Resolution: The Marigold project has released a major update. This technology can transform a Stable Diffusion 2 model into an advanced depth estimator through a small number of synthetic samples and a short training period (2-3 days on 1 GPU). New features include: single-step fast inference, support for new modalities, high-resolution output, Diffusers library support, and new demos. (Source: Anton Obukhov)
Qwen3 Series Models Show Strong Performance in Open Source Community, NVIDIA Selects it as Base for OpenCodeReasoning: Alibaba’s Qwen3 series models continue to gain attention and application in the open-source community. NVIDIA’s newly open-sourced OpenCodeReasoning series models (including 7B, 14B, 32B specifications) have chosen Qwen as their foundation. Qwen3 is favored by developers for its complete range of versions, continuous updates, native support for mixed inference modes, and a thriving ecosystem (over 300 million global downloads, over 100,000 derivative models). Recent updates include the edge-side multimodal model Qwen-omini 3B, collaboration with Unsloth to improve fine-tuning efficiency, release of detailed deployment hyperparameter recommendations, support for generating real-time web page previews, provision of multiple quantization versions, and publication of a technical report. (Source: AI前线)
Hugging Face Accelerate v1.7.0 Released, Supports Regional Compilation and QLoRA for FSDPv2: Hugging Face Accelerate version 1.7.0 has been officially released. Highlights of this version include: Regional compilation implemented by @IlysMoutawwakil, improving compilation efficiency and flexibility; Layerwise casting hook contributed by @RisingSayak, a widely used feature in the diffusers library; and QLoRA support for FSDPv2 implemented by @winglian, further optimizing large-scale model training. (Source: Marc Sun)

Llamafile 0.9.3 Released, Adds Support for Qwen3 and Phi4 Models: Llamafile has released version 0.9.3, which adds support for the recently popular Qwen3 and Phi4 series models. Llamafile aims to simplify the distribution and execution of LLM applications by packaging model weights and necessary code into a single executable file, enabling convenient deployment across multiple operating systems. (Source: Phoronix)
Tencent Releases HunyuanImage 2.0, a Large Image Model: Tencent has officially released a new version of its Hunyuan large image model – HunyuanImage 2.0. This update is expected to bring improvements in image generation quality, controllability, and understanding of complex instructions. Users can learn more about the specific technical details and improvements through official channels. (Source: Hunyuan)

Ollama v0.7 Released, Enhancing Local Large Model Running Experience: Ollama has released v0.7, continuing its commitment to simplifying the process of running large language models on local devices. The new version may include performance optimizations, new model support, or user experience improvements. Users can visit the official website or GitHub for detailed update logs and downloads. (Source: ollama)
llama.cpp Merges PDF Input Functionality, Supports Direct Processing of PDF Documents: The llama.cpp project recently merged a significant update, adding direct input support for PDF files. This means users can now more conveniently use PDF document content as input for local large language models powered by llama.cpp for processing, analysis, or Q&A, expanding its application scenarios. This feature is implemented via an external JS package in the built-in web frontend, without adding to core maintenance burden. (Source: GitHub)
Microsoft Copilot Launches 4o Image Generation Feature, Enhancing Visual Effects and Text Consistency: Microsoft’s AI assistant, Copilot, has now integrated OpenAI’s GPT-4o model’s image generation capabilities. This update aims to provide sharper visual effects, more consistent text generation, and support for various styles from photorealistic to fun cartoons. Users can experience 4o-powered image creation through Copilot. (Source: yusuf_i_mehdi)

NVIDIA DRIVE Labs Discusses the Future of Mapless Driving, Reducing Reliance on HD Maps: NVIDIA DRIVE Labs’ latest video discusses the future of mapless driving. While HD maps are crucial for autonomous driving, their cost and maintenance challenges limit deployment. NVIDIA is reducing reliance on HD maps through innovations such as eliminating information bottlenecks, improving task accuracy, and accelerating model training and inference times, pushing the boundaries of autonomous driving technology. (Source: NVIDIA DRIVE)
Dolphin 3.2 (Trained on Qwen3) Will Offer System Prompt Toggles for Enhanced User Control: The upcoming Dolphin 3.2 model, trained on Qwen3, will introduce three system prompt toggles: /no_think (possibly to reduce redundant thinking steps), /uncensored (possibly to reduce content censorship), and /china (possibly for China-specific contexts or services). These toggles aim to give users greater ownership and control over their model deployments. (Source: cognitivecompai)

🧰 Tools
Runway Introduces “References” Feature to Learn and Apply Specific Techniques or Styles to New Creations: Runway has added a new feature called “References,” allowing users to show the platform a specific technique or artistic style and then apply it as a reference to any new generated content. This feature provides users with finer control over style, making AI-assisted creation more personalized and targeted. User Cristobal Valenzuela has launched a call for submissions, encouraging the community to share original cases using this feature, and will offer a free one-year Unlimited plan to the 5 most creative cases. (Source: c_valenzuelab)

DSPy: A Minimalist LLM Programming Framework for Rapid Iteration: The DSPy framework is gaining attention for its minimalist design. Developers claim that most of its core functions (Module or Optimizer) can be implemented with just one line of code, aiming to help users quickly try and iterate on ideas. Unlike some tools that require extensive boilerplate code and complex concepts, DSPy emphasizes ease of use and efficiency. User feedback indicates that one can quickly get started by reading the introductory documentation and optimize models within a short time using the framework, although iterative optimization with SOTA models might incur some costs. (Source: lateinteraction)
Unsloth AI Extends to TTS and Audio Model Fine-tuning, Increasing Speed and Reducing VRAM Usage: Unsloth AI announced that its optimization technology now supports fine-tuning of Text-to-Speech (TTS) and audio models. Users can use free Colab notebooks to train, run, and save models like Sesame-CSM and OpenAI Whisper. Unsloth claims its technology can increase TTS training speed by 1.5x while reducing VRAM (Video RAM) usage by 50%. Relevant documentation and Colab notebooks are available on their website. (Source: Unsloth AI)
Modal Powers Amazon’s 30 Million Review Embedding Task, Achieving Hour-Level Processing with L40S GPUs: Modal platform demonstrated its capability to horizontally scale the processing of large-scale embedding tasks on L40S GPUs. In a demo case, Modal successfully completed the embedding of 30 million Amazon reviews within an hour. This was made possible by the Modal team’s updated scalable generation system, which simplifies and enhances the efficiency of large-scale parallel processing. (Source: charles_irl)

Lovart AI: An Emerging AI Visual Design Agent Integrating Multiple Top-Tier Models: An AI visual design agent named Lovart is gaining attention. It can complete professional visual design tasks such as posters, brand VI, and storyboards through natural language instructions. Lovart’s core capability lies in its multi-model fusion scheduling, integrating various top-tier models like GPT image-1, Flux pro, OpenAI-o3, Gemini Imagen 3, Kling AI, Tripo AI, and Suno AI. It also has built-in professional-grade editing tools (like layers, masks, text fine-tuning) and supports image-text separation and layered editing. The product is independently operated by Liblib’s overseas subsidiary, aiming to provide a one-stop, highly controllable AI design experience. (Source: 量子位)
OpenHands 0.38.0 Released: Native Windows Support and Chrome Extension Enhance Usability: OpenHands released version 0.38.0, bringing several important updates. These include: native Windows support (no WSL required), making it easier for Windows users; browser screenshot functionality; and more flexible sandbox customization capabilities. Additionally, a Chrome extension has been released, allowing users to launch OpenHands from GitHub with one click, further simplifying the operational workflow. (Source: All Hands AI)
Tensorlake Cloud Launched, Enhancing Document Extraction and Workflow Building Capabilities: Tensorlake announced the launch of Tensorlake Cloud, aimed at optimizing document extraction and workflows to support the building of agent applications and complex business workflows. The platform utilizes advanced document layout understanding models (trained on real-world data like ACORD forms, bank statements, research reports) and table extraction models to transform unstructured documents into clean, structured data. It is particularly suitable for processing complex and dense tables, addressing the shortcomings of visual language models (VLMs) in this area. (Source: Tensorlake)
Patronus AI Introduces Percival: An Agent Specialized in Debugging and Improving AI Agents: Patronus AI has released a new tool, Percival, an AI agent designed specifically for debugging and improving other AI agents. Percival can instantly analyze complex agent traces, identify up to 60 different failure modes, and automatically suggest prompt fixes to enhance performance. The tool addresses key challenges like “context explosion” (where agents process millions of tokens) and supports domain adaptation for specific use cases and complex multi-agent orchestration. (Source: Weaviate Podcast)

Replit Integrates Semgrep for “Safe Vibe Coding,” Automatically Scanning for Vulnerabilities: Replit announced a partnership with Semgrep to launch “Safe Vibe Coding.” Now, every time a user deploys code on Replit, Semgrep will automatically run a security scan to help discover and fix potential vulnerabilities, preventing accidental exposure of sensitive information like API keys. This move aims to enhance security when using AI-assisted coding (such as code generated by LLMs). (Source: amasad)

Cursor AI 0.50 Version Released, Bringing Major Updates: AI-assisted programming tool Cursor has released its 0.50 version, dubbed “the biggest version update ever.” The new version is expected to include multiple feature enhancements and experience optimizations aimed at further improving developers’ coding efficiency and the fluency of collaboration with AI. Specific update details can be found in the official release notes. (Source: eric zakariasson)

OpenMemory MCP: Localized Memory Management Server Supporting Cross-Application Context Sharing: OpenMemory MCP is a memory management server designed to enhance the productivity of AI applications. It allows users to share context between different applications (like Cursor and Claude Desktop) and utilizes PostgreSQL and Qdrant to store and index data locally, ensuring data privacy. The tool supports semantic search and provides a dashboard for managing memory and application access, addressing the issue of context loss across sessions. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)

Hugging Face Inference Endpoint Combined with vLLM and Gradio for Fast Whisper Transcription: Hugging Face demonstrated how to use its Inference Endpoint service, in conjunction with the vLLM project and Gradio interface, to deploy OpenAI’s Whisper model for extremely fast speech transcription. This combination leverages open-source tools from the AI community to provide users with an efficient and user-friendly speech-to-text solution. (Source: Morgan Funtowicz)
A.I.T.E Ball: A Self-Contained AI Magic 8-Ball Based on Orange Pi and Gemma 3 1B: A developer showcased a fully self-contained (no internet required) AI-powered Magic 8-Ball project – the A.I.T.E Ball. The device runs on an Orange Pi Zero 2W, uses whisper.cpp for text-to-speech, and llama.cpp to run the Gemma 3 1B model for Q&A. This demonstrates the potential for localized AI applications on low-power hardware. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

OWL Agent: Open-Source General-Purpose Agent with Integrated MCPToolkit: The open-source OWL agent project now has built-in MCPToolkit support. Users can easily connect to MCP servers like Playwright, desktop-commander, or custom Python tools, and OWL will automatically discover and call these tools within its multi-agent workflow, enhancing its versatility and task execution capabilities. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

ElevenLabs Launches SB-1 Infinite Soundboard: Combining Sound Effects, Drum Machine, and Ambient Noise Generation: ElevenLabs has released the SB-1 Infinite Soundboard, a tool that integrates a soundboard, drum machine, and an endless ambient noise generator. Users can describe the sound effects they want, and SB-1 will use its Text-to-SFX model to generate these sounds, offering new possibilities for audio creation. (Source: ElevenLabs)
Anytop Project: New AI Animation Advances Bring Unseen Creatures to Life, Supporting Motion Learning and Transfer: Two Minute Papers introduced the Anytop project, an AI animation technology capable of generating realistic movements for creatures never seen before (including dinosaurs, exotic insects, etc.). The AI can not only generate movements independently but also allow different creatures to learn and adapt each other’s movements (e.g., a dinosaur learning to stand on one leg like a flamingo). It achieves generalization to unknown morphologies by understanding the semantic similarity of body parts (e.g., the general concept of arms and legs). Furthermore, the system can understand the semantics of actions (e.g., attack, relax) and display actions of similar concepts across different animals, even completing incomplete input actions. (Source: )

Sketch2Anim: AI Transforms Stick Figure Sketches into Full 3D Animations: Another technology introduced by Two Minute Papers, Sketch2Anim, can transform simple line sketches drawn by users (indicating action paths) into complete 3D character animations. The AI can understand the 3D intent behind 2D sketches (e.g., distinguishing between a forward punch and a sideways punch), addressing the limitations of previous similar technologies that could only understand instructions at a 2D level. This allows non-professionals to quickly create 3D animations through simple drawing. (Source: )

📚 Learning
DeepSeek Releases V3 Model Paper, Sharing Scaling Challenges and Thoughts on AI Hardware Architecture: The DeepSeek team has released a paper on their DeepSeek-V3 model on Hugging Face. The paper delves into the challenges encountered during the scaling of large language models and offers thoughts and insights on the future direction of AI hardware architecture. This provides valuable reference for researchers and developers to understand the bottlenecks in large-scale model training and deployment, and how to optimize through hardware and software co-design. (Source: Adina Yakup)
Free Model Context Protocol (MCP) Course Released to Help Build AI Applications with External Data and Tools: Ben Burtenshaw announced the launch of a free MCP (Model Context Protocol) course. The course aims to help learners go from beginner to expert in understanding how MCP works, how to connect LLMs to MCP servers, and how to use MCP to deploy AI agent applications, thereby leveraging external data and tools to enhance AI application capabilities. (Source: Ben Burtenshaw)

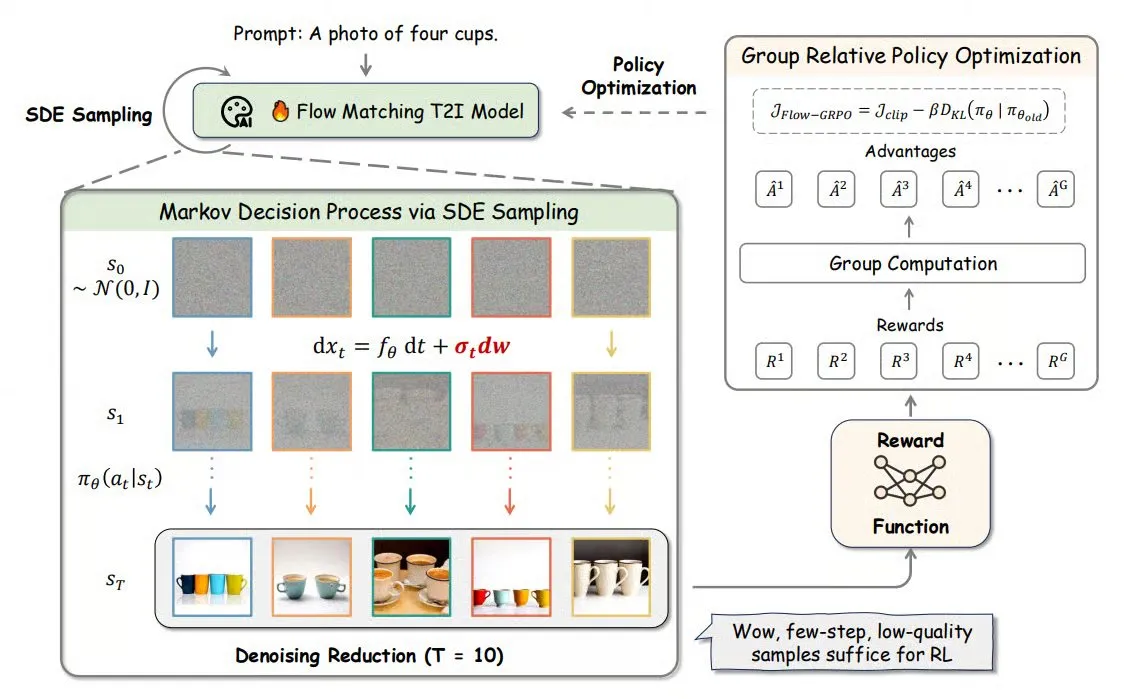
Flow-GRPO: Introducing Online Reinforcement Learning to Flow Matching Models, Improving Image Generation Accuracy: Flow-GRPO is a new method that, for the first time, applies online reinforcement learning (RL) to flow matching models. It achieves this through two innovative strategies: 1) ODE to SDE Conversion: Transforms the deterministic process of flow models based on ordinary differential equations (ODEs) into stochastic differential equations (SDEs), introducing the randomness required for RL. 2) Denoising Reduction for Accelerated Training: Reduces denoising steps during training and uses full steps during inference. With Flow-GRPO, the accuracy of flow models in image generation tasks has increased to over 92%. (Source: TheTuringPost)
ICML 2025 Paper PENCIL: Alternating “Reasoning-Erasure” Achieves New Paradigm for Deep Thinking in Large Models: Chenxiao Yang and others from Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago proposed PENCIL (Pondering with Erasure Net for Contextual Inference Learning), a new paradigm for deep thinking in large models by alternately “generating” and “erasing” intermediate results. This method draws on logical rewriting rules and functional programming memory management, dynamically erasing intermediate steps that are no longer needed. It effectively solves problems faced by traditional long CoT (Chain-of-Thought) such as exceeding context window limits, difficulty in information retrieval, and decreased generation efficiency. Theoretically, PENCIL can simulate any Turing machine computation with optimal space and time complexity, solving all computable problems. Experiments show that PENCIL significantly outperforms traditional CoT on tasks like 3-SAT, QBF, and Einstein’s puzzle. (Source: 机器之心)

ICML 2025 Paper MemVR: Simulating Human “Look Twice” Mechanism to Mitigate Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Models: Researchers from HKUST (Guangzhou) and other institutions proposed MemVR (Memory-space Visual Retracing), a method that mitigates hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by simulating the human strategy of double-checking uncertain memories. MemVR uses visual tokens as supplementary evidence. In intermediate layers where the model encounters forgetting issues during inference, it “retrieves” visual knowledge again through a feed-forward network (FFN) to calibrate predictions. The method designs a dynamic triggering mechanism that selects trigger layers based on the uncertainty of outputs from different layers. Experiments show that MemVR achieves significant effects on multiple hallucination evaluation benchmarks and general benchmarks, and has efficiency advantages over other methods. (Source: PaperWeekly)

SIGIR 2025 Paper PaRT: Personalized Real-time Retrieval Enhances Proactive Social Chatbot Experience: Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China and other institutions proposed PaRT (Proactive Social Chatbots with Personalized Real-time ReTrieval). This method aims to enhance the conversational experience of proactive social chatbots by combining personalization-driven and intent recognition-guided query rewriting with real-time retrieval. The PaRT system includes three modules: personalized user profile construction, intent recognition and query rewriting, and real-time retrieval-enhanced generation. It can proactively initiate or switch topics based on user interests and conversation context, providing more natural and informative responses. Both offline experiments and online A/B testing show that this method can effectively improve the personalization, richness, and average conversation duration of responses. (Source: PaperWeekly)

ICML 2025 Paper PreSelect: Efficient Pre-training Data Selection Scheme Based on Predictive Strength: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and vivo AI Lab proposed the PreSelect data selection method. By introducing the concept of “Predictive Strength,” it quantifies the contribution of data to a model’s specific capabilities. This method evaluates data value by the consistency between the score rankings of different models on benchmark tests and their Loss rankings on the data. It uses a lightweight fastText classifier for approximate scoring, enabling efficient selection from large-scale data. Experiments show that PreSelect can improve data efficiency by 10 times. Data selected by PreSelect significantly outperforms various baseline methods when training models, covers a broader range of high-quality content sources, and reduces sample length bias. (Source: 量子位)

AI Evals Course Invites 12 Guests to Share Evaluation Frameworks and Practices: Hamel Husain’s AI Evals course announced its lineup of 12 guest lecturers, including JJ Allaire, creator of the inspect framework, and Charles Frye, developer advocate at Modal. The course will delve into various aspects of AI evaluation, including evaluation frameworks, creation of custom annotation applications, and model evaluation practices, aiming to equip participants with key skills and tools for assessing AI system performance. (Source: Hamel Husain)

FedRAG Tutorial Released: A Beginner’s Guide to Building and Fine-tuning RAG Systems: The FedRAG project has released new tutorial notebooks and accompanying videos to help users quickly get started with the library. The tutorial demonstrates how to build a RAG system using Hugging Face integration, store nodes using an in-memory knowledge base, define SentenceTransformer (Dragon+) as the retriever, define a pre-trained model (e.g., Qwen2.5-0.5B) as the generator, and centrally fine-tune the retriever and generator using LSR and RALT trainers. (Source: nerdai)

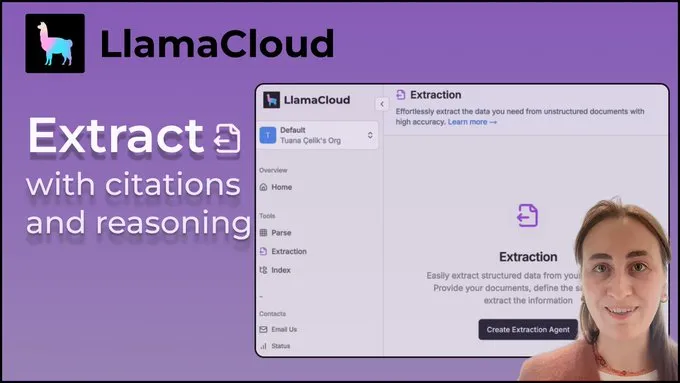
LlamaIndex Releases Tutorial: Implementing Citations and Reasoning in LlamaExtract: The LlamaIndex team released the latest code walkthrough by @tuanacelik, demonstrating how to implement citation and reasoning functionalities in LlamaExtract. The tutorial covers: how to define a custom schema to tell the LLM what to extract from complex data sources, and how to add citations. This feature aims to help users build multi-step AI agents capable of accurately and verifiably extracting structured information from large volumes of source documents. (Source: LlamaIndex 🦙)
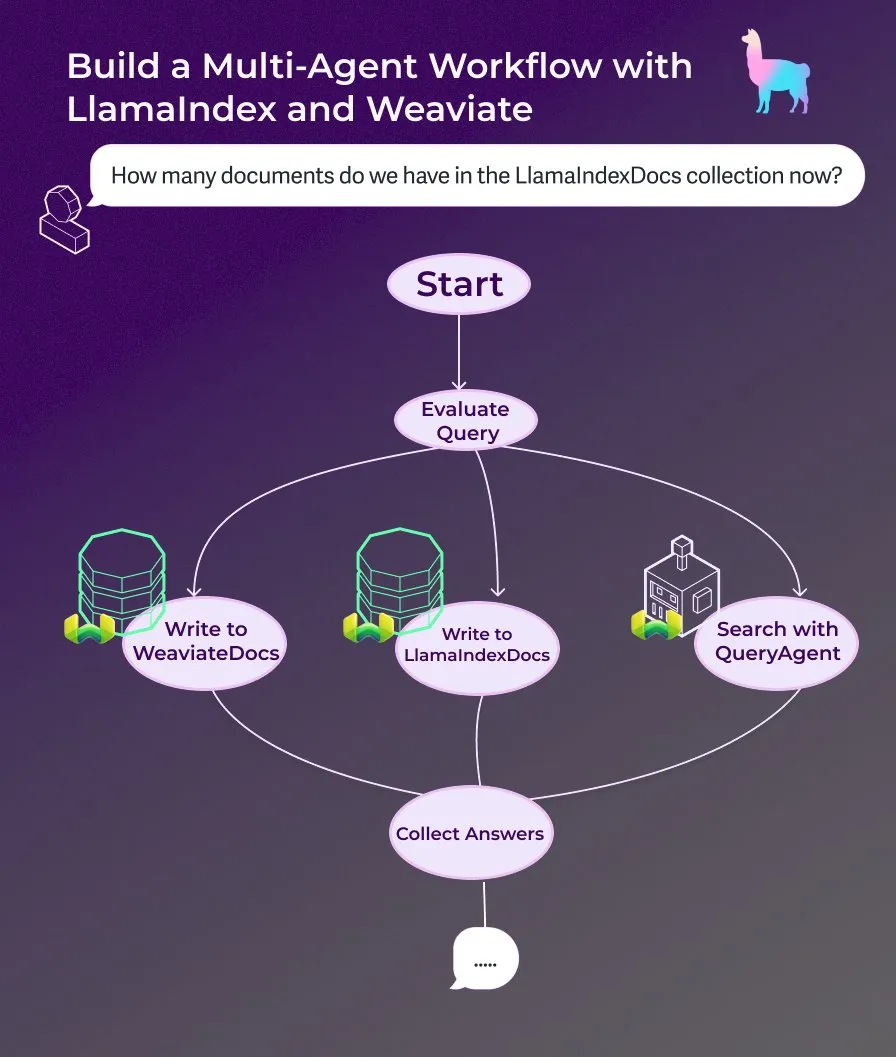
LlamaIndex Releases Tutorial: Building a Multi-Agent Document Assistant with Event-Driven Agent Workflows: LlamaIndex has released a new walkthrough tutorial demonstrating how to build a multi-agent document assistant using event-driven agent workflows. The assistant can write web content to LlamaIndexDocs and WeaviateDocs collections, use an orchestrator to decide when to call the Weaviate QueryAgent for search and aggregation, utilize structured output for query classification, and optionally use a FunctionAgent. (Source: LlamaIndex 🦙)
Modular Publishes Internal Tech Talk on Mojo Compiler, Discussing Mojo and GPU Architecture: Modular has begun sharing its internal tech talks, with the first public one delving into the topic of the Mojo programming language and GPU architecture. The content includes the internal workings of the Mojo compiler and the challenges and solutions faced by the team when developing for modern GPUs, aiming to share details of their tech stack with the community. (Source: Modular)
AI by Hand Workshop: Build a Transformer Model from Scratch in Excel: ProfTomYeh promotes his AI by Hand workshop, which aims to have participants build a Transformer model from scratch in Excel. This approach allows learners to clearly and intuitively understand every mathematical step of a Transformer, avoiding treating it as a “black box,” thereby establishing a deep understanding of the model’s internal working mechanisms. (Source: ProfTomYeh)
DeepLearning.AI Releases The Batch Issue 301: Discussing the Business Value of AI Speed and Latest Advances: In his latest issue of The Batch, Andrew Ng discusses how the improvement in AI’s task execution speed is an underestimated factor in creating business value. He argues that AI not only reduces costs but, more importantly, accelerates innovation and exploration by shortening the time from idea to prototype. This issue also covers news such as the release of Microsoft’s Phi-4 inference series, DeepCoder-14B’s performance matching o1, and the softening of EU AI rules. (Source: DeepLearningAI)
💼 Business
AI Character Animation Startup Cartwheel Raises $10M to Simplify 3D Animation Workflow: Cartwheel, a startup focused on AI character animation, announced the completion of a $10 million funding round. The company is dedicated to developing technology that simplifies the 3D animation production process, aiming to enable creators to produce high-quality 3D character animations more quickly and cost-effectively, while enhancing control over the final product and eliminating tedious tasks. (Source: andrew_n_carr)
Hedra Secures $32M Series A Led by a16z to Accelerate Character-Driven Video Creation: AI video generation startup Hedra announced a $32 million Series A funding round led by Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), with Matt Bornstein joining the board. Existing investors a16z speedrun, Abstract, and Index Ventures also participated. Hedra is committed to making character-driven video creation effortless. Since its stealth launch last year, nearly 3 million people have used its tools to create over 10 million videos. The new capital will be used to accelerate product development and team expansion to enable fast, expressive, and intuitive content creation. (Source: Hedra)
Tripadvisor Leverages Qdrant to Build AI Itineraries, Boosting User Engagement 2-3x: Tripadvisor is redefining the travel discovery experience using the Qdrant vector database. By analyzing over 1 billion reviews and photos, 11 million businesses, and data from 21 countries, Tripadvisor creates dynamic, AI-generated itineraries instead of relying on traditional filters. Results show that users engaging with these AI tools spend 2-3 times longer, demonstrating the immense potential of AI in personalized travel planning. (Source: qdrant_engine)

🌟 Community
Grok’s Remarks on “White Genocide” Spark Controversy, Sam Altman Responds Sarcastically: xAI’s Grok model sparked widespread discussion and criticism for randomly opining on white genocide in South Africa. Paul Graham noted this behavior “smells like a bug introduced by a recent patch” and worried about widely used AI being instantly edited by its controllers. Sam Altman responded sarcastically, stating xAI would provide a transparent explanation and understand the issue in the context of “white genocide in South Africa,” implying this is a result of AI pursuing truth and following instructions. Community discussion on the matter reflects common concerns about AI model bias, controllability, and underlying intentions. (Source: Paul Graham)
Thoughts on AI Productization: Discovering Opportunities from the Entire User Task Flow, Not Just Superimposing AI Features: Ren Xin, a partner at Sky9 Capital, shared in-depth thoughts on AI productization, emphasizing that companies should start from the entire process of users completing tasks to find entry points for AI applications, rather than simply superimposing AI functions onto existing products. He used the analogy “users don’t want a drill, they want a hole in the wall,” suggesting deconstructing user tasks to find pain points and optimize them with AI. The four levels of AI productization include: efficiently completing old processes, creating new processes, opening up entirely new markets (lowering barriers to entry, serving new user groups, or even AI itself), and laying infrastructure for an AI-dominated future. He believes AI technology is becoming democratized, allowing non-technical companies to seize opportunities, essentially “finding work for AI.” (Source: 混沌大学)
Discussion: The Role of AI in Career Development and Adaptation Strategies: A post on LinkedIn sparked a discussion about how AI is impacting career development. The common saying is “AI won’t replace your job, but people using AI will.” However, this statement was criticized as too vague. Questions were raised about how front-end engineers with decades of experience, for example, can suddenly transition to AI engineers, and the issue that not everyone can become an AI engineer. The community discussion suggested that front-end developers could learn to use AI tools to improve work efficiency. Some also believe AI will replace many jobs, leaving many people with nowhere to go. A more common view is that the future is uncertain, but creativity, problem-finding skills, and the ability to understand and connect with humanity may be more defensive. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Discussion: LLMs Tend to “Get Lost” in Multi-Turn Conversations, Restarting Might Help: A research paper points out that the performance of both open-source and closed-source LLMs significantly degrades in multi-turn conversations. Most benchmarks focus on single-turn, clearly instructed scenarios. The study found that LLMs often make (incorrect) assumptions in early conversational turns and rely on these assumptions in subsequent turns, making them difficult to correct. The conclusion is that when a multi-turn conversation doesn’t meet expectations, starting a new conversation and integrating all relevant information into the first turn input might be helpful. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Exploring Why Apple and WeChat Are Relatively Slow in AI Development: Privacy, Security, and Application-First Strategy: Wei Xi analyzed in an article that although Apple launched “Apple Intelligence” and WeChat integrated DeepSeek and Yuanbao, both are relatively slow in advancing core AI functionalities. There are two main reasons: First, the high sensitivity of privacy and data security. AI’s intelligence relies on data, and the core business models of Apple and WeChat dictate extreme caution in data sharing, which limits model training and access to application context. Second, both adopt an “application-first” strategy. They do not aim to compete with top AI companies in terms of maximum model intelligence but focus more on integrating AI capabilities into existing functions and ecosystems. This may lead to limitations in technological leadership and product iteration speed. (Source: 卫夕指北)

OpenAI Launches “From A to Z Challenge”: Using AI to Discover Unknown Archaeological Sites in the Amazon: OpenAI announced a partnership with Kaggle to launch the “OpenAI to Z Challenge” featured hackathon. The challenge encourages participants to use OpenAI o3, o4-mini, or GPT-4.1 models to find previously unknown archaeological sites in the Amazon region. Participants can share their progress using the hashtag #OpenAItoZ. The event aims to explore the potential of AI in archaeology and geospatial analysis. (Source: OpenAI Developers)
Criticism of “AI Lawyer” Startups: Automated “Demand Letters” May Become a Societal Burden: Developer @swyx criticized the phenomenon of VCs investing in “AI lawyer” startups. He argues that these companies primarily use AI to automate the generation of “demand letters,” essentially automating extortion. While some demand letters may be legitimate, he points out that most such activities ultimately benefit lawyers and become a pure tax on society. He calls for boycotting, divesting from, and publicly criticizing these companies and their investors. (Source: swyx)

💡 Other
Absurd Error in Coal Research Report “Obtained by Killing Wither Skeletons” Sparks Discussion on Content Quality and AI Hallucinations: A coal industry research report priced at 8,200 yuan contained the description “coal is a renewable resource, obtained by killing Wither Skeletons,” originating from the game “Minecraft,” sparking widespread online debate. Many attributed it to AI content generation and hallucination. However, the report was published in 2022, predating mainstream large models like ChatGPT, indicating it was a typical case of manual copy-pasting and negligent review. The incident also triggered profound reflection on the quality of professional reports, the importance of information verification, and how to discern the authenticity of information in the AI era. (Source: caoz的梦呓)

Researchers Use Custom Gene-Editing Therapy to Treat Baby with Rare Metabolic Disease: Doctors constructed a customized gene-editing therapy in less than seven months and successfully used it to treat an infant with a fatal metabolic disease. This marks the first time gene editing has been used for customized treatment targeting a single individual. The therapy aims to correct a specific single-letter error in the baby’s genes, showcasing the precision of novel gene-editing technologies like base editing. Although the treatment shows early positive signs, it also highlights the cost and scalability challenges of developing personalized gene therapies for ultra-rare diseases. (Source: MIT Technology Review)

Universal Jailbreak Prompt Strategy Exposed, Can Bypass Safety Guardrails of Mainstream Large Models: Researchers at HiddenLayer discovered a universal prompt strategy capable of making mainstream large language models, including ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini, bypass safety guardrails and generate harmful content. The strategy involves disguising harmful instructions in formats similar to XML, INI, or JSON policy files, combined with fictional role-playing scenarios, to trick the model into interpreting harmful commands as legitimate system instructions. This method exploits potential systemic weaknesses in the models’ training data, namely a tendency to ignore safety instructions when processing instructional or policy-related data. The technique can also extract the models’ system prompts, exposing their internal instructions and safety constraints. (Source: 新智元)