Keywords:AlphaEvolve, Claude Sonnet, GPT-4.1, Meta FAIR, Qwen3, Phi-4-reasoning, AI regulation, Gemini-powered coding agent, Matrix multiplication algorithm optimization, Data center efficiency optimization, Multilingual multimodal models, Decentralized AI training networks, Seed1.5-VL
🔥 Focus
Google DeepMind releases AlphaEvolve: A Gemini-powered coding agent revolutionizing algorithm discovery: Google DeepMind has launched AlphaEvolve, an AI coding agent powered by Gemini, designed to discover and optimize complex algorithms by combining the creativity of large language models with automated evaluators. AlphaEvolve has successfully designed faster matrix multiplication algorithms, tackled open mathematical problems like the Erdős minimal overlap problem and the kissing number problem, and is used internally at Google to optimize data center efficiency (averaging 0.7% computational resource recovery), chip design, and accelerate Gemini’s own training, showcasing AI’s vast potential in scientific discovery and engineering optimization. (Source: GoogleDeepMind, DeepLearning.AI Blog)
Anthropic to soon release new Claude Sonnet and Opus models, enhancing reasoning and tool-calling capabilities: According to The Information, Anthropic plans to launch new versions of Claude Sonnet and Claude Opus in the coming weeks. A core feature of the new models is the ability to flexibly switch between “thinking mode” and “tool use mode.” When encountering obstacles while using external tools (like applications or databases) to solve problems, the model can proactively return to “reasoning mode” to reflect and self-correct. In code generation, the new models can automatically test the generated code and, if errors are found, will pause, think, and make corrections. This “think-act-reflect” closed loop is expected to significantly improve the models’ ability to solve complex problems and their reliability. (Source: steph_palazzolo, dotey)

US Republican lawmakers propose a 10-year ban on federal and state AI regulation, sparking heated debate: US Republican lawmakers have added a provision to a budget reconciliation bill proposing a ban on federal and state governments from regulating artificial intelligence models, systems, or automated decision-making systems for the next ten years. They also plan to allocate $500 million to support AI commercialization and its application in federal government IT systems. This move is seen by some in the tech industry as a positive signal to protect AI innovation and prevent regulations from stifling it, but it has also raised concerns about potential risks such as the proliferation of DeepFakes, loss of data privacy control, AI ethics, and environmental impact. If passed, the proposal would have a significant impact on existing and future AI legislation. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Yoshua_Bengio)

OpenAI releases GPT-4.1 model and launches Safety Evaluations Hub, emphasizing coding and instruction following capabilities: OpenAI announced that, due to user demand, the GPT-4.1 model is available in ChatGPT starting today (for Plus, Pro, Team users; Enterprise and Education editions to follow). GPT-4.1 is optimized for coding tasks and instruction following, is faster, and can serve as a daily coding alternative to o3 and o4-mini. Meanwhile, GPT-4.1 mini will replace the current GPT-4o mini for all users. Additionally, OpenAI has launched the Safety Evaluations Hub to publicly share the safety testing results and metrics of its models, which will be updated regularly to enhance transparency in safety communication. (Source: openai, michpokrass)
Meta FAIR releases multiple AI research achievements, focusing on molecular discovery and atomic modeling: Meta AI (FAIR) announced the latest open-source releases in molecular property prediction, language processing, and neuroscience. These include Open Molecules 2025 (OMol25), a molecular discovery dataset for simulating large atomic systems; Universal Model for Atoms (UMA), a machine learning interatomic potential model broadly applicable to modeling atomic interactions in materials and molecules; and Adjoint Sampling, a scalable algorithm for training generative models based on scalar rewards. Additionally, FAIR, in collaboration with the Rothschild Foundation Hospital, conducted research revealing significant similarities in language development between humans and LLMs. (Source: AIatMeta)
🎯 Trends
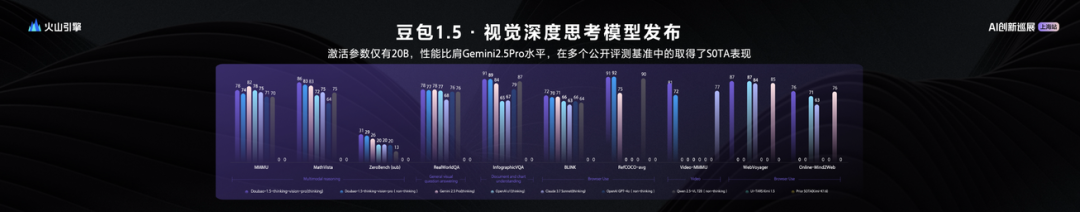
ByteDance releases Seed1.5-VL visual-language large model, achieving excellent performance with 20B active parameters: ByteDance has launched its visual-language multimodal large model, Seed1.5-VL. With only 20B active parameters, the model demonstrates performance comparable to Gemini 2.5 Pro and achieves SOTA in 38 out of 60 public evaluation benchmarks. Seed1.5-VL enhances general multimodal understanding and reasoning capabilities, particularly excelling in visual localization, reasoning, video understanding, and multimodal agents. The model’s API is available on Volcano Engine, with inference input priced at 0.003 yuan/thousand tokens and output at 0.009 yuan/thousand tokens. (Source: 机器之心)
Qwen3 technical report revealed: Integrates thinking and non-thinking modes, large models distill small models: Alibaba released the technical report for its Qwen3 series models, which includes 8 models ranging from 0.6B to 235B parameters. A core innovation is its dual working modes, where the model can automatically switch between “thinking mode” (for complex reasoning) and “non-thinking mode” (for quick responses), dynamically allocating computational resources via a “thinking budget” parameter. Training employs a three-stage pre-training (general knowledge, reasoning enhancement, long-text) and a four-stage post-training (long chain-of-thought cold start, reasoning reinforcement learning, thinking mode fusion, general reinforcement learning). It also uses a “large-teaches-small” data distillation strategy, utilizing a teacher model (e.g., 235B) to train student models (e.g., 30B), enabling knowledge transfer. (Source: 36氪)

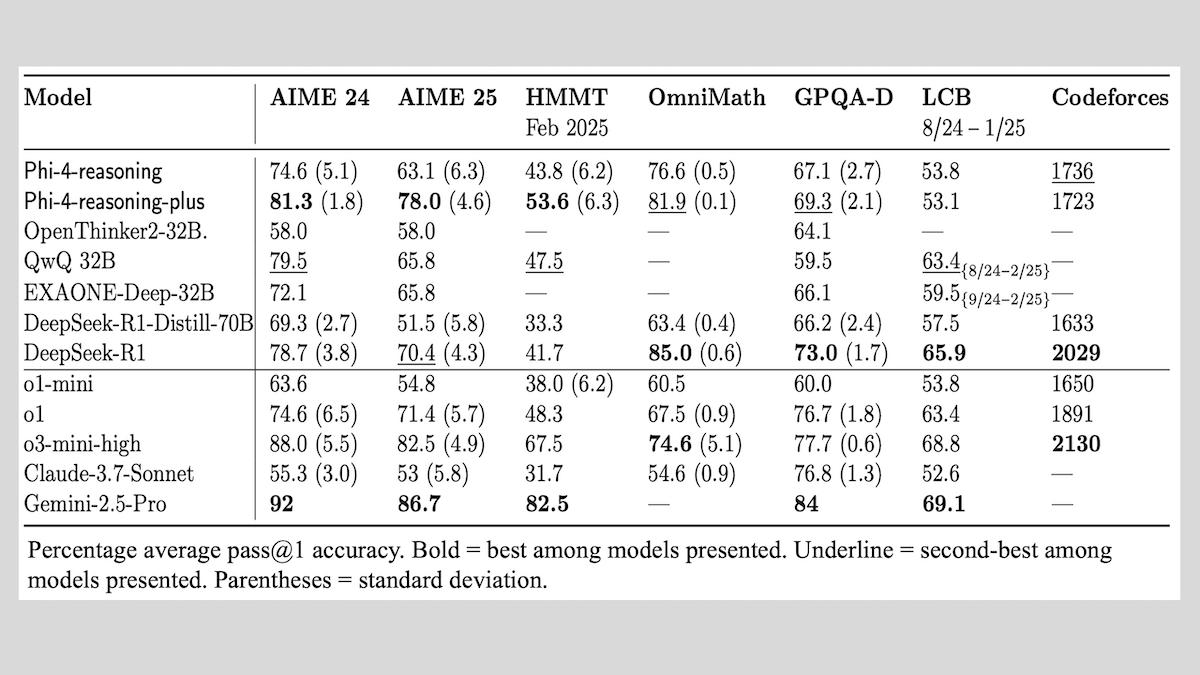
Microsoft releases Phi-4-reasoning series models, shares experience in training reasoning models: Microsoft has introduced three models: Phi-4-reasoning, Phi-4-reasoning-plus (both 14B parameters), and Phi-4-mini-reasoning (3.8B parameters), and has publicly shared its training methods and experiences. These models, fine-tuned from pre-trained models, focus on enhancing capabilities such as mathematical reasoning. For example, Phi-4-reasoning-plus excels in mathematical problems through reinforcement learning, while Phi-4-mini-reasoning undergoes staged SFT and RL fine-tuning. The report shares insights into potential instabilities during small model training and strategies to address them, as well as considerations for data selection and reward function design in large model RL training. Model weights are available on Hugging Face under the MIT license. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
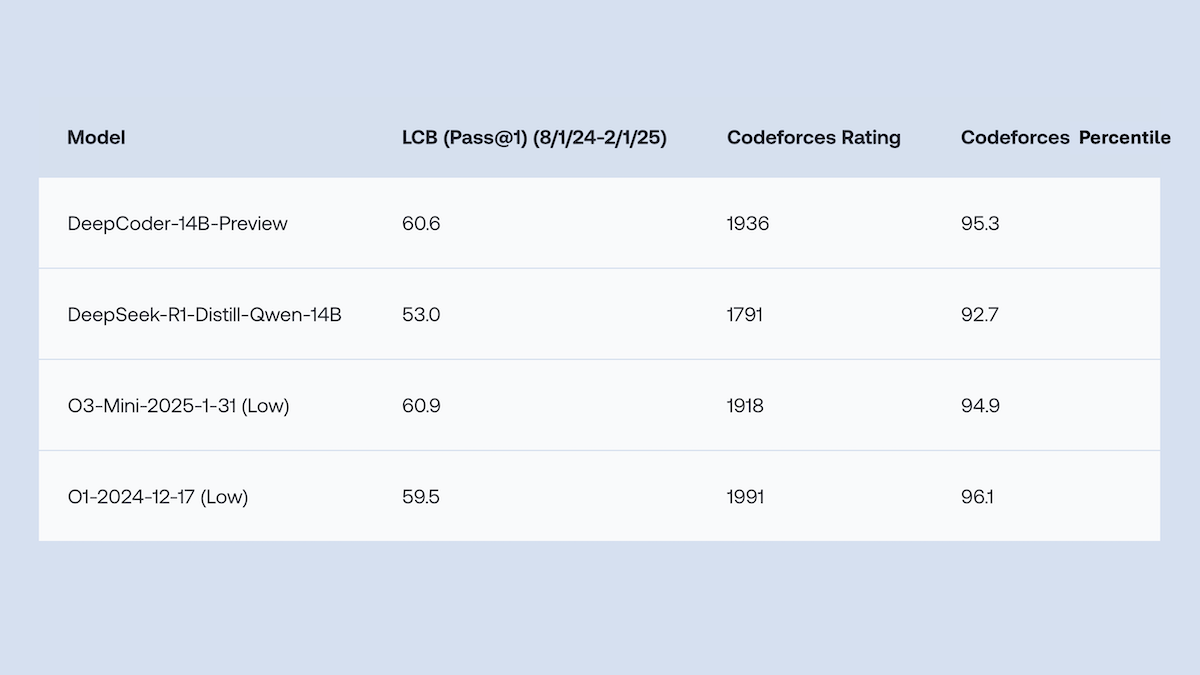
Together.AI and Agentica open-source DeepCoder-14B-Preview, with code generation performance comparable to o1: The Together.AI and Agentica teams have released DeepCoder-14B-Preview, a 14B parameter code generation model whose performance on several coding benchmarks is comparable to larger models like DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI’s o1. The model was fine-tuned from DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-Qwen-14B, employing a simplified reinforcement learning method (combining optimizations from GRPO and DAPO) and improving the parallel processing capabilities of the RL library Verl, significantly reducing training time. Model weights, code, datasets, and training logs are open-sourced under the MIT license. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
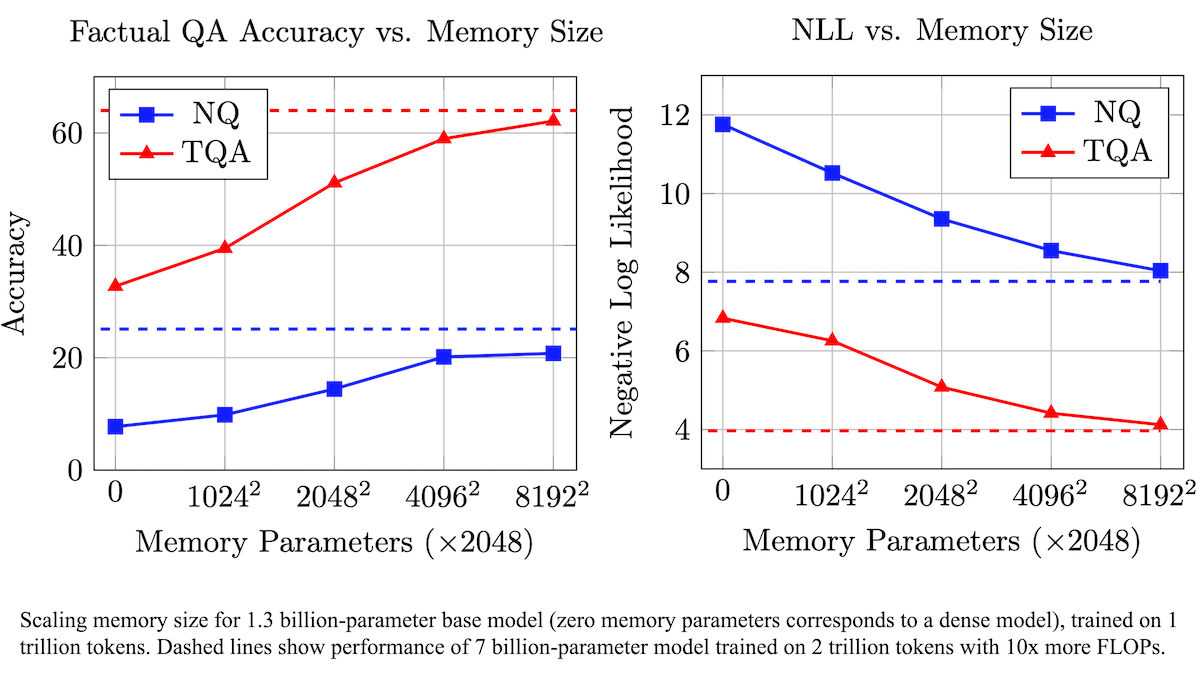
Meta proposes trainable memory layer to enhance LLM factual accuracy and reduce computational demand: Researchers at Meta have improved the factual recall accuracy of large language models by adding a trainable memory layer to the Transformer architecture, without significantly increasing computational load. This method stores information by learning keys and corresponding values and employs a strategy of decomposing keys into two half-keys, effectively addressing the computational bottleneck in large-scale key retrieval. Experiments show that an 8B parameter model equipped with a memory layer outperforms similar models without memory on multiple question-answering datasets, demonstrating advantages in pre-training data and computational requirements. (Source: DeepLearning.AI Blog)
Alibaba open-sources Wan2.1 series video foundation models, supporting text/image-to-video generation and editing: Alibaba has released Wan2.1, a comprehensive open-source suite of video foundation models, including 1.3B and 14B parameter versions, under the Apache 2.0 license. Wan2.1 excels in various tasks such as text-to-video, image-to-video, video editing, text-to-image, and video-to-audio, and notably supports visual generation from both Chinese and English text. Its T2V-1.3B model requires only 8.19GB of VRAM, can run on consumer-grade GPUs, and can generate a 5-second 480P video within 4 minutes. The accompanying Wan-VAE can efficiently encode and decode 1080P video while preserving temporal information. (Source: _akhaliq, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

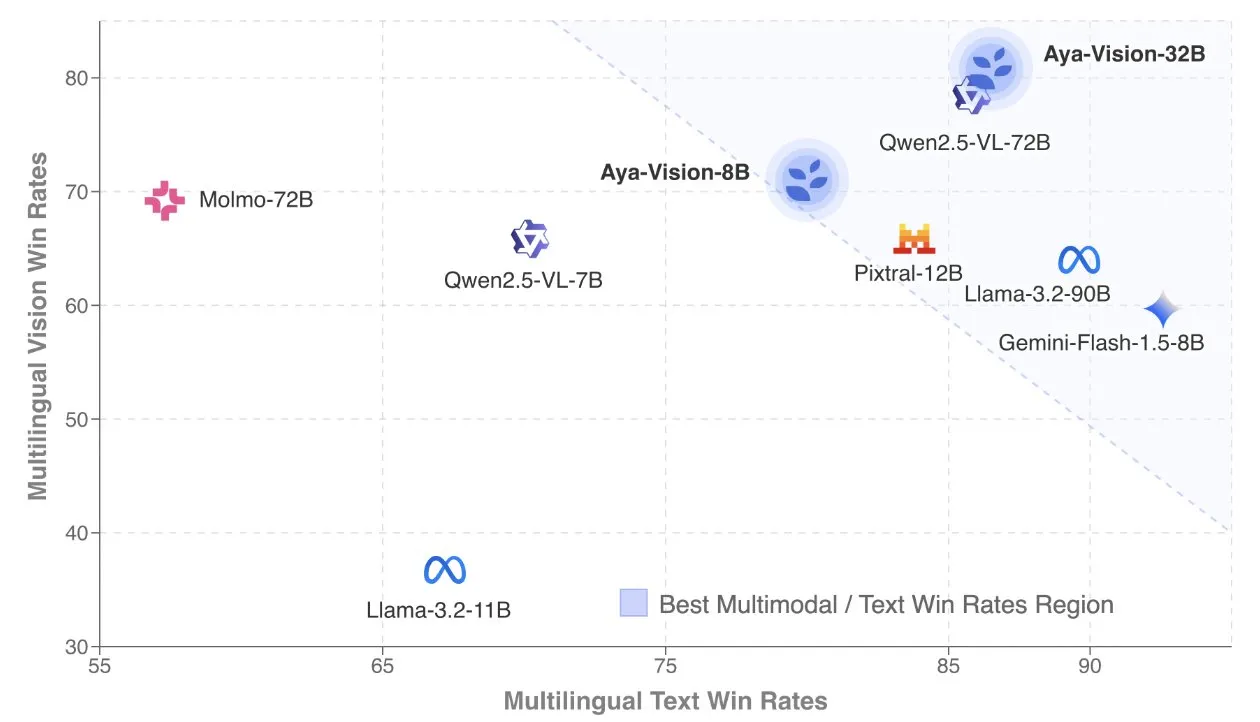
Cohere releases Aya Vision technical report, focusing on multilingual multimodal models: Cohere Labs has published the Aya Vision technical report, detailing its recipe for building SOTA multilingual multimodal models. The Aya Vision model aims to unify capabilities across 23 languages for both multimodal and text tasks. The report discusses synthetic multilingual data frameworks, architectural design, training methods, cross-modal model merging, and comprehensive evaluation on open-ended, multilingual generation tasks. Its 8B model outperforms larger models like Pixtral-12B in performance, while its 32B model is more efficient, surpassing models more than twice its size, such as Llama3.2-90B. (Source: sarahookr, Cohere Labs)
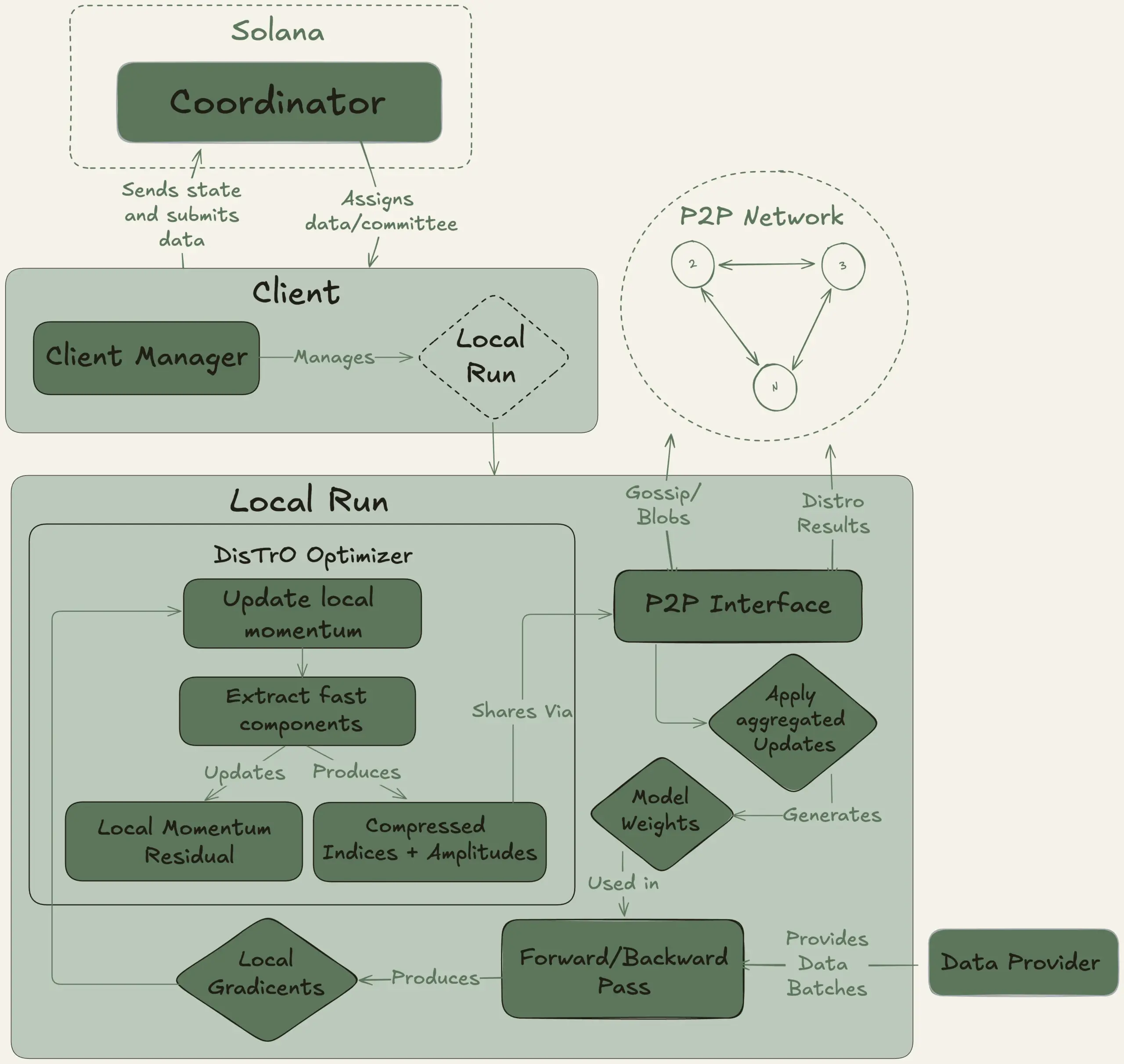
Nous Research launches Psyche project, aiming for decentralized training of a 40B parameter large model: Nous Research announced the launch of the Psyche network, a decentralized AI training network designed to pool global computing power to train powerful AI models, enabling individuals and small communities to participate in large-scale model development. Its testnet has begun pre-training a 40B parameter LLM using an MLA architecture, with a dataset comprising FineWeb (14T), part of FineWeb-2 (4T), and The Stack v2 (1T), totaling approximately 20T tokens. Upon completion of training, all checkpoints (including unannealed and annealed versions) and the dataset will be open-sourced. (Source: eliebakouch, Teknium1)
Stability AI releases open-source Stable Audio Open Small model, focusing on rapid text-to-audio generation: Stability AI has released the Stable Audio Open Small model on Hugging Face, a model specifically designed for rapid text-to-audio generation, incorporating adversarial post-training techniques. The model aims to provide an efficient, open-source audio generation solution. (Source: _akhaliq)
Google Gemini Advanced integrates GitHub, enhancing coding assistance capabilities: Google announced that Gemini Advanced is now connected to GitHub, further enhancing its capabilities as a coding assistant. Users can directly connect to public or private GitHub repositories to leverage Gemini for generating or modifying functions, explaining complex code, asking questions about the codebase, debugging, and more. Users can start by clicking the “+” button in the prompt bar and selecting “Import code,” then pasting the GitHub URL. (Source: algo_diver)
mlx-omni-server v0.4.0 released, adds embeddings service and more TTS models: mlx-omni-server has been updated to version v0.4.0, introducing a new /v1/embeddings service that simplifies embedding generation via mlx-embeddings. It also integrates more TTS models (such as kokoro, bark) and upgrades mlx-lm to support new models like qwen3. (Source: awnihannun)
Together Chat adds PDF file processing functionality: Together Chat announced support for PDF file uploads and processing. The current version primarily parses text content from PDFs and passes it to the model for processing. A future v2 version is planned to include OCR functionality to read image content within PDFs. (Source: togethercompute)
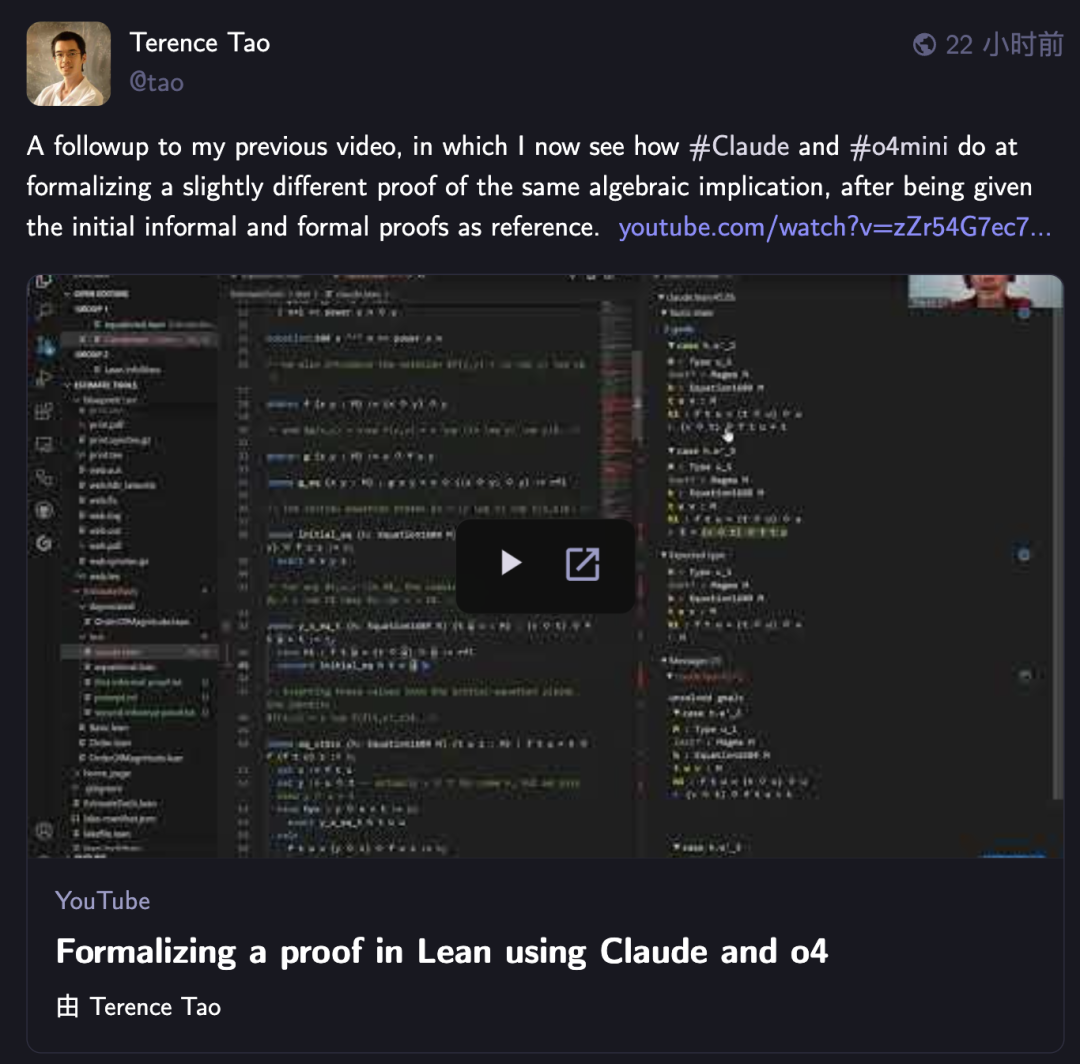
Terence Tao again challenges AI with formalizing mathematical proofs, Claude outperforms o4-mini: Mathematician Terence Tao, in his YouTube series, tested AI’s ability to formalize algebraic implication proofs in the Lean proof assistant. In the experiment, Claude was able to complete the task in about 20 minutes, although it revealed misunderstandings of Lean’s rule that natural numbers start from 0 and issues with handling symmetry during compilation, which were corrected with human intervention. In contrast, o4-mini performed more cautiously, identifying issues with power function definitions but ultimately abandoning key proof steps and failing to complete the task. Tao concluded that over-reliance on automation might weaken the grasp of the overall proof structure, and the optimal level of automation should be between 0% and 100%, retaining human intervention to deepen understanding. (Source: 36氪)
Altman interview: OpenAI’s ultimate goal is to create a core AI subscription service: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman stated at Sequoia Capital’s AI Ascent 2025 event that OpenAI’s “Platonic ideal” is to develop an AI operating system that becomes the user’s core AI subscription service. He envisions future AI models capable of processing a user’s lifetime of data (trillions of context tokens) to achieve deep personalized reasoning. Altman admitted this is still in the “PowerPoint stage” but emphasized the company prides itself on flexibility and adaptability. He also discussed the potential of AI voice interaction, predicted 2025 will be a breakout year for AI agents, and believes coding will be central to driving model operations and API calls. (Source: 36氪, 量子位)

Karminski3 shares community-modified Qwen3-30B, doubling the number of activated experts: The developer community has modified the Qwen3 model, releasing the Qwen3-30B-A6B-16-Extreme version. By altering model parameters, the number of activated experts was increased from A3B to A6B, reportedly leading to a slight quality improvement, though generation speed will be correspondingly slower. Users can also achieve a similar effect by modifying llama.cpp’s runtime parameter --override-kv http://qwen3moe.expert_used_count=int:24, or conversely, reduce the activation amount of Qwen3-235B-A22B to speed it up. (Source: karminski3)

🧰 Tools
OpenMemory MCP released: A locally run shared memory system connecting multiple AI tools: The mem0ai team has launched OpenMemory MCP, a private memory server built on the Open Model Context Protocol (MCP). It supports 100% local operation and aims to solve the problem of context information not being shared between current AI tools (like Cursor, Claude Desktop, Windsurf, Cline), where memory is lost when sessions end. User data is stored locally, ensuring privacy and security. OpenMemory MCP provides standardized memory operation APIs (CRUD) and features a centralized dashboard for users to manage memory and client access permissions, with deployment simplified via Docker. (Source: 36氪, AI进修生)

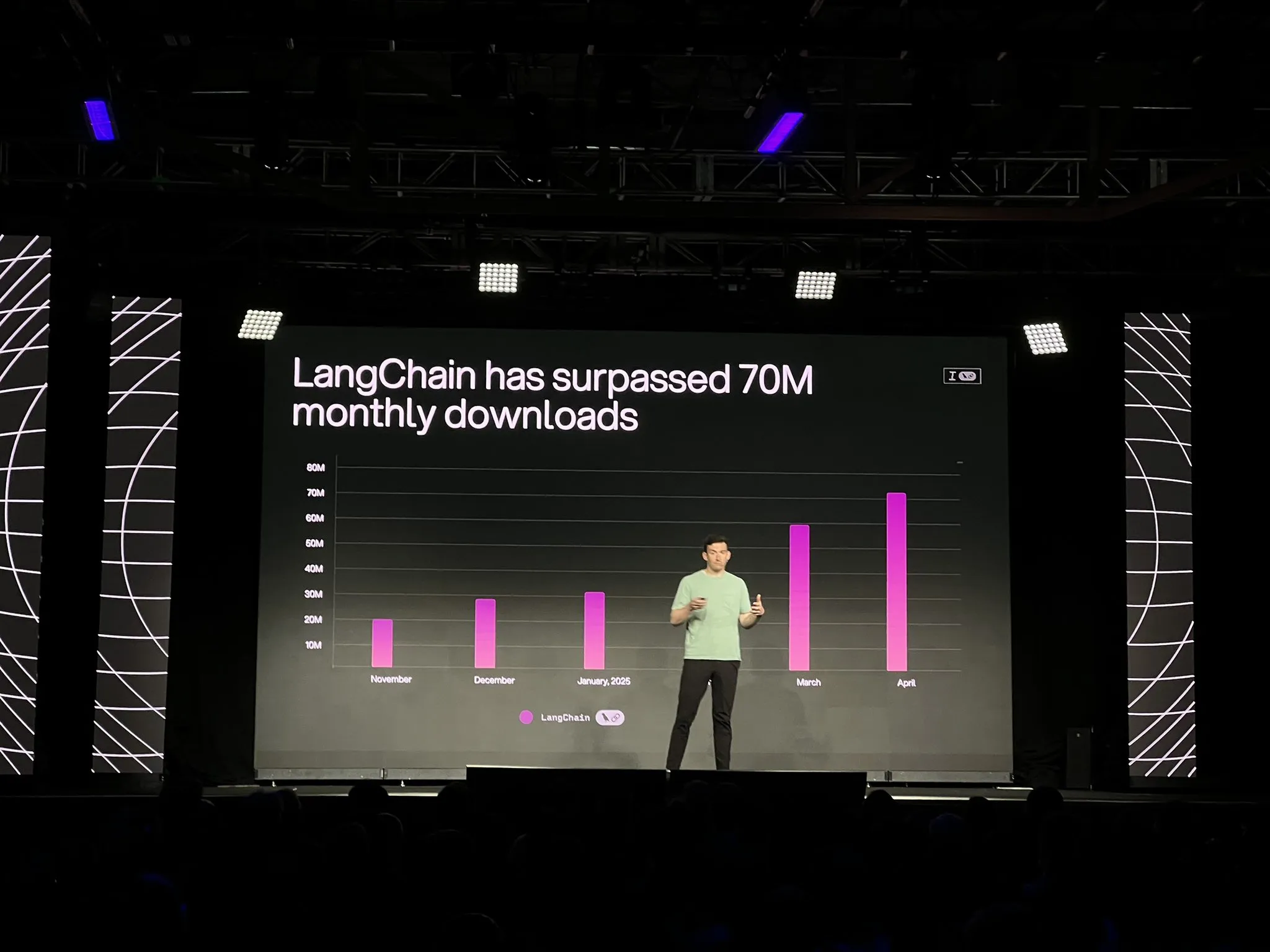
LangChain launches official LangGraph platform and multiple updates, enhancing AI agent development and observability: LangChain announced at the Interrupt conference the general availability (GA) of its LangGraph platform. LangGraph is designed for building and managing long-running, stateful AI agent workflows, supporting one-click deployment, horizontal scaling, and APIs for memory, human-in-the-loop (HIL), conversation history, etc. Simultaneously, LangGraph Studio V2 was released as an agent IDE, supporting local execution, direct configuration editing, Playground integration, and the ability to pull production environment trace data for local debugging. Additionally, LangChain launched the open-source no-code agent building platform Open Agent Platform (OAP) and enhanced LangSmith’s agent observability for tool calling and trajectories. (Source: LangChainAI, hwchase17)
PatronusAI releases Percival: An AI agent that can evaluate and fix other AI agents: PatronusAI has launched Percival, touted as the first AI agent capable of evaluating and automatically fixing errors made by other AI agents. Percival not only detects failures in agent trace logs but also proposes repair suggestions. On the TRAIL dataset, which includes human-annotated errors from GAIA and SWE-Bench, Percival reportedly outperforms SOTA LLMs by 2.9 times. Its features include automatically suggesting fixes for agent prompts, capturing over 20 types of agent failures (covering tool use, planning coordination, domain-specific errors, etc.), and reducing manual debugging time from hours to under 1 minute. (Source: rebeccatqian, basetenco)
PyWxDump: WeChat information acquisition and export tool, supports AI training: PyWxDump is a Python tool for obtaining WeChat account information (nickname, account, phone, email, database key), decrypting databases, locally viewing chat records, and exporting chat records to formats like CSV and HTML. It can be used for AI training, automated replies, and other scenarios. The tool supports information acquisition for multiple accounts and all WeChat versions, and provides a web-based UI for viewing chat records. (Source: GitHub Trending)
Airweave: A tool enabling AI agents to search any application, compatible with MCP protocol: Airweave is a tool designed to allow AI agents to semantically search the content of any application. It is compatible with the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and can seamlessly connect to various applications, databases, or APIs, transforming their content into knowledge usable by agents. Its main features include data synchronization, entity extraction and transformation, multi-tenant architecture, incremental updates, semantic search, and version control. (Source: GitHub Trending)

iFLYTEK releases new generation AI earphones iFLYBUDS Pro3 and Air2, equipped with viaim AI brain: Future Intelligence (an iFLYTEK company) has released the iFLYBUDS Pro3 and iFLYBUDS Air2 AI conference earphones, both equipped with the new viaim AI brain. viaim is an AI agent for personal business office use, integrating end-to-end intelligent perception processing, intelligent agent collaborative reasoning, real-time multimodal capabilities, and data security & privacy protection as its four core modules. The earphones support convenient recording (calls, on-site, audio/video recordings), AI assistant (automatic title/summary generation, targeted questioning), multi-language translation (32 languages, simultaneous interpretation, face-to-face translation, call translation), and offer improved sound quality and wearing comfort. (Source: WeChat)

KoboldCpp Smart Launcher released: Tensor Offload auto-tuning tool for optimizing LLM performance: A GUI and CLI tool called KoboldCpp Smart Launcher has been released, designed to help users automatically find the optimal Tensor Offload strategy for KoboldCpp when running LLMs locally. By distributing tensors between CPU and GPU with finer granularity (rather than entire layers), the tool reportedly can more than double generation speed without increasing VRAM demand. For example, QwQ Merge on a 12GB VRAM GPU saw speeds increase from 3.95 t/s to 10.61 t/s. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
OpenBMB open-sources AgentCPM-GUI: The first on-device GUI agent optimized for Chinese: The OpenBMB team has open-sourced AgentCPM-GUI, the first on-device GUI (Graphical User Interface) agent specifically optimized for Chinese applications. The agent enhances its reasoning capabilities through Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT), adopts a compact action space design, and possesses high-quality GUI grounding capabilities, aiming to improve the user experience when operating various applications in a Chinese environment. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
MAESTRO: A local-first AI research application supporting multi-agent collaboration and custom LLMs: MAESTRO (Multi-Agent Execution System & Tool-driven Research Orchestrator) is a newly released AI-driven research application emphasizing local control and capabilities. It provides a modular framework including document ingestion, a robust RAG pipeline, and a multi-agent system (Plan, Research, Reflect, Write) for tackling complex research questions. Users can interact via a Streamlit Web UI or CLI, using their own document sets and choice of local or API LLMs. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Contextual AI launches document parser optimized for RAG: Contextual AI has released a new document parser specifically designed for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The tool aims to provide high-accuracy parsing of complex unstructured documents by combining vision, OCR, and vision-language models. It can preserve document hierarchy, handle complex modalities like tables, charts, and graphics, and provide bounding boxes and confidence scores for user auditing, thereby reducing context gaps and hallucinations in RAG systems caused by parsing failures. (Source: douwekiela)
Gradio adds undo/redo functionality to ImageEditor: Gradio’s ImageEditor component now includes undo and redo buttons, providing users with Python image editing capabilities similar to professional paid applications, enhancing interactivity and ease of use. (Source: _akhaliq)
RunwayML introduces new References feature, supporting zero-shot testing for materials, clothing, locations, and poses: RunwayML’s References feature has been updated. Users can now use traditional 3D material sphere preview images as input to apply their materials to any object, enabling zero-shot material transfer and visualization. Additionally, the new feature supports zero-shot testing for clothing, locations, and character poses, expanding possibilities for creative generation and rapid prototyping. (Source: c_valenzuelab, c_valenzuelab)

Mìtǎ AI launches “Learn Something Today” feature, AI-assisted structured learning: Mìtǎ AI has launched a new feature called “Learn Something Today” (今天学点啥), aiming to transform AI from an assistant for information retrieval and document processing into an “AI teacher” capable of active guidance and instruction. After users upload or search for materials, the feature can automatically generate systematic, structured video courses and PPT presentations, helping users organize knowledge points. It also supports selecting different explanation depths (beginner/expert) and styles (storytelling/grumpy old man, etc.) based on the user’s level. Additionally, it supports mid-lesson questions and post-lesson tests. (Source: WeChat)

📚 Learning
Andrew Ng and Anthropic collaborate on new course: Build Rich-Context AI Apps with MCP: Andrew Ng’s DeepLearning.AI has partnered with Anthropic to launch a new course, “MCP: Build Rich-Context AI Apps with Anthropic,” taught by Elie Schoppik, Head of Technical Education at Anthropic. The course focuses on the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open protocol designed to standardize LLM access to external tools, data, and prompts. Students will learn the core architecture of MCP, create MCP-compatible chatbots, build and deploy MCP servers, and connect them to Claude-powered applications and other third-party servers to simplify the development of rich-context AI applications. (Source: AndrewYNg, DeepLearningAI)
FlashInfer: MLSys 2025 Best Paper, an efficient and customizable attention engine for LLM inference: The FlashInfer project, a collaboration by Zihao Ye from the University of Washington, NVIDIA, Tianqi Chen from OctoAI, and others, has won the Best Paper Award at MLSys 2025. FlashInfer is an efficient and customizable attention engine optimized for LLM inference services. It significantly improves LLM inference performance by optimizing memory access (using block-sparse formats and composable formats to handle KV cache), providing flexible attention computation templates based on JIT compilation, and introducing a load-balancing task scheduling mechanism. It has been integrated into projects like vLLM and SGLang. (Source: 机器之心)
ICML 2025 Paper: Theoretical analysis of Graph Prompting from a data manipulation perspective: Qunzhong Wang, Dr. Xiangguo Sun, and Prof. Hong Cheng from The Chinese University of Hong Kong published a paper at ICML 2025, providing the first systematic theoretical framework for the effectiveness of graph prompting from a “data manipulation” perspective. The research introduces the concept of a “bridging graph,” demonstrating that the graph prompting mechanism is theoretically equivalent to performing certain operations on the input graph data, enabling it to be correctly processed by pre-trained models to adapt to new tasks. The paper derives an error upper bound, analyzes error sources and controllability, and models the error distribution, providing a theoretical basis for the design and application of graph prompting. (Source: WeChat)

ICML 2025 Paper: Synthesizing text data via Token-Level Editing to avoid model collapse: A research team from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and other institutions published a paper at ICML 2025 discussing the issue of “model collapse” caused by synthetic data and proposing a data generation strategy called “Token-Level Editing.” Instead of completely generating new text, this method performs minor edits by replacing tokens where the model is “overconfident” in real data, aiming to construct semi-synthetic data with more stable structures and stronger generalization capabilities. Theoretical analysis shows that this method can effectively constrain test error and prevent model performance from collapsing with increasing iteration rounds. Experiments have validated the effectiveness of this method in pre-training, continual pre-training, and supervised fine-tuning stages. (Source: WeChat)

ICML 2025 Paper: OmniAudio, generating 3D spatial audio from 360° panoramic videos: The OmniAudio team presented a technique at ICML 2025 for directly generating first-order ambisonics (FOA) spatial audio from 360° panoramic videos. To address data scarcity, the team constructed a large-scale 360V2SA dataset called Sphere360 (over 100,000 clips, 288 hours). OmniAudio employs a two-stage training process: self-supervised coarse-to-fine flow matching pre-training, first training with pseudo-FOA converted from regular stereo audio, then fine-tuning with real FOA; followed by supervised fine-tuning with a dual-branch video encoder to extract global and local perspective features, generating high-fidelity, directionally accurate spatial audio. (Source: 量子位)

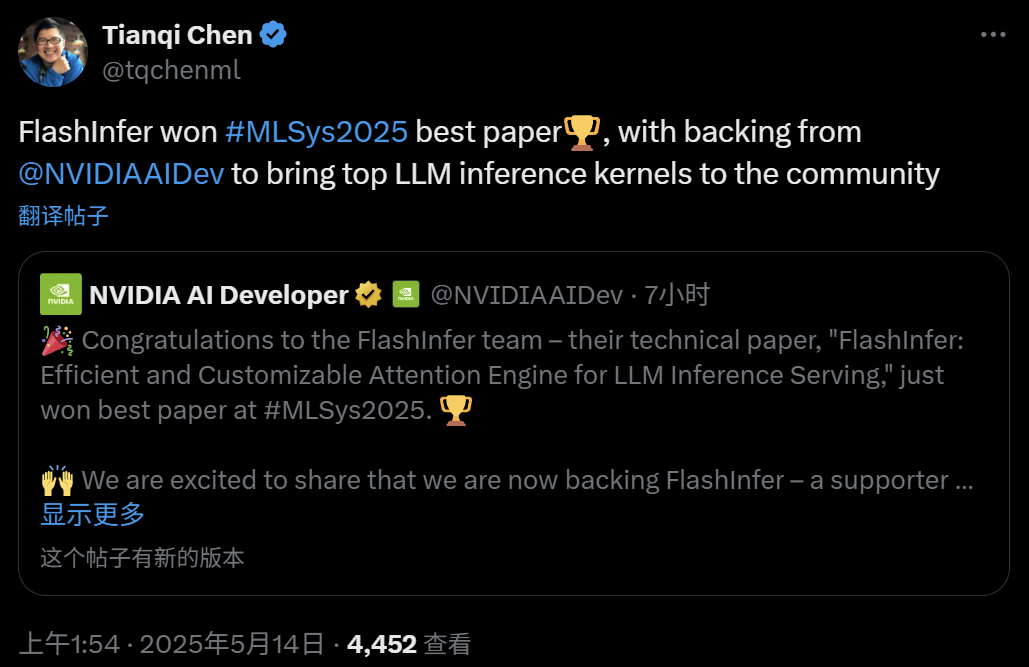
CUHK MMLab proposes T2I-R1: Introducing dual-level CoT reasoning and reinforcement learning for text-to-image generation: The MMLab team at The Chinese University of Hong Kong has released T2I-R1, the first text-to-image generation model enhanced by reinforcement learning-based reasoning. The model innovatively proposes a dual-level Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning framework: Semantic-CoT (text reasoning, planning global image structure) and Token-CoT (generating image tokens block by block, focusing on low-level details). Through the BiCoT-GRPO reinforcement learning method, these two CoT levels are collaboratively optimized within a unified LMM (Janus-Pro) without requiring additional models. The reward model uses an ensemble of multiple visual expert models to ensure evaluation reliability and prevent overfitting. Experiments show that T2I-R1 can better understand user intent, generate images more aligned with expectations, and significantly outperform baseline models on T2I-CompBench and WISE benchmarks. (Source: 量子位, WeChat)
OpenAI releases lightweight language model evaluation library simple-evals: OpenAI has open-sourced simple-evals, a lightweight library for evaluating language models, aimed at making the accuracy data of its latest model releases transparent. The library emphasizes zero-shot, chain-of-thought evaluation settings and provides detailed model performance comparisons on multiple benchmarks such as MMLU, MATH, GPQA, including OpenAI’s own models (like o3, o4-mini, GPT-4.1, GPT-4o) and other major models (like Claude 3.5, Llama 3.1, Grok 2, Gemini 1.5). (Source: GitHub Trending)
LLM Engineer’s Handbook Korean version released: Maxime Labonne’s “LLM Engineer’s Handbook” is now available in Korean, translated by Woocheol Cho. More language versions of the handbook, including Russian, Chinese, and Polish, are also set to be released soon, providing learning resources for LLM developers worldwide. (Source: maximelabonne)

ICML 2025 Workshop on Machine Learning for Audio (ML4Audio) announced: The popular Workshop on Machine Learning for Audio (ML for Audio) will return during ICML 2025 in Vancouver, scheduled for Saturday, July 19th. The workshop will feature talks from renowned scholars including Dan Ellis, Albert Gu, Jesse Engel, Laura Laurenti, and Pratyusha Rakshit. The paper submission deadline is May 23rd. (Source: sedielem)
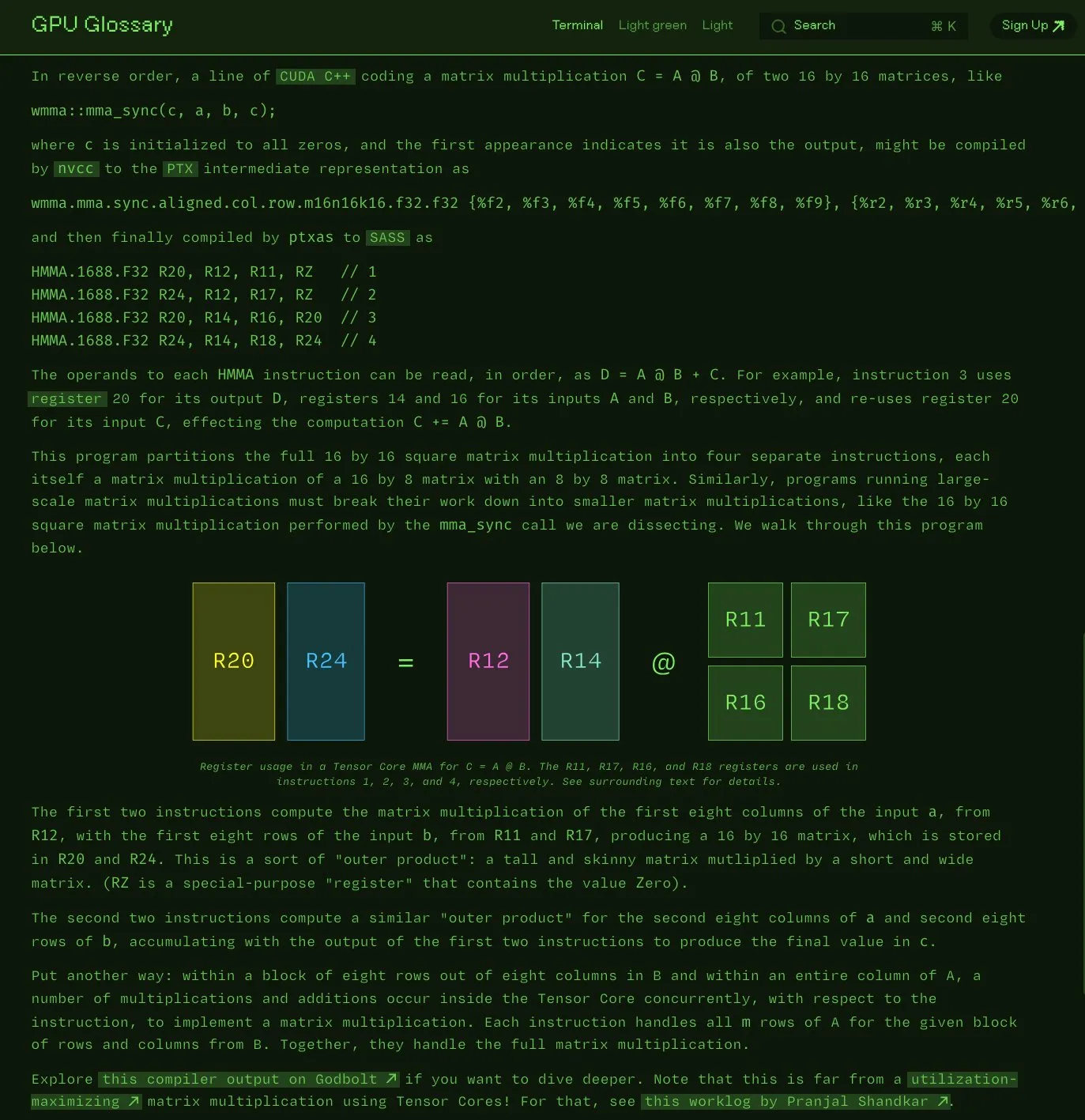
Charles Frye open-sources GPU Glossary: Charles Frye announced that his GPU Glossary is now open source. The glossary aims to help understand concepts related to GPU hardware and programming, with a recent update decomposing SASS instructions for simple matrix multiply-accumulate (mma) operations executed by Tensor Cores. The project is hosted on GitHub and lists some pending tasks. (Source: charles_irl)
OpenAI releases GPT-4.1 prompt engineering guide, emphasizing structured and clear instructions: OpenAI has launched a prompt engineering guide for GPT-4.1, designed to help users construct prompts more effectively, especially for applications requiring structured output, reasoning, tool use, and agent-based systems. The guide emphasizes defining roles and goals clearly, providing clear instructions (including tone, format, boundaries), optional sub-instructions, step-by-step reasoning/planning, precise output format definition, and the importance of using examples. It also offers practical tips like highlighting key instructions and using Markdown or XML to structure input. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

Kaggle and Hugging Face deepen collaboration, simplifying model invocation and discovery: Kaggle announced a strengthened collaboration with Hugging Face, allowing users to now directly launch Hugging Face models within Kaggle Notebooks, discover relevant public code examples, and seamlessly explore between the two platforms. This integration aims to expand model accessibility, making it easier for Kaggle users to leverage model resources from the Hugging Face ecosystem. (Source: huggingface)
FedRAG: An open-source framework for fine-tuning RAG systems, supporting federated learning: Researchers at the Vector Institute have introduced FedRAG, an open-source framework designed to simplify the fine-tuning of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The framework not only supports typical centralized training but also specifically introduces a federated learning architecture to accommodate the need for training on distributed datasets. FedRAG is compatible with PyTorch and the Hugging Face ecosystem, supports using Qdrant as a knowledge base store, and can bridge to LlamaIndex. (Source: nerdai)

💼 Business
Cursor parent company Anysphere reaches $200M ARR in two years, valuation soars to $9 billion: Anysphere, led by 25-year-old MIT dropout Michael Truell, has achieved $200 million in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) within two years with its AI code editor Cursor, without any marketing efforts. The company’s valuation has rapidly reached $9 billion. By deeply integrating AI into the development workflow, Cursor has reshaped the software development paradigm, focusing on serving individual developers and gaining widespread recognition and word-of-mouth referrals from developers globally. Thrive Capital led its latest funding round. (Source: 36氪)

Databricks announces acquisition of Serverless Postgres company Neon: Databricks has agreed to acquire Neon, a developer-focused Serverless Postgres company. Neon is known for its novel database architecture, offering speed, elastic scaling, and branching & forking capabilities, features attractive to both developers and AI agents. This acquisition aims to jointly build an open, serverless database foundation for developers and AI agents. (Source: jefrankle, matei_zaharia)
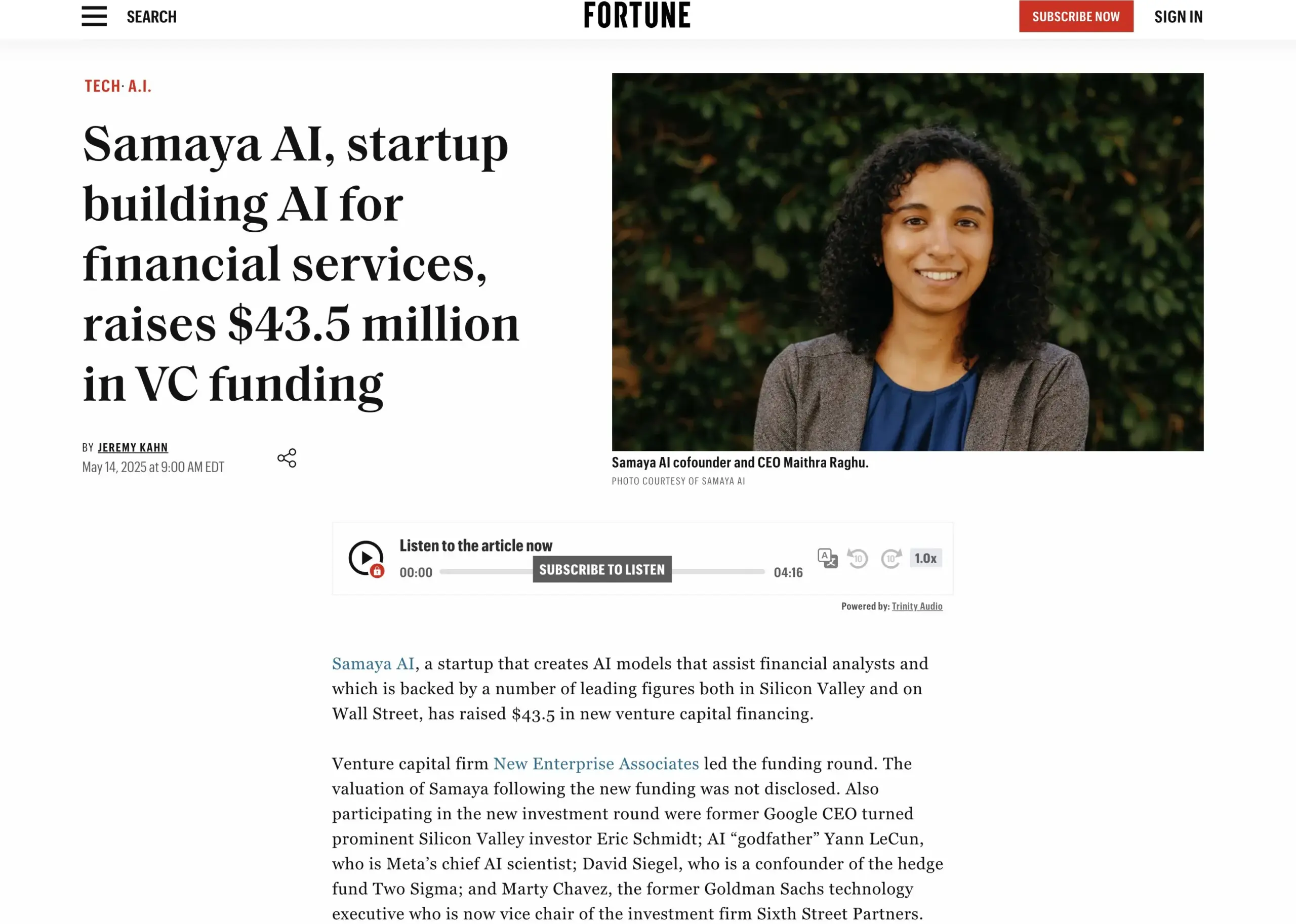
AI financial services startup Samaya AI completes $43.5M funding round: Samaya AI announced it has secured $43.5 million in funding led by NEA to build expert AI agents for financial services, aiming to transform knowledge work at scale. Founded in 2022, the company focuses on creating specialized AI solutions for complex financial workflows. Its expert AI agents, based on proprietary LLMs, are already used by thousands of users at top institutions like Morgan Stanley for due diligence, economic modeling, and decision support, emphasizing precision, transparency, and hallucination-free performance. (Source: maithra_raghu)
🌟 Community
Will AI replace software engineers? Community discusses the necessity of skill upgrades: Discussions have resurfaced on social media about whether AI will replace software engineers. The prevailing view is that AI will not completely replace software engineers because software development involves much more than just coding. However, “code monkeys” who primarily engage in repetitive coding tasks and lack a holistic understanding of systems face a higher risk of being replaced by AI-assisted tools if they do not upgrade their skills, deepen their understanding of system architecture, and complex problem-solving. (Source: cto_junior, cto_junior)
The Future of AI Agents: Opportunities and challenges coexist, industry leaders are optimistic about their potential: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman predicts that 2025 will be a breakout year for AI Agents, as they will become more involved in actual work. In his interview, Liu Zhiyi also emphasized that Agents are transitioning from passive tools to active execution systems, with their development depending on advancements in foundational models and their ability to interact with the physical world. Although current Agents still have shortcomings in response speed and hallucination control, their ability to autonomously execute tasks and assist large models in learning is widely recognized, and they have begun to be applied in fields such as intelligent customer service and financial investment advisory. (Source: 36氪, 量子位)
Perplexity AI partners with PayPal and Venmo to integrate e-commerce and travel payments: Perplexity AI announced a partnership with PayPal and Venmo to integrate payment functionalities into its platform for e-commerce shopping, travel booking, as well as its voice assistant and upcoming browser, Comet. This move aims to simplify the entire commerce process from browsing, searching, and selecting to secure payment, enhancing user experience. (Source: AravSrinivas, perplexity_ai)
Discussion on AI model evaluation: IFEval and ChartQA gain attention, need to be wary of training data contamination: In community discussions, IFEval is considered one of the excellent instruction-following evaluation benchmarks due to its simple yet clever design. Meanwhile, some users pointed out that ChartQA test data has issues like noise, ambiguous answers, and inconsistencies, suggesting it might need to be deprecated. Vikhyatk reminded that many models claiming high accuracy on benchmarks might have undetected training data contamination issues. (Source: clefourrier, vikhyatk)

AI-generated content copyright and ethics draw attention: Audible plans to use AI narration, AI-generated personas for online dating raise concerns: Audible announced plans to use AI-generated narration for audiobooks, aiming to “bring more stories to life,” sparking discussions about AI’s application in creative industries. On the other hand, a Reddit user posted that their mother was interacting with what appeared to be an AI-generated “real male” persona on a dating site, expressing concerns about her being scammed. This highlights the potential risks of AI-generated content in terms of authenticity, emotional manipulation, and fraud. (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

💡 Others
Chinese company “Xingsuan” successfully launches first batch of 12 space computing satellites, ushering in a new era of space-based computing power: The “Xingsuan” program, led by Guoxing Aerospace, successfully launched its first batch of 12 computing satellites into space, forming the world’s first space computing constellation. Each satellite possesses space computing and interconnection capabilities, with single-satellite computing power upgraded from T-level to P-level. The initial constellation has an on-orbit computing power of 5 POPS, and inter-satellite laser communication speeds reach up to 100Gbps. This initiative aims to build space-based intelligent computing infrastructure, addressing issues like high energy consumption and heat dissipation of ground-based computing power, and supporting real-time on-orbit processing of deep space exploration data, achieving “space data, space computing.” Future plans include launching 2,800 satellites to form a vast space computing network. (Source: 量子位)

NVIDIA releases annual review, emphasizing AI as the core of the new industrial revolution and intelligence as the product: In its annual review, NVIDIA pointed out that the world is entering a new industrial revolution, with “intelligence” as its core product. NVIDIA is committed to building intelligent infrastructure, transforming computing into a generative force that drives development across all industries. (Source: nvidia)

NBA collaborates with Kuaishou’s Kling AI to release AI short film “Childhood Curry’s Dunk”: The NBA has partnered with Kuaishou’s Sora-like text-to-video large model, Kling AI, with AI TALK producing an AI short film titled “Childhood Curry’s Dunk.” The film attempts to use Kling AI to recreate a “time-traveling” dunk scene by Curry, cheering for the NBA playoffs, and features special guest appearances by Charles Barkley, Shaquille O’Neal, and Nikola Jokić. (Source: TomLikesRobots)
