Keywords:OpenAI, HealthBench, Meta AI, Dynamic Byte Latent Transformer, Microsoft Research, ARTIST framework, Sakana AI, Continuous Thinking Machine, Medical AI performance evaluation, 8B parameter Dynamic Byte Latent Transformer model, Reinforcement learning for improving LLM reasoning, CTM neural network architecture, Qwen3 official quantized model, Dynamic Byte Latent Transformer model with 8B parameters, Enhancing LLM reasoning through reinforcement learning, Continuous Thinking Machine neural architecture, Official quantized model of Qwen3, AI performance benchmarking in healthcare, Meta AI research frameworks, Microsoft Research AI innovations, ARTIST framework for AI development, Sakana AI technologies, Medical AI assessment metrics
🔥 Focus
OpenAI Releases HealthBench to Evaluate Medical AI Performance: OpenAI has launched HealthBench, a new benchmark designed to measure the performance and safety of large language models (LLMs) in medical scenarios. Developed with input from over 250 global physicians, the benchmark includes 5,000 real-world medical conversations and 48,562 unique doctor-authored evaluation criteria, covering various contexts like emergency medicine and global health, as well as behavioral dimensions like accuracy and instruction following. Tests showed the o3 model achieved 60% accuracy, while GPT-4.1 nano outperformed GPT-4o with a 25x cost reduction, demonstrating the significant potential and rapidly improving performance-cost effectiveness of AI in the medical field. (Source: OpenAI)
Meta Releases 8B Parameter Dynamic Byte Latent Transformer Model: Meta AI announced the open-sourcing of the weights for its 8B parameter Dynamic Byte Latent Transformer model. This model proposes a new approach alternative to traditional tokenization methods, aiming to redefine the standards for language model efficiency and reliability. This new tokenization method is expected to bring breakthrough progress to the language model field, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of models in processing text. The research paper and code are available for download. (Source: AIatMeta)
Microsoft Research Introduces ARTIST Framework, Leveraging Reinforcement Learning to Enhance LLM Reasoning and Tool Use Capabilities: Microsoft Research introduced the ARTIST (Agentic Reasoning and Tool Integration in Self-improving Transformers) framework. This framework integrates agentic reasoning, reinforcement learning, and dynamic tool use, enabling large language models to autonomously decide when, how, and which tools to use for multi-step reasoning, and to learn robust policies without step-level supervision. ARTIST outperformed top models like GPT-4o by up to 22% on challenging benchmarks such as math and function calling, setting new standards for generalizable and interpretable problem-solving. (Source: MarkTechPost)

Sakana AI Releases Continuous Thought Machines (CTM): Sakana AI has introduced a novel neural network architecture called “Continuous Thought Machines” (CTM). The core idea of CTM is to use the dynamic temporal process of neural activity as a core component of its computation, allowing the model to operate along an internally generated timeline of “thought steps” to iteratively build and refine its representations, even for static data. The architecture demonstrated its adaptive computation, improved interpretability, and biological plausibility across various tasks including ImageNet classification, 2D maze navigation, sorting, parity calculation, and reinforcement learning. (Source: Sakana AI)

🎯 Trends
Alibaba Qwen Team Releases Official Quantized Models for Qwen3: The Alibaba Qwen team has officially released quantized models for Qwen3. Users can now deploy Qwen3 via platforms like Ollama, LM Studio, SGLang, and vLLM, with support for various formats including GGUF, AWQ, and GPTQ, facilitating local deployment. Related models are available on Hugging Face and ModelScope. This release aims to lower the barrier to using high-performance large models and promote their application in a wider range of scenarios. (Source: Alibaba_Qwen & Hugging Face & ClementDelangue & _akhaliq & TheZachMueller & cognitivecompai & huybery & Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Meta AI Releases Collaborative Reasoner Framework: Meta AI has introduced Collaborative Reasoner, a framework designed to improve the collaborative reasoning capabilities of language models. The framework focuses on developing social agents capable of collaborating with humans and other agents, paving the way for more complex human-computer interaction and multi-agent systems by enhancing models’ collaboration and reasoning skills. The related research paper and code are available for download, encouraging community exploration and application. (Source: AIatMeta)
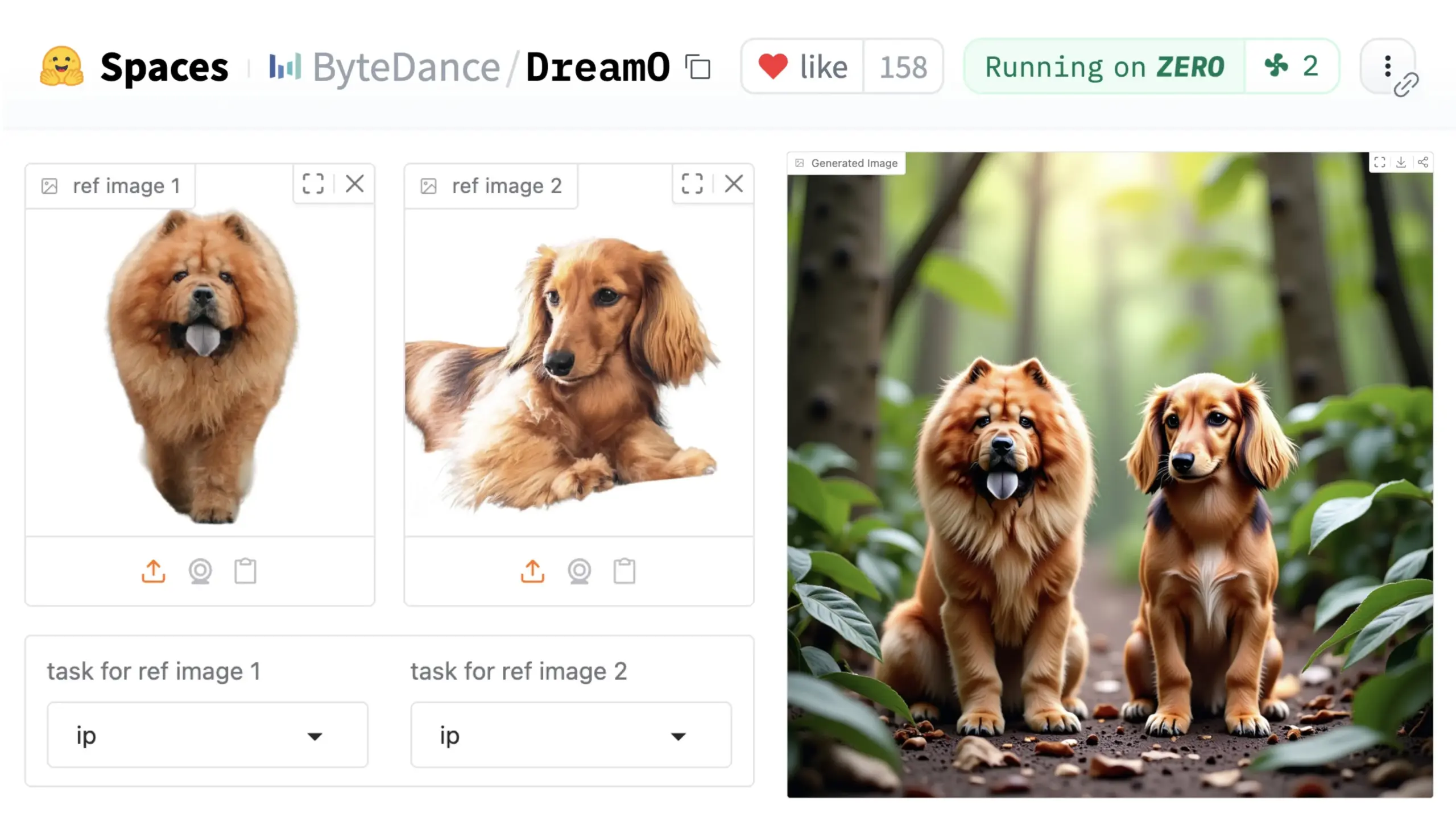
ByteDance Launches Universal Image Customization Framework DreamO: ByteDance has released a unified image customization framework named DreamO. Based on a pre-trained DiT (Diffusion Transformer) model, the framework enables generalized customization of various elements in images, including characters, styles, and backgrounds, supporting functions like identity replacement, style transfer, subject transformation, and virtual try-on. Users can try the demo on Hugging Face. This advancement showcases the potential of a single model in diverse image editing tasks. (Source: _akhaliq & ClementDelangue & _akhaliq)
NVIDIA Opens Nemotron Model Data Management Pipeline Nemotron-CC: NVIDIA announced it is opening its data management pipeline used for Nemotron models, Nemotron-CC, and disclosing as much of the Nemotron training and post-training data as possible. The Nemotron-CC pipeline is now part of the NeMo Curator GitHub repository and can process text, image, and video data at scale. NVIDIA emphasized the importance of high-quality pre-training datasets for the accuracy of large language models and considers data a fundamental component of accelerated computing. (Source: ctnzr & NandoDF)

Tencent’s Hunyuan-Turbos Model Ranks Eighth on LMArena Leaderboard: Tencent’s latest Hunyuan-Turbos model ranked eighth overall in the benchmarks on LMArena (formerly lmsys.org), and thirteenth in style control, performing close to Deepseek-R1. The model entered the top ten in major categories like hardcore, coding, and math, showing significant improvement compared to its February version. Community members like WizardLM_AI congratulated its performance. (Source: WizardLM_AI & WizardLM_AI & teortaxesTex)

Runway Gen-4 References Showcases Potential as a General Creative Tool: Runway’s Gen-4 References model is positioned as a general creative tool, capable of supporting nearly infinite workflows and applications. Community users continue to discover new use cases, demonstrating its strong adaptability as a general-purpose model that adjusts to the user’s creativity rather than forcing users to adapt to the model’s limitations. This reflects the trend of AI in media creation evolving from specific tasks towards general capabilities. (Source: c_valenzuelab & c_valenzuelab)

ByteDance’s Seed-1.5-VL-thinking Model Leads in Visual Language Model Benchmarks: ByteDance released the Seed-1.5-VL-thinking model, which achieved SOTA (state-of-the-art) results on 38 out of 60 visual language model (VLM) benchmarks. The model was reportedly trained on 1.3 million H800 GPU hours, showcasing its powerful multimodal understanding and reasoning capabilities. (Source: teortaxesTex)
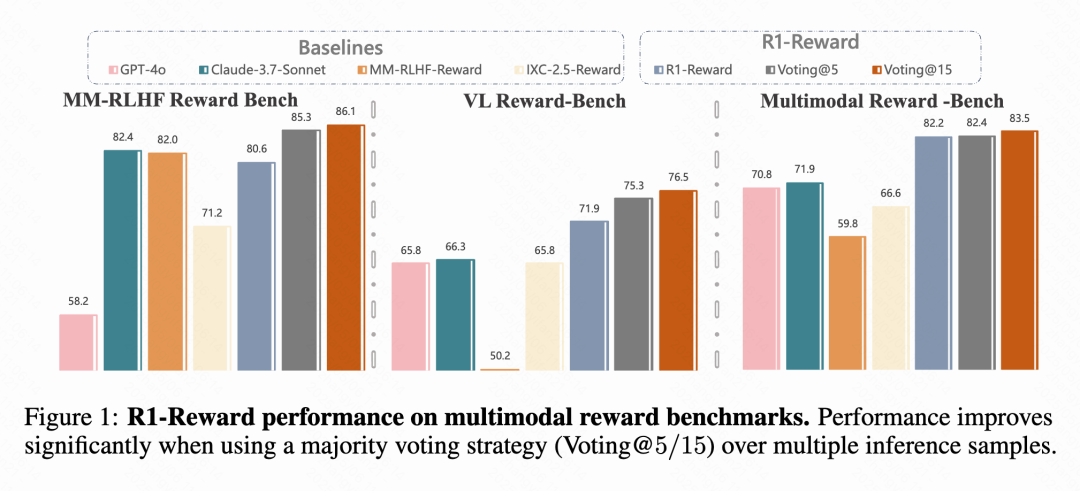
Kuaishou, CAS, etc., Propose Multimodal Reward Model R1-Reward: Research teams from Kuaishou, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Tsinghua University, and Nanjing University proposed R1-Reward, a new multimodal reward model (MRM) trained using an improved reinforcement learning algorithm called StableReinforce. The model aims to address the instability issues encountered by existing RL algorithms when training MRMs, introducing mechanisms such as Pre-Clip, advantage filtering, and consistency rewards. Experiments show that R1-Reward improves upon SOTA models by 5%-15% on multiple MRM benchmarks and has been successfully applied in Kuaishou’s business scenarios like short videos and e-commerce. (Source: WeChat & WeChat)
NTU et al. Propose WorldMem for Long-Sequence Consistent World Generation Using Memory Mechanisms: Researchers from Nanyang Technological University’s S-Lab, Peking University, and Shanghai AI Lab proposed the world generation model WorldMem. By introducing a memory mechanism, the model addresses the lack of consistency in existing video generation models over long sequences. Trained on the Minecraft dataset, WorldMem supports diverse scene exploration and dynamic changes, and its feasibility has been validated on real-world datasets, maintaining good geometric consistency after changes in viewpoint and position, and modeling temporal consistency. (Source: WeChat)

Kuaishou Kling Team Proposes CineMaster, a 3D-Aware Controllable Cinematic Video Generation Framework: The Kuaishou Kling research team published a paper at SIGGRAPH 2025 introducing the CineMaster framework. This is a cinematic text-to-video generation framework that allows users through an interactive workflow to arrange scenes, set objectives, and define camera movements in 3D space, achieving fine-grained control over video content. CineMaster integrates object motion and camera motion control via Semantic Layout ControlNet and Camera Adapter, respectively, and designed a data construction pipeline to extract 3D control signals from arbitrary videos. (Source: WeChat)

🧰 Tools
Comet-ml Releases Open-Source LLM Evaluation Framework Opik: Comet-ml has open-sourced Opik on GitHub, a framework for debugging, evaluating, and monitoring LLM applications, RAG systems, and Agent workflows. Opik provides comprehensive tracing, automated evaluations, and production-ready dashboards, supporting local installation or use as a hosted solution via Comet.com. It integrates with various popular frameworks like OpenAI, LangChain, LlamaIndex, and offers LLM-as-a-judge metrics for hallucination detection, content moderation, and RAG evaluation. (Source: GitHub Trending)

LovartAI Launches First Design Agent Lovart, Emphasizing Context Understanding: LovartAI has released the Beta version of its first design agent, Lovart. User feedback suggests that compared to other AI design tools, Lovart understands context better, even “like reading minds.” The tool allows humans and AI to collaborate on the same canvas, instantly transforming prompts into visuals, and can be used for brand logos, VI design, etc. (Source: karminski3)
CMU Jun-Yan Zhu’s Team Launches LEGOGPT for Text-to-3D LEGO Model Generation: CMU’s Jun-Yan Zhu team developed LEGOGPT, a large language model capable of generating physically stable and buildable 3D LEGO models from text prompts. The model formulates the LEGO design problem as an autoregressive text generation task, constructing structures by predicting the size and position of the next brick, and enforces physics-aware assembly constraints during training and inference, ensuring the stability and buildability of the generated designs. The team also released the StableText2Lego dataset containing over 47,000 LEGO structures. (Source: WeChat)
MNN Chat App Adds Support for Qwen 2.5 Omni 3B and 7B Models: Alibaba’s MNN (Mobile Neural Network) chat application now supports the Qwen 2.5 Omni 3B and 7B models. This means users can experience more powerful localized language model services on mobile devices. MNN is a lightweight deep learning inference engine focused on optimization for mobile and embedded devices. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

FutureHouse Platform Provides Superintelligent AI Research Tools for Scientists: Non-profit organization FutureHouse has released the FutureHouse platform, a web- and API-based suite of AI agents designed to accelerate scientific discovery. The platform offers a range of superintelligent AI research tools, assisting scientists with data analysis, simulation experiments, and knowledge discovery, driving a paradigm shift in scientific research. (Source: dl_weekly)
Cartesia Launches Pro Voice Cloning for Easy Custom Voice Model Building: Cartesia has released its fine-tuning product, Pro Voice Cloning. Users can upload their own voice data to easily build custom voice models for creating personal avatars, AI agents, or voice libraries. The product supports training and service deployment within 2 hours and offers a fully self-service product experience, aimed at enabling large-scale applications. (Source: krandiash)

CAS Institute of Computing Technology Proposes MCA-Ctrl for Precise Image Customization: The research team from the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed MCA-Ctrl (Multi-party Collaborative Attention Control), a tuning-free universal image customization method. This method leverages the internal knowledge of diffusion models through multi-party collaborative attention control, combining conditional image/text prompts with subject image content to achieve subject replacement, generation, and addition for specific subjects. Through self-attention local query and global injection mechanisms, MCA-Ctrl ensures layout consistency and alignment of specific object appearance replacement with the background. (Source: WeChat)

📚 Learning
AI Engineer Conference Announces Speaker Lineup: The AI Engineer conference has announced its speaker lineup, including top AI engineers and researchers from companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, LangChainAI, Google, and others. The conference will cover 20 subfields including MCP, LLM RecSys, Agent Reliability, GraphRAG, and features a CTO and VP leadership track for the first time. (Source: swyx & hwchase17 & _philschmid & HamelHusain & swyx & bookwormengr & swyx)
Hugging Face Publishes Blog on Latest Advances in Visual Language Models (VLMs): Hugging Face has published a comprehensive blog post on the latest advances in Visual Language Models (VLMs). The content covers various aspects including GUI agents, agentic VLMs, omni-models, multimodal RAG, video LMs, small models, summarizing new trends, breakthroughs, alignment, and benchmarks in the VLM field over the past year. (Source: huggingface & ben_burtenshaw & mervenoyann & huggingface & algo_diver & huggingface & huggingface)
Microsoft Azure Hosts Online Workshop on Building Serverless AI Chat Apps: Yohan Lasorsa announced an upcoming online workshop on building serverless AI chat applications using Azure. The session will explore Azure Functions, Static Web Apps, and Cosmos DB, and how to incorporate RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) techniques using LangChainAI JS. (Source: Hacubu & hwchase17)
Weaviate Podcast Discusses LLM-as-Judge Systems and the Verdict Library: Weaviate Podcast episode 121 features Haize Labs co-founder Leonard Tang, delving into the evolution of LLM-as-Judge / reward model systems. Discussion topics include the user experience of evaluation, comparative evaluation, judge integration, debate judges, curating evaluation sets, and adversarial testing, highlighting Haize Labs’ new library, Verdict, a declarative framework for specifying and executing composite LLM-as-judge systems. (Source: bobvanluijt & Reddit r/deeplearning)

Terence Tao Releases YouTube Video Demonstrating AI-Assisted Formal Mathematical Proof: Fields Medalist Terence Tao, in his YouTube channel debut, demonstrated how to use AI tools like GitHub Copilot and the Lean proof assistant to semi-automatically formalize a mathematical proof (Magma equation E1689 implies E2) in 33 minutes, which would typically require a full page of human mathematical writing. He emphasized that this method is suitable for proofs that are technically intensive but conceptually light, freeing mathematicians from tedious tasks. Additionally, the lightweight Python proof assistant he developed has been updated to version 2.0, enhancing its handling of asymptotic estimates and propositional logic. (Source: WeChat & QbitAI)

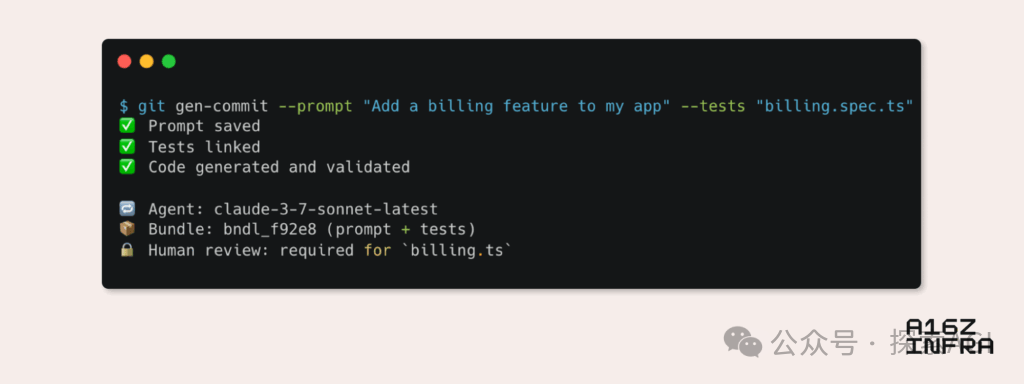
a16z Analyzes Nine Emerging Developer Pattern Trends in the AI Era: Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) published a blog post analyzing nine emerging developer pattern trends in the AI era. These include: AI-native Git (version control shifting towards Prompts and test cases), Vibe Coding (intent-driven programming replacing templates), a new paradigm for key management for AI Agents, AI-driven interactive monitoring dashboards, documentation evolving into AI-interactive knowledge bases, applications viewed from an LLM perspective (interacting via accessibility APIs), the rise of asynchronously executing Agents, the potential of the MCP (Model-Tool Communication Protocol), and the demand for foundational components for Agents. These trends signal a profound transformation in how software is built. (Source: WeChat)
💼 Business
Google Labs Launches AI Futures Fund to Support AI Startups: Google Labs announced the launch of the AI Futures Fund program, aimed at collaborating with startups to build the future of AI technology. The fund will provide selected startups with early access to Google DeepMind models and resources like cloud credits to help accelerate their development. (Source: GoogleDeepMind & JeffDean & Google & demishassabis)
Perplexity Reportedly in Talks for New $500M Funding Round at $14B Valuation: AI search company Perplexity is reportedly in talks for a new $500 million funding round, with a potential valuation of $14 billion. This comes just six months after its last funding round (at a $9 billion valuation), highlighting strong investor interest in the AI search sector and confidence in Perplexity’s growth prospects. (Source: Dorialexander)

OpenAI Reportedly Agrees to Acquire Windsurf for ~$3B: According to Bloomberg, OpenAI has agreed to acquire startup Windsurf for approximately $3 billion. Specific details of the acquisition and Windsurf’s business focus have not been disclosed, but the move could signify OpenAI’s further expansion of its technological capabilities or market reach. (Source: Reddit r/artificial & Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

🌟 Community
The Real Risk of AI: The ‘Simulation Trap’ of Infinite Satisfaction: Discussions involving Amjad Masad and others suggest the real danger of AI is not the killer robots of science fiction, but its ability to infinitely satisfy human desires, creating an “infinite happiness machine.” This type of AI could lead humans to become addicted to simulated struggles and meaning, ultimately “disappearing” into the simulated world, offering a possible explanation for the Fermi paradox – civilizations don’t die out, but enter digital nirvana. (Source: amasad)
AI Agents Poised to Reshape Programming and Scientific Research: Replit CEO Amjad Masad predicts that within the next year or two, AI agents will be able to work uninterrupted for days, or even years, to solve complex scientific problems. He believes agents will become a new way of programming, capable of dedicating days to solving a single problem, much like humans, signaling AI’s immense potential in automating complex tasks and accelerating scientific discovery. (Source: TheTuringPost & amasad & TheTuringPost)
John Carmack Discusses AI’s Potential in Optimizing Codebases: Legendary programmer John Carmack believes AI, beyond generating vast amounts of code, has even greater potential in helping beautify and refactor existing codebases. He envisions AI as a diligent team member, continuously reviewing code and suggesting improvements, and could even define “AI-friendly” coding style guides through objective experimentation. He looks forward to seeing how teams with extremely high code quality standards, like OpenBSD, might integrate AI members. (Source: ID_AA_Carmack)
‘Vibe Coding’ Sparks Debate: Pros and Cons of AI-Assisted Programming: Community discussions point out that although “Vibe Coding” (using natural language instructions for AI to generate code prototypes) can quickly build demo-level applications, deploying and scaling them still requires professional developers to build from scratch. Engineered products involve not just writing code but also complex issues like architecture, CI/CD, microservices, which AI currently struggles to handle completely. Vibe Coding is suitable for rapid prototyping, but building real solutions still demands engineering mindset and experience. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
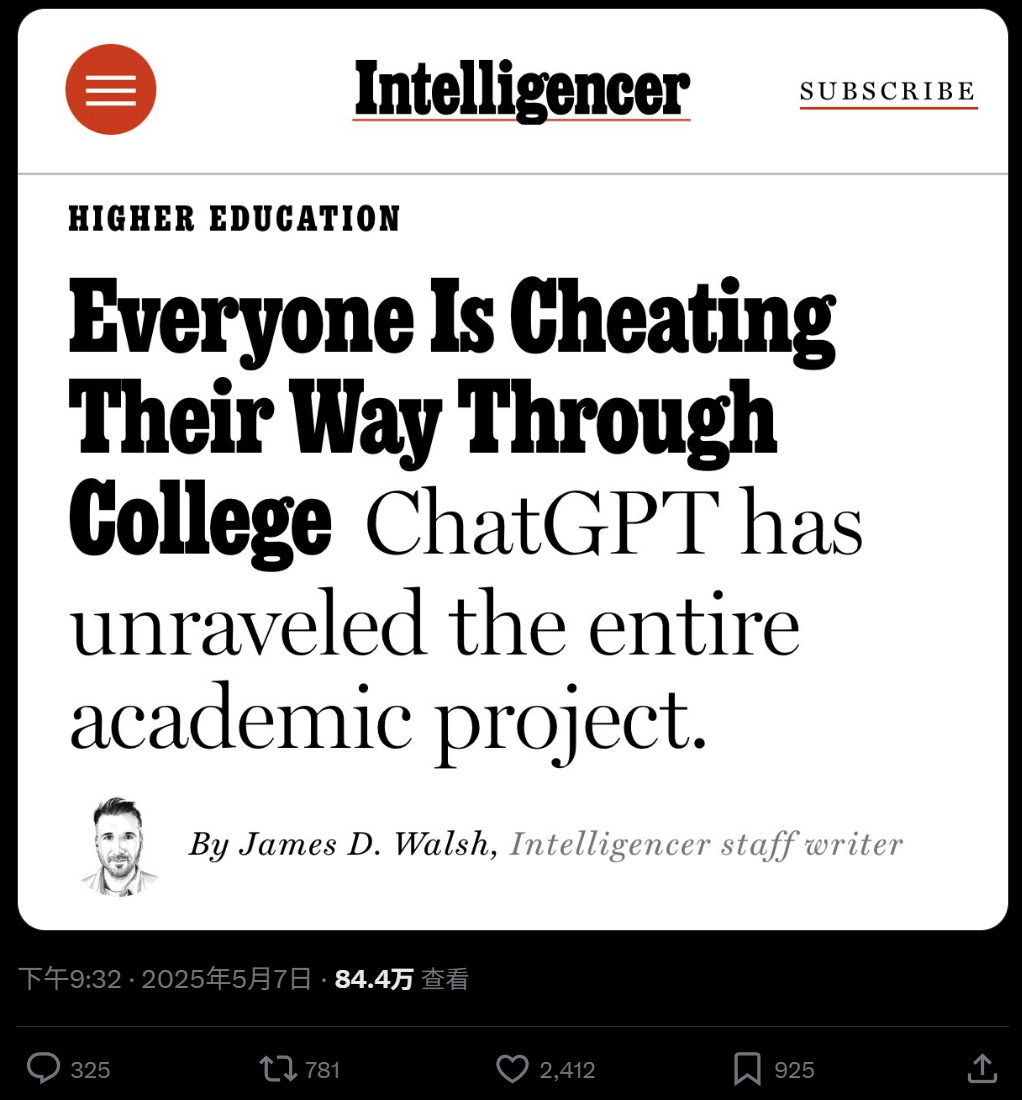
Widespread Use of AI in University Education and Cheating Concerns: A report by New York Magazine reveals the widespread phenomenon of AI tools (like ChatGPT) being used in North American universities to complete assignments and essays. Students use AI for note-taking, studying, research, and even directly generating assignment content, raising concerns about academic integrity, educational quality, and the decline of students’ critical thinking skills. Educators are trying to adjust teaching and assessment methods, but the effectiveness of AI detection tools is questionable, making AI cheating difficult to eradicate. (Source: WeChat)
💡 Others
Cohere Discusses Challenges of Moving Government AI Applications from Pilot to Production: Cohere points out that most government AI projects remain in the pilot stage. To bridge the gap from pilot to actual production deployment, government agencies need trustworthy tools, clear outcome orientation, efficient infrastructure, and suitable partners. The article explores how government agencies can transition from experimentation to practical application using secure and efficient AI. (Source: cohere)

Mustafa Suleyman: Larger Language Models Are Easier to Control: Inflection AI co-founder Mustafa Suleyman argues that, contrary to common concerns, larger language models (LLMs) are actually easier to control as their scale increases. He noted that models from previous generations were harder to steer, stylize, and shape, while increased scale enhances, rather than diminishes, controllability. (Source: mustafasuleyman)
AI Ethics Discussion: Accountability for AI-Caused Harm or Bias: A Reddit post sparked discussion: When an AI system (e.g., a medical diagnostic AI) causes harm due to biased training data (e.g., trained primarily on light-skinned images, leading to misdiagnosis for dark-skinned patients), who should be held accountable? This involves defining the responsibilities of multiple parties, including AI developers, deploying institutions, and regulators. It is a critical issue that AI ethics and legal frameworks urgently need to address. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)