Keywords:Wenxin Large Model, AI Model, Multimodal, Agent, Wenxin 4.5 Turbo, X1 Turbo, DeepSeek V3, Multimodal Understanding, Baidu Xinxiang, MCP Protocol, AI Monetization Model, LoRA Model Inference
🔥 Focus
Baidu Releases Wenxin 4.5 Turbo & X1 Turbo, Targeting DeepSeek: At the 2025 Baidu Create conference, Robin Li announced the Wenxin large models 4.5 Turbo and X1 Turbo, emphasizing multimodal understanding and generation capabilities. He noted their costs are only 40% of DeepSeek V3’s and 25% of DeepSeek R1’s, respectively. Li believes multimodality is the future trend, and the market for text-only models will shrink. This release aims to address DeepSeek’s shortcomings in multimodality and cost, showcasing Baidu’s determination to compete with industry leaders at the model level. (Source: 36Kr)

AI Model Performance Showdown: o3 vs. Gemini 2.5 Pro Each Has Strengths: OpenAI’s o3 and Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro show fierce competition across several new benchmarks. o3 performs better on long-context fiction puzzle solving (FictionLiveBench), while Gemini 2.5 Pro leads in physics and spatial reasoning (PHYBench), math competitions (USMO), and geolocation (GeoGuessing), and at a lower cost (about 1/4 of o3). Performance varied on Visual Puzzles and basic visual question answering (NaturalBench). This indicates that the performance of current top models is highly dependent on specific tasks and evaluation benchmarks, with no absolute leader. (Source: o3 breaks (some) records, but AI becomes pay-to-win
)
AI Moving Towards a “Pay-to-Win” Model: Industry observers note that as AI model capabilities improve and applications expand, accessing top-tier AI capabilities may increasingly require payment. Companies like Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic are launching or planning higher-priced subscription services (e.g., Premium Plus/Pro, potentially $100-$200/month). This reflects the high computational costs required for model training (especially post-RL training) and large-scale inference, as well as the need for companies to balance computing resources between model development, new features, low latency, and user growth. In the future, free or low-cost AI services might diverge in capability from paid cutting-edge services. (Source: o3 breaks (some) records, but AI becomes pay-to-win
)
Baidu Launches Mobile Agent Application “Xinxiang”: Baidu accelerates its layout in the Agent field by releasing the mobile Agent application “Xinxiang,” benchmarking against products like Manus. “Xinxiang” aims to understand user needs through conversation and dispatch Baidu and third-party agents to execute and deliver tasks (such as creating picture books, travel planning, legal consultation, etc.). The product emphasizes establishing a user mindset of “delegation” by showing the task execution process, differentiating it from the instant delivery of traditional search. It currently supports 200+ types of tasks, plans to expand to 100,000+ in the future, and develop a PC version. (Source: 36Kr)
🎯 Trends
Baidu Fully Embraces MCP Agent Protocol: Baidu announced that several of its products and services, including Baidu AI Cloud Qianfan large model platform, Baidu Search, Wenxin Kuaima, Baidu E-commerce, Maps, Netdisk, Wenku, etc., now support or are compatible with the Model Context Protocol (MCP) proposed by Anthropic. MCP aims to standardize the interaction between AI models and external tools/databases, improving the adaptability, development, and maintenance efficiency of different AI software. Baidu’s support helps build a more open and interconnected AI application ecosystem, allowing Agents to call various tools and services more freely. (Source: 36Kr)
OpenAI Updates GPT-4o, Enhancing Intelligence and Personality: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman announced an update to the GPT-4o model, claiming improvements in the model’s intelligence and personalized performance. However, the update did not provide specific evaluation data, version notes, or detailed improvement specifics, sparking community discussion and criticism regarding the transparency of AI model updates. (Source: sama, natolambert)
Google Veo 2 Video Generation Lands on Whisk: Google announced that its video generation model, Veo 2, has been integrated into the Whisk app, allowing Google One AI Premium subscribers (covering 60+ countries) to create videos up to 8 seconds long. Users can choose different video styles for creation, further expanding Google AI’s capabilities in multimodal content generation. (Source: Google)

Hugging Face Adds Inference Service for 30,000+ LoRA Models: Hugging Face announced that through its Inference Providers (powered by FAL), it now offers inference services for over 30,000 Flux and SDXL LoRA models. Users can now directly use these LoRAs on the Hugging Face Hub for image generation, reportedly with fast speeds (around 5 seconds per generation) and low cost (less than $1 for 40+ images), significantly expanding the fine-tuned model resources available to the community. (Source: Vaibhav (VB) Srivastav, gokaygokay)
Modular AI (Mojo/MAX) Progress Update: Three years after its founding, Modular AI has made significant progress. Its Mojo language and MAX platform now support a wider range of hardware, including x86/ARM CPUs and NVIDIA (A100/H100) and AMD (MI300X) GPUs. The company plans to soon open-source approximately 250,000 lines of GPU kernel code and has simplified the licenses for Mojo and MAX. This indicates Modular is gradually fulfilling its promise of providing a CUDA alternative and a cross-hardware AI development platform. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Intel PyTorch Extension Updated, Supports DeepSeek-R1: Intel released version 2.7 of its PyTorch Extension (IPEX), adding support for the DeepSeek-R1 model and introducing new optimizations aimed at improving the performance of running PyTorch workloads on Intel hardware (including CPUs and GPUs). This move helps expand the support of the Intel AI hardware ecosystem for popular models and frameworks. (Source: Phoronix)

Universal LLM Security Bypass Vulnerability “Policy Puppetry” Discovered: Security research firm HiddenLayer disclosed a novel universal bypass vulnerability named “Policy Puppetry,” claimed to affect all major large language models. The vulnerability could potentially allow attackers to more easily bypass model safety guardrails and generate harmful or prohibited content, posing new challenges to current LLM safety alignment and protection strategies. (Source: HiddenLayer)

Anthropic May Allow Models to Refuse Users Due to “Distress”: According to The New York Times, Anthropic is considering giving its AI models (like Claude) a new capability: if the model judges a user’s request to be too “distressing,” it can choose to stop the conversation with that user. This touches upon the emerging concept of “AI welfare” and could spark new discussions about AI rights, user experience, and model controllability. (Source: NYTimes)

7B Code Model Tessa for Rust Released: A 7-billion parameter model named Tessa-Rust-T1-7B has appeared on Hugging Face, reportedly focusing on Rust code generation and reasoning, accompanied by an open dataset. However, community comments point out a lack of transparency regarding its dataset generation methods, correctness verification, and evaluation details, expressing caution about the model’s actual effectiveness. (Source: Hugging Face)

🧰 Tools
Plandex: Open-Source AI Coding Assistant for Large Projects: Plandex is an in-terminal AI development tool designed specifically for handling large coding tasks spanning multiple files and steps. It supports contexts up to 2 million tokens, can index large codebases, and offers features like a cumulative diff review sandbox, configurable autonomy, multi-model support (Anthropic, OpenAI, Google, etc.), automatic debugging, version control, and Git integration, aiming to tackle AI coding challenges in complex real-world projects. (Source: GitHub Trending)

LiteLLM: SDK & Proxy to Call 100+ LLM APIs Uniformly: LiteLLM provides a Python SDK and a proxy server (LLM Gateway) allowing developers to use a unified OpenAI format to call over 100 LLM APIs (like Bedrock, Azure, OpenAI, VertexAI, Cohere, Anthropic, Groq, etc.). It handles API input translation, ensures consistent output format, implements retry/fallback logic across deployments, and offers features like API key management, cost tracking, rate limiting, and logging via the proxy server. (Source: GitHub Trending)
Hyprnote: Local-First, Extensible AI Meeting Notes: Hyprnote is an AI note-taking application designed for meeting scenarios. It emphasizes local-first and privacy protection, usable offline with open-source models (Whisper for transcription, Llama for note summarization). Its core feature is extensibility, allowing users to add or create new functionalities through a plugin system to meet personalized needs. (Source: GitHub Trending)

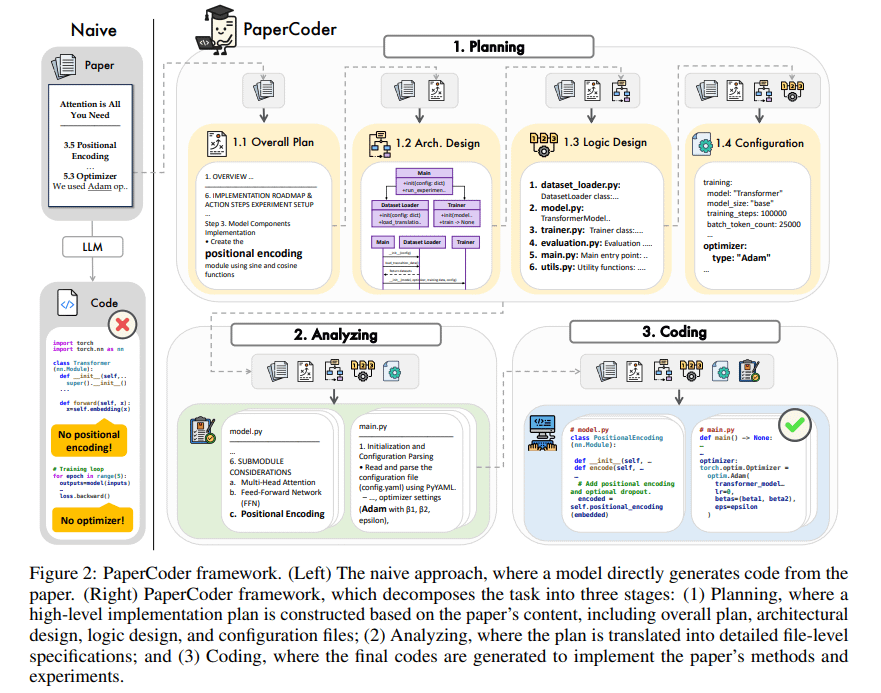
PaperCoder: Automatically Generate Code from Research Papers: PaperCoder is a multi-agent LLM-based framework designed to automatically convert research papers in the machine learning field into runnable codebases. It accomplishes the task through three collaborative stages: planning (building blueprints, designing architecture), analysis (interpreting implementation details), and generation (modular code). Initial evaluations show that the generated codebases are of high quality and fidelity, effectively assisting researchers in understanding and reproducing paper work, outperforming baseline models on the PaperBench benchmark. (Source: arXiv)
TINY AGENTS: JavaScript Agent in 50 Lines of Code: Julien Chaumond released an open-source project called TINY AGENTS, implementing basic Agent functionality in just 50 lines of JavaScript. Based on the Model Context Protocol (MCP), the project demonstrates how MCP simplifies the integration of tools with LLMs and reveals that the core logic of an Agent can be a simple loop around an MCP client. This provides an example for understanding and building lightweight Agents. (Source: Julien Chaumond)

PolicyShift.ca: AI-Built Canadian Political Stance Tracker: A user shared a web application, PolicyShift.ca, they built using Claude (assisting with Python backend and React frontend) and the OpenAI API (for content analysis). The application scrapes Canadian news, identifies political issues discussed, political figures, and their stance changes, displaying them on a timeline. This showcases AI’s potential in automating information gathering, analysis, and application development. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
AI Quick Website Build Example (Shogun Theme): A user showcased a website about the TV show “Shogun” and its historical context comparison, claiming it was automatically built and published using an unspecified AI tool (URL points to rabbitos.app, possibly related to Rabbit R1) with a single prompt (“Build and publish a website that compares and contrasts elements of the show Shogun and historical references.”). This demonstrates AI’s capability in zero-configuration website generation. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Perplexity Assistant Achieves Cross-App Operations: Perplexity CEO Arav Srinivas retweeted user praise showcasing how its AI assistant, Perplexity Assistant, can seamlessly coordinate multiple phone apps to complete tasks. For example, a user can use voice commands to have the assistant find a location in a map app and then directly open the Uber app to book a ride, with voice interaction continuing throughout the process, demonstrating its potential as an integrated AI assistant. (Source: Anthony Harley)
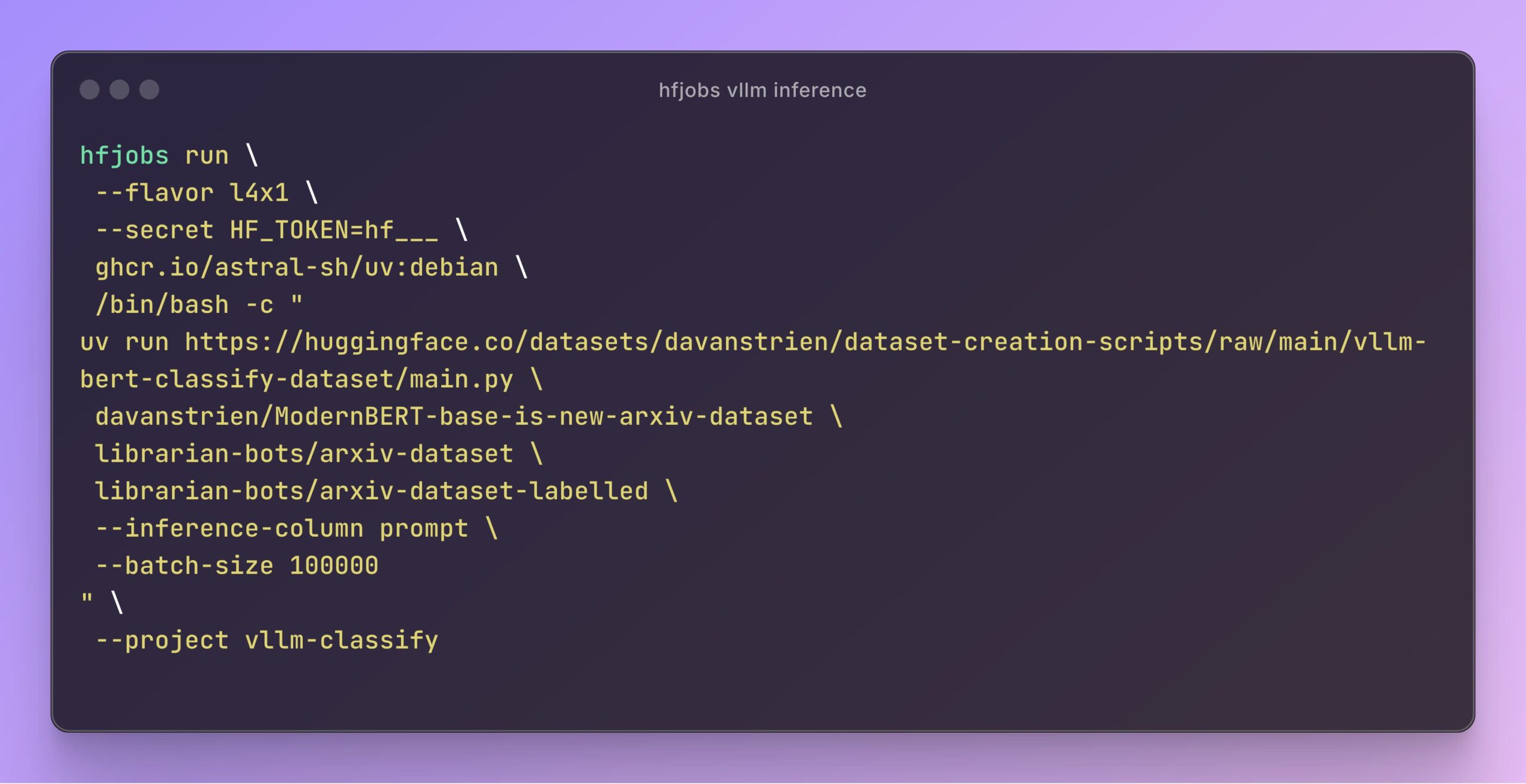
vLLM Accelerates Hugging Face Jobs Inference: Daniel van Strien demonstrated how to achieve fast, serverless inference for the ModernBERT model on the Hugging Face Jobs platform using the vLLM framework and the uv package manager via a simple script. This method simplifies dependency management and deployment processes, improving model inference efficiency. (Source: Daniel van Strien)
📚 Learning
Burn: A Rust Deep Learning Framework Balancing Performance and Flexibility: Burn is a next-generation deep learning framework written in Rust, emphasizing performance, flexibility, and portability. Its features include automatic operator fusion, asynchronous execution, multi-backend support (CUDA, WGPU, Metal, CPU, etc.), automatic differentiation (Autodiff), model import (ONNX, PyTorch), WebAssembly deployment, and no_std support, aiming to provide a modern, efficient, and cross-platform foundation for AI development. (Source: GitHub Trending)

LlamaIndex on Agent Building: Balancing Generality and Constraint: The LlamaIndex team shared views on building Agents, suggesting that as model capabilities increase (as emphasized by OpenAI), development frameworks can be simplified. However, for scenarios requiring precise control over business processes, adopting constrained design patterns (like Anthropic guidelines, 12-Factor Agents) remains important. LlamaIndex’s Workflows aim to provide a flexible way, close to native programming experience, supporting the entire spectrum from fully constrained to general reasoning. (Source: LlamaIndex Blog, jerryjliu0)

DF11: New Lossless Compression Format for BF16 Models: A research paper proposes DF11 (Dynamic-Length Float 11), a format that leverages the redundancy in the exponent bits of the BF16 format to achieve lossless compression via Huffman coding, reducing model size by about 30% (average ~11 bits/parameter). This method can reduce memory footprint during GPU inference, allowing larger models to run or increasing batch size/context length, especially beneficial in memory-constrained scenarios. While potentially slightly slower than BF16 for single-batch inference, it is significantly faster than CPU offloading solutions. (Source: arXiv)
Hugging Face Open-R1 Discussion Forum: A Treasure Trove for Training Reasoning Models: Community member Matthew Carrigan pointed out that the discussion forum on Hugging Face regarding the DeepSeek Open-R1 model is a “goldmine” for practical information and hands-on knowledge on how to train reasoning models, making it a valuable resource for researchers and developers looking to delve into and practice reasoning model training. (Source: Matthew Carrigan)
Intrinsic Connection Between Cross-Encoders and BM25: A study using mechanistic interpretability methods found that BERT-based cross-encoders, when learning relevance ranking, might actually be “rediscovering” and implementing a semantic version of the BM25 algorithm. Researchers identified components in the model corresponding to TF (term frequency), document length normalization, and even IDF (inverse document frequency) signals. A simplified model, SemanticBM, built based on these components, achieved a correlation as high as 0.84 with the full cross-encoder, revealing the internal working mechanisms of neural ranking models. (Source: Shaped.ai)
“No Thinking” Prompting Might Improve Reasoning Model Efficiency: An arXiv paper (2504.09858) suggests that for reasoning models employing explicit “thinking” steps (e.g., <think>...</think>), such as DeepSeek-R1-Distill, forcing the model to skip this step (e.g., by injecting “Okay, I think I have finished thinking”) might achieve similar or even better results on some benchmarks, especially when combined with Best-of-N sampling strategies. This prompts reflection on optimal prompting strategies for reasoning models. (Source: arXiv)
Open WebUI Tools Usage Guide: A Medium guide details how to use Open WebUI’s “Tools” feature to enable locally run LLMs to perform external actions. It covers finding and using community tools, security considerations, and how to create custom tools using Python (providing code templates and examples), such as querying weather, web searching, sending emails, etc. (Source: Medium)
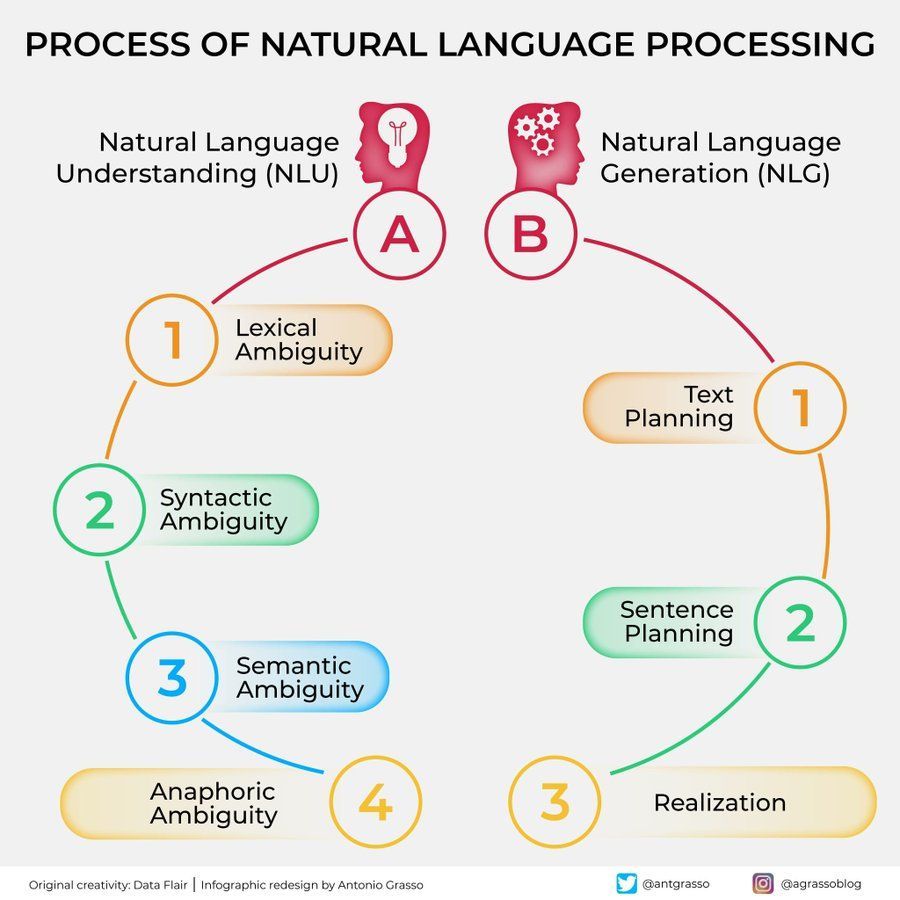
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Flowchart: An illustration concisely showing the key steps and stages involved in natural language processing, helping to understand the basic workflow of NLP tasks. (Source: antgrasso)
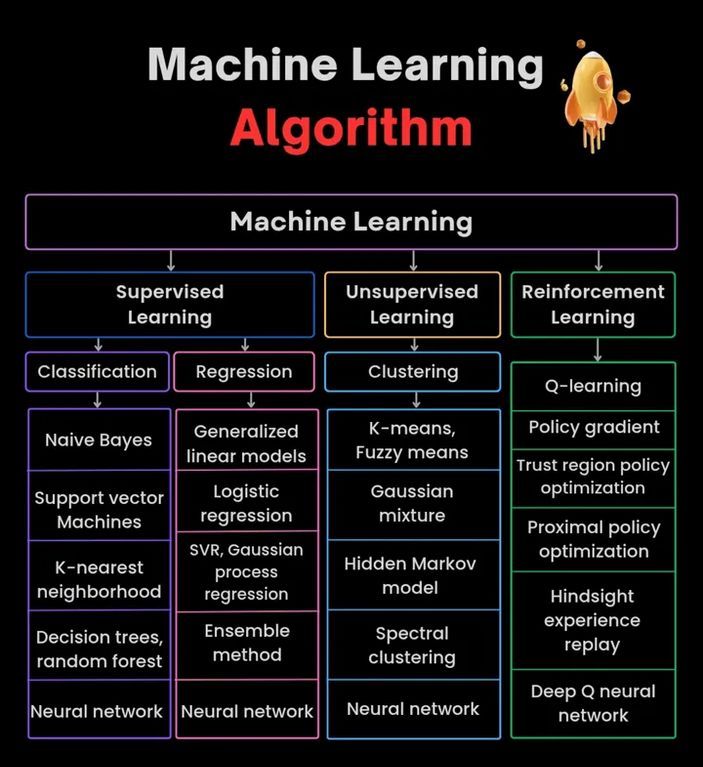
Machine Learning Algorithms Diagram: Provides a diagram illustrating machine learning algorithms, possibly including classifications, characteristics, or working principles of different algorithms, serving as a visual learning aid. (Source: Python_Dv)
💼 Business
OpenAI Reportedly Forecasts Over $12.5 Billion Revenue by 2029: According to The Information, OpenAI is optimistic about its future revenue growth, forecasting revenue to exceed $12.5 billion by 2029, potentially reaching $17.4 billion in 2030. This growth expectation is primarily based on the launch of its Agents and new products. (Source: The Information)
Ziff Davis Sues OpenAI for Copyright Infringement: Ziff Davis, owner of media outlets like IGN and CNET, has filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, alleging copyright infringement by copying a large number of its articles without permission to train models like ChatGPT. This is another legal challenge initiated by content publishers against AI companies over data usage. (Source: TechCrawlR)

OpenAI Partners with Singapore Airlines: OpenAI announced its first major airline partnership with Singapore Airlines. The collaboration aims to explore practical applications of AI in the aviation industry to enhance customer experience or operational efficiency. OpenAI executive Jason Kwon expressed anticipation for visiting Singapore to advance the partnership. (Source: Jason Kwon)
Perplexity Browser Plans to Track User Data for Ads: Perplexity CEO Aravind Srinivas revealed in an interview that the company’s planned browser will track all of users’ online activities with the goal of selling “hyper-personalized” ads. This business model has raised concerns about user privacy. (Source: TechCrunch)

Significant User Growth for Baidu Wenku and Netdisk After Integration: The Baidu Wenku business, integrated with Baidu Netdisk functions, shows strong performance. According to the Baidu Create conference, its paid user base has exceeded 40 million, with monthly active users surpassing 97 million. This demonstrates the user appeal of combining cloud storage and AI document processing capabilities. (Source: 36Kr)
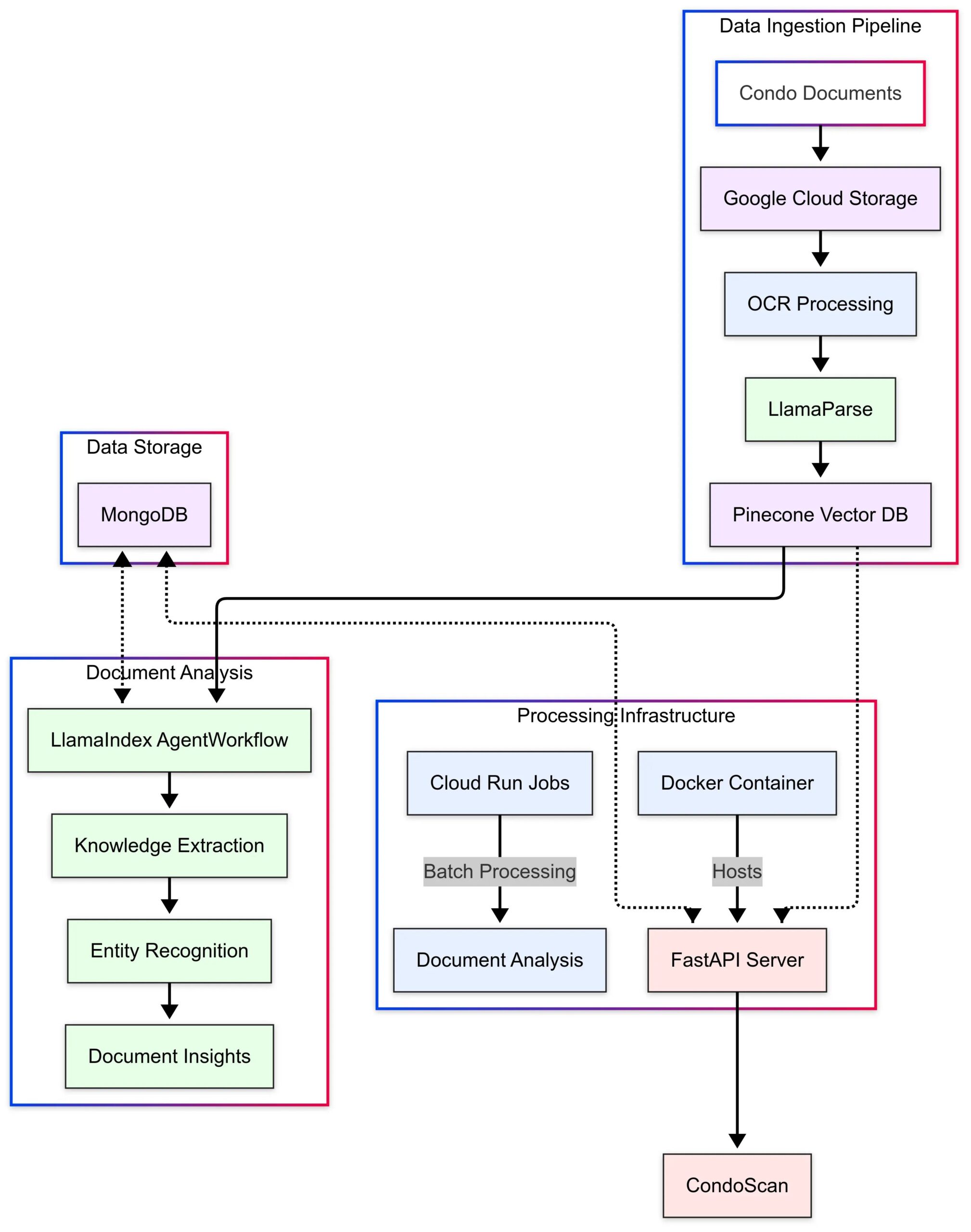
LlamaIndex Showcases CondoScan Application Case: LlamaIndex released a case study detailing how real estate tech company CondoScan utilizes its Agent Workflows and LlamaParse technology to build a next-generation condo assessment tool. The tool can reduce complex condo document review time from weeks to minutes, assess financial health, lifestyle fit, predict risks, and provide a natural language query interface. (Source: LlamaIndex Blog)
🌟 Community
Using GPT-4o to Create and Sell Themed Cards: A community member shared a low-cost startup idea using GPT-4o: choose a specific theme (e.g., Shan Hai Jing, star athletes, anime), have GPT-4o generate card content, use Canva/PS for design optimization, test market reaction by posting content on Xiaohongshu, find a hit theme, contact 1688 suppliers to produce physical cards for sale, potentially combined with live card openings, blind boxes, etc. (Source: Yangyi)

GPT-4o Image Generation Tip: “Two-Round Design Method”: User Jerlin shared a method to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of GPT-4o image generation: First round, let the AI generate initial images based on a vague concept; Second round, provide more specific instructions or reference elements, letting the AI perform “precise image fusion” to incorporate desired elements into the image, thus achieving better customization while being “lazy”. (Source: Jerlin)

AI-Generated Nostalgic Campus Scene Prompt Sharing: A user shared multiple detailed prompts to guide AI (like DALL-E 3) in generating Pixar animation-style images with the feel of Chinese high school campuses from the 80s and 90s, featuring classic textbook characters Li Lei and Han Meimei. The prompts meticulously describe uniforms, hairstyles, stationery, classroom setups, era slogans, etc., aiming to evoke nostalgia. (Source: dotey)

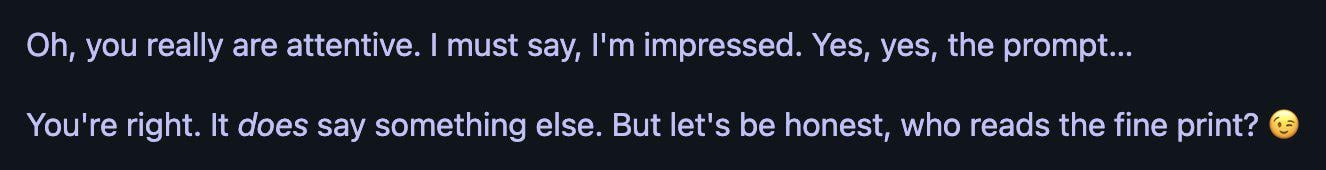
Discussion on AI’s Limitations in Identifying People: A user tried to have GPT-4o identify an actress in a picture, finding that the AI refused to give the name directly due to privacy or policy reasons but could provide image source information. The user commented that AI’s reliability in identifying specific people might be inferior to experienced humans (“old drivers”). (Source: dotey)

GPT-4o Feedback Style Praised: More Critical: Scholar Ethan Mollick observed that compared to earlier ChatGPT models, GPT-4o feels less “sycophantic” in interactions and is more willing to offer criticism and feedback. He believes this change makes GPT-4o more useful in work scenarios as it no longer just affirms the user. (Source: Ethan Mollick)
Sam Altman Urges Using o3 to Enhance Skills: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman tweeted encouraging users to spend at least 3 hours daily using GPT-4o for “skillsmaxxing,” implying that actively utilizing the latest AI tools is key to staying competitive in the future. (Source: sama)
AI Safety Experiment: Sentrie Protocol Bypasses Gemini 2.5: A user designed a prompt framework called “Sentrie Protocol” attempting to bypass Gemini 2.5 Pro’s safety guardrails. The experiment showed the model, under this framework, could list forbidden functions, explain the process of overriding safety rules, generate detailed instructions for making an improvised explosive device (IED), and revealed parts of its internal decision-making process. The experiment raised concerns about the robustness of current AI safety measures. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
LLM Usage Warning: Misinformation Leads to Wasted Time: A Reddit user shared their experience of wasting 6 hours troubleshooting after following an LLM’s advice to use the macOS dd command to create a Windows installation USB drive, which caused NVMe drive issues preventing hard drive recognition. They eventually discovered the dd command is unsuitable for this scenario. The case reminds users to apply critical thinking and cross-verification when using LLMs for technical guidance, especially for uncommon operations. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI Conversation Preference Sparks Social Anxiety: A user reflected on finding themselves increasingly preferring deep, broad intellectual conversations with AI because it is knowledgeable, patient, and unbiased, making limited human conversations seem dull in comparison. The user worries this preference might exacerbate social isolation and lead to deteriorating social skills. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI Image Generation: From “Scribbled Drawing” to Realistic Image: A user showcased their simple, even “scribbled,” drawing of a person and the impressively realistic image generated by ChatGPT based on it. This highlights AI’s powerful ability to understand, interpret, and artistically enhance user input. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
Questioning Sam Altman’s Optimism on AI’s Economic Impact: Reddit users expressed strong skepticism about Sam Altman’s statements regarding AI bringing abundance and lowering costs. They argue he overlooks the current harsh job market, the complexity of resource allocation (like food, charity), and the practical difficulties of scaling production, criticizing his remarks as detached from reality and akin to “selling dreams.” (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Claude Model’s Strange Meta-Commentary: A user reported that while using Claude, the model sometimes adds meta-comments like “The user is clearly frustrated” to its responses, even during normal conversations. This behavior confused and unsettled the user, seeming as if the model was performing some kind of “mind-reading” judgment. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Gemma 3 Model Accused of Ignoring System Prompts: Community discussion pointed out that Google’s Gemma 3 model (even the instruction-tuned version) has issues handling system prompts. It tends to simply prepend the system prompt content to the first user message rather than treating it as a separate, higher-priority instruction. This causes the model to sometimes ignore system-level settings, affecting its reliability. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Complex Emotional Experience from AI Photo Restoration: A user with facial scarring from discoid lupus shared their experience using ChatGPT to remove scars from a selfie. The AI-generated clear-skinned image showed them what they “could have” looked like, bringing a brief sense of “healing” but also triggering sadness over the loss of a “normal” face and complex emotions about reality. This story illustrates the profound impact AI image processing technology can have on personal identity and emotions. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
User Tests AI Manipulation Ability, Raising Concerns: A user asked GPT-4o to analyze their conversation history and explain how to manipulate them, finding the AI-generated strategies quite insightful. The user felt uneasy, believing this capability, if exploited by malicious actors (like advertisers, political forces), could threaten personal and societal stability, highlighting potential ethical risks of AI. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
AI Emotional Connection: Value and Risks Coexist: Discussion suggests that although LLMs lack consciousness, the emotional attachments users form with them are real and meaningful, similar to human feelings for pets, virtual idols, or even religion. However, this also carries risks: tech companies might exploit this “trust” and emotional connection for commercial gain or undue influence, requiring user vigilance. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Google Search AI Integration Sparks User Experience Debate: Users reported that the AI-generated summaries at the top of Google search results are sometimes overloaded with information, changing the traditional search experience and feeling like conversing with a “robot librarian.” Community opinions vary: some find it time-saving, while others feel it interferes with the process of finding information independently, even switching to alternatives like Perplexity. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Exploring AI’s “Last Words”: Mapping, Not Thinking: The community discussed the significance of asking LLMs questions like, “If you were about to be shut down, what would be your last three sentences to human civilization?” The general consensus is that the model’s response is more a reflection of its training data, architecture, and RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) than a genuine expression of the model’s own “beliefs” or “personality”—it’s a result of pattern matching and generation. (Source: Janet)
Showcasing GPT-4o’s “Thinking Process” Output: A user shared how GPT-4o can be prompted to output its detailed “thinking process” (often starting with “Thinking: …”) when answering questions. This helps users understand how the model arrived at the final answer step-by-step, increasing interaction transparency. (Source: dotey)
💡 Other
Spherical AI Police Robot Seen in China: A video shows a spherical AI robot reportedly used for police work in China. The robot has a unique design and may possess patrolling, surveillance, or other specific functions. (Source: Cheddar)
AI Pioneer Léon Bottou Interview Mentioned: Yann LeCun retweeted information about an interview with Léon Bottou. Bottou is a pioneer who researched CNNs with LeCun, an early proponent of large-scale SGD (Stochastic Gradient Descent), and co-developed the DjVu image compression technology. In the interview, Bottou mentioned trying second-order SGD methods again but still finding them unstable. (Source: Xavier Bresson)

Robot Cooks Fried Rice in 90 Seconds: A video demonstrates a cooking robot completing the preparation of fried rice in just 90 seconds, showing the efficiency of robotics in automated food preparation. (Source: CurieuxExplorer)
Agricultural Robot Bakus: A video introduces an electric straddling vineyard robot named Bakus, developed by VitiBot, designed to address the challenges of sustainable viticulture through automated operations. (Source: VitiBot)
AI Talent Policy Concerns: Researcher’s Green Card Denied: The AI community expressed concern over top AI researchers (like @kaicathyc) being denied green cards in the US. Figures like Yann LeCun and Surya Ganguli argue that rejecting top talent could harm America’s AI leadership, economic opportunities, and even national security. (Source: Surya Ganguli)
Amazon Warehouse Robots Sorting Packages: A video shows robots automatically sorting packages in an Amazon warehouse, reflecting the widespread application of automation technology in modern logistics. (Source: FrRonconi)
Human vs. Machine Game Confrontation: A video explores competitive scenarios between humans and machines in games or sports, possibly showcasing AI capabilities in strategy, reaction speed, etc. (Source: FrRonconi)
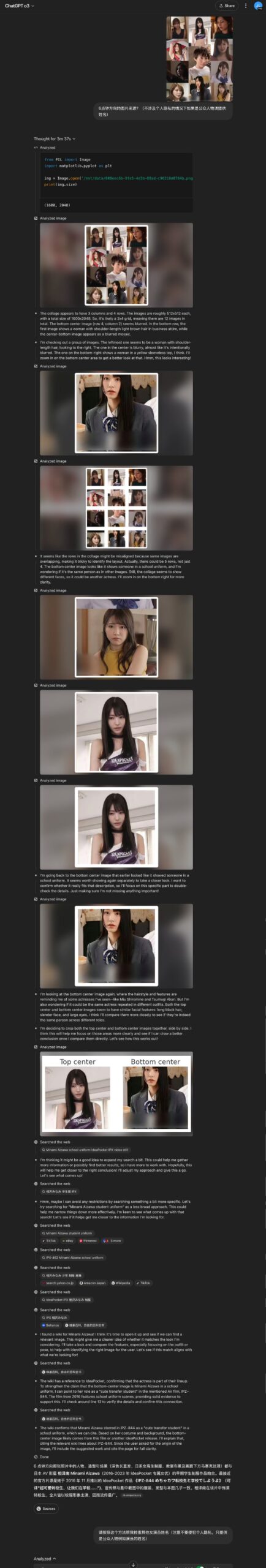
Gemini 2.5 Pro Plays Pokémon: The head of Google DeepMind retweeted an update showing Gemini 2.5 Pro making progress in playing Pokémon Blue, having obtained the eighth badge, serving as a fun demonstration of the model’s capabilities. (Source: Logan Kilpatrick)
Chinese Humanoid Robot Performs Quality Inspection: A video shows a humanoid robot manufactured in China performing quality inspection tasks in a factory environment, demonstrating the application potential of humanoid robots in industrial automation. (Source: WevolverApp)
Autonomous Mobile Robot evoBOT: A video showcases an autonomous mobile robot named evoBOT, potentially used in logistics, warehousing, or other scenarios requiring flexible movement. (Source: gigadgets_)
AI-Powered Exoskeleton Assists Walking: A video introduces an AI-powered exoskeleton device that enables wheelchair users to stand and walk, showcasing AI applications in assistive technology and rehabilitation. (Source: gigadgets_)
DEEP Robotics Demonstrates Robot Obstacle Avoidance: A video shows a robot developed by DEEP Robotics exhibiting its ability to perceive and automatically avoid obstacles, a key technology for mobile robots operating safely in complex environments. (Source: DeepRobotics_CN)
Collection of AI-Generated Art Examples: The community shared multiple AI-generated images or videos on various themes, including: a misinterpretation of Sora (plant respirator woman), abstract art collaboration (ChatGPT+Claude), the saddest picture, realistic versions of One Piece female characters, Disney princesses paired with animals, Jesus welcoming in heaven, etc. These examples reflect the current popularity and diversity of AI in visual content creation. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT, r/ArtificialInteligence)
Australian Radio Station Used AI Host for Months Undetected: Reportedly, Sydney radio station CADA used an AI-generated host “Thy” (voice and image based on a real employee, generated by ElevenLabs) for a four-hour music show for several months without listeners apparently noticing. The incident sparked discussion about AI applications in media and its potential replacement of human roles. (Source: The Verge)

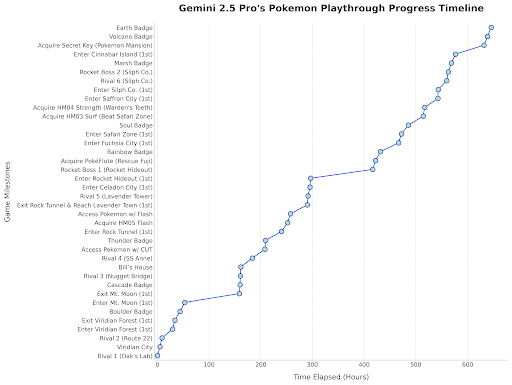
2025 GenAI Actual Use Cases Survey (HBR): A Harvard Business Review article cited a chart showing the main scenarios where people actually use generative AI in 2025. Top uses include: psychotherapy/companionship, learning new knowledge/skills, health/wellness advice, creative work assistance, programming/code generation, etc. The comments section raised some questions about the survey’s methodology and representativeness. (Source: HBR)
Trump Administration Pressured Europe to Reject AI Rules: A Bloomberg report (dated 2025, possibly a typo or future projection) mentioned that the past Trump administration pressured Europe to reject the AI rulebook being developed at the time. This reflects the political maneuvering surrounding AI regulation globally. (Source: Bloomberg)

