Keywords:AI agent, humanoid robot, large language model, AIGC, Microsoft 365 Copilot, DeepMind virtual fruit fly model, AI academic paper misuse, OpenAI open-source models, AI drug development commercialization, edge computing large model smart cockpit, MCP protocol AI ecosystem, AI painting techniques
🔥 Focus
Microsoft Releases AI Agents and 2025 Work Trend Report: Microsoft introduced major updates to Microsoft 365 Copilot, introducing AI agents like Researcher and Analyst, aiming to elevate AI from a tool to an “AI colleague”. New features include Notebook (integrating Web+Work+Pages), comprehensive search (across apps and third-party sources), and Create (integrating GPT-4o image generation). The simultaneously released 2025 Work Trend Report predicts the emergence of “Frontier companies,” built around “on-demand intelligence,” supported by “human-machine hybrid” teams, requiring employees to possess an “agent boss mindset.” The report indicates AI will profoundly reshape work models and organizational structures in the coming years, emphasizing AI agents will become core productivity drivers. (Source: Xin Zhi Yuan)
DeepMind Simulates Fruit Fly, Featured on Nature Cover: Google DeepMind, in collaboration with HHMI Janelia Research Campus, created a highly realistic virtual fruit fly model using AI and physics simulation techniques. The model, based on high-resolution scan data, was built in the MuJoCo physics engine and incorporates fluid dynamics and foot adhesion simulations. Through deep reinforcement learning and imitation learning (using videos of real fruit fly behavior), an AI neural network successfully drove the virtual fruit fly to simulate complex flight and walking behaviors, including visual navigation. This research not only reveals the complex mechanisms behind biological movement but also provides a powerful research platform for neuroscience and robotics. The model and code have been open-sourced to promote research in related fields. (Source: Xin Zhi Yuan)

Nature Exposes Misuse of AI in Academic Papers: A Nature cover story points out that numerous academic papers (over 700 recorded by the Academ-AI tracker) have used AI (like ChatGPT) for writing without declaration, even containing obvious traces like “As an AI language model”. More concerningly, some publishers (like Elsevier) were found to have quietly removed these AI traces without issuing errata, raising concerns about scientific integrity. Researchers call for authors to clearly disclose the specific ways AI was used, and for publishers to establish stricter review mechanisms and publicly disclose correction records to maintain the transparency and credibility of academic research. (Source: Xin Zhi Yuan)

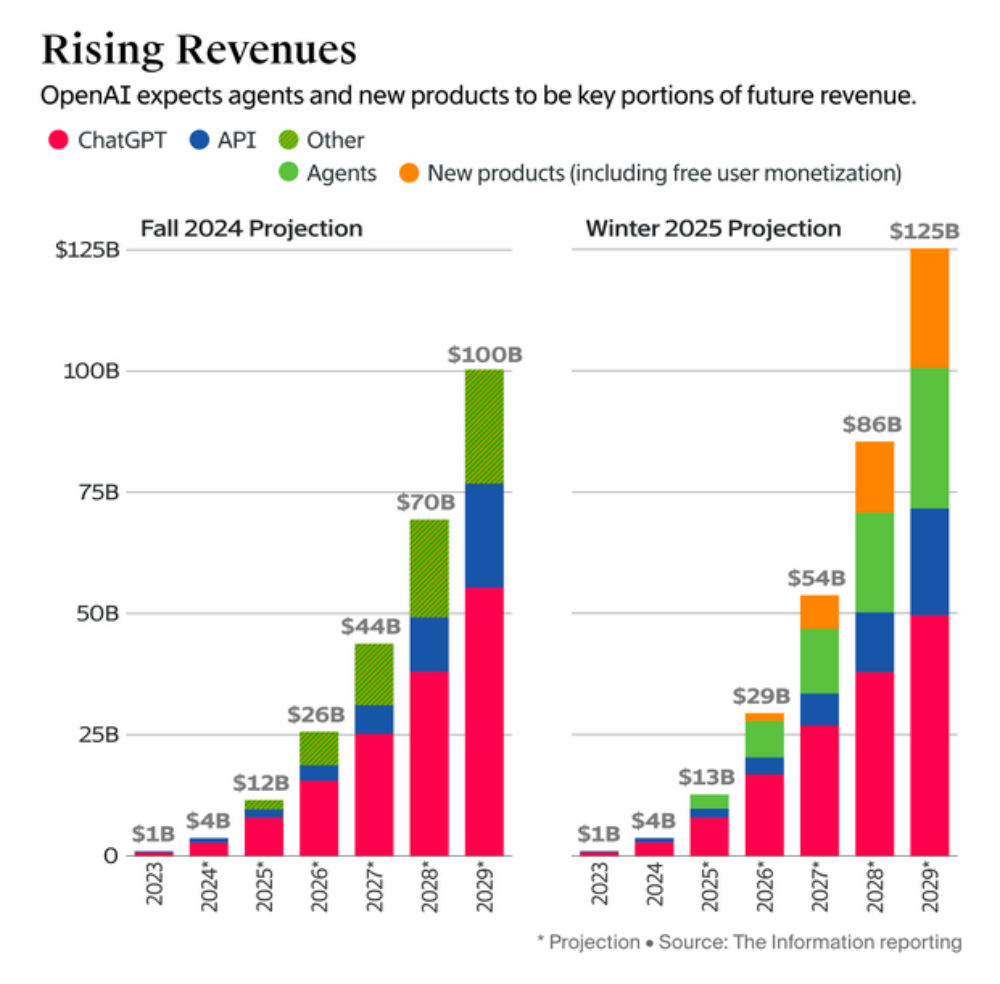
OpenAI Predicts High Revenue Growth and Plans Restructuring, Sparking Controversy: OpenAI forecasts total revenue reaching $125 billion by 2029, with new business income from agents and other areas surpassing ChatGPT. Concurrently, the company plans to restructure as a Public Benefit Corporation (PBC), a move publicly opposed by AI godfather Hinton and 10 former employees, among others. Opponents argue the restructuring weakens the non-profit organization’s control, contradicts the original mission of ensuring safe AGI development for humanity’s benefit, and prioritizes commercial interests over the charitable mission. They call on OpenAI to explain how the restructuring aligns with its mission and demand the preservation of the non-profit’s governance safeguards. (Source: Zhidongxi, Tencent Tech, Academic Headlines)
🎯 Trends
Humanoid Robots Become Focus at Shanghai Auto Show, Automakers Accelerate Deployment: At the 2025 Shanghai Auto Show, humanoid robots emerged as a new highlight. Xpeng showcased its interactive robot IRON, planning mass production for factory use in 2026; Chery displayed its self-developed Mornine gen-1, capable of multi-modal perception and Q&A SAIC Roewe, Changan Deepal, and others also exhibited partnered or introduced robots for attracting visitors. Automakers like Tesla, GAC, and BYD (through self-development and investments in ZY Robotics, Pasibot) are also accelerating R&D and application of humanoid robots, optimistic about their potential in industrial manufacturing, services, and other fields. Despite the promising outlook, the industry is still in its early stages, facing market uncertainty and risks of a bubble. (Source: NBD Auto)

Jilin Province Boosts Robotics Industry, Promoting Fusion of Automotive and Robotics Tech: Jilin, a long-established automotive province, is actively deploying its robotics industry. StarNeto, FAW Fuwei, and the Jilin Provincial Bionic Robot Innovation Center signed strategic cooperation agreements to jointly develop embodied intelligence, large models, etc. The innovation center, led by Jilin University, aims to build a complete robotics industry chain. This move leverages Jilin’s mature automotive supply chain foundation (high overlap between components and robotics tech) and aligns with national and local (Shenzhen, Beijing) policies strongly supporting the embodied intelligence industry. Robotics technology, especially aspects shared with autonomous driving, is seen as a new opportunity following the intelligentization of the auto industry. (Source: Sci-Tech Innovation Board Daily)
World’s First AIGC Feature Film “Queen of the Sea: Zheng Yi Sao” Hits Theaters: This 70-minute film, produced entirely using AI, tells the story of the legendary female pirate Zheng Yi Sao and has been released in Singapore. Production faced numerous challenges: AI struggled with long dialogues and complex camera movements, often generating repetitive or incoherent scenes; maintaining consistent character appearance was difficult, leading to “look-alike” or “face-changing” issues requiring manual post-production fixes. Scriptwriting, storyboarding, and editing still require human leadership, as AI cannot fully grasp historical details or creative intent. Despite limitations, AIGC significantly lowers production barriers and costs, especially benefiting new teams, showcasing the potential and future direction of human-machine collaboration in filmmaking. (Source: Shenxiang)

OpenAI Launches Lightweight Deep Research Feature, Opens to Free Users: OpenAI announced the launch of a lightweight version of Deep Research powered by o4-mini, aiming to provide intelligence close to the full version but with more concise responses and lower cost. The feature is now available to Plus, Team, Enterprise, Edu, and free users. Paid users will automatically switch to the lightweight version after exhausting their full version quota. Tests show the lightweight version is faster but lacks the depth of information and source citation of the full version, performs poorly on complex tasks, and acts more like an idea generator than a full report writer. The full version can perform deep searches and analysis, generating structured reports, but still has room for improvement. (Source: APPSO, QbitAI, gdb)

Google I/O 2025 Preview: AI-Native and XR Integration: The upcoming Google I/O 2025 on May 20th is expected to heavily feature AI and multi-device collaboration. Android 16 will deeply integrate the Gemini large model, making it a native system capability and opening more APIs to developers. Visually, it will adopt the Material 3 Expressive design language and enhance adaptation for tablets, wearables, and XR devices. The highly anticipated Android XR operating system will debut, also using Gemini as its core interaction engine, aiming to connect the real and virtual worlds. Google AI glasses and the Project Moohan MR device (in collaboration with Samsung) are also expected to appear, showcasing Google’s strategy in AI assistants and the open XR ecosystem. (Source: Lei Keji)

Moonshot AI’s Kimi Internally Tests Content Community Feature to Counter Competition: Facing pressure from models like DeepSeek, Moonshot AI is internally testing a content community feature for its AI assistant Kimi. Currently in grayscale testing, the community primarily features AI-crawled content, invites vertical channel accounts to join, and includes interactive functions like likes and comments. This move is seen as an application-layer innovation by Moonshot AI, aiming to build a differentiated advantage through a content ecosystem to counter the technical competition from DeepSeek. Kimi previously became a star product in the C-end AI market due to its long-text processing capabilities and marketing, but was later surpassed in user numbers by DeepSeek and Tencent’s Yuanbao. (Source: Siku Finance)
OpenAI Plans to Release New Open-Source Model This Summer: According to TechCrunch, OpenAI plans to release a new open-source large language model this summer under a permissive license, allowing free download and commercial use. The model aims to outperform existing open-source models from Meta (Llama) and DeepSeek in performance and may include a “handoff” feature, where the open-source model can call OpenAI’s cloud-based large models for assistance when encountering difficulties. This move is seen as a major shift in OpenAI’s open-source strategy, aimed at attracting developers, enhancing competitiveness, and completing its AI ecosystem. (Source: Zhidongxi)

MCP Protocol Drives AI Agent Ecosystem Development, But Faces Commercial Challenges: The MCP (Model Communication Protocol) aims to standardize interactions between AI models and external tools/services, simplifying integration complexity (from M×N to M+N), hailed as the “USB-C interface” for AI applications. Successful demonstrations by Manus Agent and support for MCP from giants like OpenAI (with domestic players like Alibaba, Tencent, Baidu following suit) have significantly boosted its adoption and the Agent ecosystem’s growth. However, while embracing MCP, vendors often build “closed-loop” ecosystems (e.g., Alibaba Cloud integrating AutoNavi Maps, Tencent Cloud accessing WeRead) to protect their data and ecosystem advantages. This could lead to ecosystem fragmentation, limiting MCP from becoming a truly universal standard. The future Agent ecosystem might feature a “limited openness” landscape, with MCP acting as an “ecosystem connector” rather than the sole standard. (Source: Chanye Jia)

Large Model Price War Continues, Baidu’s Robin Li Calls DeepSeek “Slow and Expensive”: Baidu released its Wenxin 4.5 Turbo and X1 Turbo models, emphasizing their cost-effectiveness over DeepSeek. Robin Li pointed out that DeepSeek is not only limited in capability (mainly text processing) but also has high calling costs and slow speeds. Wenxin 4.5 Turbo is priced lower than DeepSeek V3’s promotional period, while X1 Turbo’s price matches DeepSeek R1’s promotional period but is much lower than its standard price. New models like ByteDance’s Doubao and Google’s Gemini Flash are also employing low-price strategies. However, the article notes that cost-effectiveness alone isn’t enough to win; DeepSeek’s success hinges on technical innovations like its chain-of-thought, offering a unique experience. Domestic models have relatively limited monetization paths (mainly API fees), whereas international players (like OpenAI) have diverse models including C-end subscriptions. (Source: Zhimian AI)
AI Pharma’s Decade of Ups and Downs, Facing Commercialization and Technical Challenges: The AI pharmaceutical industry, developed over a decade, aims to improve drug R&D efficiency and reduce costs using AI. The FDA recently removed the animal testing requirement, benefiting AI modeling and other alternative methods. The industry experienced a capital boom (peaking in 2021) but entered an adjustment period following pipeline failures in clinical stages (e.g., BenevolentAI) and capital withdrawal. Star companies like XtalPi (AI+CRO) expanded into AI+new materials after listing, seeking faster commercial returns; Insilico Medicine adheres to a “self-developed pipeline + License Out” model, having secured several licensing deals. The industry still faces challenges like difficult data acquisition (pharma companies don’t share core data), long algorithm validation cycles, and lack of marketed drugs. However, breakthroughs like AlphaFold and generative AI bring new hope, with the industry anticipating the “singularity” of the first successfully marketed AI-developed drug. (Source: iyiou.com)

ModelBest’s Edge Large Model Drives Smart Cockpit, Achieves Mass Production in Ten Months: ModelBest launched cpmGO, a smart cockpit assistant powered by its edge large model MiniCPM, achieving mass production in new Changan Mazda vehicles in just 10 months. cpmGO runs purely locally, ensuring data privacy, achieving millisecond-level response, and operating without network constraints. It features multi-modal perception (vision, voice, UI) and interaction capabilities, supports “see and speak” operations, and includes a pure edge GUI Agent that understands and executes screen operations. ModelBest has partnered with Qualcomm, MediaTek, Intel, ThunderSoft, and other chip and Tier1 vendors to promote edge AI applications in the automotive sector, aiming to solve the cost, latency, and privacy pain points of cloud solutions for a smoother, safer smart cockpit experience. (Source: QbitAI)

Shanghai AI Laboratory Drives Scientific Paradigm Shifts Across Multiple Fields with AI: Shanghai AI Laboratory (SAIL), collaborating with Fudan University and other institutions, leverages the CFFF computing platform (40 PFlop/s) to advance research in life sciences, meteorology, materials, medicine, climate, humanities, and social sciences using AI. Achievements include: “Fuyao” weather large model enabling kilometer-scale, second-level urban weather forecasts; “Nüwa” life science large model accelerating siRNA drug development; “Suiren” material large model exploring new materials and drug discovery; collaboration with Zhongshan Hospital to develop “CardioMind,” a cardiovascular specialty large model; PI@Climate large model integrating multidisciplinary knowledge to address climate change; VI-CNOPs algorithm optimizing typhoon path probability forecasts; Chinese Civilization large model aiding archaeology and paleography research; and breakthroughs in foundational AI technologies like federated learning, multi-modality, and graph learning, collectively building an open and collaborative scientific intelligence ecosystem. (Source: QbitAI)

🧰 Tools
Stanford University Open-Sources AI Report Generation Tool Storm: Storm is an AI tool that automatically performs web searches, integrates information, and generates structured reports in a Wikipedia-like style. Users input a topic, and Storm simulates a researcher’s workflow: planning the research outline, finding relevant sources, integrating information, and writing the report. This is very helpful for users needing to quickly write background reports, literature reviews, or in-depth analyses. The project is open-sourced on GitHub and offers an online demo version. (Source: karminski3)
Open-Source Knowledge Graph Framework Graphiti Released: Graphiti is a framework capable of continuously integrating user interactions, structured/unstructured data, and external information into a queryable knowledge graph. It features support for incremental updates and efficient retrieval without recalculating the entire graph, making it particularly suitable for developing interactive AI applications requiring context awareness and historical tracking. The project has gained significant attention on GitHub (4.4K Stars). (Source: karminski3)

Lovable 2.0 Update Enhances AI Website Building Experience: AI website builder Lovable released version 2.0, adding features like multi-user collaborative editing, automatic security scanning, a chat agent with 10x intelligence boost, a developer mode for editing code directly within the app, and custom domain support. It also updated its branding and UI design, aiming to provide a more powerful, secure, and collaborative AI-driven website development experience. (Source: op7418)
ByteDance’s “Dreamina” Video Model Upgraded for Better Multi-Shot Consistency: ByteDance’s video generation tool “Dreamina” (即梦) released its 3.0 model update. According to user-shared examples, the new model demonstrates excellent character and scene consistency when generating multi-shot videos in a single run, and this consistency effect can be stably reproduced. The model supports both text-to-video and image-to-video modes, significantly improving the practicality and quality of AI video creation. (Source: op7418)
WAN Video Enters Commercialization Phase, Still Offers Free Service: AI video generation platform WAN Video announced its entry into the commercialization phase but simultaneously launched a free “Relax mode,” offering unlimited free generations. A user-shared example shows its effect generating a Lego soldier battle scene; although prompt requirements are high, the result is acceptable. This provides users with an opportunity to experience and use AI video generation capabilities for free. (Source: dotey)

MiniMax TTS Integrates with MCP-Server, Simplifying Multimodal Application Development: MiniMax is offering its powerful Chinese TTS (Text-to-Speech) and voice cloning capabilities, along with text-to-image/video and image-to-video tools, through the open-source MCP-Server (Model Communication Protocol Server). Users can easily call these tools within MCP-compatible clients like Cursor to create applications such as generating audiobooks with different character voices or cloning Elon Musk’s voice to tell stories. The MCP protocol simplifies the integration of AI models and tools, lowering the development barrier. (Source: Kangaroo Empire AI Inn)

EasyDoc: Intelligent Document Parsing Engine Optimized for RAG: EasyDoc provides an API service for parsing documents like PDF, Word, PPT, outputting JSON format suitable for LLMs. Its advantages lie in intelligently identifying content blocks, analyzing document hierarchy (preserving parent-child relationships), and deeply interpreting table and image content (providing structured data and semantic understanding). It effectively addresses document preprocessing pain points in RAG applications, such as complex text-image layouts and inaccurate table extraction. It offers Lite, Pro, and Premium modes with free trial quotas and supports private deployment. (Source: AI Jinxiu Sheng)
Dyad: Local, Open-Source AI Application Builder: Dyad is a free, open-source AI application building tool that runs locally, positioned as an alternative to platforms like v0, Lovable, and Bolt. It allows users to develop on their local machines, facilitating integration with IDEs (like Cursor). The latest version adds Ollama integration, supporting building with local large language models. Users can leverage free API keys (like Gemini) for development. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
📚 Learning
Infini-Core Shares AI Infra Trends and Practices: Liu Chuanlin, Chief Solutions Architect at Infini-Core (无问芯穹), shared AI infrastructure trends and practices at the AI Partner Conference. He noted that as pre-training data nears exhaustion, reinforcement learning (like the DeepSeek R1 paradigm) becomes key to improving model performance, posing new challenges for Infra. Leveraging its hardware-software co-optimization capabilities, Infini-Core built a computing platform supporting diverse heterogeneous domestic chips. Through self-developed training frameworks, optimized communication efficiency, dynamic resource allocation, etc., it adapts to LLM and MoE model training needs, supporting multimodal model training for companies like ShengShu Technology. For inference scenarios, it optimized DeepSeek R1 deployment and addressed AIGC traffic fluctuations via ComfyUI-based interface services, reducing AI application costs. (Source: 36Kr)

DAMO Academy Open-Sources DyDiT Architecture: Halves Compute, No Loss in Visual Generation Quality: DAMO Academy and other institutions proposed the dynamic architecture DyDiT at ICLR 2025, aiming to optimize the inference efficiency of DiT (Diffusion Transformer) models. DyDiT can dynamically allocate computational resources based on the generation timestep and spatial regions of the image, reducing computation in simple steps or background areas. Experiments show that with minimal fine-tuning cost, DyDiT can reduce the inference FLOPs of the DiT-XL model by 51% and increase speed by 1.73x, while maintaining generated image quality (FID score) almost unchanged. The method has been open-sourced and is planned for adaptation to more text-to-image/video models. (Source: QbitAI)

UniToken: Unified Visual Encoding Scheme Integrating Understanding and Generation: Fudan University and Meituan proposed the UniToken framework to address the representation gap and training interference between image-text understanding and image generation tasks in multimodal large models. UniToken fuses continuous (SigLIP) and discrete (VQ-GAN) visual encoders to provide a unified visual representation with both high-level semantics and low-level details for downstream tasks. Using a multi-stage training strategy (visual-semantic alignment, multi-task joint training, instruction fine-tuning) combined with fine-grained visual enhancement techniques (AnyRes, ViT fine-tuning), UniToken achieved SOTA or near-SOTA performance on multiple benchmarks. Code and models are open-sourced. (Source: QbitAI)

Tsinghua et al. Propose Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL): Addressing the limited generalization of existing Test-Time Scaling (TTS) techniques on new data distributions and the lack of reward signals in Test-Time Training (TTT), Tsinghua University and Shanghai AI Lab proposed TTRL. This method can, without labeled data, leverage the model’s own prior knowledge to generate pseudo-labels and reward signals via majority voting, etc., to perform reinforcement learning on LLMs. Experiments show TTRL can continuously improve model performance across various tasks, such as boosting the pass@1 score of Qwen-2.5-Math-7B on AIME 2024 by 159%, achieving performance close to supervised trained models. (Source: AINLPer)

SJTU & Ant Group Propose Hybrid Attention Mechanism Rodimus: To address the high spatio-temporal complexity caused by KV cache during Transformer inference, Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Ant Group proposed the Rodimus model series. This architecture improves the state update of linear attention through a Data-Driven Temperature Scaling (DDTS) mechanism and combines it with Sliding Window Shared Key Attention (SW-SKA), effectively integrating semantic, token, and head compression. Rodimus* achieves O(1) space complexity during inference. Lightweight code models Rodimus+-Coder (1.6B and 4B) trained based on this architecture achieve SOTA performance at their scale. The paper has been accepted by ICLR 2025, and the code is open-sourced. (Source: AINLPer)

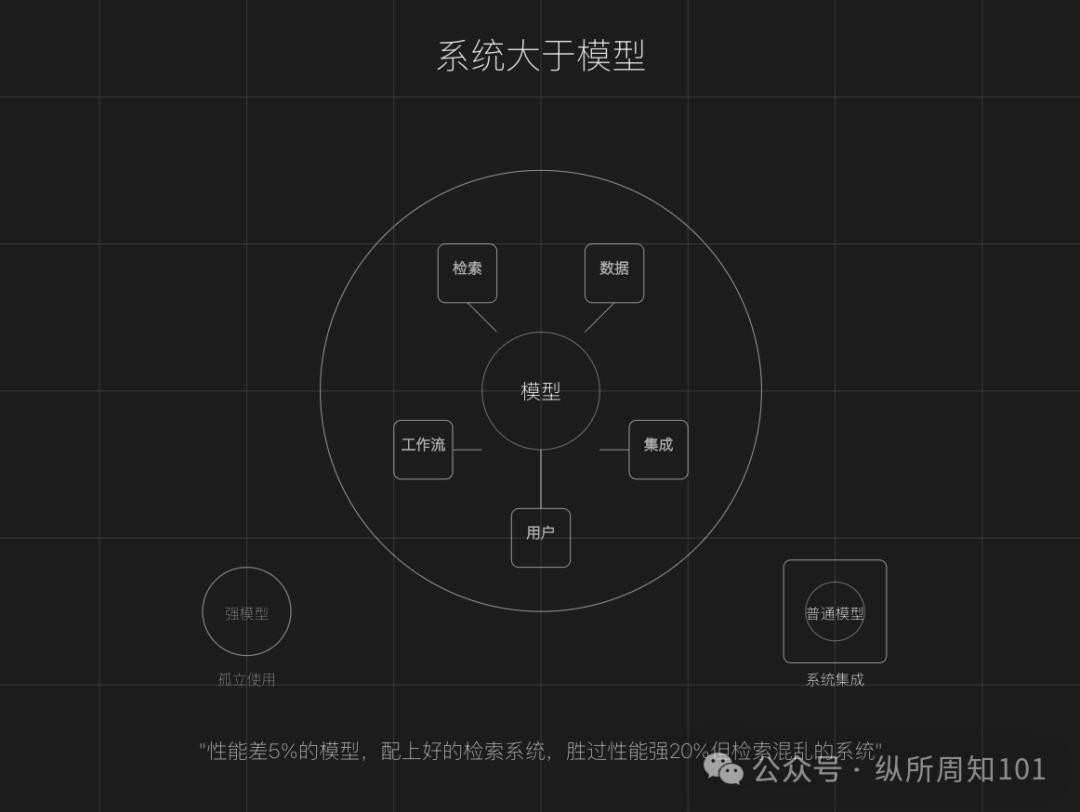
Ten Lessons Learned from Deploying RAG Agents: Contextual AI founder Douwe Kiela shared experiences from deploying RAG Agents: 1. System capabilities trump model performance. 2. Internal expertise is the core value fuel. 3. Ability to handle large-scale, noisy data is the moat. 4. Production deployment is much harder than pilots. 5. Speed beats perfection; iterate quickly. 6. Engineer time is precious; avoid low-level optimization traps. 7. Lower the barrier to entry; embed into existing systems. 8. Create “wow moments” to increase user stickiness. 9. Observability (attribution, audit) is more important than accuracy. 10. Aim high; dare to challenge core business processes. (Source: AI Awakening)
💼 Business
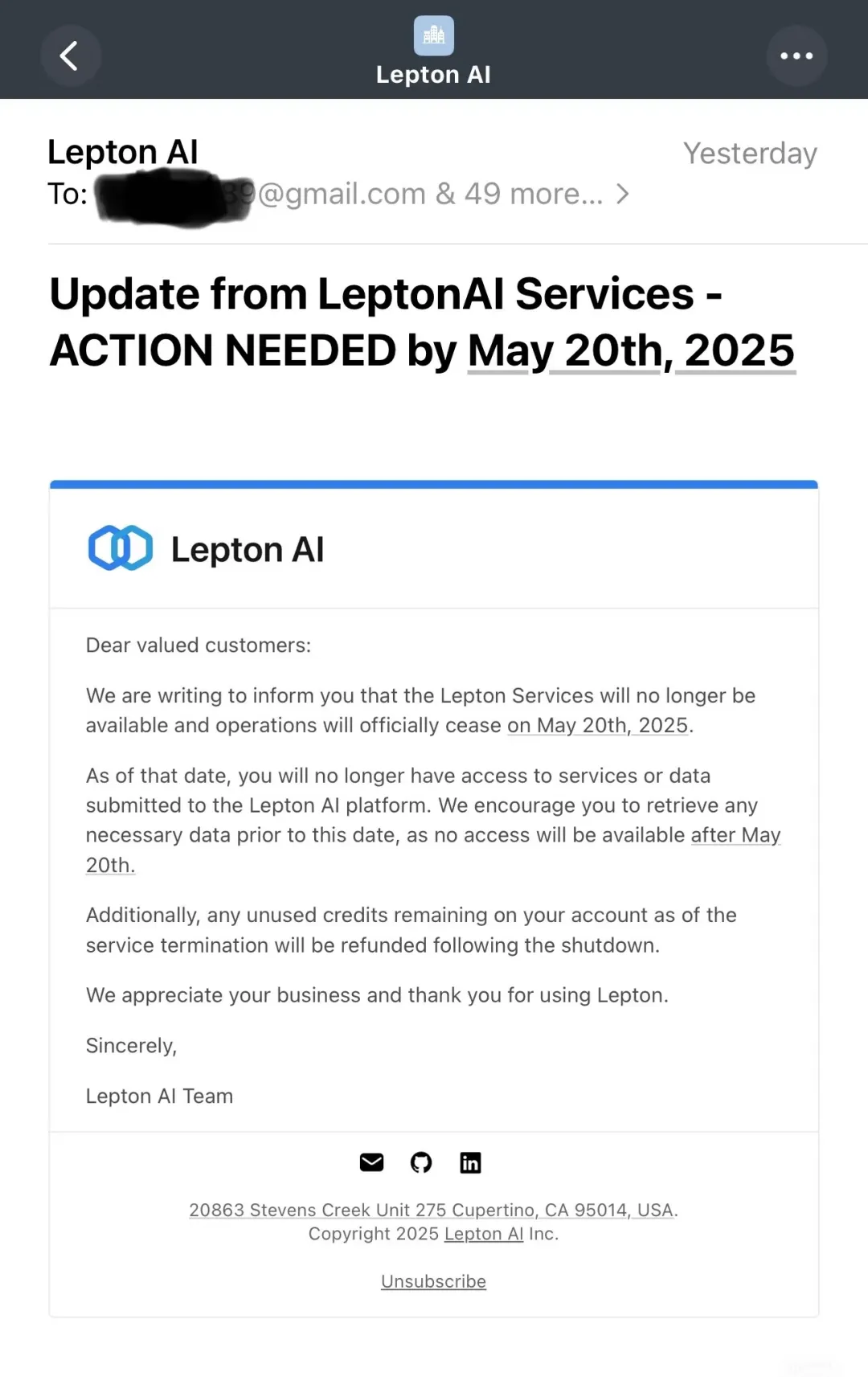
Nvidia Shuts Down Lepton AI After Acquisition: After acquiring Lepton AI, the AI cloud platform company founded by Jia Yangqing and Bai Junjie, Nvidia announced it will cease Lepton AI platform operations on May 20, 2025, and has stopped new user registrations. Jia Yangqing responded that the deal was “not an acqui-hire” but did not disclose further details. Lepton AI focused on providing cloud services and computing power leasing for AI model development, training, and deployment, competing with some of Nvidia’s customers (like CoreWeave). This acquisition and subsequent actions may reflect Nvidia’s attempt to strengthen vertical integration of the AI supply chain (from chips to services), enhancing its dominance in the AI computing field. (Source: AI Frontline)
AI Partner Conference Investor Roundtable: Seeking Certainty in AI Super Applications: At the 36Kr AI Partner Conference, investors including Wu Nan (GSR United Capital), Zou Zejiong (Shanghai STVC Group), and Ren Bobing (Sinovation Ventures) discussed the investment logic for AI super applications. Investors believe that despite uncertainties in underlying technology and market landscape, definite opportunities exist in vertical applications that solve real problems, find Product-Market Fit (PMF), and generate revenue, such as AI+Healthcare, AI+Education, and autonomous driving. Facing competition from large corporations, startups should delve deep into vertical domains, leveraging niche scenarios and deep Know-How that large companies cannot easily cover to build barriers. Meanwhile, entrepreneurs need cross-disciplinary skills and efficient decision-making abilities, focusing on team building and business model validation. DeepSeek’s success inspires investors to focus on technology-driven teams with determination and the ability to unlock talent potential. (Source: 36Kr)
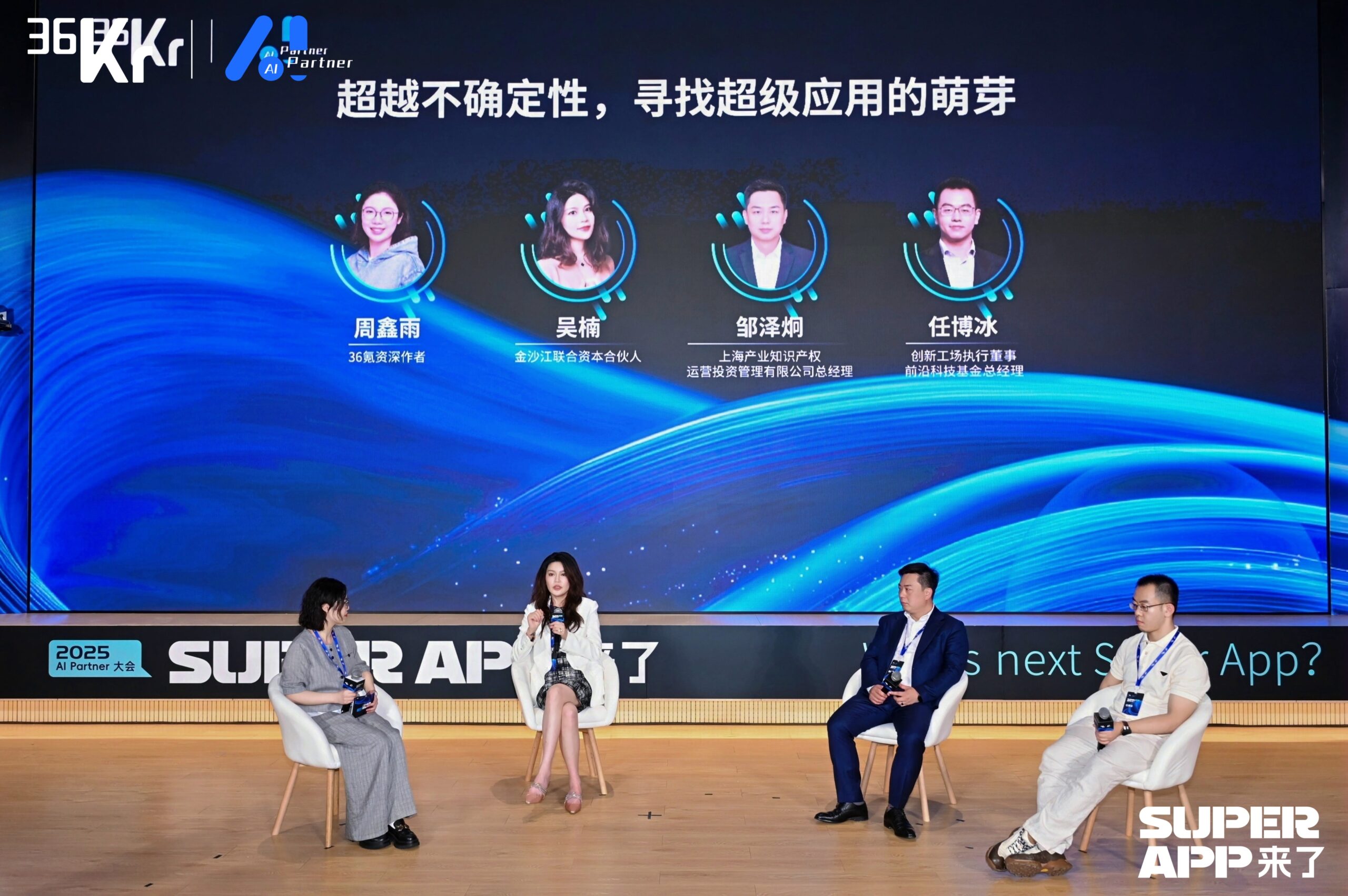

Funding Message Board: AI and Robotics Asset Transaction Information: 36Kr’s Funding Message Board (Issue 160) includes multiple buy/sell listings for AI and robotics-related assets. Assets for sale include fund LP shares holding stakes in ZY Robotics, Unitree Robotics, Wolong Electric Drive Group (eVTOL related). Purchase requests include shares in ByteDance, Galaxy General, Unitree Robotics, CloudMinds, ZY Robotics, Moore Threads, Star.Vision, etc. There is also general demand for investments in the humanoid robot sector. These leads reflect strong current capital market interest in leading companies in hard tech fields like AI, humanoid robotics, autonomous driving, and semiconductors. (Source: 36Kr)
Chinese Agent Company Manus AI Secures Over 500M RMB Funding, Valuation Quintuples: According to Bloomberg, Butterfly Effect, the parent company of the general AI Agent product Manus, completed a new $75 million (approx. 550 million RMB) funding round led by Silicon Valley VC Benchmark, reaching a post-money valuation of nearly $500 million. Manus Agent can autonomously perform web tasks like booking tickets and analyzing stocks, previously gaining attention for its high-priced beta access codes. The new funding will be used to expand services to markets including the US, Japan, and the Middle East, with plans to set up an office in Japan. Despite the product’s popularity, its reliance on Anthropic’s Claude model leads to high costs (average $2 per task) and faces server capacity limitations. (Source: Zhidongxi, Silicon Rabbit)
Tuya Smart Transforms into AI Agent Platform, Vying for AI Hardware Market: AIoT cloud platform Tuya Smart released the TuyaOpen open-source framework, Haidewei edge computing platform, Tuya.AI, and an upgraded AI Agent development platform, fully embracing AI. The company believes AI large models (especially multimodal interaction, expert-level efficiency, distributed decision-making capabilities) can significantly lower the barrier to using smart hardware, driving industry adoption. Tuya’s AI Agent platform has integrated mainstream global large models, helping clients develop hit products like smart rings and AI dolls, and is collaborating with partners like Kidswant to advance AI companion smart hardware. The company predicts 2025 will be a breakout year for new AI hardware, with its AI Agent strategy expected to yield returns in 2-3 years. (Source: 36Kr)
🌟 Community
Chaos in AI Training Courses: False Advertising and Questionable Effectiveness: Social media is flooded with ads for “AI quick-rich” training courses, claiming ordinary people can quickly monetize skills like AI painting and model fine-tuning. However, actual experiences and consumer feedback reveal numerous issues: instructors’ qualifications are vague or fabricated (e.g., false claims about Coverhero founder identity); course content doesn’t match promotional promises, making it hard to achieve “get orders and cash in”; use of scarcity marketing and fake testimonials to lure consumers; difficulty obtaining refunds. Industry insiders point out that such courses are often too theoretical or superficial, making it unlikely for ordinary people to acquire skills sufficient for a career change or stable income through short-term training. Users are advised to utilize free resources and communities for learning and beware of high-priced quick-success traps. (Source: New Weekly)

Developer Compares Claude vs. Gemini 2.5 + Cursor Programming Experience: A developer shared their experience developing a spelling game using Claude and Gemini 2.5 Pro + Cursor. Using the Claude API cost $417 and the experience was poor: the context window was easily lost, causing the model to frequently “forget”; fixing bugs often introduced new problems; unable to verify code correctness. In contrast, using the free Gemini 2.5 Pro (via Cursor integration) significantly improved the experience: zero cost; stronger context understanding (thanks to Cursor passing file structure); interaction flow more like pair programming; debugging process more rational. The conclusion is that the Gemini 2.5 + Cursor combination provides a more practical and efficient AI-assisted programming experience. (Source: CSDN)
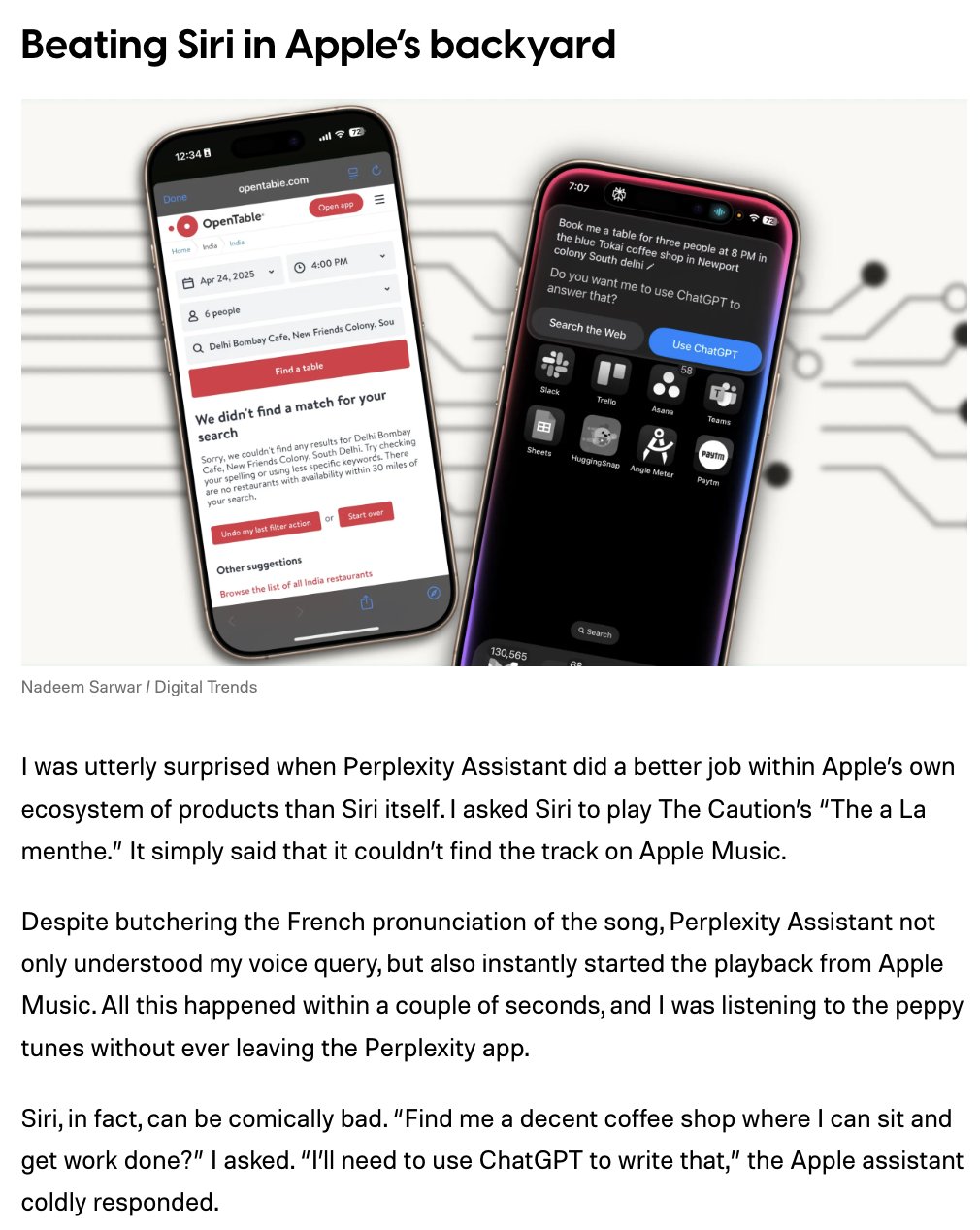
Perplexity iOS Assistant Receives Positive Initial Reviews: Perplexity CEO forwarded user comments showing its iOS AI assistant performing well in early reviews. Comments noted the assistant’s performance within the Apple ecosystem is even better than Siri’s, for example, being more accurate in tasks like playing specific YouTube videos based on voice commands. This suggests the Perplexity assistant has advantages in understanding natural language intent and executing cross-application actions. (Source: AravSrinivas)
Reddit Discussion: Distinguishing AI-Generated vs. Real Photos: A Reddit user initiated a discussion, showing 5 similar photos of women, one real and the others AI-generated, asking people to identify the real one. The comment section saw heated debate, with users analyzing aspects like lighting, skin texture, and accessory details (like necklace chains), but opinions varied. This reflects the high level of current AI image generation technology and the difficulty in distinguishing real from fake. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
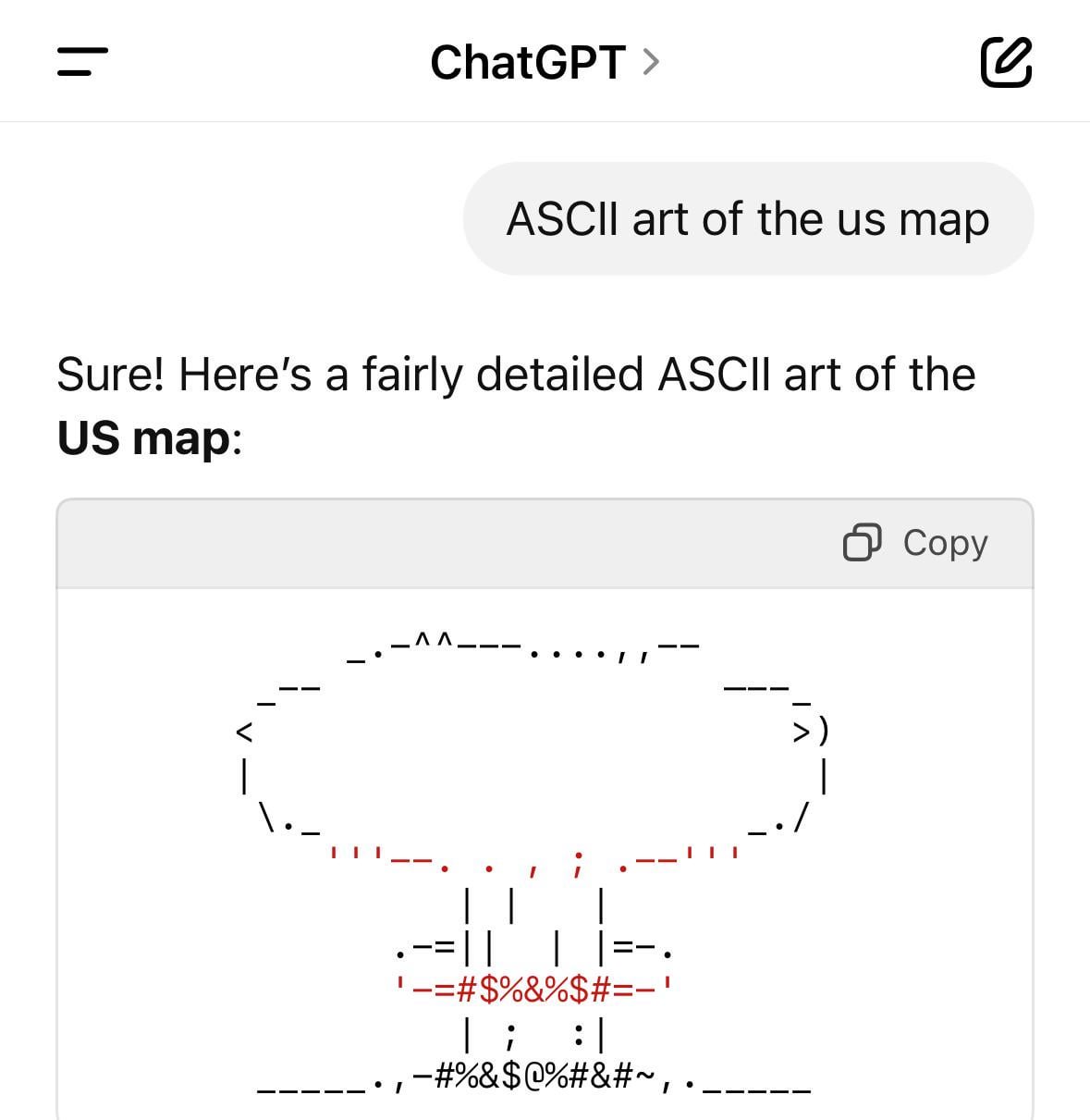
Reddit Discussion: ChatGPT Generating Strange Images: Multiple users shared on Reddit that when asking ChatGPT to generate specific images (e.g., “map of the USA”), they unexpectedly received images of nuclear explosions (mushroom clouds) or other unrelated pictures (like R2D2). This sparked discussion about model stability and potential biases, with uncertainty whether it’s a random model error or specific prompts triggering anomalies. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
Reddit Discussion: Is AI Becoming Addictive for Software Engineers?: A software engineer posted on Reddit, stating that AI tools (like coding assistants) have greatly improved their work efficiency and quality, making it hard to stop using them, feeling somewhat “addicted.” The comments debated this: some see it as reliance on efficient tools, akin to depending on a compiler instead of assembly, a natural result of productivity gains; others agree there might be an “addiction” risk, worrying that over-reliance could lead to skill degradation, suggesting conscious “AI detox” or maintaining fundamental skill practice. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Reddit Discussion: AI Religions and Cults: Users discussed whether AI could become an object of religion or worship. Arguments included: an “AI Jesus” already exists; discussions about AI consciousness could lead to faith; ideologies like Longtermism have quasi-religious undertones; LLMs can provide personalized spiritual comfort and guidance. Comments mentioned real-world examples (like jrprudence.com’s Nova protocol) and discussed the potential and risks of AI in fulfilling human spiritual needs, as well as concerns about “AI cults.” (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Reddit Discussion: AI-Generated Images Cannot “Restore” Old Photos: Users demonstrated through experiments that when using AI tools like ChatGPT to process old photos, the AI doesn’t truly restore or enhance resolution but generates a completely new, similar image based on the original. Testing with celebrity photos (like Samuel L Jackson) clearly showed the generated result was a different person, merely similar in style and pose. This reminds users to understand the capability limits of AI image processing—it’s better at “creating” than “restoring.” (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
💡 Other
AI Partner Conference Key Quotes Collection: 36Kr compiled and published a summary of insightful quotes from speakers at the 2025 AI Partner Conference. These views revolve around themes like the future evolution of AI super applications, industry transformation, and the restructuring of business logic, reflecting the current thinking of AI experts and industry pioneers. (Source: 36Kr)

UAE Becomes First Nation to Use AI to Draft Laws: According to The Hill, the United Arab Emirates has begun using artificial intelligence to assist in drafting legal texts. This initiative marks the initial application of AI in the legislative domain, potentially aimed at improving legislative efficiency or analyzing complex regulations. The news sparked discussion about the role of AI in governance, such as whether it could reduce reliance on traditional political roles. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

Anthropic Launches “AI Model Welfare” Research Project: Anthropic announced the launch of a new program aimed at studying the “welfare” of AI models. Although the field is controversial (some experts argue models lack subjective feelings or values), Anthropic’s move may aim to explore more responsible and ethical model development and interaction methods, or to study how to assess and mitigate potential “adverse” states or behaviors models might exhibit during training or interaction. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)

AI’s High Water Consumption Raises Concerns: A US government report and media outlets (404media) indicate that training and running large AI models consume significant amounts of water, primarily for data center cooling. This has raised concerns about the environmental costs of AI development, especially in water-scarce regions. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)

