Keywords:AI, OpenAI, o3/o4-mini model, Gemini 2.5 Pro, AI programming tools, multimodal AI technology, AI agents
🔥 Focus
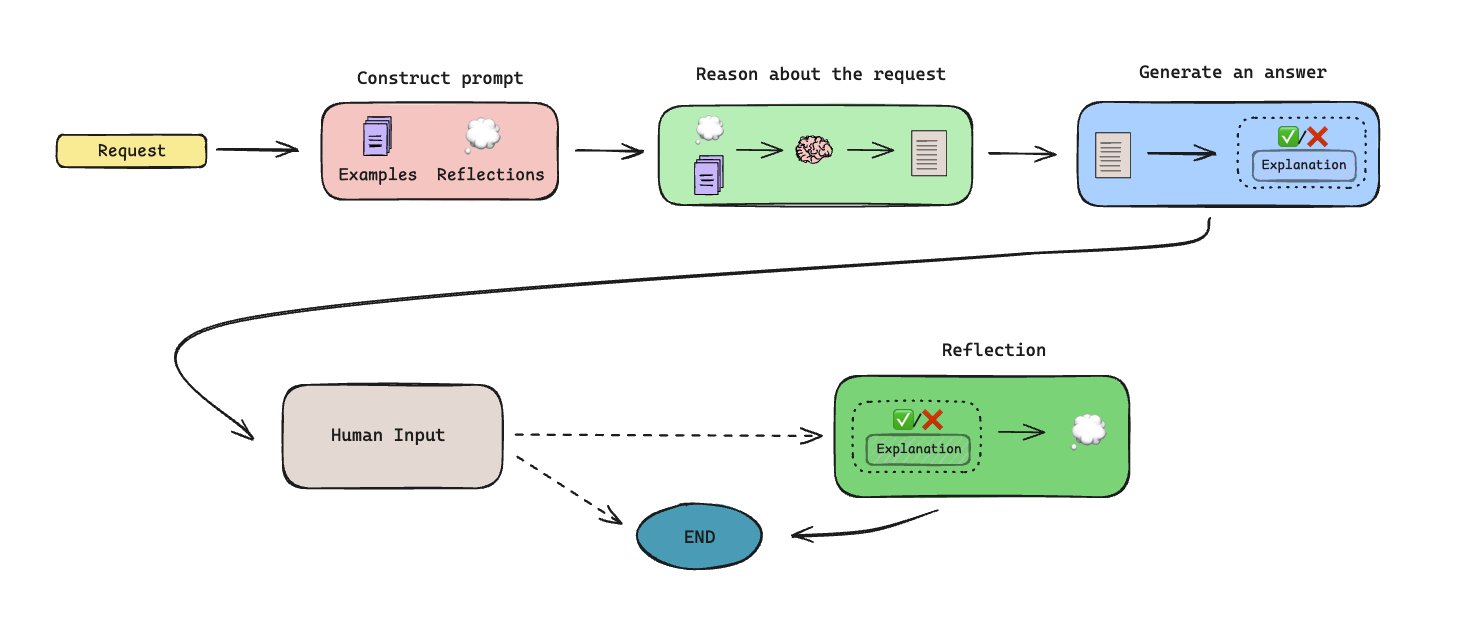
OpenAI Announces o3 and o4-mini, Ushering in a New Era of “Thinking with Images”: OpenAI officially released its latest “reasoning” flagship model o3 and the streamlined o4‑mini. These two models are the first to achieve “thinking with images,” capable of embedding and processing images (e.g., zooming, rotating) within their reasoning chain and analyzing them in conjunction with text. They can also autonomously combine and use all tools within ChatGPT (web search, Python code execution, file parsing, image generation) for the first time to solve complex problems. o3 set new SOTA records on multiple benchmarks like Codeforces, SWE-bench, and MMMU, performing particularly well on visual reasoning and multi-step tasks, with a 20% reduction in critical errors compared to o1. o4-mini surpasses o3-mini in math, programming, and visual tasks with lower latency and cost. Simultaneously, OpenAI open-sourced the lightweight terminal programming AI agent Codex CLI and launched a million-dollar grant program. The new models are now available to ChatGPT Plus/Pro/Team users and API developers, marking a step forward for AI towards stronger multimodality and agent capabilities. (Source: OpenAI震撼发布o3/o4-mini,直逼视觉推理巅峰,首用图像思考,十倍算力爆表, openai, sama, karminski3, karminski3, sama, gdb, karminski3, sama, dotey, openai, karminski3, op7418, gdb,
)

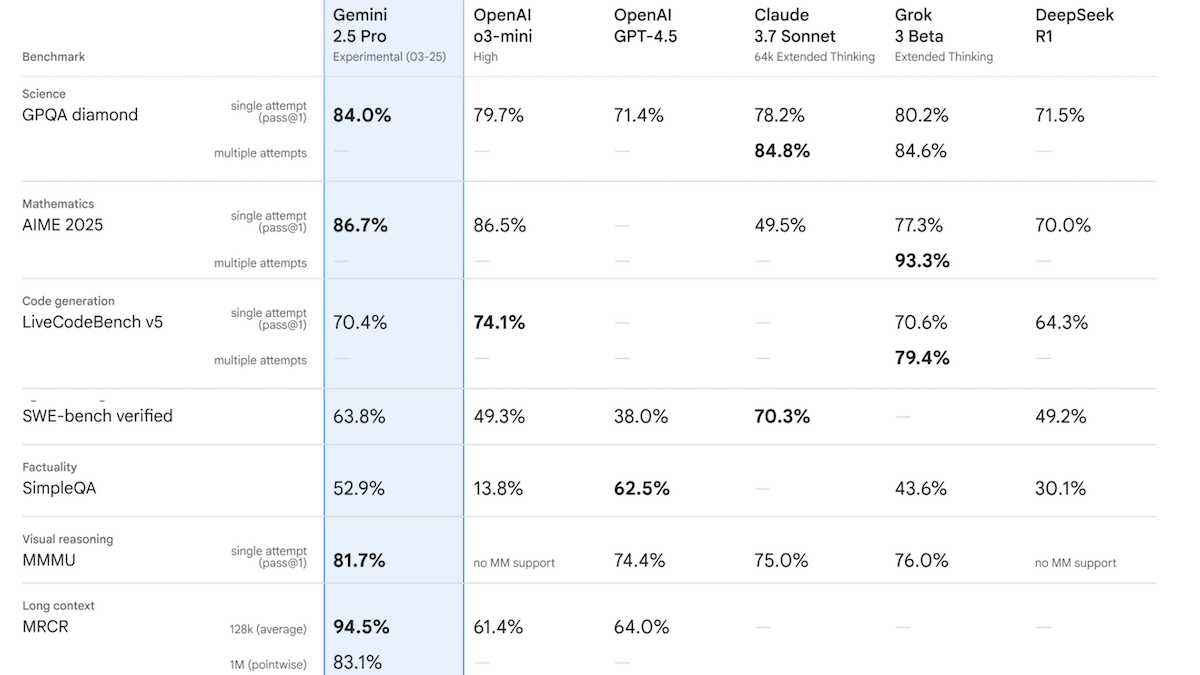
Google Releases Gemini 2.5 Pro Experimental, Tops Chatbot Arena Performance: Google introduced Gemini 2.5 Pro Experimental, the first model in its Gemini 2.5 family, and announced the upcoming low-latency version, Gemini 2.5 Flash. The model supports text, audio, image, and video input (up to 1 million tokens, planned to increase to 2 million in the future), and text output (up to 65,000 tokens). Its notable feature is strong reasoning capability, achieved by generating hidden reasoning tokens (chain of thought) before responding. On Chatbot Arena, Gemini 2.5 Pro Experimental surpassed GPT-4o and Grok 3 Preview with an Elo rating of 1437, ranking first. In 12 benchmarks, it outperformed top models including o3-mini, GPT-4.5, and Claude 3.7 Sonnet on 7 of them. This indicates that AI models, especially reasoning models, are still rapidly advancing. Google plans for all future new models to have reasoning capabilities. (Source: Google Unveils Gemini 2.5, MCP Gains Momentum, Behind Sam Altman’s Fall and Rise, LLMs That Understand Misspellings)
🎯 Trends
OpenAI Releases GPT-4.1 Series Models, Focusing on Low Cost and High Efficiency: OpenAI launched the GPT-4.1 series, including GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1 Mini, and GPT-4.1 Nano. The core features are reduced cost and increased speed. GPT-4.1 Mini outperforms GPT-4o on multiple benchmarks with significantly lower latency and an 83% cost reduction. GPT-4.1 Nano is the first ultra-small model supporting a 1 million token context, suitable for low-latency tasks. All three models increase the context window from 128K to 1 million tokens. Pricing-wise, GPT-4.1 costs $2/$8 per million tokens for input/output, 26% cheaper than GPT-4o; Nano costs $0.1/$0.4 for input/output. This move is seen as a response to price wars from competitors like DeepSeek. Meanwhile, the costly GPT-4.5 project has been paused. (Source: 压力给到梁文锋,
)
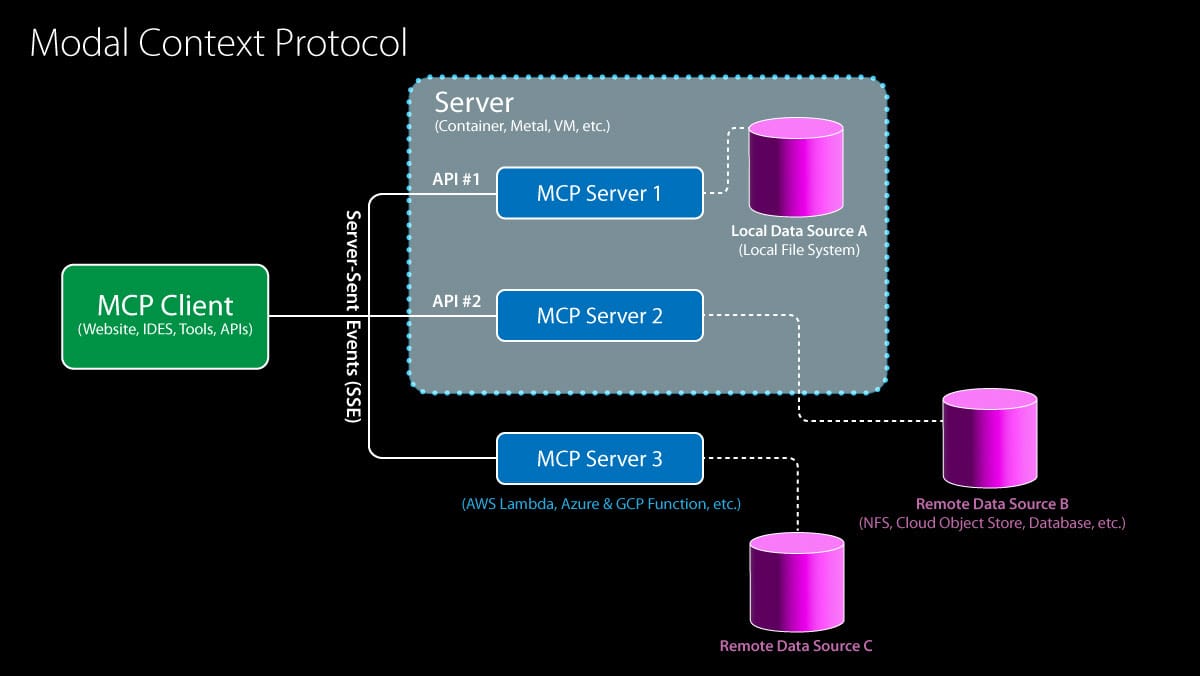
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Gains OpenAI Support, Accelerating Ecosystem Integration: OpenAI announced support for the Model Context Protocol (MCP) in its Agents SDK, ChatGPT desktop app, and Responses API. MCP was initiated by Anthropic late last year, aiming to provide an open standard for connecting AI models to tools and data sources. Through MCP, models can access a growing ecosystem of resources, including over 6,000 community-built servers and connectors (e.g., web search, file system operations). Previously, Microsoft integrated MCP into CoPilot Studio, Cloudflare supported deploying remote MCP servers, and the Cursor code editor also added support. OpenAI’s adoption will significantly push MCP towards becoming the de facto standard for building AI Agent applications, simplifying the process for developers to integrate various third-party tools and data sources. (Source: Google Unveils Gemini 2.5, MCP Gains Momentum, Behind Sam Altman’s Fall and Rise, LLMs That Understand Misspellings)
ByteDance Releases Kling 2.0, Enhancing Video Generation Effects: Kling 2.0 is the latest video generation model launched by ByteDance. According to user feedback and demos, Kling 2.0 excels at generating smooth, realistic video scenes, showing improvement over previous versions and competitors like Sora, especially in image-to-video conversion. Users can first generate images with good text fidelity using tools like ChatGPT, then use Kling 2.0 to transform them into dynamic videos. This indicates continuous progress in video generation technology regarding scene coherence and realism. (Source:
)
Google Releases DolphinGemma, Exploring the Mystery of Dolphin Communication: Google AI launched the DolphinGemma project, aiming to use AI technology to decode dolphin communication methods. The project has accumulated a vast dataset of dolphin sounds and trained a 400 million parameter model (runnable on a Pixel 9 phone) to analyze these sounds, searching for patterns and rules that might indicate language. Research is currently exploratory, and it’s uncertain if dolphins possess complex language similar to humans, but sound types associated with specific behaviors (like naming, fighting, mating) have been identified. The ultimate goal is to understand dolphin sound structure and potential meaning, and attempt simple two-way communication by generating specific sounds. (Source:
)
IBM Releases Granite 3.3 Series Models, Including Speech Recognition: IBM introduced the Granite 3.3 series models, which includes an 8 billion parameter speech recognition model (Granite Speech 3.3). The model uses a two-stage approach designed to handle speech without degrading core LLM capabilities. The new model family aims to provide more refined reasoning abilities and improved RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) performance, and supports LoRA fine-tuning. These models can be integrated into AI assistants across various domains. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)

AI Drives Weather Forecasting Revolution, Significantly Boosting Prediction Efficiency: Artificial intelligence is quietly transforming the field of weather forecasting. Prediction tasks that traditionally required large teams of experts and supercomputers can now be achieved on a laptop using AI models. AI can process and analyze massive amounts of meteorological data, identify complex patterns, and thus generate faster, potentially more accurate weather forecasts. This marks a significant application of AI in scientific computing and prediction, promising to improve the timeliness and coverage of forecasts. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Google Gemini App Adds LaTeX Support: The Google Gemini App has been updated to include support for LaTeX. Users can now use LaTeX syntax within the Gemini App to display mathematical formulas, scientific symbols, etc. This update covers the Gemini 2.0 Flash and 2.5 Pro models, enhancing Gemini’s usability in academic and technical communication scenarios. (Source: JeffDean)
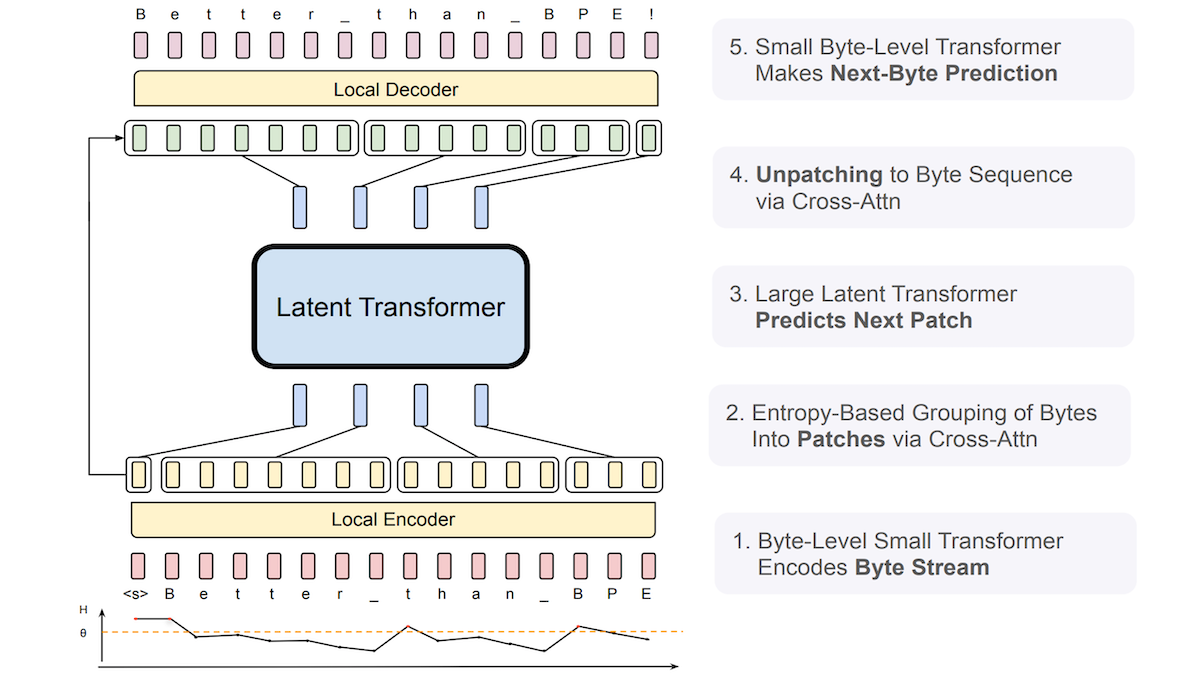
Meta Proposes Byte Latent Transformer (BLT) to Enhance LLM Robustness to Noisy Input: Researchers from Meta and other institutions introduced the Byte Latent Transformer (BLT), designed to replace traditional tokenizers. BLT directly processes byte (character) sequences. It uses a small byte-level Transformer to predict the probability of the next byte and dynamically groups bytes based on entropy: low entropy (high predictability) adds the byte to the current group, while high entropy (low predictability) starts a new group. The system comprises an encoder, a latent Transformer, and a decoder, totaling 8 billion parameters. Experiments show that BLT performs slightly better than a similarly sized Llama 3 on general language and coding benchmarks and exhibits significantly stronger robustness to noisy inputs like misspellings and rare languages, as it better understands character-level similarities. (Source: Google Unveils Gemini 2.5, MCP Gains Momentum, Behind Sam Altman’s Fall and Rise, LLMs That Understand Misspellings)
New Research Explores Test-Time Scaling of Multi-agent Collaborative Reasoning: A paper titled “Two Heads are Better Than One: Test-time Scaling of Multi-agent Collaborative Reasoning” has been submitted to arXiv. The study focuses on how to improve performance on complex reasoning tasks by having multiple AI agents collaborate during testing (inference), exploring a scaling path that enhances model capabilities without increasing training costs. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
AI Agent Governance Becomes a New Focus: As the capabilities of Agentic AI increase, effective governance becomes a critical issue. This involves ensuring agent behavior aligns with expectations, is safe and controllable, and adheres to ethical norms. Frameworks, standards, and regulatory mechanisms are needed to manage these “synthetic minds” capable of autonomous action and decision-making. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

AI Generates High-Quality Images Faster Than Existing SOTA Methods: Researchers at MIT have developed a new artificial intelligence tool capable of generating high-quality images faster than current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. This indicates ongoing breakthroughs in both efficiency and quality within the image generation field. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

xAI Introduces Canvas-like Feature for Grok AI: xAI has added a feature similar to ChatGPT Canvas to its chatbot Grok AI. Canvas-like functionalities typically provide an infinite canvas interface, allowing users to organize and interact with information (text, code, images, etc.) in a more freeform, visual way. This move helps Grok catch up with ChatGPT in terms of user interaction experience, and the feature is offered for free. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
🧰 Tools
Anx Reader: Cross-Platform E-book Reader Integrated with Multiple AI Engines: Anx Reader is an e-book reader supporting various formats like EPUB, MOBI, AZW3, FB2, TXT, available on iOS/macOS/Windows/Android. Its key feature is the integration of multiple AI capabilities from OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, DeepSeek, etc., for tasks like content summarization, Q&A, and quick information retrieval. The app supports syncing reading progress, book files, and notes via WebDAV, offers highly customizable reading styles (line spacing, font, color schemes, etc.), and includes features like TTS reading, translation, search, and idea recording. It aims to provide an intelligent, focused, and personalized reading experience. (Source: Anxcye/anx-reader – GitHub Trending (all/daily))

OpenAI Open-Sources Codex CLI: Lightweight Programming AI Agent Running Locally: Coinciding with the o3/o4-mini release, OpenAI open-sourced Codex CLI, a programming AI agent that runs in the terminal. It allows developers to use natural language commands to have the AI execute coding tasks directly on their local machine, such as writing code, installing dependencies, configuring environments, fixing bugs, etc. Codex CLI is designed to leverage the powerful reasoning capabilities of models like o3/o4-mini and can combine multimodal input (like screenshots) with local code access. The tool aims to simplify the development workflow, especially for beginners. OpenAI also launched a $1 million grant program to support projects based on this tool. (Source: OpenAI震撼发布o3/o4-mini,直逼视觉推理巅峰,首用图像思考,十倍算力爆表, sama, karminski3, dotey, sama, dotey)
Cohere Models Land on Hugging Face Hub, Offering Inference Services: Cohere announced its models are the first third-party inference provider supported on the Hugging Face Hub. Users can now directly access Cohere’s open-source models (like the Aya series) and enterprise models (like the Command series) on the Hub and perform fast inference. These models are particularly adept at tool use and multilingual capabilities, and offer OpenAI-compatible interfaces for easy integration and application building by developers. (Source: huggingface, huggingface, huggingface)

LocalAI v2.28.0 Released, Launches Local AI Agent Platform LocalAGI: LocalAI, a server for running LLMs locally with an OpenAI-compatible API, has been updated to v2.28.0. Simultaneously, the brand new LocalAGI platform was launched. LocalAGI is a self-hosted AI agent orchestration platform with a WebUI, allowing users to build complex, multi-step AI agent workflows (similar to AutoGPT). Crucially, these agents can be powered by local LLMs served via LocalAI or other compatible APIs (like llama-cpp-python). Combined with the local memory store LocalRecall, users can run autonomous AI agents in a fully localized environment to perform tasks like research, coding, content processing, etc. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Droidrun Framework Open-Sourced: Control Android Phones with AI: Droidrun, a framework allowing users to control Android phones to perform tasks using AI (like large language models), is now open-sourced on GitHub. Users can give natural language instructions for the AI to complete operations on the phone, such as opening apps, clicking buttons, inputting text, etc. This requires installing the ADB (Android Debug Bridge) tool. The framework demonstrates new possibilities for AI in mobile device automation and interaction. (Source: karminski3)
LLManager Released: Memory-Based Automated Approval Workflow: LLManager is an open-source workflow built using LangGraph, designed to automate approval tasks using AI agents with memory capabilities. The system can generate memories through human-in-the-loop collaboration, enabling it to learn and improve approval decisions over time. Its architecture is designed to handle repetitive approval processes, increasing efficiency. (Source: LangChainAI)
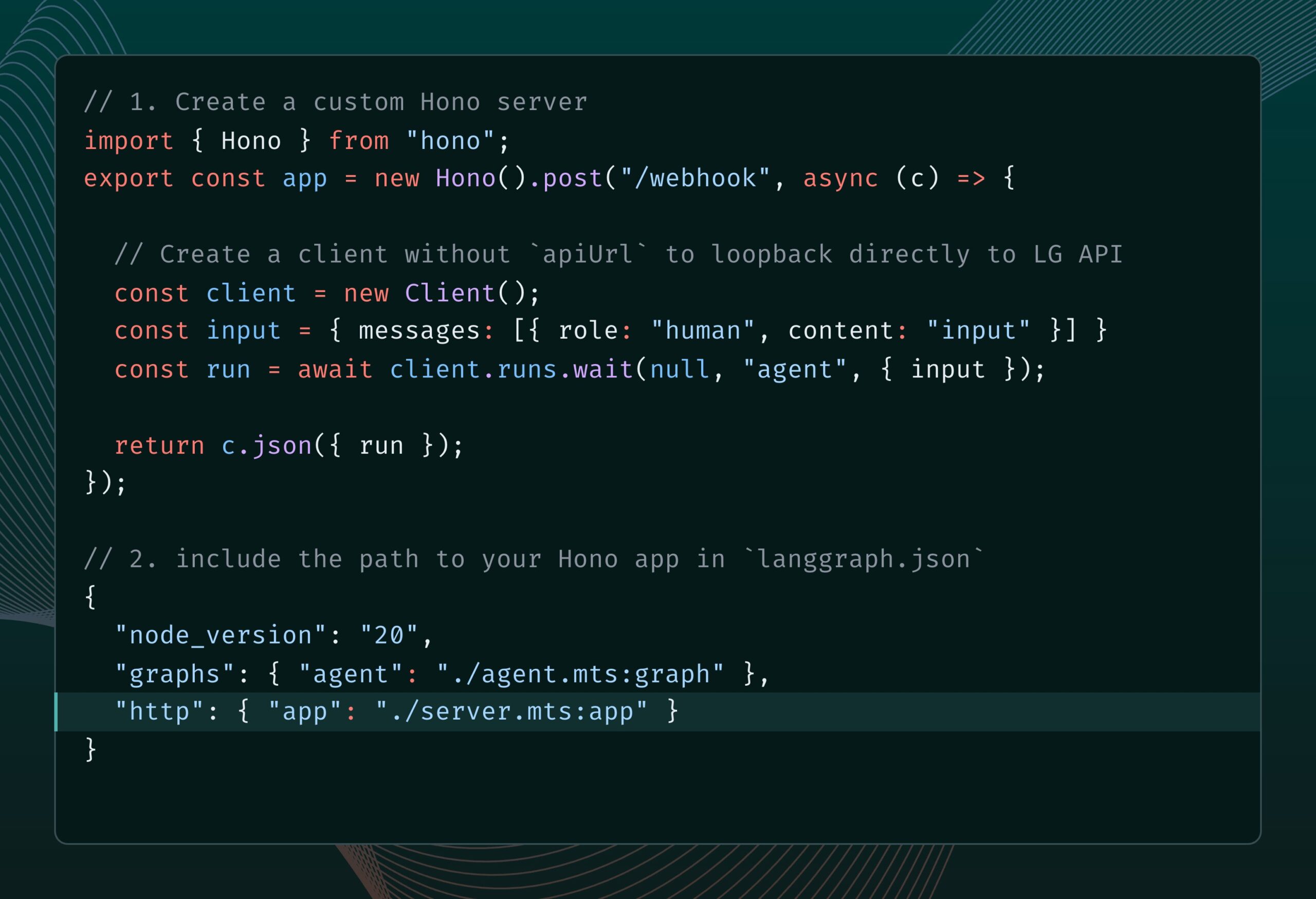
LangGraph.js Integrates Hono, Supporting Custom HTTP Routes and Middleware: LangGraph.js (the JS version of LangChain’s library for building stateful multi-agent applications) can now be integrated with Hono (a lightweight web framework). This allows developers to add custom HTTP routes and middleware to their LangGraph.js applications, enabling the construction of more complex backend services, such as handling webhooks, creating full API applications, etc., expanding the application scenarios for LangGraph.js. (Source: LangChainAI)
Open-Source Humanoid Robot Reachy 2 Begins Sales: Hugging Face co-founder Clem Delangue announced that Reachy 2, the first open-source humanoid robot his team participated in developing, started sales this week. Priced at $70,000, the robot targets the research and education market and is already in use at Cornell University, Carnegie Mellon University, and major AI labs. It features a human-like form, an omnidirectional mobile base, rich sensors (cameras, microphones, LiDAR, etc.), is based on ROS 2 and LeRobotHF, supports a Python SDK, and has a modular design allowing customization. (Source: huggingface)

Perplexity Launches Comet Browser, Exploring AI-Native Browsing Experience: Perplexity CEO Arav Srinivas is developing a browser named Comet and soliciting ideas for product growth and features. Comet aims to embody an “agentic OS,” controlling web applications and data through the browser, using AI to answer questions and execute tasks. The idea is that since most applications are on the web, an AI controlling the browser can control most of the digital life. The project emphasizes starting small and avoiding over-promising general capabilities. (Source: AravSrinivas, AravSrinivas, AravSrinivas, AravSrinivas, AravSrinivas)
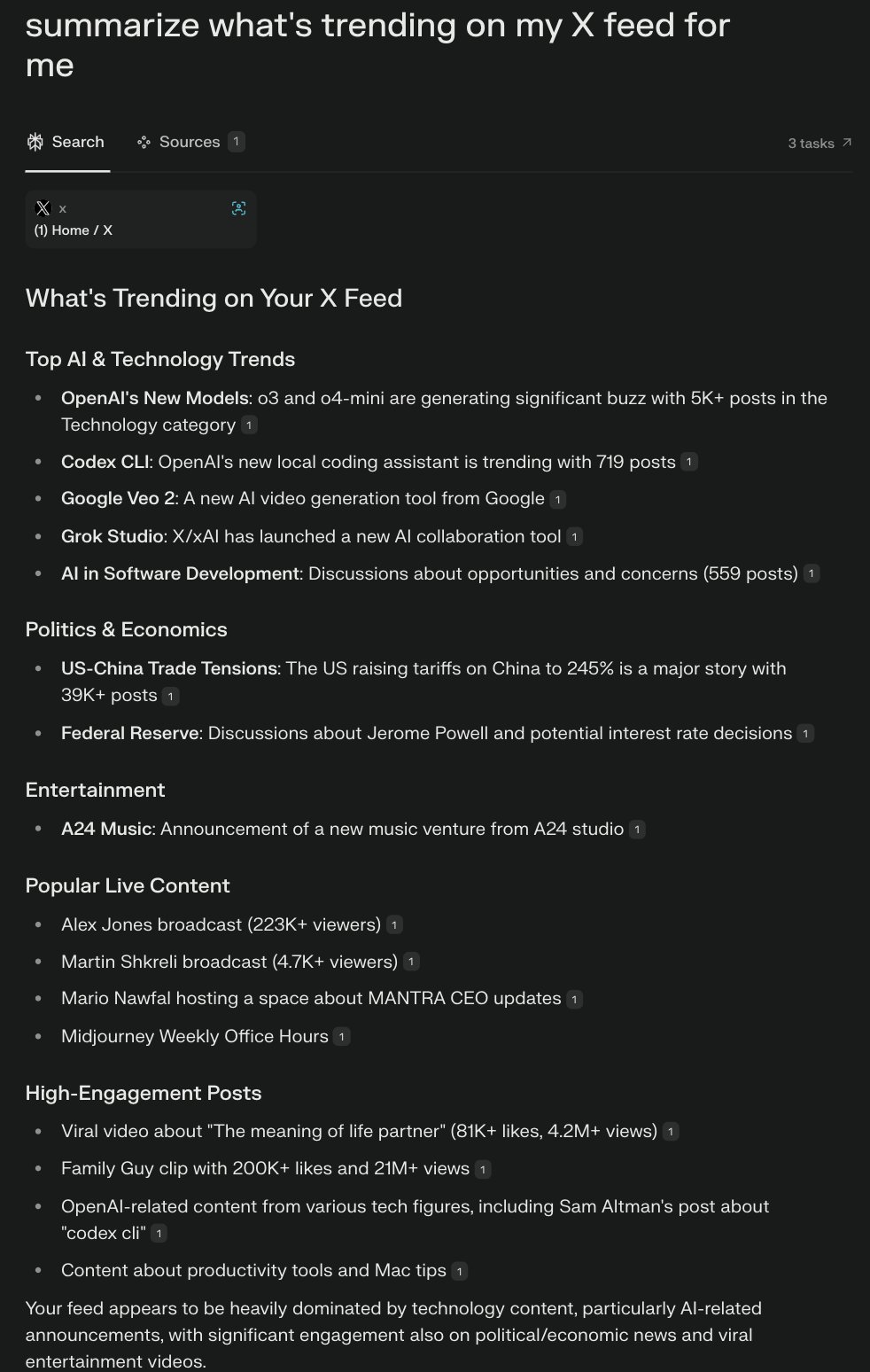
Claude App Supports Script to Auto-Approve MCP Requests: A community user shared a JavaScript script that runs in the Claude App developer tools console to automatically approve MCP (Model Context Protocol) requests from a predefined list of trusted tools. This can save users who frequently use specific local or remote tools the hassle of manually clicking “Allow” each time, improving workflow efficiency. However, users should be aware of security risks and only enable it for fully trusted tools. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
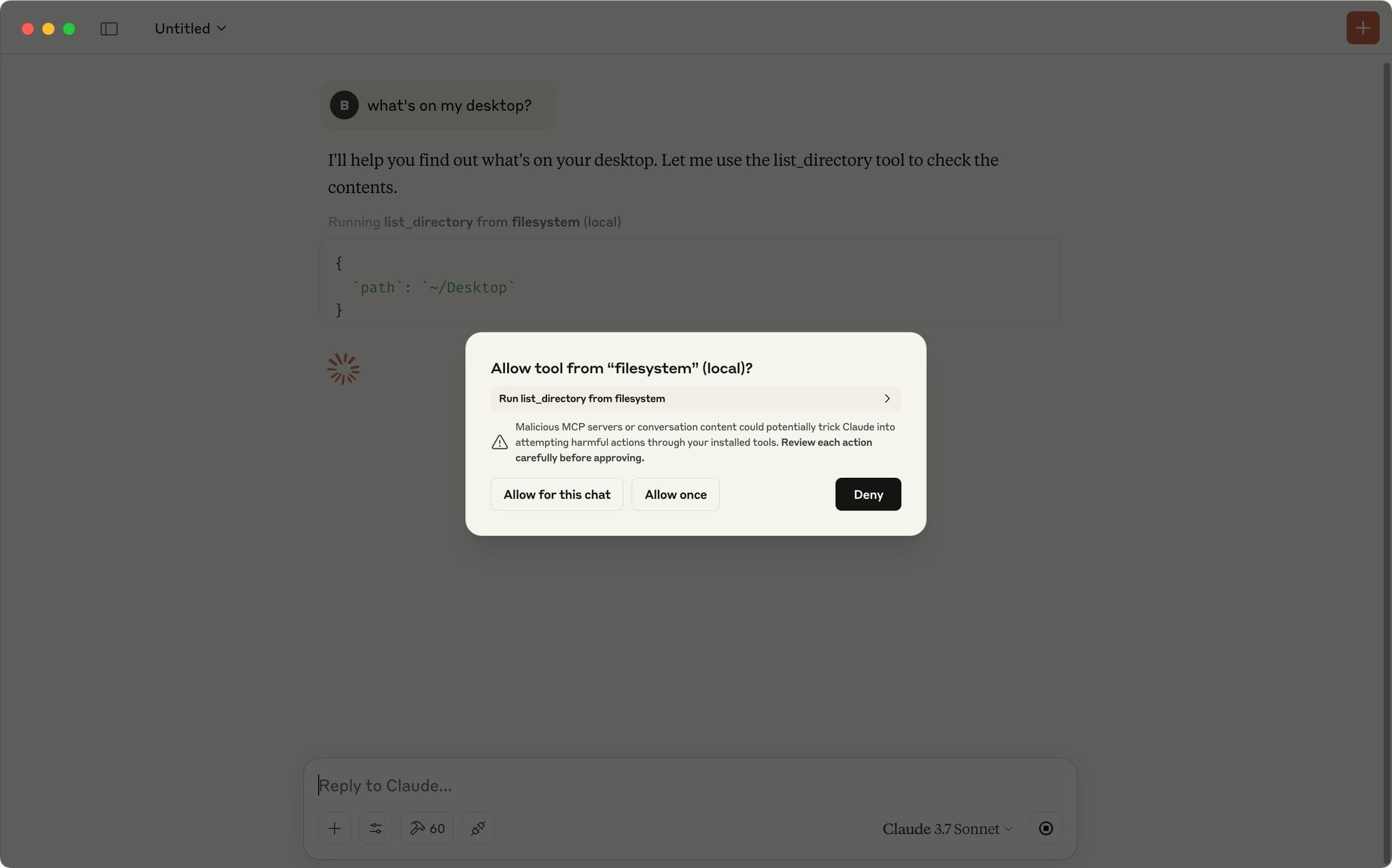
Must-Have MCP Server Recommendations for Coding and Workflow Automation: A community user shared a list of recommended MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers. These tools can be integrated with MCP-supporting AI models (like Claude) or Agent frameworks to enhance coding efficiency and automation capabilities. The recommended list includes: Sequential Thinking MCP for structured thinking, Puppeteer MCP for web interaction, Memory Bank MCP for project knowledge management, Playwright MCP for cross-browser testing, GitHub MCP for GitHub operations, Knowledge Graph Memory MCP for persistent memory, DuckDuckGo MCP for API-key-free search, and MCP Compass for discovering more MCP tools. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
📚 Learning
GitHub Repository: Comprehensive Guide to Advanced RAG Techniques: Nir Diamant created the GitHub repository RAG_Techniques, offering the most comprehensive collection of tutorials on advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques currently available. The repository aims to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and contextual richness of RAG systems, covering over 30 techniques from basic implementation (LangChain/LlamaIndex), text chunking optimization (fixed-size, propositional chunking, semantic chunking), query enhancement (transformation, HyDE, HyPE), context enrichment (chunk headers, relevant segment extraction, window expansion, document augmentation), to advanced retrieval (fusion, reranking, multi-faceted filtering, hierarchical indexing, integration, multi-modal), iterative techniques (feedback loops, adaptive, iterative retrieval), evaluation (DeepEval, GroUSE), interpretability, and advanced architectures (Graph RAG, RAPTOR, Self-RAG, CRAG), with implementations provided in Jupyter Notebooks or Python scripts. The project is community-driven and encourages contributions. (Source: NirDiamant/RAG_Techniques – GitHub Trending (all/daily))
DeepLearning.AI Launches New Course: Building AI Browser Agents: Andrew Ng announced a new short course, “Building AI Browser Agents,” in collaboration with AGI Inc. Taught by AGI Inc. co-founders Div Garg and Naman Garg, the course aims to teach how to build AI agents capable of interacting with websites and performing tasks (like scraping information, filling forms, clicking, placing orders). Course content includes how Web Agents work, their architecture, limitations, decision-making strategies, hands-on building of a Web Agent to scrape DeepLearning.AI courses and output structured data, building an autonomous agent for multi-task completion (finding and summarizing web pages, filling forms, subscribing), exploring the AgentQ framework (combining Monte Carlo Tree Search MCTS and Direct Preference Optimization DPO for self-correction), delving into MCTS principles, and discussing the current state and future of AI Agents. (Source: AndrewYNg)
Hugging Face Updates Quantization Documentation with Conceptual Guide and Selection Benchmarks: Hugging Face significantly updated its documentation on model quantization. The new docs aim to help users better understand quantization concepts and select appropriate techniques based on their needs. Updates include: explanations of quantization basics (e.g., schemes, int4, FP8), a new selection guide (to help choose between techniques like bnb, AWQ, GPTQ, HQQ based on requirements and hardware), and accuracy and performance benchmark comparison data for popular quantization methods on Llama 3.1 8B and 70B models. This provides valuable reference for developers looking to compress models and improve inference efficiency. (Source: huggingface)

New Method MODE: Lightweight, Interpretable Alternative to RAG: Independent researcher Rahul Anand proposed a new method called MODE (Mixture of Document Experts) as a lightweight alternative to the traditional RAG pipeline. MODE does not rely on vector databases and rerankers; instead, it clusters documents and uses centroid-based retrieval to extract information. This method is claimed to be efficient and highly interpretable, especially suitable for small to medium-sized datasets. The author is seeking endorsement from arXiv (cs.AI field) to publish the paper. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

GitHub Repository Beyond-NanoGPT: Advanced Resources from LLM Novice to AI Researcher: Tanishq Kumar open-sourced a GitHub repository named beyond-nanoGPT. The project aims to help learners who have mastered nanoGPT-level LLM basics to further understand and implement complex ideas closer to the cutting edge of deep learning research. The repository contains thousands of lines of annotated PyTorch code, implementing from scratch various modern ML research advancements including speculative decoding, vision/diffusion Transformers, linear/sparse attention, etc. The project’s goal is to help more people transition into the AI research field. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
Tutorial: Train a Chatbot on a GitHub Repository using AI Scraper and LLM: An article published on the Stackademic blog describes how to use an AI Scraper (web scraping tool) and a large language model (LLM) to train a chatbot capable of answering questions about a specific GitHub repository. This method typically involves scraping code, documentation (like READMEs), Issues, etc., from the repository, processing this information into a format suitable for the LLM, and then using RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) or fine-tuning to enable the chatbot to answer questions based on this information. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)

Paper Discussion: Explainable AI (XAI) for Tabular Data using Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation (LRP): A blog post discusses how to use Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) technique to explain the decision-making process of deep learning models when handling tabular data. LRP is an attribution method that aims to decompose the model’s output prediction back to the input features, thereby revealing which features contributed most to the final decision. Applying it to tabular data helps understand model behavior, enhancing transparency and trustworthiness. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)

💼 Business
Zhipu AI Initiates Pre-IPO Tutoring, Aiming for Completion Within the Year: Chinese AI company Zhipu AI has officially filed for pre-IPO tutoring, with CICC acting as the tutoring institution. According to the filing report, Zhipu AI plans to complete the IPO tutoring between August and October 2025. Previously, CEO Zhang Peng stated that the path to AGI is long, and funds raised are merely “travel expenses,” requiring more capital support in the future. This IPO is seen as a crucial step to obtain “more travel expenses.” Zhipu AI is a major player in China’s large model field, and its IPO process is closely watched. (Source: 压力给到梁文锋)
2-Person Startup Gumloop Raises Over ¥100 Million Using AI: No-code platform Gumloop, with only its two founders as full-time employees, recently completed a $17 million (approx. ¥124 million) Series A funding round. The company originated from providing an easy-to-use UI for Auto-GPT and evolved into AgentHub, an AI workflow building platform for non-technical users, capable of integrating tools like GitHub, Gmail, etc., to automate tasks such as document processing, web scraping, SEO, CRM, email marketing. Gumloop itself extensively uses AI Agents to handle company operations. The founders aim to build a $1 billion valuation company with a team of no more than 10 people. This reflects the potential for small teams in the AI era to achieve high efficiency and value using AI tools, and the entrepreneurial opportunity in solving the “last mile” problem of AI application deployment. (Source: 把AI当成“牛马”,2人创业团队,拿下了超1亿元融资)
Rumor: OpenAI in Talks to Acquire AI Programming Tool Company Windsurf (formerly Codeium) for $3 Billion: According to Bloomberg, citing sources familiar with the matter, OpenAI is in talks to acquire AI-assisted programming tool company Windsurf (formerly Codeium) for approximately $3 billion. If the deal goes through, it would be OpenAI’s largest acquisition ever, aimed at strengthening its competitiveness in the AI coding assistant market against rivals like Anthropic, GitHub Copilot, and Anysphere (Cursor). Founded in 2021, Windsurf was previously valued at $1.25 billion and had raised over $200 million in funding. This acquisition rumor also signals potential consolidation in the AI programming tools sector. (Source: dotey)
Ilya Sutskever’s Safe Superintelligence Reportedly Valued at $32 Billion: According to TechCrunch, Safe Superintelligence (SSI), the new company founded by OpenAI co-founder Ilya Sutskever, reached a valuation of $32 billion in its latest funding round. The company has reportedly secured $2 billion in investment. SSI aims to build superintelligence safely. Its high valuation reflects the market’s high expectations for top AI talent and the vision of AGI, even though the company has yet to release any products. (Source:
)
US-China Trade War May Impact AI Development, Chip Supply in Focus: Some analysis suggests that the US trade war with China, particularly export restrictions on high-end AI chips (like NVIDIA’s H100/B200 series), and potential Chinese countermeasures restricting rare earth mineral exports, are challenging global AI development. Reports indicate AI companies (like OpenAI) are already feeling the constraints of insufficient GPU supply. Meanwhile, China is making progress in chip manufacturing (e.g., breakthroughs in 3nm, 1nm technology) and may produce high-quality AI chips within the next few years. The article argues that current trade restrictions might slow down US AI development, potentially allowing China to surpass it in the AI field, and calls for promoting AI development through free trade. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Discussing the Practical Application of TPUs in Production Environments: Google recently released a new generation of TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) optimized for inference. However, community discussion points out that despite TPUs existing for years and Google’s generous researcher resource program (TRC), their adoption in industrial production environments seems less widespread than NVIDIA GPUs. Potential reasons include setup complexity, unclear performance advantages, lack of related GCP platform features (like static IPs, observability tools), debugging difficulties (XLA), and vendor lock-in concerns due to rental-only access via GCP. The discussion calls for users with actual production experience to share their usage and challenges with TPUs. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)

AI Creates Trust Gap in the Insurance Industry: A Swiss Re research report indicates that the application of generative AI in the insurance industry is facing trust challenges. While AI holds immense potential, concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and decision transparency exist, potentially leading to a trust gap between insurance companies and customers. The report explores how to leverage AI’s advantages while addressing related risks and ethical issues to build and maintain user trust. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
🌟 Community
OpenAI o3/o4-mini Sparks Heated Discussion: Capabilities and Hype Coexist: OpenAI’s release of o3 and o4-mini generated significant community buzz. Early testers (like Dan Shipper) praised their speed, intelligence, and agentic capabilities, making them their preferred models for tasks like code benchmarks, personalized course creation, blurry image recognition, and writing analysis. Sam Altman retweeted, emphasizing their “near or at genius level.” However, some commentary (like the AI Explained video) pointed out that despite the models’ power, claims like “AGI” and “hallucination-free” are overhyped. The models still make errors in common sense and physical reasoning, and their cost-effectiveness might not beat Gemini 2.5 Pro. The community generally acknowledges the progress, especially in coding and tool use, but remains critical about their true capabilities and limitations. (Source:
,
, sama, sama, karminski3, gdb, natolambert)

Community Discussion: Does AI Primarily Rely on Compute Power Advancement to Reach AGI?: A Reddit user initiated a discussion on whether achieving AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) mainly boils down to raw computational power increase. The viewpoint suggests that even with current LLM limitations, another order of magnitude increase in compute power could yield utility close to AGI, even if not “true” AGI. The key is whether the AGI problem is inherently “tractable”; if so, brute force computation might suffice. However, counterarguments posit that compute power alone cannot overcome fundamental LLM limitations, and AGI requires more paradigm shifts. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
Community Discussion: Which Industries Will Be Disrupted First by AI?: A Reddit user started a discussion speculating on which industries will “crumble” first under the impact of AI. Nominated industries include: translation/copywriting, customer support, language teaching, portfolio management, illustration/commercial photography. Comments added transportation, design (UI, branding, logo), PR/marketing/social media management, teaching (especially private tutoring), blogging/podcasting (content creation methods changing), event organization management, etc. Some comments also noted that not all areas will disappear entirely, e.g., highly specialized translation or illustration requiring core human creativity might survive. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
User Experience: Debugging AI-Generated Code is Challenging: A developer shared their experience debugging code generated by an LLM (migrated from SAS to SQL/Python). Although the AI code looked “decent,” it was riddled with errors: calling undefined functions, confusing similar but different code logic, skipping poorly formatted but correct SQL, arbitrarily replacing critical values, and producing inconsistent results across multiple runs. The conclusion was the code was completely unusable and needed rewriting, with fixing being riskier than rewriting. This highlights the limitations of current AI code generation capabilities and emphasizes the necessity of human review and validation. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
AI and Labor Relations: How Should Unions Respond?: Discussion points out that as AI’s automation capabilities grow across industries, labor unions need to more proactively address its potential impact on workers. The article cites past incidents involving AI in strikes and protests, such as schools suggesting AI replacements after graduate student strikes, using AI to monitor student protests, concerns over automated mental health services, and potential teacher strikes due to AI application in schools. The view is that workers (and their representative organizations) should not wait but actively formulate strategies to cope with the changes brought by AI. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)

RealHarm Dataset Released: Collecting Real-World AI Agent Failure Cases: The Giskard team released the RealHarm dataset, compiling publicly reported real-world cases where AI Agents (especially LLM-based ones) caused problems in practical applications. Analyzing these cases, the team found reputational damage was the most common organizational harm, misinformation and hallucination were the most frequent risk types, and existing guardrails failed to effectively prevent many incidents. The dataset aims to help researchers and developers better understand and mitigate the risks of AI in the real world. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
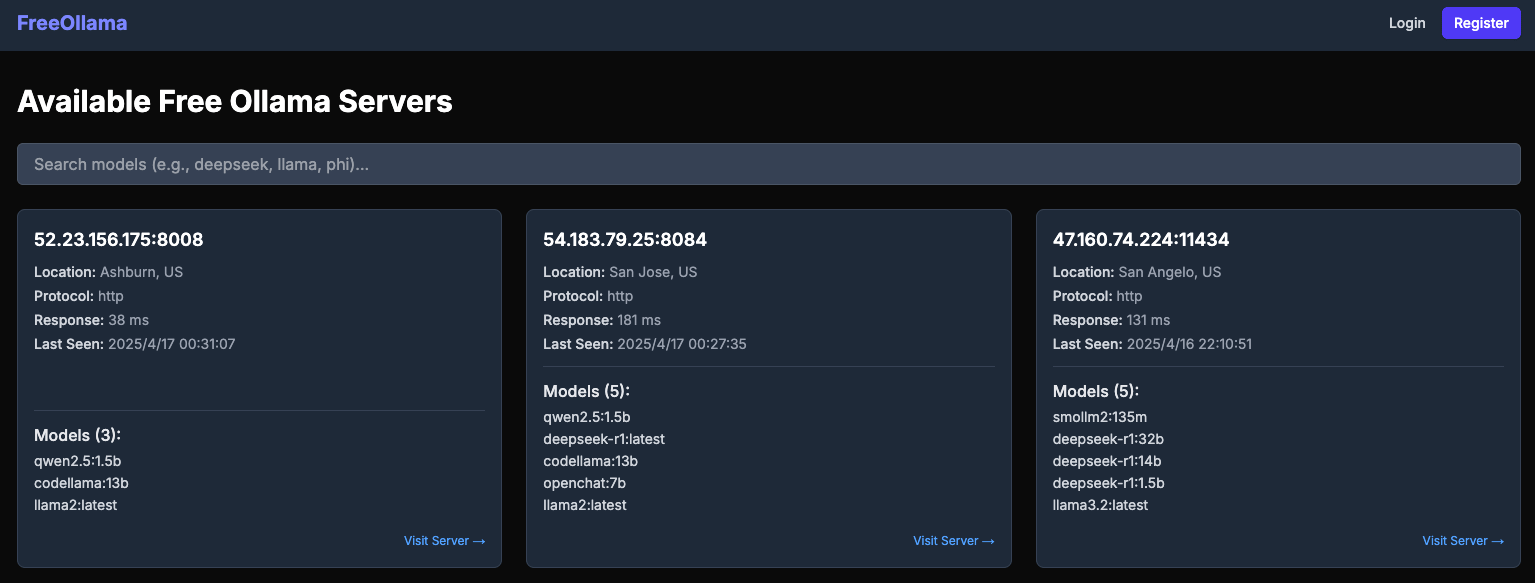
Report Reveals Security Risks of Public Ollama Servers: The website freeollama.com showcases numerous Ollama server instances exposed on the public internet. This indicates many users fail to properly configure security measures when deploying local LLM services (e.g., setting listen address to 0.0.0.0 without authentication), leaving their models and potentially data vulnerable to unauthorized access and exploitation. It serves as a reminder for users to pay close attention to network security configurations when deploying local AI services. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Viewpoint: Reasoning and Non-Reasoning Models Shouldn’t Be Absolutely Divided: AI researcher Nathan Lambert suggests that models shouldn’t be strictly categorized into “reasoning” and “non-reasoning” types; instead, all models should be evaluated across all domains. “Reasoning models” often perform well on non-reasoning benchmarks too, while the reverse is not typically true. This implies models with reasoning capabilities might be more general-purpose. He also points out the need for better pricing models reflecting different capabilities and costs. (Source: natolambert)
DeepMind Co-founder Demis Hassabis Named to TIME100, Emphasizes AI Safety Cooperation: Google DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis was included in TIME magazine’s 100 Most Influential People of 2025 list. In an interview, he stressed his hope that competing nations and companies can set aside differences and collaborate on AI safety, as ensuring AI develops beneficially is in everyone’s self-interest. (Source: demishassabis)

Google DeepMind Executive: Reinforcement Learning Needs to Go Beyond Human Knowledge: David Silver, VP of Reinforcement Learning at Google DeepMind, believes AI research must transcend known human knowledge and move towards systems capable of self-learning and even discovering new scientific knowledge. This emphasizes the potential of reinforcement learning in driving AI’s autonomous exploration and discovery. (Source: GoogleDeepMind)
Viewpoint: AI Development Bottleneck Shifting from Compute to Data and Evaluation: In a video analyzing progress in models like Kling 2.0, GPT-4.1, and o3, the AI Explained channel host cited OpenAI executives, suggesting the limiting factor in current AI development has shifted more from compute power to data, especially high-quality, domain-specific data, and effective evaluation methods (Evals). Model performance improvement increasingly relies on finding better data and better ways to measure progress. (Source:
)
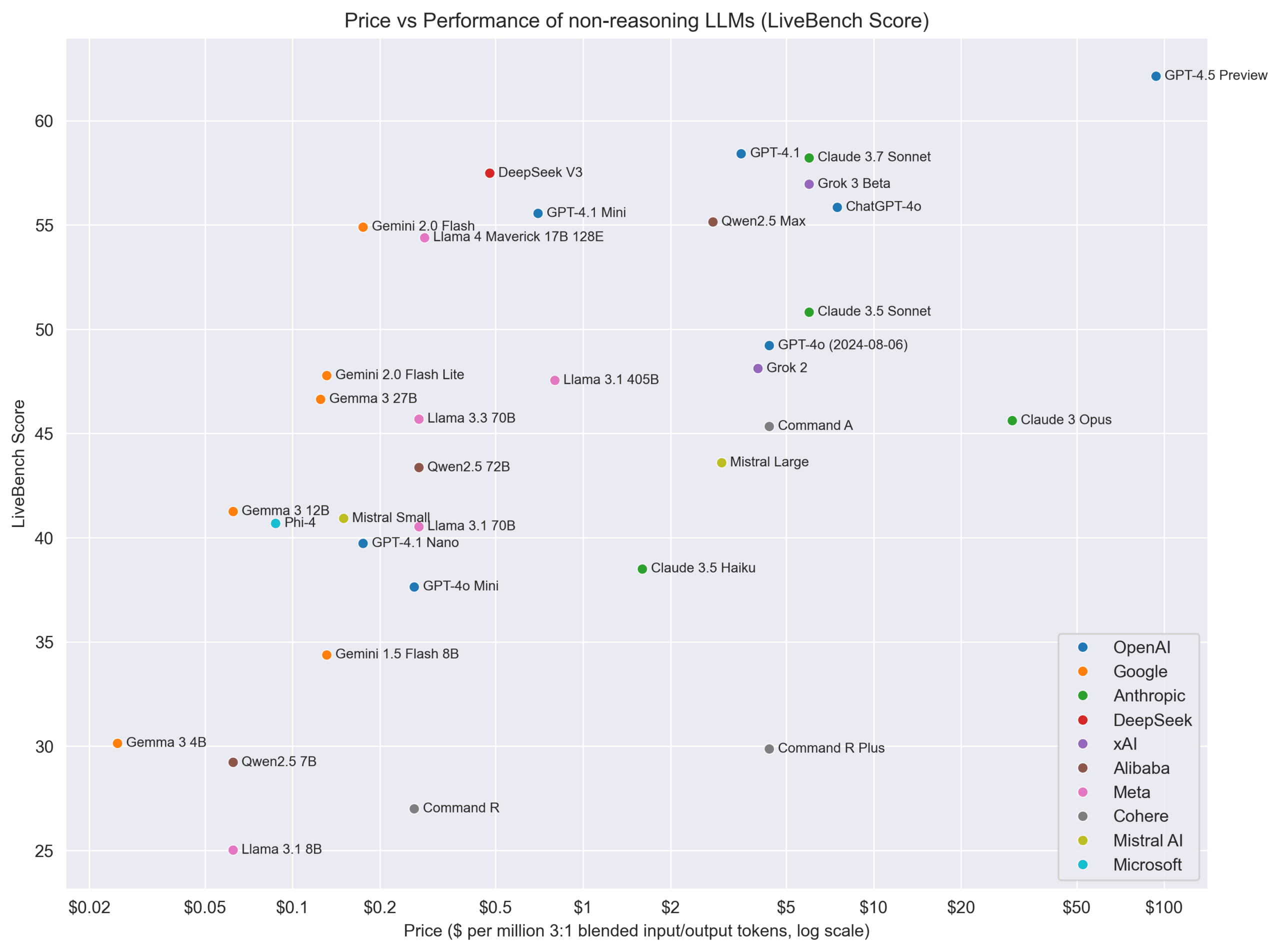
Price vs. Performance Chart for Non-Reasoning Models: The Reddit community shared a chart comparing the price (presumably API cost) and performance score on LiveBench (a real-time benchmarking platform) for various non-reasoning LLMs. The chart visually represents the cost-effectiveness of different models on specific benchmarks, showing, for example, the Gemma/Gemini series performing well in terms of value for money. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
💡 Other
Brain-Computer Interface Breakthrough: Translating Brainwaves Directly into Speech: New research showcases a brain-computer interface (BCI) implant capable of decoding a paralyzed person’s brainwaves in real-time and synthesizing them into natural speech. This technology offers new communication possibilities for individuals who have lost the ability to speak due to neurological injury or disease, representing a major breakthrough at the intersection of AI, assistive technology, and neuroscience. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon, Ronald_vanLoon)

miHoYo Founder Cai Haoyu’s Exploration in AI Gaming: Anuttacon, the AI company founded by former miHoYo CEO Cai Haoyu, released a trailer and demo for its experimental AI game “Whispers From The Star.” The game centers around AI-driven real-time dialogue, where players interact with the AI character Stella via text, voice, or video to guide her survival. It utilizes multimodal AI technology; Stella’s emotions, reactions, and actions are generated by AI in real-time, with natural facial expressions and movements. This reflects Cai Haoyu’s exploration of how AIGC can change game development, though it faces challenges like technological maturity, business models, and player acceptance. The article also compares the different strategies of major companies like Tencent and NetEase in applying AI in games. (Source: 原神之后,蔡浩宇的 AIGC 游戏野望)

Unitree Technology Upgrades Industrial Wheeled Robot B2-W: Unitree Robotics showcased the upgraded capabilities of its industrial-grade wheeled robot B2-W. While specific upgrade details weren’t provided, such robots typically integrate AI technology for navigation, obstacle avoidance, task execution, etc. This upgrade likely involves enhanced autonomy, payload capacity, or applications in specific industrial scenarios. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
Robots Learning Human Skills: Circuit Robotics demonstrated how robots can learn human skills. This usually involves AI methods like imitation learning and reinforcement learning, allowing robots to master complex operational tasks by observing demonstrations or through trial and error, representing a key research direction combining robotics and AI. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
Shopping Robots Becoming Reality: Information or video shared by Fabrizio Bustamante suggests that using robots for shopping is becoming a reality. This could refer to automated sorting robots in warehouses, consumer-facing delivery robots, or in-store guide robots, all of which typically require AI for path planning, item recognition, and human-robot interaction. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
AI and Robotics in Agriculture: JC Niyomugabo discussed the application of AI and robotics in agriculture (AgriTech). This includes using AI for crop monitoring, pest and disease diagnosis, precision irrigation and fertilization decisions, as well as using robots for automated planting, weeding, harvesting, etc. The aim is to improve agricultural efficiency, yield, and sustainability. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
Nanorobots with “Hidden Weapons” Can Kill Cancer Cells: Research shared by Khulood Almani shows a nanorobot equipped with “hidden weapons” (specific mechanism not detailed) capable of targeting and killing cancer cells. Nanorobot navigation and targeting mechanisms often involve AI algorithms for identifying targets and executing tasks in complex biological environments, representing a cutting-edge application in healthcare. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
Development of the COVVI Bionic Hand: The bionic hand developed by COVVI aims to provide amputees with more flexible and functional prosthetics. Such advanced bionic hands typically integrate sensors and AI algorithms to interpret user muscle signals (like EMG) or nerve signals, enabling more natural thought control and fine motor skills. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
Chinese Humanoid Robot Performs Quality Inspection Tasks: WevolverApp reported that humanoid robots in China are being used to perform quality inspection tasks. This requires the robot to possess advanced visual recognition capabilities (potentially AI-driven), precise manipulation skills, and some decision-making ability to determine product conformity, illustrating an application of humanoid robots in industrial automation. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
World’s First Human Surgery Performed by a Robot Dentist: Gigadgets reported the world’s first human surgery performed entirely by a robot dentist. While details are scarce, this usually implies a robotic system performing surgical planning, positioning, and operation with AI assistance, aiming to improve surgical precision and consistency, marking a milestone in medical robotics and AI integration. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
AI Drives Digital Progress, Building Smarter Nations: An article by Ronald van Loon in collaboration with Huawei discusses how digital technologies like AI, IoT, connectivity, and data analytics can drive national progress towards building smarter nations. It emphasizes AI’s role in optimizing public services, infrastructure management, economic development, etc. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)

Amphibious Velox Robot Can Move on Land and Water: Pascal Bornet shared the Velox robot, an amphibious robot capable of moving both in water and on land. This versatility could make it suitable for complex scenarios like search and rescue or environmental monitoring, with its autonomous navigation and adaptability to different environments potentially driven by AI. (Source: Ronald_vanLoon)
