Keywords:AI, Agent, Google A2A protocol, TPU v7 specifications, AI Agent collaboration, Gemini 2.5 Flash model, MCP protocol integration
🔥 Focus
Google Releases A2A Protocol and 7th Gen TPU, Accelerating the Era of AI Agents and Inference: Google has launched the open-source Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol, designed to enable secure communication and collaboration between AI Agents from different vendors and frameworks. It complements, rather than replaces, the MCP protocol (MCP connects Agents to tools, A2A connects Agents to Agents). A2A adheres to principles like capability discovery, task management, collaboration, and user experience negotiation, and has already gained support from over 50 partners. Concurrently, Google unveiled its 7th generation TPU (Ironwood/TPU v7), optimized for AI inference. It boasts an FP8 compute power of 4614 TFlops, 192GB of HBM per chip with 7.2 TBps bandwidth, and twice the energy efficiency of its predecessor. The highest configuration cluster (9216 chips) achieves a computing power of 42.5 ExaFlops. This hardware aims to support “thinking” models like Gemini and next-generation AI Agent applications, signaling a shift in AI from reactive responses to proactive insight generation. (Source: 36Kr, 36Kr, WeChat Official Account, WeChat Official Account, WeChat Official Account, WeChat Official Account)
MCP Becomes AI Agent Ecosystem Hub, Fully Embraced by Alibaba and Tencent: The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the standard interface connecting AI Agents with external tools and data sources, hailed as the “USB” of the AI ecosystem. Alibaba Cloud’s Bailian platform launched the industry’s first full-lifecycle MCP service, integrating Function Compute, over 200 large models, and more than 50 MCP services, enabling rapid Agent setup in 5 minutes. Tencent Cloud also released an “AI Development Kit” supporting MCP plugin hosting. By decoupling hosts, servers, and clients, MCP reduces redundant development costs and enhances the interoperability of AI tools, crucial for enabling complex Agent collaboration. Despite early challenges like an immature ecosystem and incomplete toolchains, MCP is poised to accelerate AI application explosion and industry development, with support from OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and major Chinese tech companies. (Source: 36Kr)
AI Achieves Breakthrough Progress in Mathematical Olympiad: Results from the second AI Mathematical Olympiad – Progress Prize 2 show significant advancements in AI’s ability to solve challenging math problems. The top model scored an impressive 34/50 in a test consisting of entirely new problems, with limited computational resources (under $1 per problem), and requiring precise integer answers (0-999). This far exceeds previous research where human evaluators estimated LLMs could only achieve around 5% accuracy. Even a relatively basic DeepSeek R1 derivative model scored 28/50. This outcome indicates that AI’s mathematical reasoning capabilities, particularly on Olympiad-level problems requiring creative problem-solving, are rapidly improving and are not merely based on pattern matching or data memorization. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
SenseTime Releases SenseNova V6, a 600 Billion Parameter Multi-modal MoE Model: SenseTime has launched its sixth-generation large model, SenseNova V6, featuring a 600 billion parameter Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture. It natively supports multi-modal input (text, image, video) and fused processing. The model demonstrates outstanding performance across various text-only and multi-modal benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4.5 and Gemini 2.0 Pro. Its core capabilities include strong reasoning (multi-modal and language deep reasoning exceeding o1, Gemini 2.0 flash-thinking), strong interaction (real-time audio-video understanding, emotional expression), and long memory (supporting long video analysis, e.g., directly reasoning about several minutes of video content). Key technologies include native multi-modal fusion training, multi-modal long chain-of-thought synthesis (supporting 64K tokens), multi-modal hybrid reinforcement learning (RLHF+RFT), and long video unified representation and dynamic compression. SenseTime emphasizes that AI should serve everyday applications, driving AI adoption across industries. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
🎯 Trends
Google Gemini 2.5 Flash Coming Soon, Focusing on Efficient Inference: At Cloud Next ’25, Google previewed the Gemini 2.5 Flash model. As a lightweight version of the flagship Gemini 2.5 Pro, Flash will focus on providing fast, low-cost inference capabilities. Its key feature is the ability to dynamically adjust inference depth based on prompt complexity, avoiding over-computation on simple questions. Developers will be able to customize inference depth to control costs. The model is expected to be available on Vertex AI soon, targeting daily applications sensitive to response speed. (Source: WeChat Official Account, X)
ByteDance Releases Seed-Thinking-v1.5 Technical Report, Demonstrating Strong Reasoning Capabilities: ByteDance has published technical details of its reasoning model, Seed-Thinking-v1.5, trained using reinforcement learning. The report shows the model performs exceptionally well on multiple benchmarks, surpassing DeepSeek-R1 and approaching the levels of Gemini-2.5-Pro and O3-mini-high, achieving a score of 40% on the ARC-AGI test. The model has 200 billion total parameters and 20 billion active parameters. While the model weights have not yet been released, its excellent reasoning ability and relatively small number of active parameters have attracted community attention. (Source: X)
ChatGPT Enhances Memory Function, Can Reference All Past Conversations: OpenAI announced an upgrade to ChatGPT’s memory feature, allowing the model to reference a user’s entire chat history to provide more personalized responses. This enhancement aims to leverage user preferences and interests to improve assistance in areas like writing, suggestions, and learning. When starting a new conversation, ChatGPT will naturally utilize these memories. Users retain full control over this feature and can disable referencing past history in settings, turn off memory completely, or use temporary chat mode. The feature has begun rolling out to Plus and Pro users (excluding some regions) and will soon cover Team, Enterprise, and Education users. (Source: X, X)
OpenAI Releases Behind-the-Scenes Podcast on GPT-4.5 Development: Sam Altman and OpenAI core team members Alex Paino, Dan Selsam, and Amin Tootoonchian recorded a podcast discussing the development process of GPT-4.5 and future directions. The team revealed that GPT-4.5 development marked a shift from optimizing computational efficiency to data efficiency, aiming for intelligence ten times greater than GPT-4. The podcast discussed the importance of the “compression” mechanism in unsupervised learning (approximating Solomonoff induction), emphasized the necessity of accurately evaluating model performance and avoiding rote memorization, and shared experiences overcoming technical hurdles and the importance of team morale. (Source: X, X)
Perplexity Integrates Gemini 2.5 Pro, Plans Grok 3 and WhatsApp Access: AI search engine Perplexity announced it has integrated Google’s latest Gemini 2.5 Pro model for Pro users, inviting them to compare it against models like Sonar, GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, DeepSeek R1, and O3. Additionally, Perplexity CEO Aravind Srinivas confirmed that development of a Perplexity WhatsApp integration is underway following significant positive user feedback. The Grok 3 model is also planned to be supported on the Perplexity platform soon. (Source: X, X, X)
Alibaba’s Qwen3 Series Models Gearing Up, Release Still Takes Time: The community eagerly anticipates Alibaba’s next-generation Qwen3 series models, including non-open-source versions, Qwen3-8B, and Qwen3-MoE-15B-A2B. However, according to responses from a Qwen developer on social media, the release of Qwen3 is not a matter of “hours” and still requires more preparation time. This indicates that Alibaba is actively developing the new generation models, but a specific release timeline is yet to be determined. (Source: X, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Mysterious High-Performing Models “Dragontail” & “Quasar Alpha” Appear on LM Arena, Sparking Speculation: Anonymous models named “Dragontail” and “Quasar Alpha” have appeared on the LMSYS Chatbot Arena (LM Arena) platform. In interactions with users, they exhibit performance comparable to, or even superior on certain math problems than, top-tier models like o3-mini-high and Claude 3.7 Sonnet. The community speculates that “Dragontail” might be a variant of the upcoming Qwen3 or Gemini 2.5 Flash, while “Quasar Alpha” is conjectured by some users to be part of OpenAI’s o4-mini series. The appearance of these anonymous models highlights the role of model arenas as platforms for testing and evaluating cutting-edge models. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Moonshot AI’s Kimi-VL-A3B-Thinking Model Demo Live on Hugging Face: Moonshot AI has launched an interactive demo of its Kimi-VL-A3B-Thinking multi-modal model on Hugging Face Spaces. Users can now publicly experience the model. Initial tests show it possesses online OCR and image recognition capabilities, but its performance may be limited on tasks requiring extensive knowledge reserves (like understanding the humor in specific memes), potentially related to its model size. (Source: X, X)
AMD to Host AI Event, Announce New Data Center GPUs: AMD plans to hold an event titled “Advancing AI 2025,” where it will unveil new GPUs for data centers. This launch will focus on AI applications rather than gaming graphics cards. The move signifies AMD’s continued investment in the AI hardware market, aiming to compete in the AI accelerator space dominated by Nvidia. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
🧰 Tools
Firecrawl: Open-Source Tool to Convert Websites into LLM-Ready Data: Launched by Mendable AI, Firecrawl is a powerful open-source tool (written in TypeScript) designed to scrape, crawl entire websites, and convert them into LLM-ready Markdown or structured data via a single API. It handles challenges like proxies, anti-bot mechanisms, and dynamic content rendering. It supports custom crawling (e.g., excluding tags, authenticated crawls), media parsing (PDF, DOCX), and page interactions (clicking, scrolling, inputting). It offers an API, SDKs for Python/Node/Go/Rust, and is integrated into various LLM frameworks (Langchain, Llama Index, Crew.ai) and low-code platforms (Dify, Langflow, Flowise). Firecrawl provides both a hosted API service and an open-source version runnable locally. (Source: GitHub)
KrillinAI: LLM-Based Video Translation and Dubbing Tool: KrillinAI is an open-source project written in Go that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide professional-grade video translation and dubbing services. It supports one-click full-process deployment and can handle the entire workflow from video download (supporting yt-dlp and local uploads), high-precision subtitle generation (Whisper), intelligent subtitle segmentation and alignment (LLM), multi-language translation, terminology replacement, AI voice dubbing and voice cloning (CosyVoice), to video synthesis (automatically adapting to horizontal/vertical screens). It aims to generate content suitable for platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Bilibili. The project offers Win/Mac desktop versions and a non-desktop version (Web UI), and supports Docker deployment. (Source: GitHub)
Second Me: Build a Localized, Personalized “AI Self”: Second Me is an open-source project aimed at building a user’s “digital twin” or “AI self” using locally running AI models. It emphasizes privacy (fully local execution) and personalization, simulating the user’s identity, memories, values, and reasoning style through Hierarchical Memory Modeling (HMM) and a “Me-alignment” structure. The project supports Docker deployment (macOS, Windows, Linux), an OpenAI-compatible API interface, and is exploring MLX training support. The community is active, having contributed integrations like a WeChat bot and multi-language support. Its vision is for AI to be an extension of the user’s capabilities, not an appendage of platforms. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
EasyControl: LoRA-Style Conditional Injection for DiT Architecture Diffusion Models: EasyControl is a newly released open-source framework designed to address the lack of mature plugins (like LoRA) for newer Diffusion models based on the DiT (Diffusion Transformer) architecture. It provides a lightweight conditional injection module, allowing users to easily add LoRA-like control capabilities to DiT models for tasks such as style transfer. The project showcases results from a model trained on 100 Asian faces and their corresponding Ghibli-style images (generated by GPT-4o) and already supports integration with ComfyUI. (Source: X)
XplainMD: Biomedical Explainable AI Pipeline Fusing GNNs and LLMs: XplainMD is an open-source end-to-end AI pipeline designed specifically for biomedical knowledge graphs. It combines Graph Neural Networks (R-GCN) for multi-relation link prediction (e.g., drug-disease, gene-phenotype relationships), uses GNNExplainer for model interpretability, visualizes prediction subgraphs with PyVis, and utilizes the LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct model for natural language explanation and sanity checks of predictions. The entire workflow is deployed in an interactive Gradio application, aiming to provide predictions along with explanations of “why,” enhancing the trustworthiness and usability of AI in sensitive fields like precision medicine. (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning, Reddit r/MachineLearning)
LaMPlace: New AI-Driven Method for Chip Macro Placement Optimization: Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China, Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab, and Tianjin University propose LaMPlace, an AI-based method for optimizing chip macro placement. By using a structured metric predictor (modeling the impact of inter-macro distances on cross-stage metrics like WNS/TNS using Laurent polynomials) and a learnable mask generation mechanism, it guides placement decisions early in the layout stage to optimize final chip performance (PPA). LaMPlace aims to shift the optimization target from easily computed intermediate metrics (like wirelength, density) to the final design goals, achieving “left-shift optimization” and improving design efficiency. The method has been accepted as an ICLR 2025 Oral presentation. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
Google Launches Agent Development Kit (ADK) and Firebase Studio: As part of its push to foster the AI Agent ecosystem, Google has released the Agent Development Kit (ADK), a development framework for building multi-agent systems. ADK supports multiple model providers (Gemini, GPT-4o, Claude, Llama, etc.), offers CLI tools, Artifact management, AgentTool (for inter-agent calls), and supports deployment to Agent Engine or Cloud Run. Concurrently, Google also launched Firebase Studio, a cloud-based AI programming tool integrated with Gemini models, supporting the full application development lifecycle from AI coding and compilation/build to cloud service deployment. (Source: WeChat Official Account, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
OpenFOAMGPT: Leveraging Domestic Large Models to Reduce CFD Simulation Costs: A collaboration between the University of Exeter (UK) and Beihang University (China) has updated the OpenFOAMGPT project, which aims to allow users to drive Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations using natural language. The new version successfully integrates domestic large models DeepSeek V3 and Qwen 2.5-Max, achieving performance comparable to GPT-4o/o1 while potentially reducing costs by up to 100 times. Furthermore, the team implemented localized deployment using the QwQ-32B model (in a single GPU environment), providing a more economical and convenient AI-assisted CFD solution for researchers and SMEs in China, lowering the professional barrier to entry. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
Slop Forensics Toolkit: Analyzing Repetitive Content in LLM Outputs: A new open-source toolkit has been released for analyzing “slop”—overly reused words and phrases—in the output of Large Language Models (LLMs). The tool uses stylometry analysis to identify words and n-grams that appear more frequently than in human writing, constructing a model’s “slop profile.” It also borrows methods from bioinformatics, treating lexical features as “mutations” to infer similarity trees between different models. The toolkit aims to help researchers understand and compare the generative characteristics and potential data contamination or training biases of different LLMs. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
vLLM Inference Framework Adds Support for Google TPUs: The popular open-source large model inference and serving framework, vLLM, has announced added support for Google TPUs. Combined with Google’s newly released 7th generation TPU (Ironwood), this update means developers can leverage vLLM for efficient model inference and deployment on Google’s high-performance AI hardware. This helps expand the TPU software ecosystem and provides users with more hardware options. (Source: X)
📚 Learning
CUHK, Tsinghua et al. Propose SICOG Framework, Exploring New Paths for LLM Self-Evolution: Addressing the reliance of large models on high-quality pre-training data and the issue of data resource depletion, institutions including the Chinese University of Hong Kong and Tsinghua University proposed the SICOG (Self-Improving Systematic Cognition) framework. This framework establishes a trinity self-evolution mechanism of “post-training enhancement – inference optimization – re-pre-training reinforcement.” Through “Chain-of-Description” (CoD) for enhanced structured visual perception and “structured Chain-of-Thought” (CoT) for improved multi-modal reasoning, combined with a self-generated data loop and consistency filtering, it enables continuous improvement of the model’s cognitive abilities with zero human annotation. Experiments demonstrate that SICOG significantly boosts model performance on various tasks, reduces hallucinations, and shows good scalability, offering a new approach to tackle pre-training bottlenecks and move towards autonomous learning AI. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
OpenAI Open-Sources BrowseComp Benchmark to Evaluate AI Agent Web Browsing Capabilities: OpenAI has released and open-sourced the BrowseComp (Browsing Competition) benchmark. This benchmark is designed to evaluate the ability of AI Agents to browse the internet to find hard-to-locate information, akin to an online scavenger hunt for Agents. OpenAI believes such tests capture the crucial capabilities of agents performing deep research-style browsing, which is vital for assessing the intelligence level of advanced web browsing Agents. (Source: X, X)
Study Finds Reasoning Models Generalize Better on OOD Coding Tasks: A new study (arXiv:2504.05518v1) compared the generalization capabilities of reasoning versus non-reasoning models through coding task experiments. The results showed that reasoning models exhibited no significant performance drop when transitioning from in-distribution tasks to out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks, whereas non-reasoning models showed performance degradation. This suggests that reasoning models are more than just pattern matchers; they can learn and generalize to tasks outside their training distribution, possessing stronger abstraction and application abilities. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
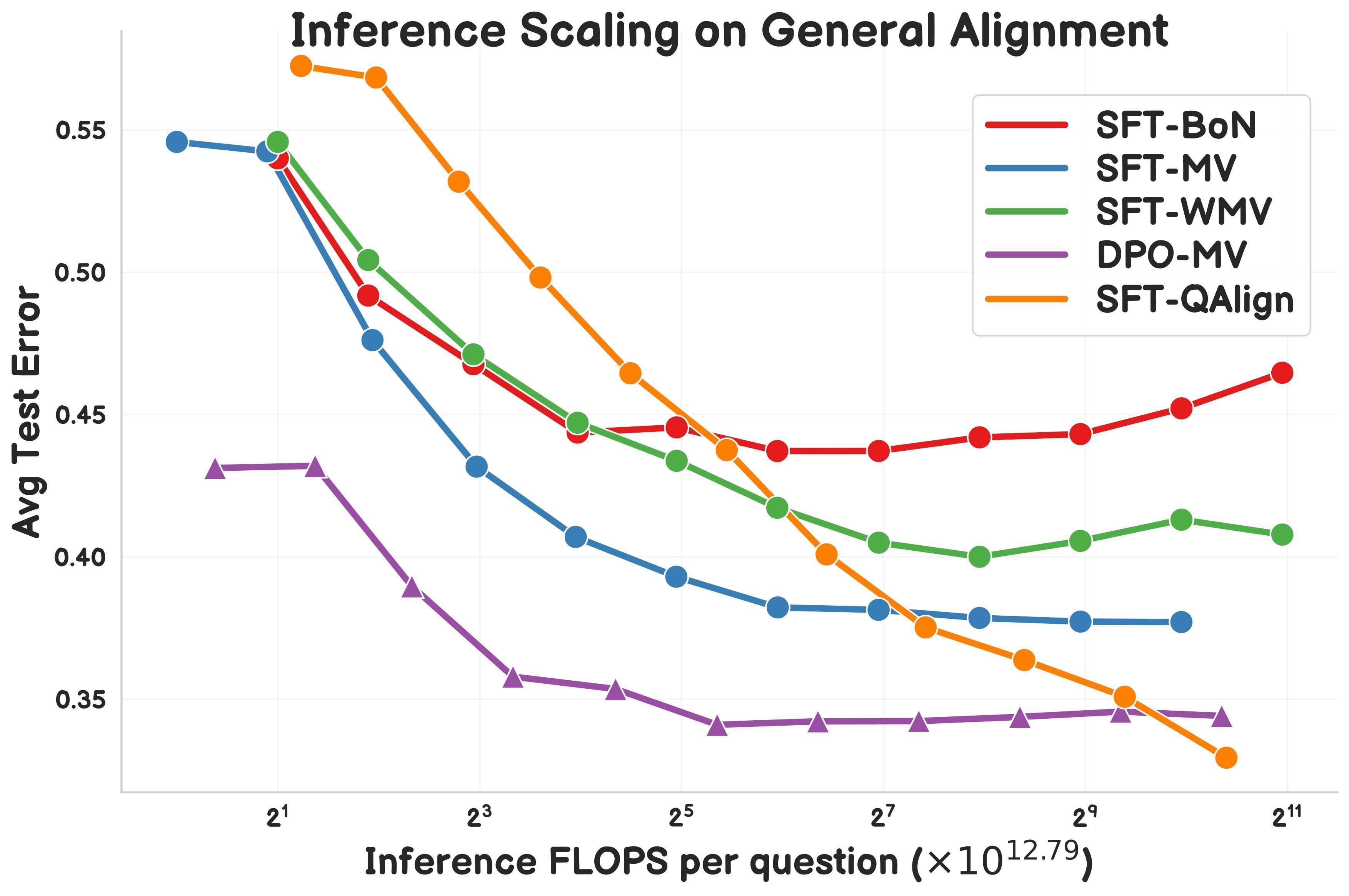
Research Proposes QAlign: MCMC-Based Test-Time Alignment Method: Gonçalo Faria et al. proposed QAlign, a novel test-time alignment method that uses Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) to enhance language model performance without retraining the model. The research indicates that QAlign outperforms models fine-tuned with DPO (Direct Preference Optimization) at the same inference compute budget. It can also overcome the limitations of traditional Best-of-N sampling (prone to over-optimizing the reward model) and majority voting (unable to discover unique answers), showing promise for applications like high-quality data generation. (Source: X)
Yann LeCun Reiterates Limitations of Auto-Regressive LLMs: In a recent talk, Meta Chief AI Scientist Yann LeCun reiterated his view on the limitations of the current mainstream Auto-Regressive Large Language Model architecture, deeming its pattern “doomed.” He argues that this word-by-word prediction approach restricts the model’s ability to perform true planning and deep reasoning. Although auto-regressive models are currently state-of-the-art, researchers like LeCun are actively exploring alternatives, such as the Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA), aiming to achieve AI systems closer to human intelligence. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
LlamaIndex Showcases Building a Report Generation Agent with Google Cloud: LlamaIndex founder Jerry Liu demonstrated at Google Cloud Next ’25 how to combine LlamaIndex workflows with Google Cloud databases (like BigQuery, AlloyDB) to build a report generation Agent. The Agent can parse SOP documents (using LlamaParse), tutorial databases, legal data, etc., to generate personalized onboarding guides for new employees. This highlights the need for robust data access and processing capabilities in knowledge-based Agent architectures and showcases LlamaIndex’s role in building such Agent applications. (Source: X)
Researcher Shares Symbolic Compression Engine and .sym File Format: An independent researcher has open-sourced an engine called Symbolic Compression and its corresponding .sym file format. The project claims to achieve compression by extracting the underlying recursive rules and structural logic of sequences (like prime numbers, Fibonacci sequence) based on the proposed Miller’s Law: κ(x) = ((ψ(x) – x)/x)², rather than just compressing the raw data. It aims to store and predict the occurrence of the structure itself, providing a format similar to JSON but for recursive logic. The project includes a CLI tool and multi-region compression features. (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
💼 Business
Grok-3 API Pricing Announced, Starting at $0.3/Million Tokens: xAI has officially opened the Grok 3 series API to the public with a tiered pricing strategy. Grok 3 (Beta), aimed at enterprise applications, is priced at $3/million tokens for input and $15/million tokens for output. The lightweight Grok 3 Mini (Beta) is priced at $0.3/million tokens for input and $0.5/million tokens for output. Both offer faster response versions (fast-beta) at higher prices. This pricing strategy positions it competitively against models like Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro, Anthropic’s Claude Max plan (starting at $100), and Meta’s Llama 4 Maverick (approx. $0.36/million tokens). (Source: WeChat Official Account)
Stanford AI Report: Alibaba Ranks Third Globally in AI Strength, US-China Gap Narrows: Stanford University’s latest “2025 AI Index Report” shows that among significant global large models, Google and OpenAI each contributed 7, tying for first place, while Alibaba ranked third globally and first in China with 6 models (Qwen series). The report notes a significant narrowing of the performance gap between US and Chinese models, decreasing from a 17.5 percentage point difference (MMLU benchmark) at the end of 2023 to just 0.3 percentage points by the end of 2024. Alibaba’s Qwen model family (over 200 models open-sourced) has become the world’s largest open-source model series, with over 100,000 derivative models. The report also mentions that top Chinese models (like Qwen2.5, DeepSeek-V3) generally require less training compute than comparable US models, indicating higher efficiency. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
Chinese Medical AI Companies Seek Breakthroughs Amid Tariffs and Technical Barriers: Facing multiple pressures including increased US tariffs and technological monopolies (e.g., GPS giants controlling imaging data interfaces), Chinese medical technology companies are accelerating domestic substitution and intelligent transformation. United Imaging Healthcare insists on self-researching core technologies, launching high-end equipment like the 5.0T MRI, and developing medical large models and intelligent agents. Mindray employs a “Device + IT + AI” strategy, building a digital intelligence ecosystem (like the Ruiying Cloud++ platform integrating DeepSeek) and cultivating international markets. Techsomed focuses on precision medicine with its iMedImage® medical imaging large model, participating in setting industry standards for differentiated competition. Driven by AI, these companies aim to break through barriers in core technology, supply chains, and clinical acceptance to reshape the market landscape. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
🌟 Community
AI Applications in Education Spark Discussion: Community discussion focuses on how Artificial Intelligence (AI) can transform education through customized learning plans. AI has the potential to tailor teaching content and methods to individual student needs, learning pace, and style, enabling personalized education and enhancing learning efficiency and effectiveness. (Source: X)
Complex Engineering Behind Cursor Editor Draws Attention: Community discussion highlights that implementing the AI code editor Cursor is no simple task. Its core goal is to eliminate manual code copy-pasting, requiring significant user experience optimization and engineering innovation. This includes inventing new code editing paradigms, developing proprietary models like FastApply for rapid edits and Fusion for code completion prediction, and implementing a two-layer RAG system (local and server-side) for optimized context handling. These efforts demonstrate the technical depth required to build a seamless AI programming experience. (Source: X)
AI Cheating Tool Sparks Ethical and Recruitment System Debates: A Columbia University student, Roy Lee, developed an AI tool “Interview Coder” to cheat in programming interviews, securing offers from several top companies before being expelled. He subsequently made $2.2 million in 50 days selling the tool. The tool runs stealthily, simulating human coding styles to generate answers. The incident sparked widespread discussion: on one hand, many developers expressed frustration with rigid, unrealistic programming interviews (like LeetCode grinding); on the other hand, the surge in AI cheating (reports suggest rates rose from 2% to 10%) challenges the validity of current technical interviews, potentially forcing companies to reshape recruitment systems and raising ethical questions about what constitutes “cheating” in the AI era. (Source: 36Kr)
Innovative General Agent Applications Emerge: Recent Agent hackathons (like flowith, openmanus) have showcased numerous innovative applications. Development & Design: Agents can automatically generate complete projects (front-end, back-end code, database structure) from UI sketches (maxcode), or autonomously gather information, determine style, and generate personal websites. Analysis & Decision-Making: Agents can calculate the best aurora viewing position on a flight, or perform self-iterating quantitative trading strategy optimization (一鹿向北). Personalized Services: Agents can intelligently recommend meeting spots (Jarvis-CafeMeet), analyze Douban data to generate “taste reports,” or serve elderly users via voice interaction (老奶奶教你用OpenManus). Artistic Creation: Agents can generate digital art in specific styles, create dances based on music, customize painting brushes, and generate real-time programmable music (strudel-manus). These examples demonstrate the vast potential of Agents across various domains. (Source: WeChat Official Account)
Andrew Ng Comments on US Tariffs’ Impact on AI Development: Andrew Ng expressed concern over the broad imposition of high US tariffs, arguing they will damage relationships with allies, hinder the global economy, create inflation, and negatively impact AI development. He noted that while the free flow of ideas and software (especially open-source) might not be significantly affected, tariffs will restrict access to AI hardware (like servers, cooling, networking equipment), increase data center construction costs, and indirectly affect compute supply by impacting power equipment imports. Although tariffs might slightly stimulate domestic demand for robotics and automation, this is unlikely to compensate for manufacturing shortcomings. He urged the AI community to maintain international cooperation and exchange. (Source: X)
Community Discusses AI’s Role in Mental Health Support: A growing number of users are sharing experiences using AI tools like ChatGPT for psychological counseling and emotional support. Many report that AI provides a safe, non-judgmental space to confide, offering immediate feedback and useful advice. Some even feel more heard and understood by AI than human therapists in certain situations, leading to positive emotional release. While users generally agree AI cannot fully replace professional licensed therapists, especially for serious mental health issues, it shows significant potential in providing basic support, coping with daily stress, and preliminary exploration of personal problems, gaining popularity due to its accessibility and low cost. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/ChatGPT)
Qualification of AI-Translated Content Sparks Discussion: The community discussed whether content translated by AI (like ChatGPT) from a human-written story should be considered human-created or AI-created. One viewpoint is that if AI acts solely as a translation tool without altering the original thought, structure, or tone, the content remains essentially human-created. However, AI text detectors might flag it as AI-generated due to analyzing text patterns. This raises questions about defining AI’s role in the creative process, the limitations of AI detectors, and how to preserve the original style in translation. (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
User Reports Issues with Gemini 2.5 Pro on Long Context Processing: User Nathan Lambert encountered connection errors while testing Gemini 2.5 Pro with very long context input queries. He observed that the model seemed to regenerate almost all input tokens during inference, leading to extremely high inference costs and eventual failure. Additionally, he noted the inability to share the Gemini chat history when errors occurred. This feedback points to potential stability and efficiency issues with current models when handling ultra-long contexts. (Source: X)
Poor Community Reception for Llama 4 Release, Performance and Openness Questioned: Meta’s release of the Llama 4 series models sparked widespread discussion and negative feedback within the community. Users generally felt that despite the Maverick model’s massive 10 million token context window and decent function calling capabilities, its 400B total parameters (17B active) did not deliver the expected reasoning performance improvements, even lagging behind models like QwQ 32B. Furthermore, its restrictive license, lack of a technical paper and system card, and accusations of “gaming” benchmarks like LMSYS have damaged Meta’s reputation in the open-source community. The community expressed disappointment that Meta failed to continue the openness and leadership demonstrated with Llama 3. (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Claude Pro Plan Perceived as Downgraded, Users Complain of Increased Limits: Following Anthropic’s launch of the higher-priced Max plan (claiming 5x or 20x the usage of the Pro plan), many Claude Pro users in the community reported feeling that the Pro plan’s own usage limits have become stricter and easier to hit. Users speculate Anthropic may have reduced the actual usable quota for the Pro plan to push users towards upgrading to the Max plan. These non-transparent adjustments and perceived service degradation have caused user dissatisfaction, especially given that Claude models still suffer from context window memory issues. (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI, Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
OpenWebUI Community Discusses Features and Issues: OpenWebUI users discussed the tool’s features and encountered problems in the community. One user asked about the possibility of integrating Nextcloud as an additional cloud storage option. Another reported issues with the knowledge base feature, where the LLM seemed to reference only the first document when multiple were uploaded. Yet another user experienced timeout errors when trying to connect to a Gemini-compatible OpenAI API endpoint. These discussions reflect user needs and concerns regarding the tool’s extensibility and stability. (Source: Reddit r/OpenWebUI, Reddit r/OpenWebUI, Reddit r/OpenWebUI)
Suno AI Community Exchanges Usage Tips and Issues: The Suno AI user community is active, discussing topics such as: how to exclude specific instruments (like drums, keyboards) when using the Cover feature to isolate solo instruments; seeking advice on generating specific music styles (like Trip Hop); reporting issues with the friend invitation feature not awarding credits; discussing lyrics copyright issues, e.g., whether specific phrases (like “You’re Dead”) trigger copyright restrictions; and sharing creative use cases, like creating background music for D&D characters. (Source: Reddit r/SunoAI, Reddit r/SunoAI, Reddit r/SunoAI, Reddit r/SunoAI, Reddit r/SunoAI, Reddit r/SunoAI)
💡 Other
Exploring AI-Generated “Accidental Photos”: Community users experimented with using AI to generate images that look like unintentionally captured photos, featuring casual composition, and even slight blurriness or overexposure. This exploration aims to challenge the tendency of AI to generate perfect images, mimicking the randomness and imperfection found in human photography, showcasing AI’s ability to understand and simulate specific photographic styles, including “bad” photo aesthetics. (Source: Reddit r/ChatGPT)
Potential of AI in Supply Chain Management: Discussion highlighted the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in enhancing supply chain traceability and transparency. By leveraging machine learning and data analysis, AI can help businesses better monitor goods flow, predict disruption risks, optimize inventory management, and provide consumers with more reliable product origin information. (Source: X)
Exploring AI Applications in Human Resources Management: Community discussion touched upon the possibility of using AI Avatars for human resources management. This could include using AI for preliminary interview screening, employee training, policy Q&A, and even emotional support tasks, aiming to improve HR process efficiency and employee experience. (Source: X)
Bank of England Warns AI Could Trigger Market Crises: The Bank of England issued a warning that artificial intelligence software could be used to manipulate markets, potentially even deliberately creating market crises for profit. This raises concerns about the regulation and risk control of AI applications in the financial sector. (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
New Method for AI to Generate Realistic 3D Shapes: Researchers at MIT have developed a new generative AI method capable of creating more realistic three-dimensional shapes. This holds significant importance for fields like product design, virtual reality, game development, and 3D printing, advancing the technology for generating complex 3D models from 2D images or text descriptions. (Source: X)
AI Inference Power Consumption and Cost Drastically Reduced: Reports indicate that new technological advancements have reduced the power consumption (measured by MAC energy) of AI inference tasks by 100x and costs by 20x. This improvement in efficiency is crucial for the feasibility and economics of deploying AI models on edge devices, mobile platforms, and at scale in the cloud. (Source: X)
Discussion on AI’s Impact on Human Cognition: Community discussion focuses on the potential effects of over-reliance on AI on the human brain, citing article headlines suggesting it could leave the brain “Atrophied And Unprepared.” This reflects concerns about the potential degradation of core human cognitive functions like critical thinking, memory, and problem-solving skills following the widespread adoption of AI tools. (Source: X)
Outlook and Concerns Regarding Future AI-Driven Work Models: Community discussion references viewpoints predicting that by 2025, AI will rewrite the rules of work, potentially ending current work models. This sparks debate and concern about the impact of AI automation on the job market, the shift in required skills, and new models of human-machine collaboration. (Source: X)